Steps of Protein Production
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is the first step of protein production?
determine the gene (nucleic acid) sequence (NCBI) that encodes desired protein
What is the second step of protein production?
obtain the best source for nucleic acid (message)
What are the best sources for nucleic acid (3)?
(1) gene synthesis, (2) genomic DNA, (3) mRNA and cDNA
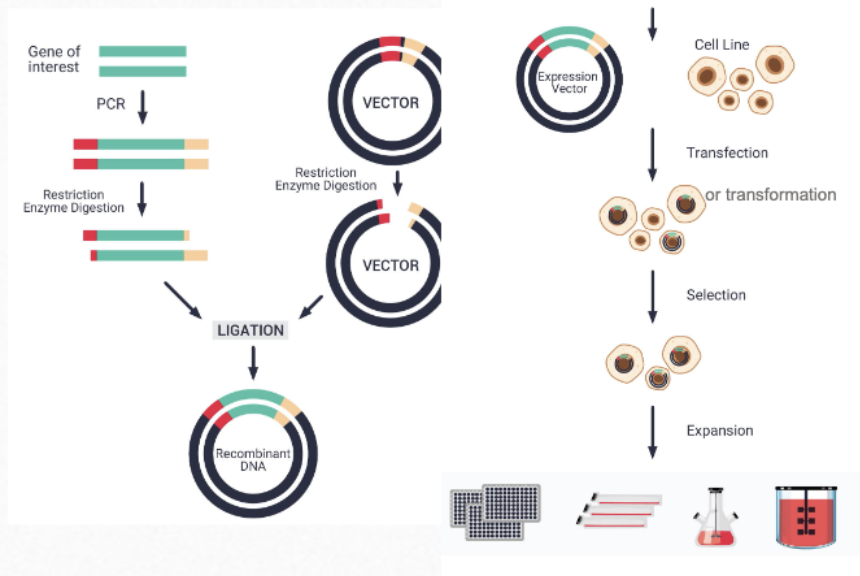
What is the third step of protein production?
clone the gene into a vector
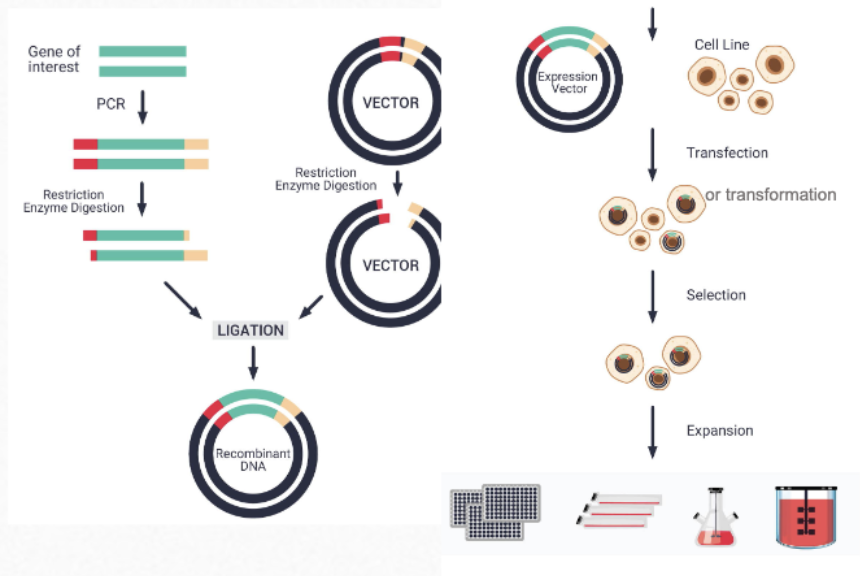
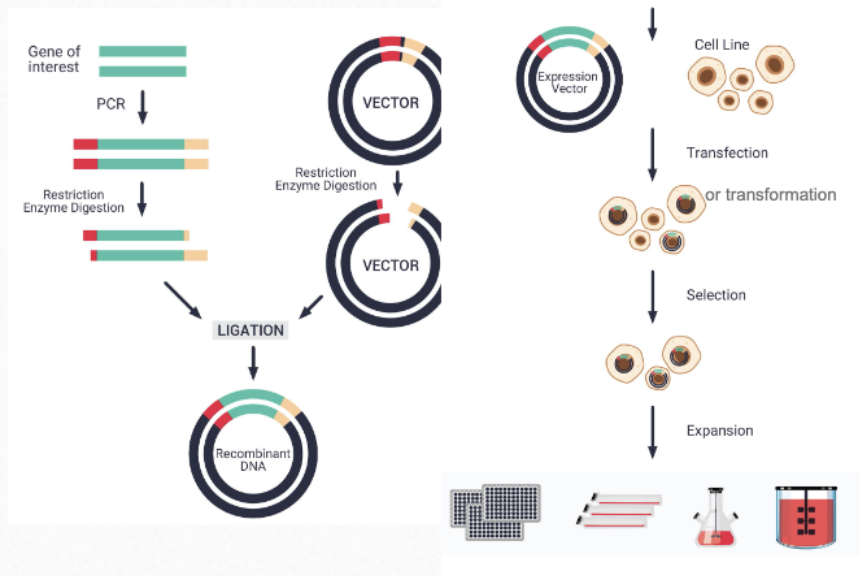
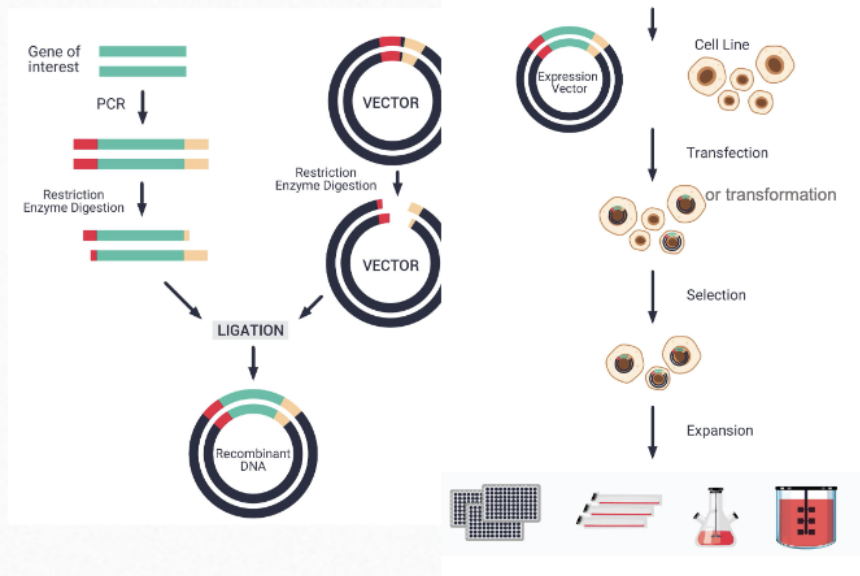
What is the fourth step of protein production?
Introduce the clone vector into the proper living cell and fermentation
What are the different living systems for producing biopharmaceuticals (3)?
prokaryotes (E. coli), Yeast, Mammalian cells (CHO, HEK293, insect)
What are the pros to prokaryotes (E.coli) (7)?
easy manipulation, rapid growth, large scale fermentation, simple and low cost media, high yield, low cost, suitable for small proteins
What are cons to prokaryotes (E.coli) (3)?
almost no post translational modifications (PTM), may aggregate or not fold properly, not appropriate for large proteins
Where is protein production done in prokaryotes (E.coli)?
inside cell
What are the pros with using yeast (3)?
relatively rapid growth, large scale fermentation, performs some PTMs
What are the cons with using yeast (1)?
does not perform all PTMs or performs them differently
Where are the produced proteins found in yeast?
sometimes in cells, sometimes in media (?) (just says sometimes in chart)
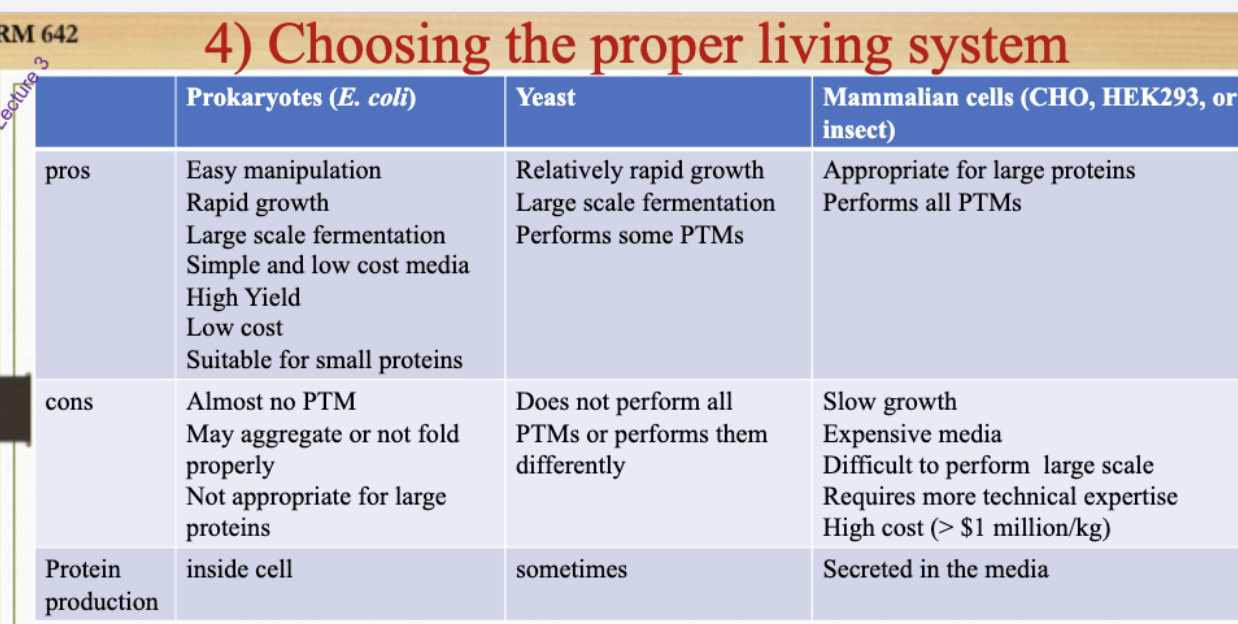
What are the pros with using mammalian cells (2)?
appropriate for large proteins, performs all PTMs
What are the cons with using mammalian cells (5)?
slow growth, expensive media, difficult to perform large scale, requires more technical expertise, high cost (> $1 million/kg)
Where are the produced proteins found after production via mammalian cells?
secreted in media