Chapter 12 notes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Problem
An obstacle between a current state and a goal, where the solution is not immediately clear.
Gestalt Approach to Problem Solving
Emphasizes problem-solving as perceiving the problem's structure correctly and restructuring mental representations.
Restructuring
The process of reorganizing mental representations to find a solution without the need for mathematical equations.
Insight
A sudden comprehension or realization leading to a solution, involving a reorganization of mental representations.
Fixation
A major obstacle in problem-solving where focus on specific characteristics hinders finding a solution.
Functional Fixedness
A type of fixation where familiar functions of objects impede problem-solving by limiting alternative uses.
Mental Set
A preconceived notion about problem-solving approaches based on past experiences.
Means-End Analysis
A strategy to reduce the difference between initial and goal states by setting subgoals.
Analogical Transfer
Using the solution to a similar problem to guide the solution of a new problem.
Expertise in Problem Solving
Experts invest time in deliberate practice, possess domain-specific knowledge, and organize information based on underlying principles.
Analytical Approach
Experts invest time in problem analysis before solving them, leading to more effective solutions.
Domain-Specific Expertise
Expertise is specialized and may not transfer to unrelated fields, hindering out-of-the-box thinking.
Cognitive Processes in Expert Problem Solving
Experts excel in pattern recognition, memory retrieval, and mental simulations for problem-solving.
Training for Expertise
Analogical encoding enhances problem-solving skills by noticing similarities between problems.
Creative Problem Solving
Creativity involves originality, utility, and practicality in solutions, as exemplified by Niels Bohr's unconventional problem-solving approaches.
Defining Creativity
Divergent thinking generates unique solutions, emphasizing the usefulness of creative solutions.
Brain Networks and Creativity
Default Mode Network (DMN), Executive Control Network, and Salience Network play roles in creativity and idea generation.
Role of the Default Mode Network (DMN) in Creativity
The DMN contributes to creative thinking through mind wandering and incubation effects.
Understanding the ECN and DMN in Creative Thinking
The ECN directs attention, while the DMN is active during mind wandering, collaborating for creativity.
Collaboration Between Networks
The ECN and DMN collaborate during creative tasks, managing imagination and exploring complex ideas.
Mindfulness and Its Impact on Creativity
Mindfulness techniques like OM meditation enhance creativity by activating the DMN and fostering a free flow of thoughts.
Analogical Problem Solving
Using solutions from similar problems to solve new ones.
Duncker’s Radiation Problem
Destroying a tumor with rays without harming surrounding tissue.
Steps in Analogical Problem Solving
Noticing, mapping, and applying analogous relationships to generate solutions.
Analogical Encoding
Identifying similarities between problems to aid in problem-solving.
Analogical Paradox
Discrepancy between real-world analogy use and lab research application difficulty.
Expertise
High skill or knowledge level in a specific field, gained through experience.
Divergent Thinking and Connectivity
Generating unique solutions and forming connections between ideas.
Factors in Generating Ideas
Role of knowledge, brainstorming, and creative cognition in idea generation.
problems are either —>
well defined or ill defined
well defined problems
initial state, goal state, and permissible operations completely specified —> we know almost everything about the question
ill defined problems
uncertainty in one or more components we don’t know everything about the question, more difficult to study.
problems of inducing structure
determines relationship among several given elements (analogy problems) four steps required to solve.
problems of inducing structure
1) encoding: identify appropriate attributes
2) inference: relate 1st and 2nd elements
3) mapping: relate 1st and 3d elements
4) application: relate 3rd and 4th elements
these four steps allow us to see where people make error if they do
coherence
representation compromised of parts connected in a way that makes sense
correspondence
internal representation “maps well” onto elements of the problem
relationship to background knowledge
problem elements linked to existing knowledge
3 requirements for understanding a problem
coherence, correspondence, relationship to background knowledge,
algorithm
set of operations that systematically and exhaustively generates a solution
heuristic
strategy that often helps generate a solution, does not guarantee success (more difficult than algorithms)
problem space
collection of nodes each representing a state of knowledge or possible action, problem solving seen as search through problem space
problem space states
initial, intermediate, goal
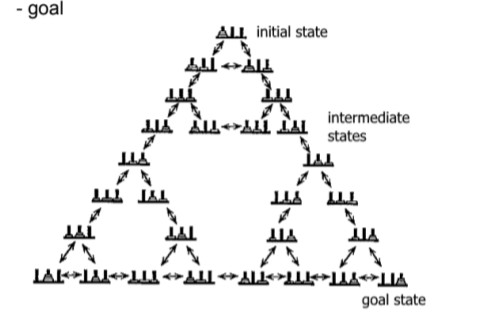
operators
links between nodes, consist of functions selected to solve problems. path constraints can rule out some possibilities.
mindlessness
thoughtless application of old ways of thinking to new situations without completely considering whether they are suitable
entrapment by categories
thinking of objects only in terms of the categories they fit into
incubation
problem solving facilitated by time away from it (effects not consistently found) but effect can be due to release from mental set/functional fixedness. retrieval of new information by changing context, recovery from fatigue, conscious problem solving, unconscious processing
reproductive thinking
based on existing associations involving what is already known (non creative thinking)
productive thinking
insights that go beyond the bounds of existing associations (creative thinking)
three process view
selective encoding insights (whats relevant and irreverent info), selective comparison insights (involve novel perception of how new info relates to old), selective combinations insights (combinding selectively encoded and compared info in a novel way.)
verbal overshadowing effect
verbal system processing interferes with insight problem solving ability
tactical learning
specific rules learned for specific problems
strategic learning
problem solving organized in an optimal way for problems in that domain (very broad)
what kind of problem is long division
problem of transformation