Introduction to Economics: Key Concepts and Theories
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is economics?
A social science concerned with the production, consumption of goods and services, resources, and wealth.
What are the two perspectives economics can take?
Economics can look at people as numbers or as human beings.
What is the primary focus of economics?
Efficiency in production and numbers.
What are some examples of resources in economics?
Your mind, land/property, tools, stocks/bonds, possessions, etc.
What is economic efficiency?
Determining the best means of production and supply by reducing waste and energy.
What is the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)?
A curve that illustrates the maximum feasible amount of two goods that can be produced with available resources.
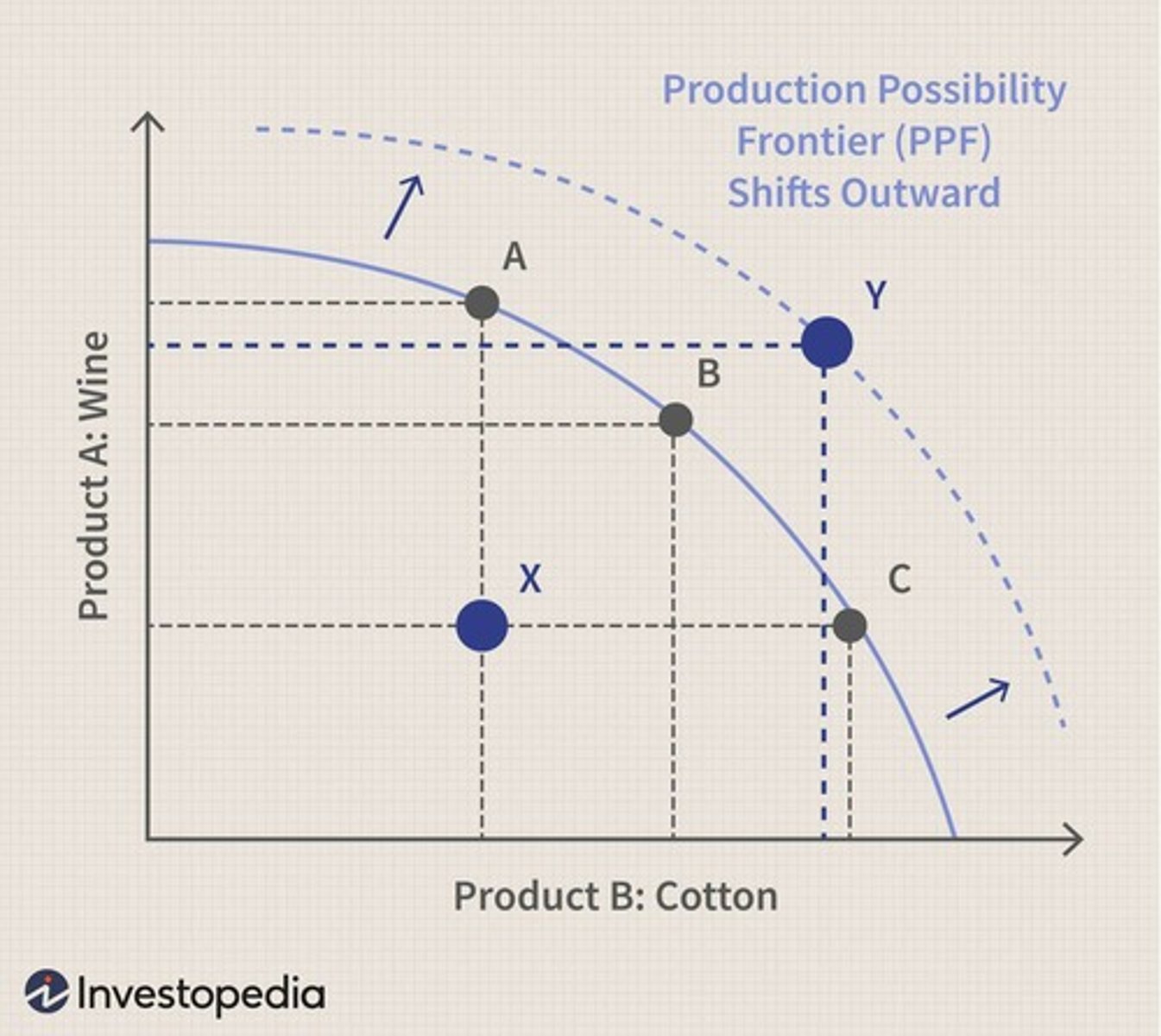
What does production efficiency refer to?
Producing at minimum cost while maximizing output.
What is opportunity cost?
The potential future benefits missed when choosing one alternative over another.
What is incurred cost?
The money spent on something that cannot be recovered.
Who were Karl Marx and Fredrick Engels?
They published the Communist Manifesto in 1848, critiquing capitalism.
What is the proletariat according to Marx?
The workers who produce goods but receive very little in return.
What is the bourgeoisie according to Marx?
The factory owners and elites who profit off the labor of the proletariat.
What does Adam Smith's 'The Wealth of Nations' focus on?
How to manage the economy, advocating for laissez-faire capitalism.
What is laissez-faire capitalism?
An economic system with minimal government intervention, allowing the market to regulate itself.
What is the significance of the year 1776 in economics?
Adam Smith published 'The Wealth of Nations' in this year.
What is market-determined wages?
Wages that are set by the market based on supply and demand, rather than by corporations.
What is the role of private property in Adam Smith's economic theory?
Laws and systems are made to protect the property of the wealthy.
What does Adam Smith suggest about income and wages?
Low income correlates with low wages, while high income correlates with high wages.
What is the significance of the 2008 recession in economic discussions?
It involved the US government bailing out the auto industry, reflecting debates on economic intervention.
What does Marx believe about the relationship between labor and profit?
He argues that workers are often unpaid for their labor, which contributes to the profits of the bourgeoisie.
What is the potential outcome of the proletariat's dissatisfaction according to Marx?
They may lead a revolution against the bourgeoisie due to their exploitation.
What is the impact of technology on labor according to Marx?
As technology advances, fewer workers are needed, leading to unemployment and reduced purchasing power.
What is the relationship between economic decisions and political pressures in the US?
Politicians may push for short-term economic changes that can harm the economy in the long run.
What does the term 'Invisible Hand' refer to in economics?
The idea that individuals pursuing their own self-interest can lead to positive societal outcomes.
What is meant by 'Blind Obedience' in economic behavior?
The tendency of individuals to follow their passions without critical thinking, necessitating mechanisms to prevent this.
How does competition influence economic behavior?
Competition helps regulate desires and can lead to better positions in life by driving efficiency.
What is the main idea behind self-betterment in economics?
Individuals seek personal benefits which can also contribute positively to the economy.
What is Keynesian economics?
An economic theory advocating for increased government spending to stimulate demand during economic downturns.
What was John Keynes' view on the Great Depression?
He believed that simply waiting for the economy to correct itself was insufficient and that government intervention was necessary.
What is the General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money?
A foundational text by John Keynes that established his economic theories and became dominant from the 1930s to the 1970s.
What is Monetarism?
An economic theory emphasizing the control of money supply by central banks to manage inflation and economic stability.
How do monetarists differ from Keynesians?
Monetarists believe in strict control of the money supply rather than increasing government spending to stimulate demand.
What is Behavioral Economics?
An approach that incorporates psychological insights into economic decision-making, recognizing that humans do not always act rationally.
What is Nudge Theory?
A concept in behavioral economics suggesting that indirect suggestions can influence the behavior and decision-making of groups.
What is the Circular Economy?
An economic model aimed at minimizing waste by repurposing, reusing, and recycling resources instead of a linear 'take-make-waste' approach.
Who was Milton Friedman?
An economist known for advocating neoliberalism, emphasizing minimal government intervention and free-market principles.
What is the concept of Economic Equity?
The idea of fairness in economics, particularly regarding the distribution of resources and taxation.
What are the five main variables of Macroeconomics?
Economic growth, employment, price stability, national debt, and income distribution.
What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
The total value of final goods and services produced within a country in one year, regardless of ownership.
What are the three methods of calculating GDP?
The output method, the income method, and the expenditure method.
What does the output method of calculating GDP measure?
It measures national income as the flow of goods and services produced in an economy during a year.
What is the income method of calculating GDP?
It measures the total value of incomes earned in the economy, not necessarily tied to production.
What does the expenditure method of calculating GDP focus on?
It measures the total spending on goods and services in the economy, including consumption, investment, and net exports.
What is Allocation Efficiency?
It occurs when the right mix of goods and services is produced to meet consumer demand effectively.
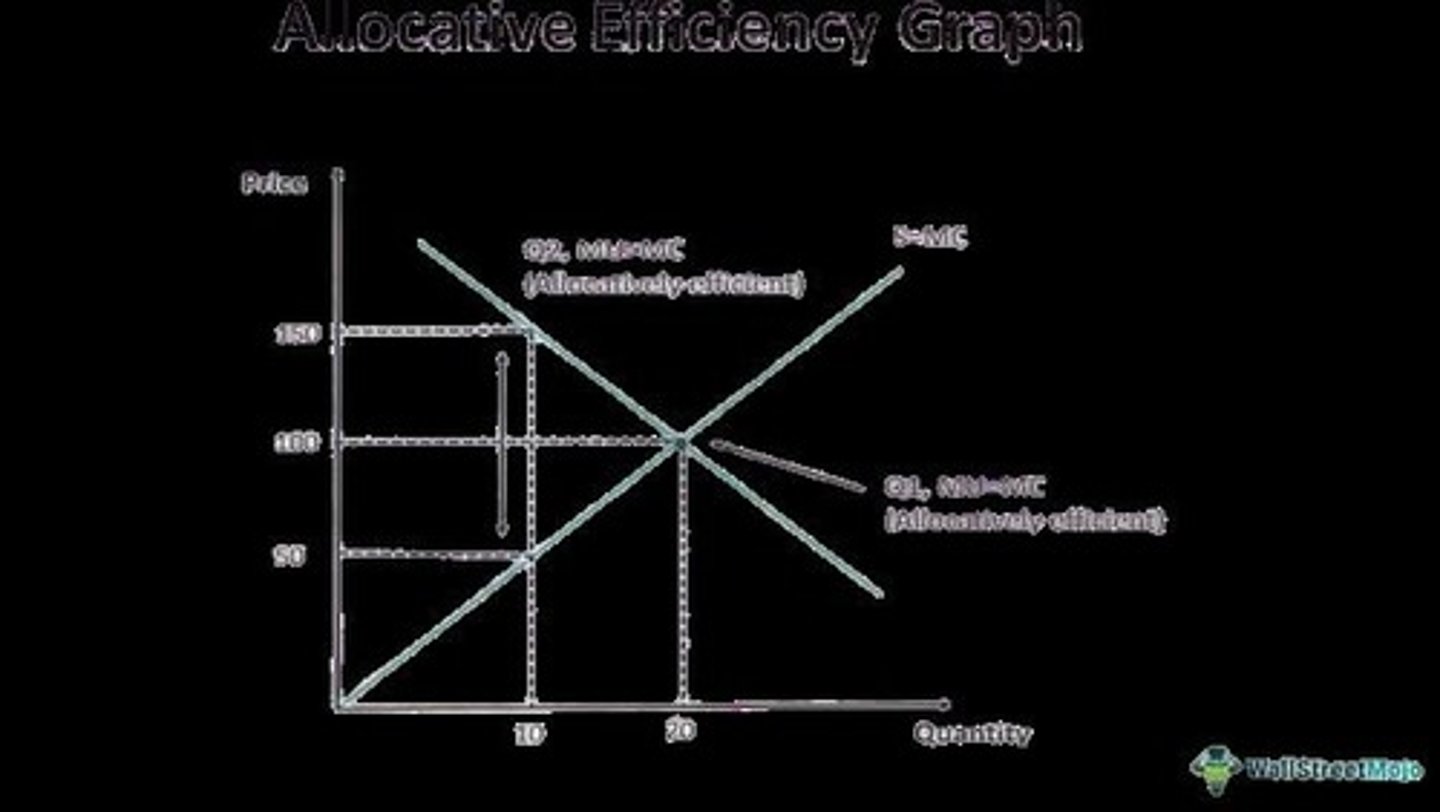
What is Allocation Inefficiency?
The condition where supply does not meet demand at the offered price, leading to wasted resources.
What is the significance of free access to information in economic efficiency?
It helps consumers and producers make informed decisions, leading to more efficient market outcomes.
What is the problem with the concept of fairness in economics?
What is considered equal may not always be equitable, leading to disparities in resource distribution.