EDS100 all flashcards
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
What are the Disciplines of Education?
History
Psychology
Biology
Sociology
Politics
Economics
Comparative
Philosophy
What is Replication Research?
This is repeating previous experiments to see if similar or different data is obtained.
Meta-analysis synthesizes previous research, whereas replications seek to verify whether previous findings are accurate.
Three types:
Operational: tests to see how accurate the obtained data is
Constructive: this tests the targeted group
Direct: helps identify biases in the study and sees if the data that was found was normal or an anomaly
What was the main factor that caused the origin of public schooling?
Urbanization
what 3 interests were in favour of public schooling?`
Economic interests
Social interests
Political interests
Who was Pro schooling in terms of Economic interests, and who was against?
For
Industry: Employable skills such as punctuality, discipline, literacy, tolerance for hours of tedious work
Urban Parents: Affordable childcare and education to meet the labour-intense demands of industrialized work
Opposed
Business Owners: Concerned that educated workers would leave menial jobs
Rural Parents: worried that schools would strip them of much-needed farm help
Who was Pro schooling in terms of social interests, and who was against?
For:
Religious leaders: Provide the young with religious and moral character
Reformers: Offer wayward children care, guidance and protection
Community leaders: Install common values across different backgrounds & classes.
Against:
French Catholics: Secular education assimilates and erodes Catholic influence
Progressives: Endanger freedom of thought and reduce personal initiative.
Who was Pro schooling in terms of Political interests, and who was against?
For:
The State: Instill within the youth an allegiance to nation and state.
Democrats: Encourage participation in the political process from young citizens
Military: Promote discipline, willingness to serve the country and recruitment.
Against:
Tax Payers: Additional taxes required to educate the entire population
Elite: An education population would refuse to obey and challenge the social order
What were Ryeron’s Reforms?
Established compulsory public education
Formalized and standardized public education (Common Curriculum
Teacher inspections
Common textbooks Libraries in schools)
Required teacher training
Was a founder of the first teacher’s college
(Provincial Normal School (1847) (later became OISE)
Used taxation to shift costs from parents to property
Who was a big proponent of Residential schooling?
Ryerson
Who were the 6 parties that were supporters of Residential schools?
Reformers
Industry
State
Church
Parents
Democrats
Why did the reformers support residential schools?
feared that if the children were not educated, they would be a menace to the social order of the country
Why did the Industry support residential schools?
wished to turn the children into farmers and farmers’ wives
Why did the state support residential schools?
wanted the children to abandon their Aboriginal identity
Why did the church support residential schools?
Christian churches sought government support for their missionary efforts
Why did parents support residential schools?
"Mom and Dad’s wishes … strongly believed that attending residential school would allow me to succeed in a white person’s world.” (Fontaine 2010).
Why did Democrats support residential schools?
Canadian politicians wished to find a cheap way out of their long-term commitments to Aboriginal people
What were the years the first residential school opened up and when did the last one close?
1883 - 1996
What were the 5 main justifications of people when using Residential schooling?
Wished to turn the children into farmers and farmers’ wives.
wanted the children to abandon their Aboriginal identity
Feared that if the children were not educated, they would be a menace to the social order of the country
Canadian politicians wished to find a cheaper way out of their long term agreement with the Aboriginal people
Christian churches sought out government support for their missionary efforts
What were the odds of a child dying in a residential school?
1/25
When did the last segregated school close in Ontario?
1965
When did the last segregated school close in Canada?
1983
What was the case that caused the striking down of segregated schools in America?
Brown vs Board of Education
Segregation of children in public schools was struck down by the Supreme Court as unconstitutional in 1954
What is the Davin Report?
Published in 1879
Basically said that the child may learn at school but parents control learning at home, so then what the child learns may be forgotten
Advised the federal government to institute residential schools for Indigenous children
Advised the federal government to institute residential schools for Indigenous children
When was the common schools act creted?
1850
What is the common schools act?
Separate schools for Protestants, Roman Catholics, or Coloured people
Needed in writing the approval of 12 or more resident heads of families to authorize separate schools for Protestants, Roman Catholics or Coloured people
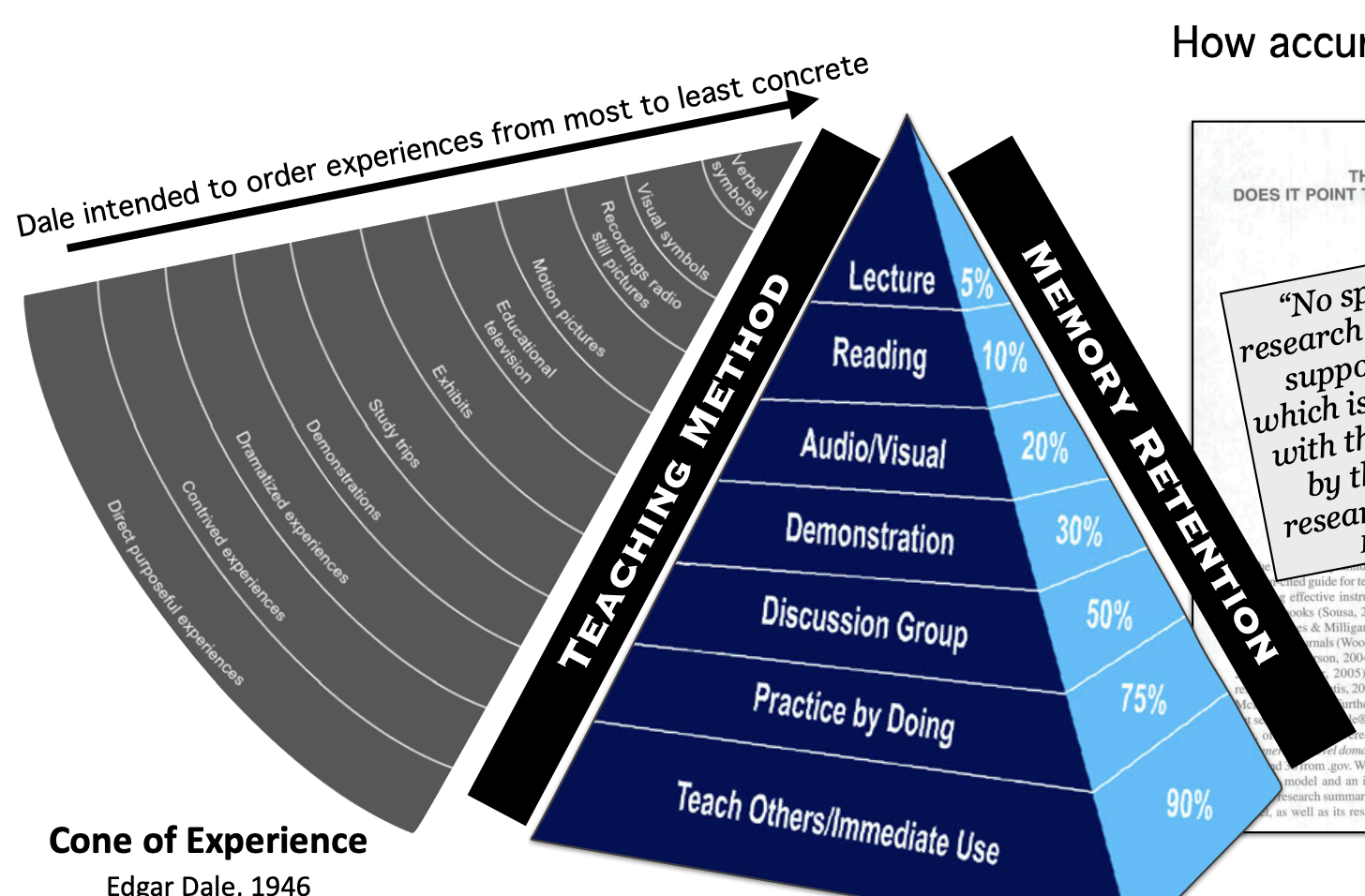
Edgar Dale
Created the cone of experience, which was later renamed Learning pyramid
Pyramid was not accurate at all, and was solely based on personal experience
“No specific credible research was uncovered to support the pyramid, which is loosely associated with the theory proposed by the well-respected researcher, Edgar Dale"
John Watson
Psychologist
Conducted the Little Albert experiment
“Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specific world to bring them up in, and I’ll guarantee to take anyone at random and train him to become any type of specialist… doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief and, yes even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talents, abilities, vocations, and race of his ancestors. I am going beyond my facts and I admit it, but so have the advocates of the contrary and they have been doing it for many thousands of years”
Makel and Plucker
Examined the entire publication history of the top 100 education posts, and found there was a lack of original replication research.
Egerton Ryeson
Centralized Education
Wanted the Prussian education system adopted completely
Was for residential schooling
“the North American Indian cannot be civilized or preserved in a state of civilization (including habits of industry and sobriety) except in connection with, if not by the influence of, not only religious instruction and sentiment but of religious feelings”
“… no child shall be compelled to read any religious book or attend any religious exercise contrary to the wishes of his parents and guardians.”
Nicholas Flood Davin
Wrote the Davin report
Made the blueprint for Residential schools
Was sent by John A. to learn about aggressive civilization
“…as the adult Indian is concerned. Little can be done with him. … The child, again, who goes to a day school learns little, and what little he learns is soon forgotten, while his tastes are fashioned at home, and his inherited aversion to toil is in no way combated. . .”
David Weikart
Conducted the Perry Preschool project
James Coleman
Wrote the Coleman report
Jacob Mincer
Mincer equation and the Mincer curve
Explained why students would go to University and stuff at the loss of some money
Gary Becker
Investment in education is analogous to investments in physical capital
Human capital
Steven Lukes
Luke’s dimensions of power
“Power over others can be productive, transformative, authoritative and compatible with dignity” (Lukes 2005)
Michel Foucault
Thought of the Panopticon
Control was minimized for schools as there were too many people in small spaces
“The perfect disciplinary apparatus would make it possible for a single gaze to see everything constantly”
Control is what keeps people in check and in line
Paolo Friere
The banking system
What the teacher does for the student
Wilhelm Wundt
Established the first psychological laboratory
Wundt’s laboratory produced no great psychological discoveries or cri6cal experiments, it established psychology as a discipline and experimenta6on as the method of acquiring and refining knowledge
John Dewey
Established the first laboratory school
Dewey never put forward any systematic surveys or suggested future directions for educational research. He never published any systematic data on the effects of their experience in the laboratory school on the children
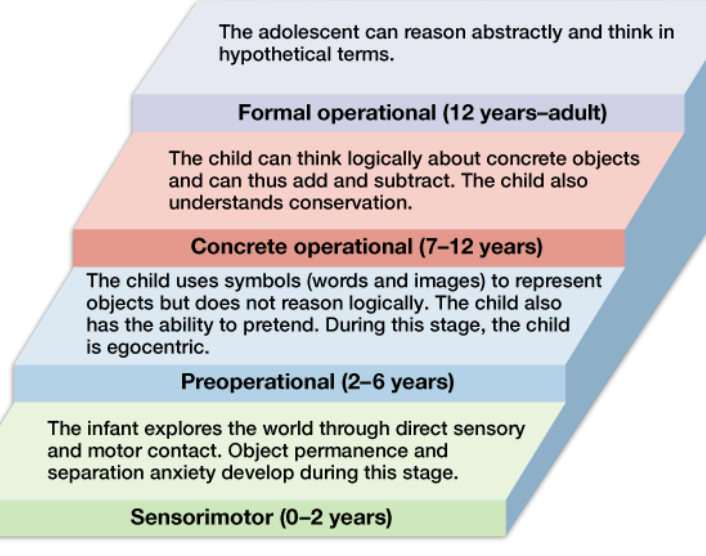
Jean Piaget
Piaget was one of the first to identify that the way that children think is different from Jean Piaget the way adults think
Hermann Ebbinghaus
WHOSE HOUSE?
The forgetting curve
conducted experiments on himself to see if he would remember a bunch of random stuff
Judy Singer
Neurodiversity
BF. Skinner
Operant conditioning
Conditioning refers to “the strengthening of behavior which results from reinforcement”
Did a rat experiment where a rat could only stop the floor from shocking by pushing a button
This was positive reinforcement and conditioned the rat to associate the button with ease
Carol Dweck
growth mindset vs fixed mindset
Marc-Antoine Jullien
Improve education
proposed governments collect and distribute statistical information on education
developed systematic comparative classification using questionnaire surveys
introduced the use of analytical tables
published the first comprehensive study of education called “Esquisse et vues préliminaires d'un ouvrage sur l'éducation comparée” (1817)
wanted to improve the French education system
Bray and Thomas
Cube
Made Bray-Thomas cube, used for comparing
Yong Zhao
Side effects of education
“I have not yet found an educational product that comes with a warning label carrying information such as “this program works in raising your students’ test scores in reading, but may make them hate reading forever.”
A side effect is ‘‘an unwanted or unexpected result or condition that comes along with the desired effects of something.’’
What is the definition of comparative education?
Comparative education is the comparison of various philosophies of education based not only on theories but the actual practices which prevail
What is the Bray-Thomas cube?
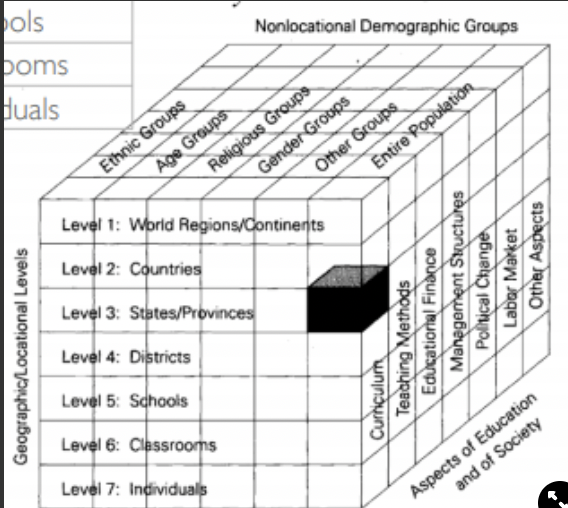
What does the Bray-thomas cube do?
It looks at focus, demographics, location
Why do we compare education with othes?
Improve education
Policy making
Cultural understanding
Possibilities (The educational systems beyond one’s national boundaries suggest what is educationally possible.)
What does Bereday’s model look like?
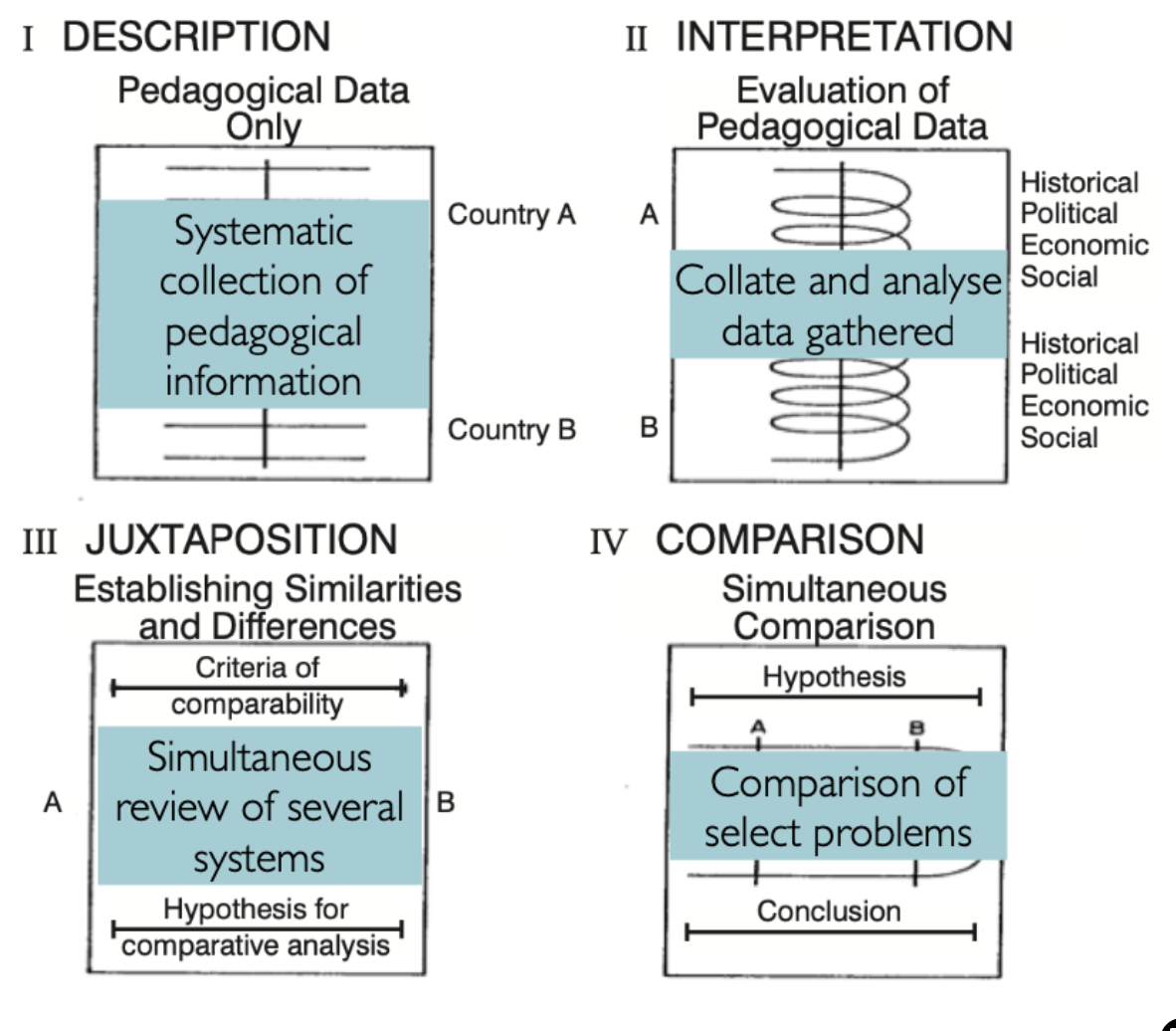
What does Bereday’s model do?
Compares different information of different countries education data and looks to compare problems between school systems of other schools
What is standardized testing?
High stakes testing results in curriculum narrowing , a reduction in the amount of time and resources devoted to other subjects
Campbell’s Law “The more any quantitative social indicator is used for social decision-making, the more subject it will be to corruption pressures and the more apt it will be to distort and corrupt the social processes it is intended to monitor” Donald Campbell
basically, if numbers are constantly used to judge the standing of schools, the more skewed it becomes and the more it will cause the things it measures to be changed
What is shadow schooling?
Shadow education are educational activities that take place outside of formal schooling.
They are often designed to enhance student's academic success or career prospects
Getting tutors to do better in school for example
Who compares?
Students
Parents
Policy makers
Principals and Teachers
Academics (to improve understandings of educational processes and impacts of processes on social development)
What are the issues of indiscriminate borrowing?
Indiscriminate borrowing of education practices without regards for geographic, demographic, social, economy and political considerations can be problematic
What is the triune brain?
Neocortex
Limbic Brain
Reptilian Brain
What does the Neocortex do?
Responsible for problem solving, reasoning & pattern recognition. Divided into two hemispheres. Explains the relationship between critical thinking and understanding
What does the Limbic brain do?
Emotional or feeling brain
Controls emotions and stores long-term memory.
An emotional connection to learning increases attention and memory retention
What does the reptilian brain do?
Instinctual or Dinosaur Brain
Controls muscles, balance and autonomic function (breathing and heartbeat).
Under stress, the reptilian brain takes over
What is a neuromyth?
A misconception generated by a misunderstanding, a misreading, or a misquoting of facts scientifically established (by brain research) to make a case for the use of brain research in education or other contexts
(ex. dyslexics seeing letters backwards)
What is dissonance?
It is a theory that describes how humans adjust actions and behaviors in the presence of personal belief
They let myths that they believe to influence their action with no actual scientific effect on the brain
What is Neuroplasticity?
The notion that your brain is not fixed
Your brain at birth is much different from when you become an adult
What is the taxi driver example used to describe neuroplasticity?
Taxi drivers in London have more densely packed parts of the brain because of how much they had to learn
They had to learn so many roads
What are the 4 changes that happen to the brain during neuroplasticity?
Chemical change
Change in the concentration of chemical signalling between neurons involved in short-term improvement of memory
Structural (physical change)
Change to the connection between neurons involved in long-term memory change
Functional change
More frequently used regions, it becomes easier to access
Pruning
The elimination of under-utilized synapses
What is a growth mindset?
This is an incremental theory
Abilities and skills can improve through learning
Your intellect can increase and grow with more learning
What is a fixed mindset?
This is an entity theory
Abilities are fixed traits over which they have little control
Intelligence is fixed and static
What is neurodiversity?
Brains CAN'T be identical, in a traditional setting people with different disabilities might struggle
Shifts the focus away from identifying deficiencies and disorders to determining utilising strength.
(dyslexics are better at seeing the visual oddities than “normal” people)
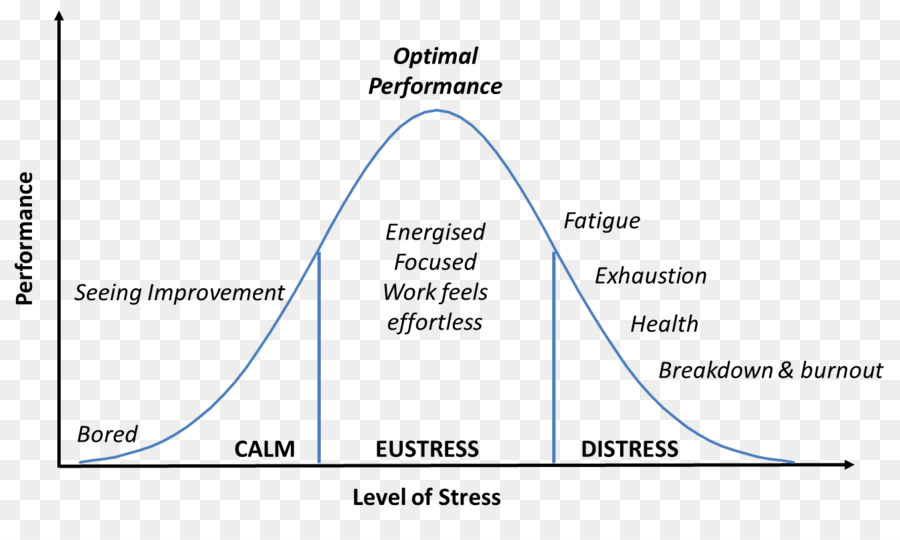
What is Eustress?
Eustress is when you’re at optimal performance (medium amount of stress)
What is the nurture vs nature argument?
Brains are structurally different
Brains change in response to their environments
What is distress?
Distress occurs when the environment is too taxing or exceeds one’s resources
What does the stress curve look like?
What is positive stress?
Brief increases in heart rate, mild elevations in stress hormone levels
What is moderate stress?
Serious, temporary stress responses, buffered by supportive relationships
What is toxic stress?
Distress
Not good environment
Prolonged activation of stress response systems in the absence of protective relationships
Toxic stress leads to changes in areas of the brain involved in learning
Toxic stress can change the stress system so that it responds at lower thresholds meaning that situations that do threaten most students may trigger a stress response in students who have experienced toxic stress
How does sleep affect learning?
helps with creativity
Gives insight (helps with problem solving and solving puzzles)
How does diet affect learning?
Excessive calories can reduce the flexibility of synapses and increase vulnerability to cell damage
Brain synapses and several molecules related to learning and memory are adversely affected by unhealthy diet
How does exercise affect memory?
Helps improve memory
Helps with creativity
Helps with attention and focusing
Improves vocabulary learning in students
What is conditioning?
Conditioning refers to “the strengthening of behavior which results from reinforcement”
What is the experiment designed by Ivan Pavlov?
Dog experiment
Wanted to see how he can his get dog to do certain things he wanted to do
He wanted his dog to be conditioned to do something based on a cue
Dog associating bell ringing with food being present, and this causes the dog to salivate even if there is no food
What was John Watson’s Experiment?
Little Albert Experiment
Watson wanted to take something cute and loveable and make Albert scared of it
He would make loud noises and bang things together to scare Albert when a cute mask or object was seen
Eventually, Albert would cry at the sight of the cute object, even without the sound cues
What is the idea of Development Psychology according Piaget?
Children and adults think very differently (first seen by Piaget)
What was found about children aging and moving through certain phases of growth?
“I have found that in his development, the child passes through certain phases, each of which has its own particular needs” (Maria Montessori)
What is developmental psychology?
Children reach stages of development at a time that is appropriate to the individual.
Both very young and very old persons are defective in memory; they are in a state of flux, the former because of their growth, the latter, owing to their decay - Aristotle
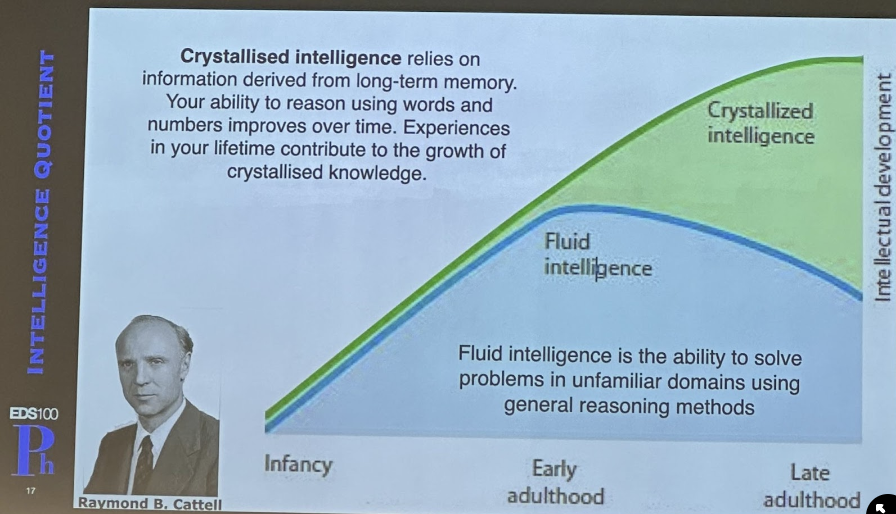
What is the Intelligence Quotient?
The Intelligence Quotient (IQ) is the ratio between the individual’s mental age and her/his chronological age
The concept of IQ was developed by William Stern
What is crystallized Intelligence?
Relies on information derived from long-term memory.
Your ability to reason using words and numbers improves over time.
Experiences in your lifetime contribute to the growth of crystallised knowledge
What is fluid intelligence?
The ability to solve problems in unfamiliar domains using general reasoning methods
(being able to solve problems that you have not been in before)
How does the curve for Fluid vs Crystallized intelligence look like?
What is a learning disability?
A learning disability is a major discrepancy between a student’s ability and some features of achievement
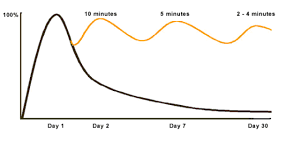
Who created the forgetting curve?
WHOSE HOUSE? EBBINGHAUS
What does the forgetting curve look like?
What were the issues of the methods used by Ebbinghaus to get the data for the forgetting curve?
His use of himself as the subject of study raised concerns about his research because he employed only one participant (himself), and it is unlikely he was unbiased or a typical learner
(his findings were later validated experimentally)
What were the 3 things that Ebbinghaus concluded after the getting his data for the forgetting curve?
Forgetting Curve: Most forgetting occurs within an hour.
Practice: Continued practice of material aIer learning enhances retention.
Spacing Effect: intermittent spacing of learning over time, increased recall.
What is mind-wandering?
This is characterized by the decoupling of thought from the current task onto internal mental events (losing focus)
What is retrieval strength?
Measures how accessible an item is at that time
What did Edward Thorndike say about memory?
Practice increases the efficiency and durability of responses. Without continued use, memory terraces decay as a function of time
What are the 4 things that are typical when processing information and how do disabilities hinder that?
input
Organization
Memory
Output
Typically disabilities do not allow for the output to match what the person wants, or there is an issue within steps 2-4
What is nudging?
Any situation where one chooses an option that alters people’s behaviour in a predictable way without forbidding any options or significantly changing their economic incentives
What is a type 1 nudge?
influence behavior
Sending parents text reminders 3 times/week to engage in a literacy activity increased the frequency of literary activities at home (York et al. 2019)
Grades improved when students were provided information about the struggles of well-known scientists (Lin-Siegler et al. 2016)
Reduced student dropout with a well-known 1 sentence message about student’s performance to parents (kraft and rogers 2015)