Microscopes and magnification
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the most common microscope?
Light microscopes.
Why are light microscopes used more?
They are cheap and easy to use and they can magnify living cells/small organisms so activity and behaviour can be studied.
When studying, what must the specimens be?
They must be thin so that light can pass through.
What is often added to light microscopes see more?
A stain is often used to colour cell structures so that everything can be seen more easily, most cells are transparent and don’t have pigments.
What is magnification?
Making the image large than the actual object.
How do you increase magnification?
We can increase magnification by using a higher powered objective lens, allows us to see in more detail as it increases the size of small details.
What can electron microscopes do?
Electron microscopes help us to see smaller organelles like ribosomes. But also details inside of organelles like mitochondria. This helps further our understanding of sub-cellular structure.
What does electron microscopes have higher of?
They have higher magnification and resolution than light microscopes.
What is resolution?
It is the ability to distinguish between two objects at separate points.
What are the disadvantages of electron microscopes?
They are large, they are very expensive and they cannot use living specimens.
What is the advantage of an electron microscope?
Images can be in 3D.
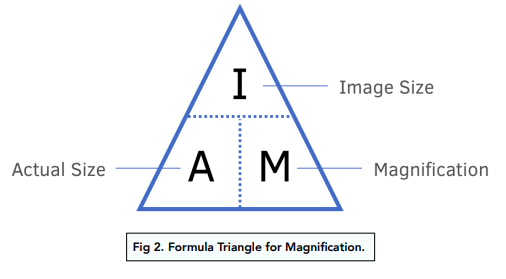
What is the formula for magnification?
Magnification = Image size / Actual size - use the IAM triangle for re-arranging.
How do you convert mm to µm?
1 mm = 1000 µm - therefore multiple by 1000, and divide by 1000 for µm to mm.
What do light microscopes use?
They use beams of light to form large detailed images.
what are the properties of a light microscope? (magnification and resolution)
They can magnify up to 1500x but their resolution is low (0.2µm) - at 1500x magnification mitochondria can only be just seen and ribosomes are too small.
What are the properties of electron microscopes?
They have a higher magnification (2×10^6) and have a resolution of 0.1nm, meaning they can clearly distinguish two points that are 0.1nm apart.
Why can electron microscopes see smaller organelles?
Electron microscopes use beams of electrons and not light, electrons wavelength is small whereas light has a much greater wavelength.
What are the two types of electron microscopes?
Transmission electron microscopes (TEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEM).
How does a TEM work?
Uses electromagnets to focus a beam of electrons at a thin slice of a sample and detects those electrons that make it through to the other side. Cells are stained with heavy/dense metals to block transmission of electrons.
How does a SEM work?
It uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons which reflect off the surface of structures. Specimen needs to be coated in metals like gold to reflect electrons.
What is the difference between TEM and SEM?
TEM cannot produce 3D images and their samples have to be thin, whereas SEM can produce 3D images and samples do not have to be thin. However SEMS give lower resolution images than TEMS.
What do electron microscopes require?
They require a vacuum as air particles would interfere with the beam of electrons, specimen must always be dead.
What are the two lenses on light microscopes?
The eyepiece lens and the objective lens.
State the difference between eyepiece lens and objective lens.
Lens near the eye is called the eyepiece lens, which is thicker, the objective lens is larger and thinner.
What are the two knobs called?
The fine focus knob and the coarse focus knob.
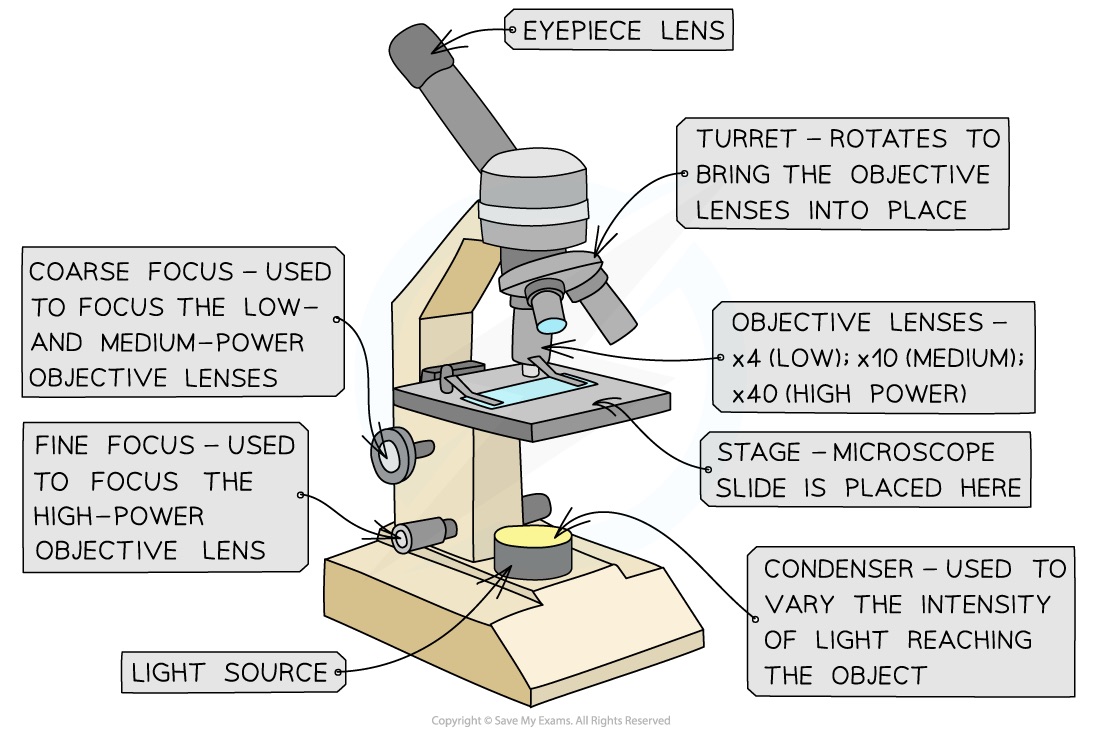
What’s the difference between either knobs?
Coarse: used to bring the specimen into approximate or near focus.
Fine: it sharpens the focus quality, after using the coarse to bring into focus.