ARTH100: Unit 2 - The Agrarian Revolution
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Neolithic (New Stone Age)
10/5,000 BCE (varies by region, focus on adoption of practices)
More sophisticated stone tools, pottery, agriculture, and settlements
Megaliths
Large stones used in monuments or structures
May have religious or spiritual significance
Sometimes carved with symbols
Examples include:
◦ Dolmen: A megalithic tomb consisting of three or more upright stones capped by a large flat stone to form a chamber and covered by a mound.
◦ Trilithons: An ancient stone monument consisting of two upright megaliths carrying a third as a lintel.
◦ Henges: Prehistoric stone circle with “hanging” elements

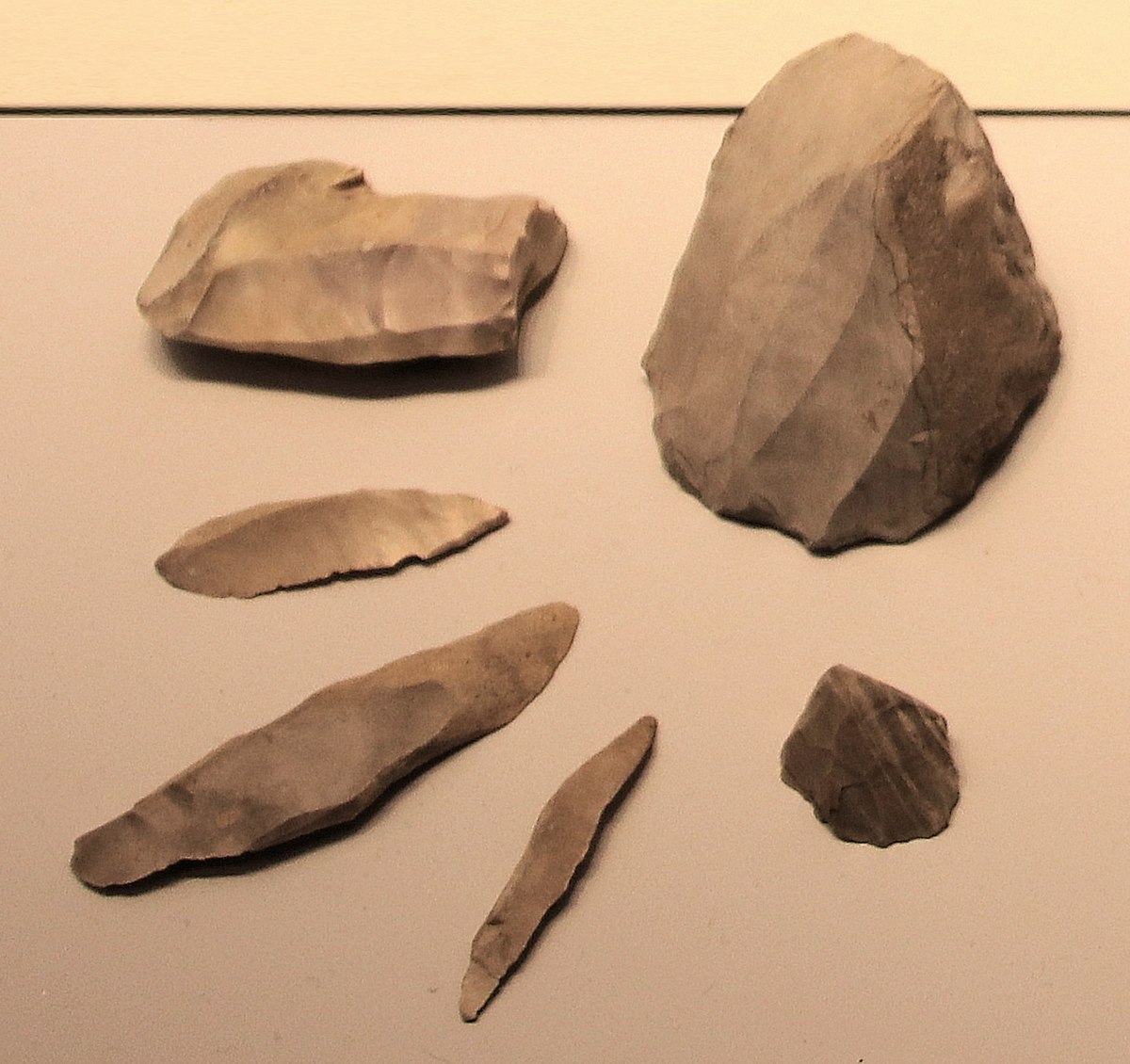
Microliths
Small, sharp stone tools used in hunting and gathering
Later incorporated into composite tools

Henges
Circular stone structures with “hanging” elements
Often associated with rituals or astronomy

Dolmen
A tomb made of three or more upright stones with a large capstone on top
Typically covered by an earthen mound

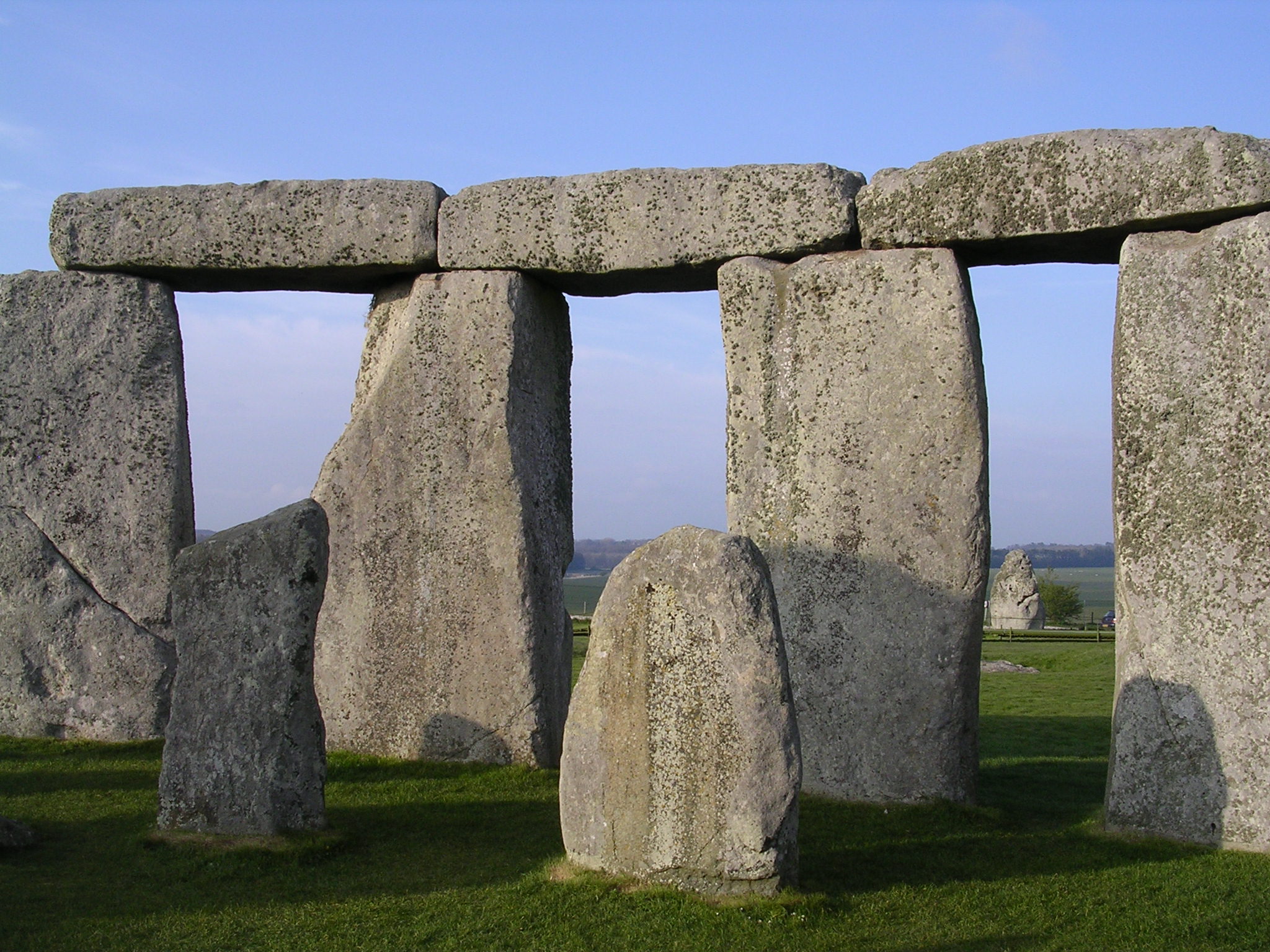
Trilithons
Two upright stones supporting a horizontal stone on top
Example: Stonehenge

Post-and-lintel
Architectural system where two upright posts support a horizontal beam
Used in doorways, tombs, and temples

Corbeling
Overlapping arrangements of stones or bricks
Used in ancient structures to create roofs or arches

Cyclopean Masonry
Large, mortarless stone walls
Used for fortifications to reduce weak points
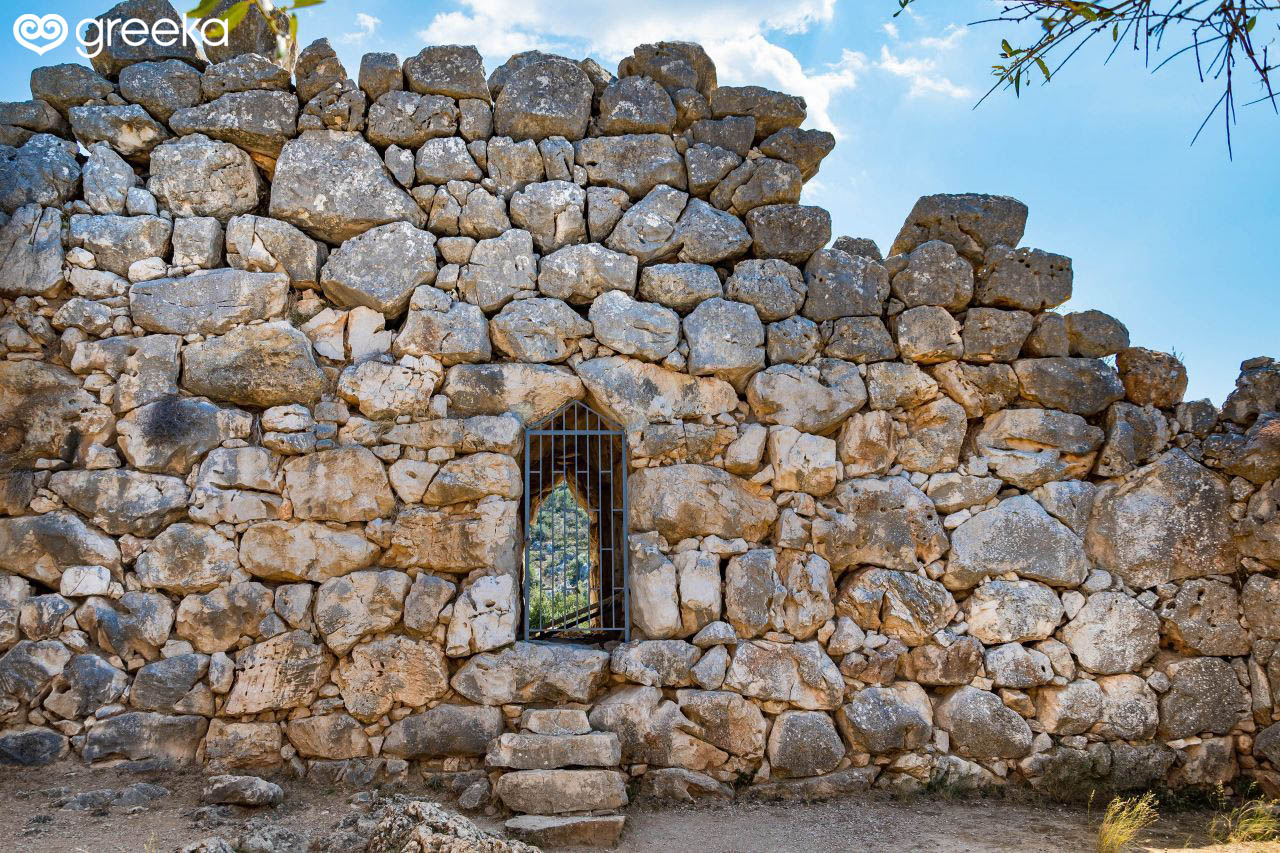

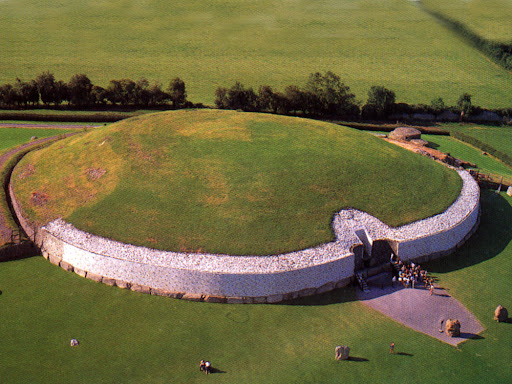
Passage Tombs
Round mounds with a central burial chamber accessed through a passage
Often found on hilltops and contain rich grave goods
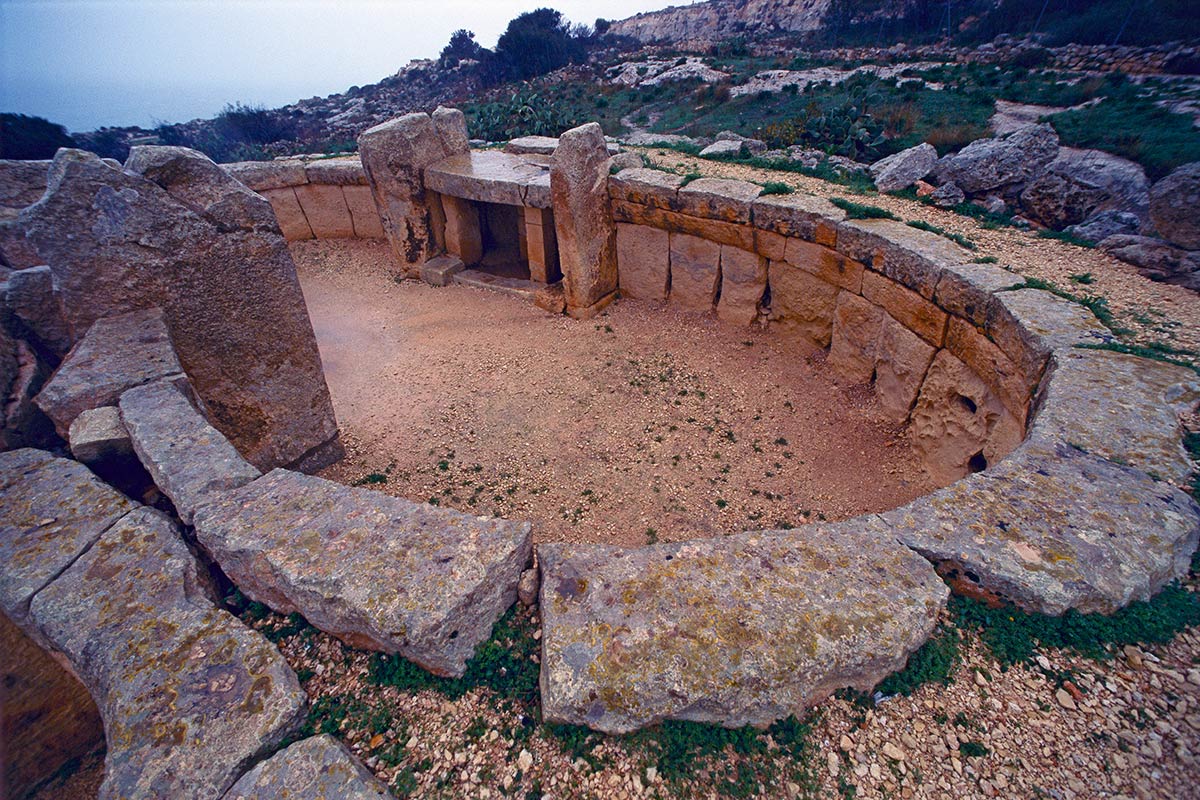
Temples
Religious structures built for worship and rituals

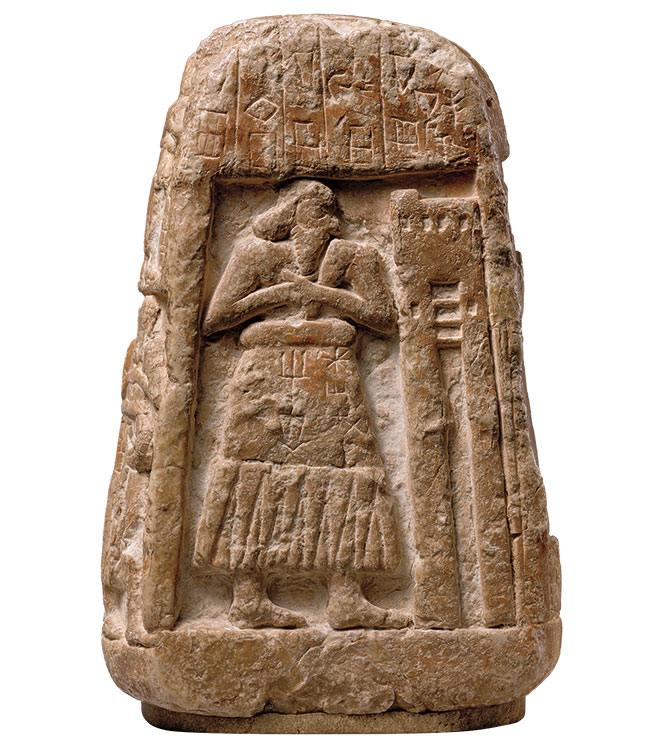
Stele
Inscribed stone or wooden slabs marking graves, sites, or historical events

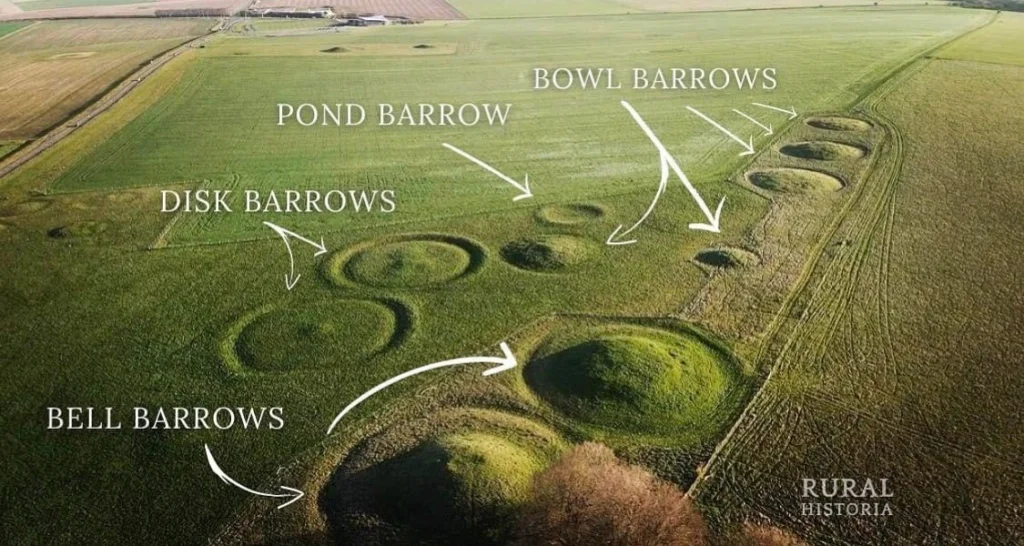
Barrows (Burial Mounds)
Large communal burial sites, often used for rituals

Geometric Wall Paintings
Abstract patterns painted on settlement walls

Bas-Relief (Low Relief)
Shallow carvings on stone surfaces

Ocher
Natural mineral rich in iron oxide, used for painting and decoration
Archaic or Large Wild Fauna Style
Often used to describe a culture before its “peak” or “classical” period
Pastoral (Cattle) Style
Nomads who depend on domesticated livestock, migrate in an established territory to find pasturage for their animals
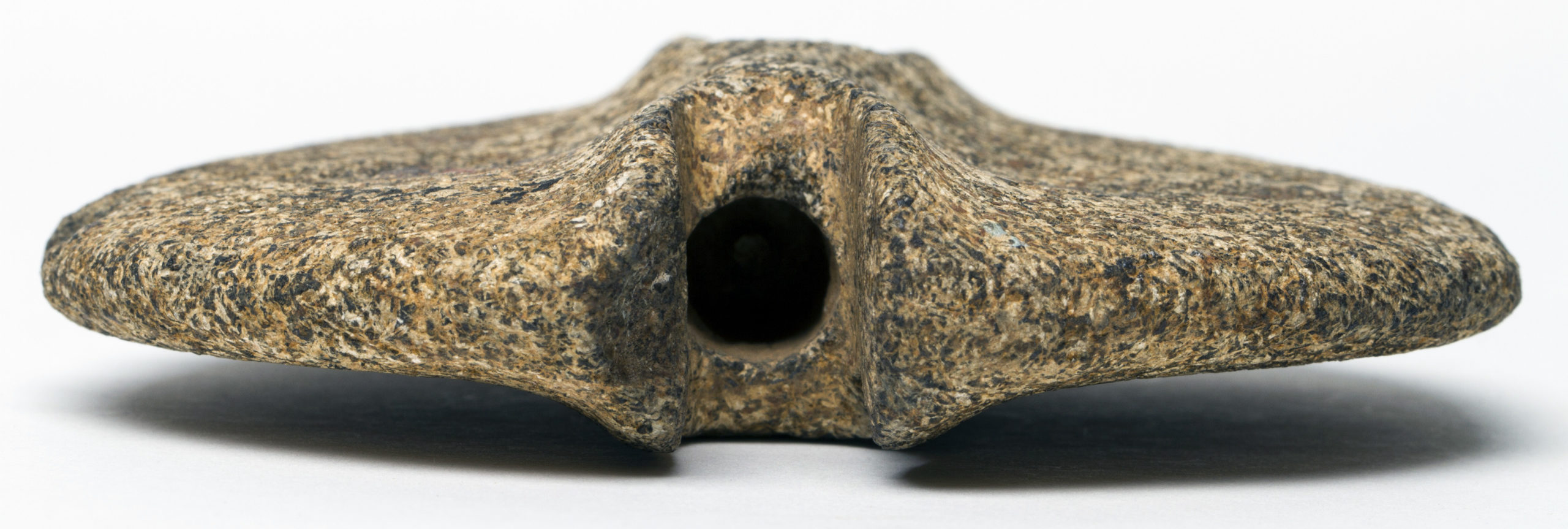
Bannerstones
Polished stone weights, possible used on spear shafts

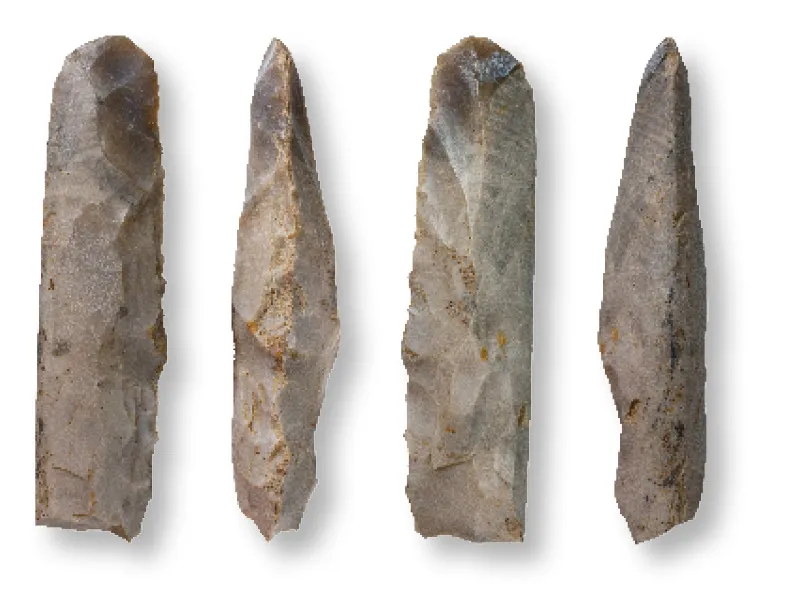
Flint Stones & Chisels
Tools used for carving and cutting

Congs
Rectangular objects with a hollow center, used in rituals

Bi discs
Circular jade discs placed in burials
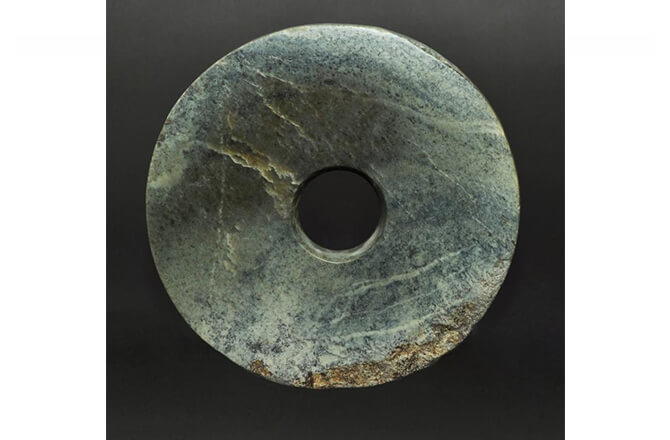

Jade
Green mineral carved into jewelry, tools, and ceremonial objects
Jomon Period
Early Japanese culture known for intricate coil pottery
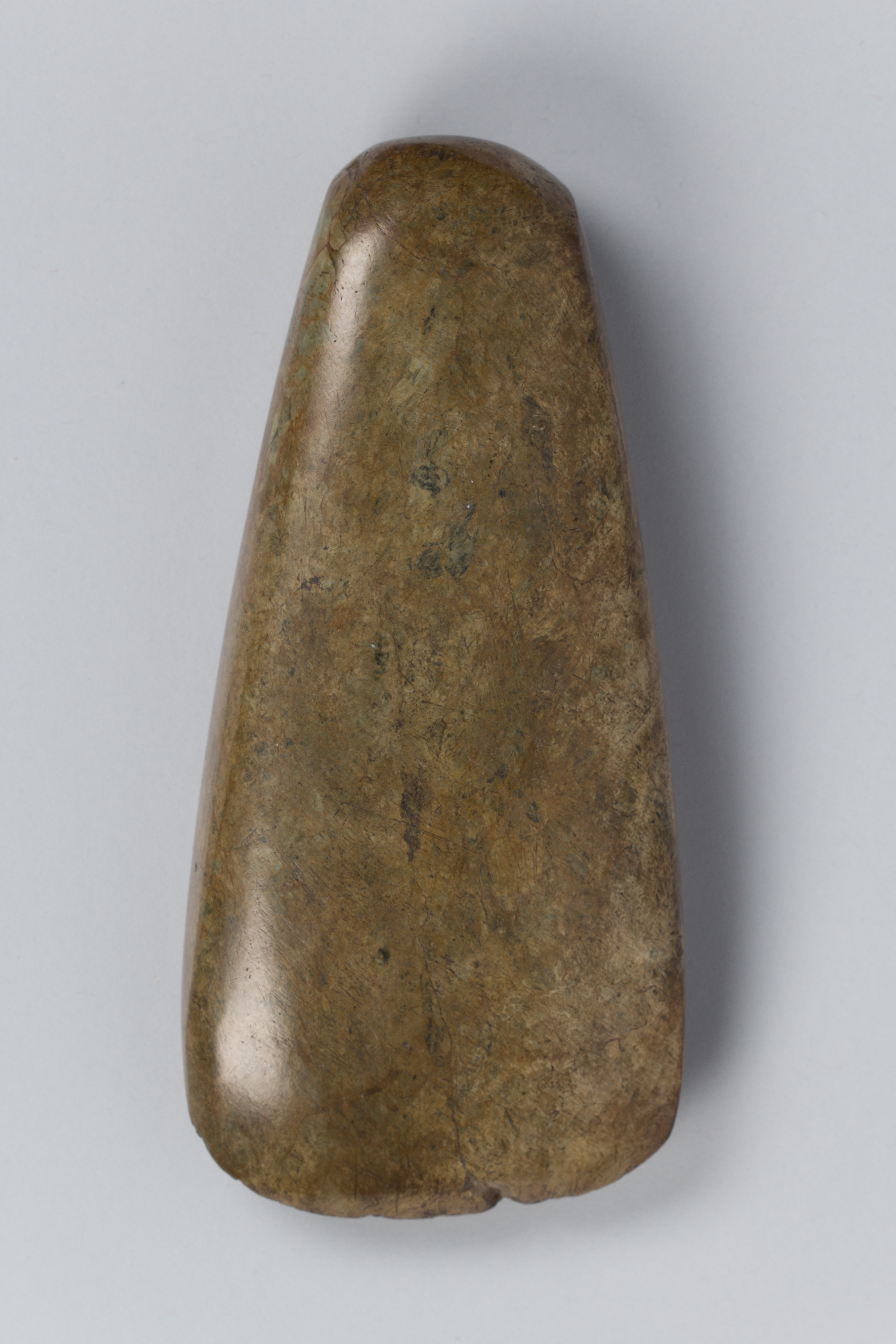
Stone Adz
Tool used for shaping wood
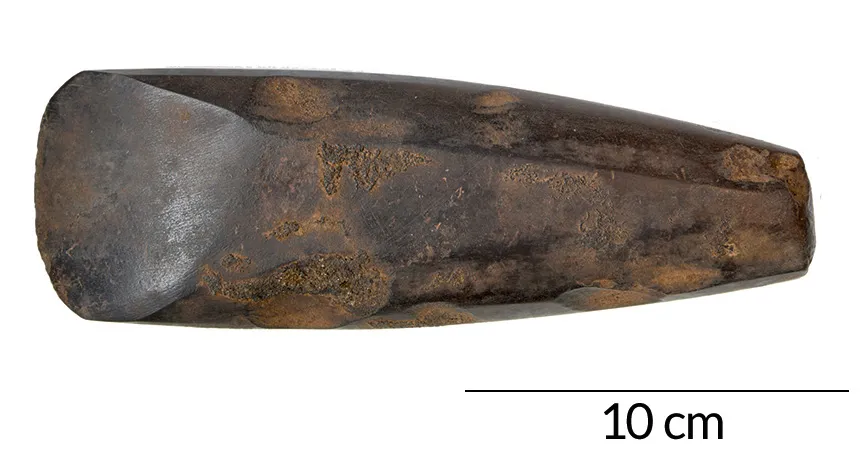

Stone Axe
Used for cutting, clearing land, and warfare

Slash-and-burn land-clearing
Technique of burning forests to create farmland
Woodworking
Craft of carving and assembling wood for structures and tools
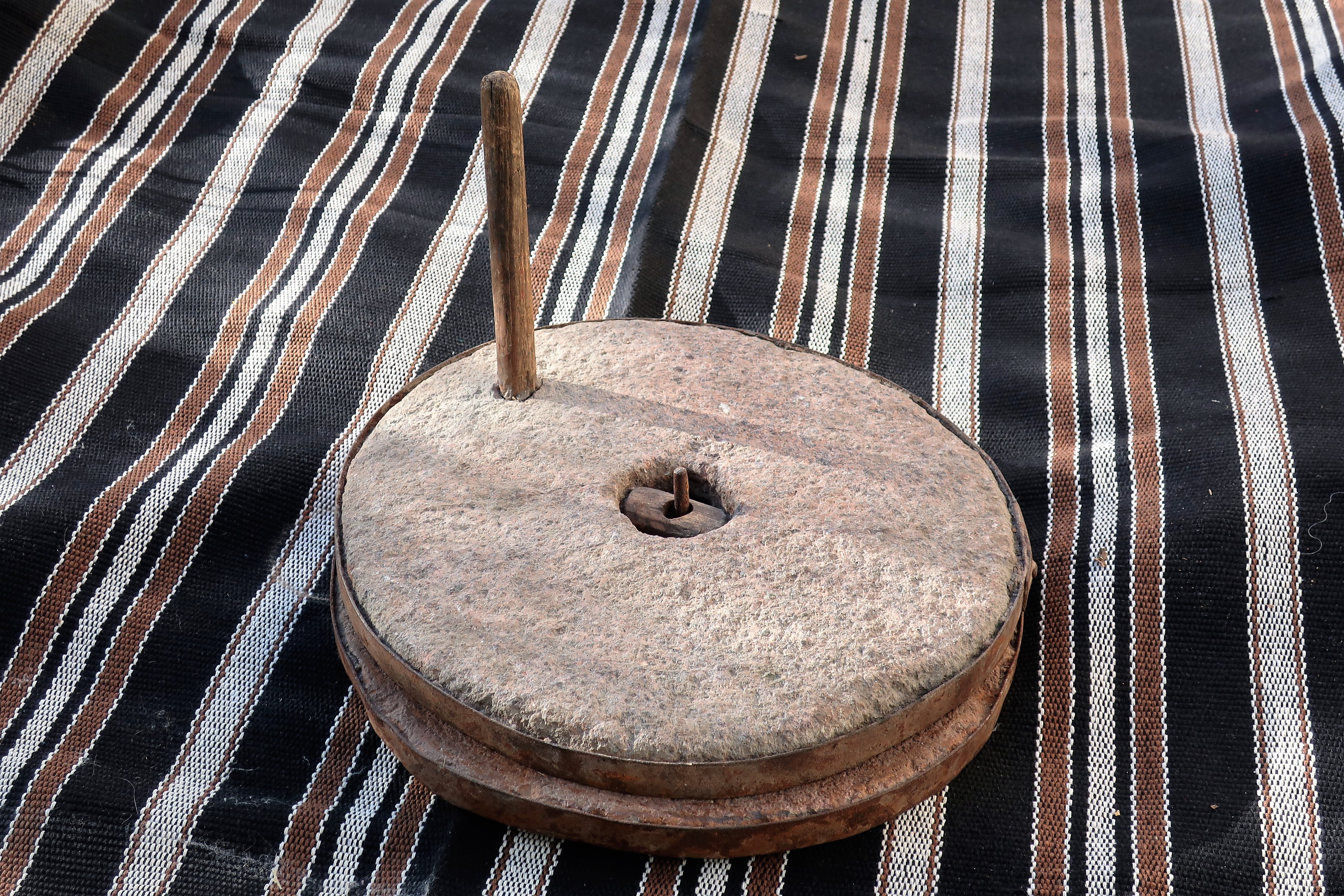
Quern
A hand-operated stone grinder for grains

Open fire pottery
Clay hardened by direct fire, reaching up to 700 degrees

Kiln-fired pottery
Pottery fired in an oven-like structure for better durability

Pit Kiln
Early method of firing pottery in a hole covered with fuel
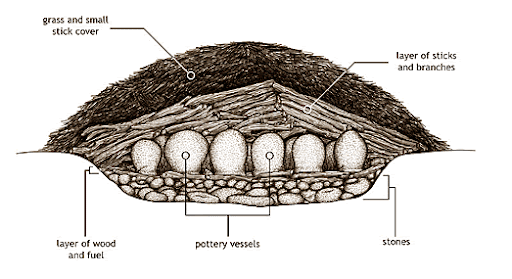
Updraft kiln
Vertical kiln that directs heat upward for better temperature control

Coil Pottery
Pots made by coiling long strips of clay and smoothing them together
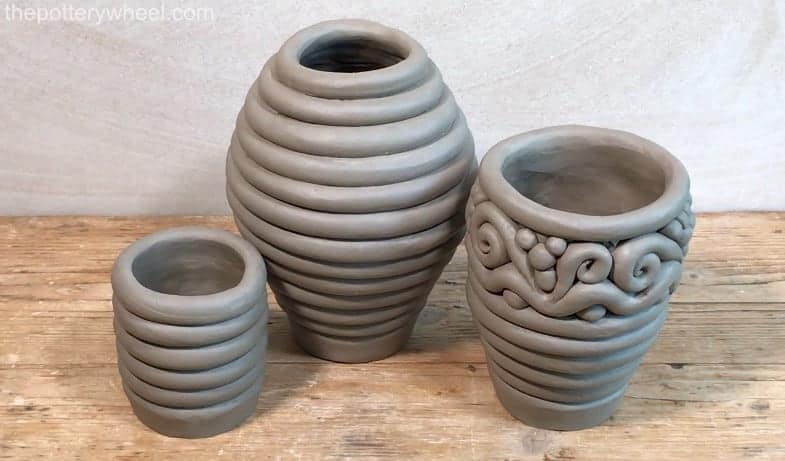

Clay-Impressed Decoration
Patterns pressed into wet clay using sticks, bones, shells, or cords
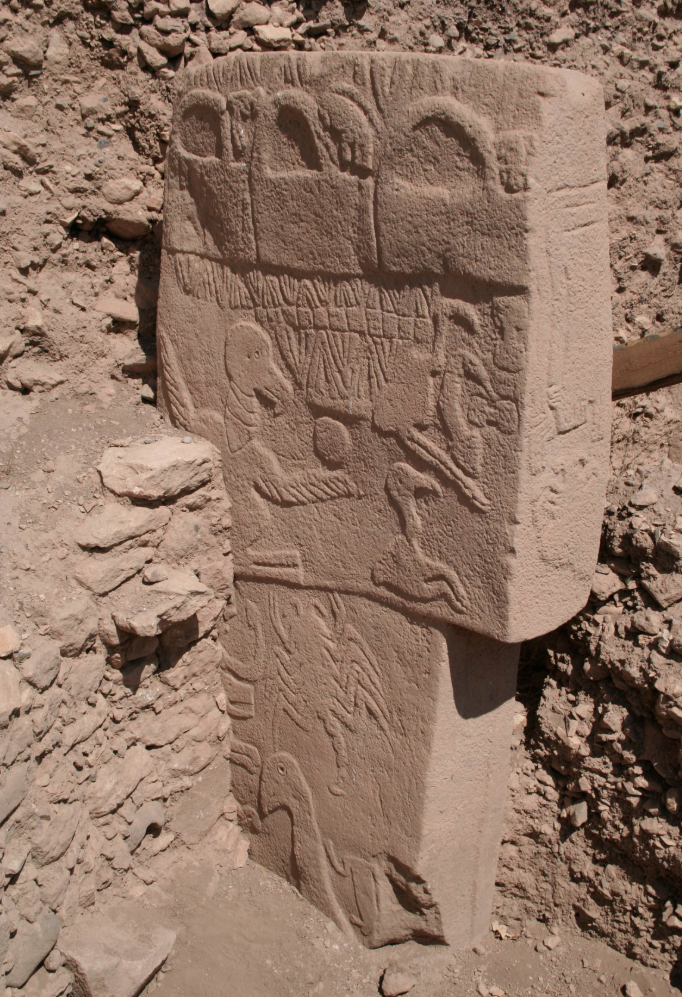

Gobekli Tepe Carved Pillars
Upper Mesopotamia, this site contains massive monumental structures (megaliths)
Decorated with animals, insects, and phallic human figures, offering insight into the way of life and beliefs of the people living in this region
This site was erected by hunter-gatherers and was used between 9600-8200 BCE
Believed to have been used for rituals, possibly funerary, and is considered an early temple complex
No evidence of permanent settlement

Jomon Pot
Highly sophisticated coil pottery which characterizes the earliest major culture of prehistoric Japan, the Jomon Period
Decorated with cord-pattern clay impressions or incisions
Some of the earliest pottery found
The Japanese people of this period put attention into details and aesthetics when creating these useful and beautiful objects

Bannerstones
Polished stone spear weights
Generally symmetrical in shape and drilled down the center, leading to the belief they were placed on wooden rods hoisted in the air
Stone used often had aesthetic properties, quality of material, and pre-existing shapes that were highlighted in their creation
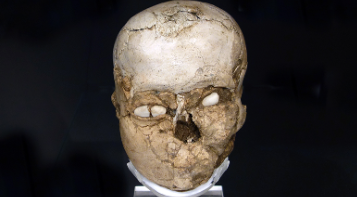
The Jericho Skull
Found in Jericho, instead of burying art objects with the body, the skulls of ancestors were buried under the floor of homes
Later, these skulls would be dug up and decorated with plaster, and the eyes were inlaid with shells
Jericho is one of the oldest continuously lived-in cities in the world, dating back to 10/9,000 BCE

Axe Head
Stone axes were used in a variety of ways, including breaking minerals, cutting down trees, slash-and-burn land-clearing, and rough wood-working
Also used in battle
Crucial for farmers in Northern Europe
The new polished axe was pleasing to the eye, sank deeper, and was more shock resistant

Newgrange Mound (3300 BCE)
Large tomb of one person,
It aligns with the setting and rising of the sun at the winter solstice, showing a spiritual understanding of the time of transition when light returns
Symbolized renewed life for crops, animals, and humans, and represented a human victory of life over death, promising new life to spirits

Seated Woman
Found at Çatalhöyük in modern-day Turkey
An important early Neolithic settlement inhabited by up to 8000 people
Figurines like this large woman between two felines may have been wish tokens or used to ward off bad spirits

Anthropomorphic Stele
Slabs of stone or wood sculpted to show a kind of human figure
They are sculpted on the front and back to look human
Found in regions first settled by Neolithic people
Meant to celebrate the dead and could have had funerary purposes, representing people who lived in the region

Pottery Vessel with Amber Beads
Illustrates the use of pottery and amber in the Neolithic period
Pierced and a strong drawn through
Spiritual quality to it
Found in graves
Took a lot of time to make
Amber was used for
decorative and ritualistic purposes,
it was considered very valuable, indicating the wealth of its owners,
was often placed in bogs and burials for spiritual reasons
was shaped and worked by human hands

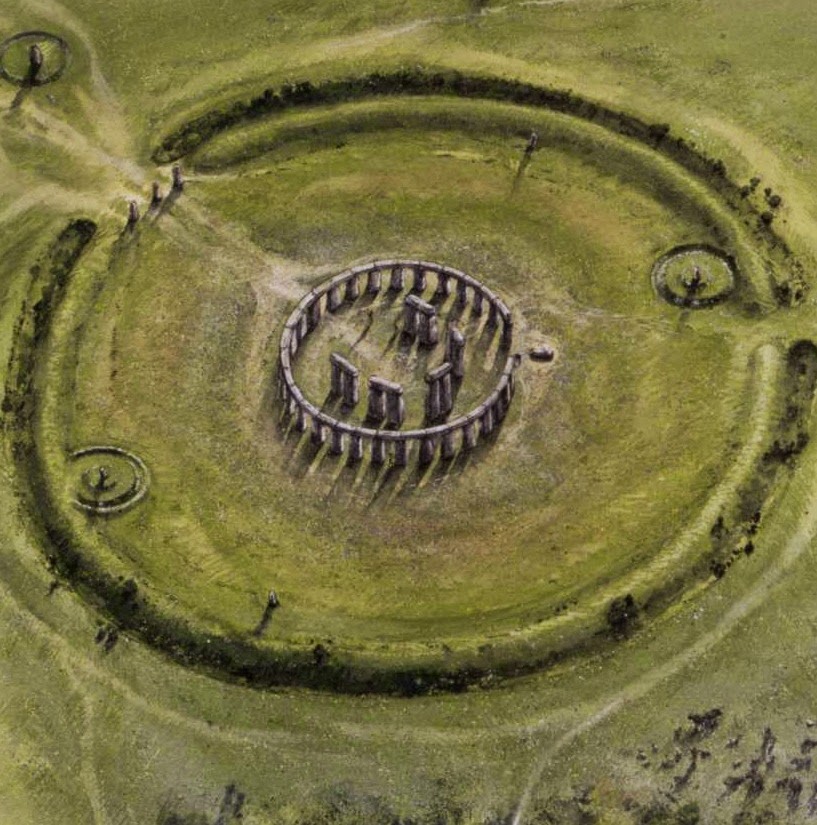
Stonehenge
Megalithic monument was constructed in phases
It was used as a funerary site
The sunrise of the midsummer solstice is framed by the end of the horseshoe and trilithons at the interior of the monument, suggesting a connection to celestial events and the longest day of the year
Phase 1 (c. 3000 BCE): A circular ditch and bank (henges) were constructed, along with 56 wooden posts, possibly marking a burial site or a ritual space.
Phase 2 (c. 2500 BCE): The iconic sarsen stones and bluestones were erected, creating the stone circle that we recognize today, possibly for ceremonial or astronomical purposes.
Phase 3 (c. 1600 BCE and beyond): Further alterations were made, including rearranging and adding stones, and it may have served more as a place for continuous ritual and pilgrimage.

House of Painting
Notable for its geometric wall paintings, which are abstract and non-figurative murals applied to the wall surface
The presence of these suggests a fascination with geometric patterns
Argued this building was a cultural space, possibly a community or spiritual space or a house of the dead with over 80 buried individuals
The earliest signs of both agriculture and human settlement are found in:
West Asia
Holocene Epoch
10,000 BCE
Marked the beginning of the Neolithic period
Beginning of extensive human settlement, domestication of animals, rise of agriculture
Some argued we have entered the “Anthropocene” or the Age of Man
Axes
Used for cutting down trees and clearing forests for agriculture
Adzes
Allowed the shaping of wooden logs into structural beams and wood-working
Coil Pottery
developed as a way to store, cook, and serve food in an increasingly agricultural society
Pit firing and kiln firing pottery
Allowed people to make more durable objects that could last a long time, freeing people to do other things
The spiritual practices of Neolithic people
Involved ritual sacrifice of people and valuable objects in nature
Included the carving of elaborate art objects and stone monuments for the dead
Often included digging up the skulls of their ancestors for ritual decoration
Used art as part of their commemoration process
Was shaped by their relationship to nature and the animal world
The art and visual culture of the Neolithic was:
Strongly shaped by spiritual practices and ancestor worship,
Included the extensive building of megalithic structures for rituals and burial mounds for elaborate graves for the dead
Funerary art is important
Ritual burying of people with ornaments and valuable objects such as amber beads and axes
Carving of stele and erecting of menhirs for the commemoration of important events, places, and people
Amber was
used for both decorative and ritualistic purposes
considered very valuable and showed the wealth of its owners
Was often placed in bogs and in burials for spiritual reasons
Was shaped and worked by human hands
The Neolithic people of Gobelki Tepe were:
Largely hunter gatherers
Practicing rituals
Engaging in ceremonies
Worked together as a community to build their complex and elaborate structures
Catalhoyuk was a settlement that was designed to
House many thousands of people in a defensive manner
The Agrarian Revolution
This period witnessed a slow but radical transformation in the human relationship with nature, moving from a dependent one to a more independent one. Key aspects include the development of agriculture (primarily cereal), animal domestication and husbandry, and a sedentary lifestyle that led to fixed village settlements.... This also spurred innovations like the division and specialization of labor, the emergence of an artisan class, the development of trade, the invention of private property, and the development of basic political and social institutions