World History IH Industrial Revolution (Orange)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is an Agricultural Revolution?
New methods and technology in farming lead to increased food production and increased population
What are enclosures?
Land that had formerly been owned in common by all members of a village, and change it to privately owned land, usually with walls, fences or hedges around it
What is crop rotation?
Rotating crops so the crops don't deplete the soil of nutrients (three-field system)
What was the Seed Drill?
Invented by Jethro Tull
Seed drills allow seeds to be buried into the seedbed at a uniform depth, in rows
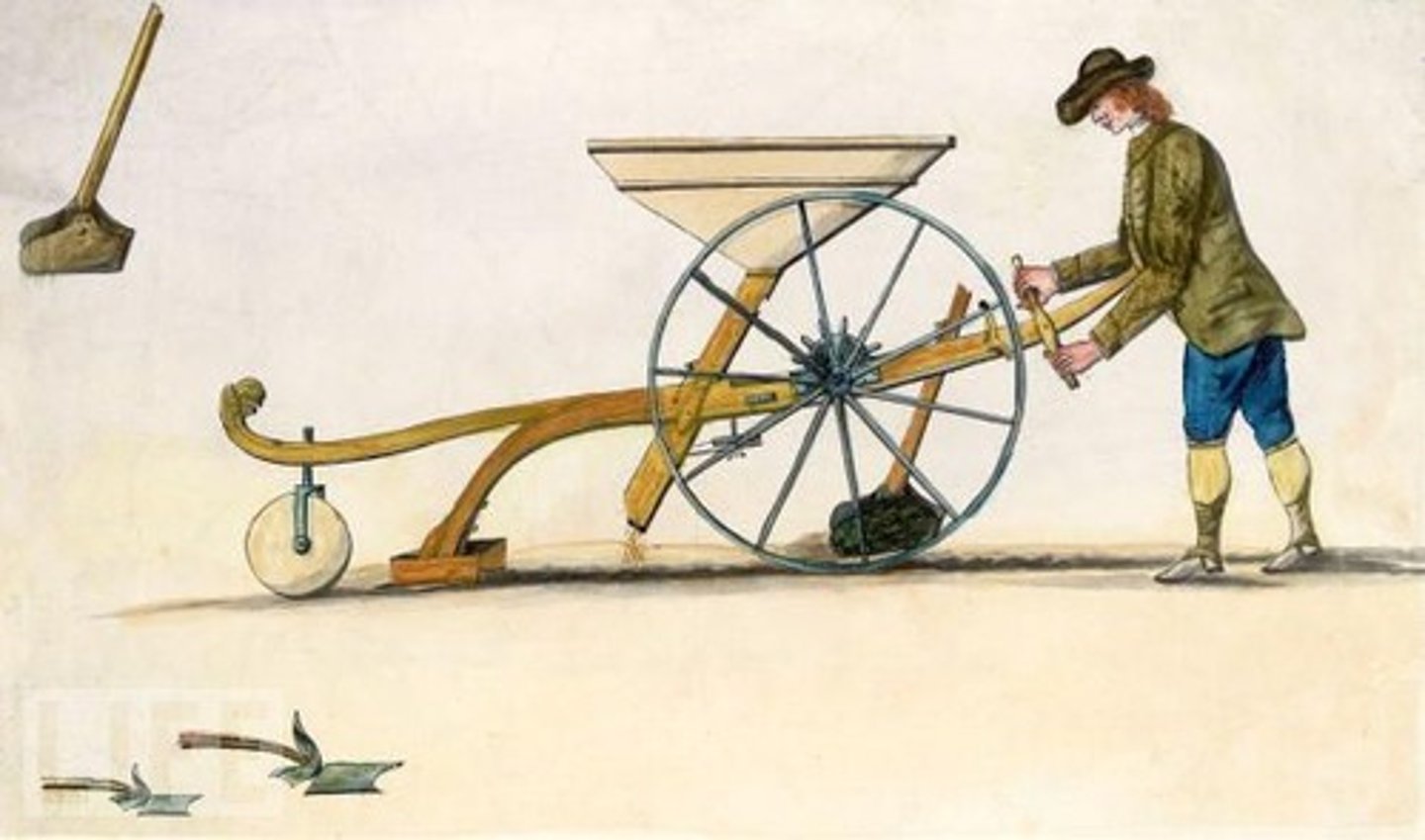
What does industrialization mean?
Process of developing machine production of goods
What does England have that allows them to become the first country to industrialize?
Natural resources
Good economy to invest in new inventions,
A stable government
They were also home to many inventors and a large population and landowners had enough money to start businesses
What was the textile industry?
The textile (clothing) industry was the first to be transformed
Powered by Watt's Steam engine
It led to inventions such as the spinning jenny that caused the production of cotton to increase
What were the dates of the Industrial revolution?
1760 - 1840
Which country was the first to be industrialized?
England
What three things should a country have to be able to industrialize?
Natural Resources
Water power and coal to fuel machines
Iron ore to construct machines, tools, and buildings
Rivers for transporting
Good economy
To invest in new inventions
A stable government
Why were some countries slow to industrialize?
They did not have the necessary resources, enough water power, and no rivers for transportation
Which industry was the first to industrialize?
Textile industry
What is Urbanization?
Movement of people from rural (farm) to urban (city) areas
What was the classes?
Wealthy - business owners
Middle - merchants, shop keepers, accountants
Poor - factory workers/jobless
What was the working class (proletariat)?
Laborers- often poor
Luddites
What was the middle class?
Some factory owners, merchants, and bankers grew wealthier than the landowners and aristocrats
Upper middle class: gov't employees, doctors, lawyers, managers of factories...
What was the Cult of Domesticity?
Belief that women belonged in the home
What was the Crystal Palace?
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851
What was the Great Exhibition of 1851?
"The Great Exhibition" displayed examples of technology developed in the Industrial Revolution
What were the First Industrial Revolution inventions?
Spinning jenny
Water frame
Steamboat
Railroad
Telegraph
Mechanized passenger elevator
What were the Second Industrial Revolution inventions?
Typewriter
Telephone
Phonograph
Lightbulb
Airplane
Automobile (Ford Model T)
What were luddites?
They destroyed machinery (machines were taking over their jobs)
What were working conditions like?
Long working hours (12-16 hrs)
Low wages
Unsafe working conditions
Safety Issues: (no fire escapes, doors often locked, no windows...)
What is a union?
Where workers join together in voluntary labor associations
What are the goals of a union?
Better working conditions and higher pay - if factory owners refused workers would go on strike
What are the government responses to labor unions?
They saw them as a threat hated them
What was the Factory Act?
Illegal to hire children under 9 yrs old
Children ages 9-12 can't work more than 8 hrs a day
Children from 13-17 could not work more than 12 hours a day
What was the Mines Act?
Prevented women and children from working in the mines
What was the Ten Hours Act?
Limited the workday to ten hours for women and children in factories
What was the Parliament Act 1911?
Asserted the supremacy of the House of Commons by limiting the legislation-blocking powers of the House of Lords
Reduced the maximum term of a Parliament member from 7 years to 5 years
Got rid of hereditary privileges of the House of Lords in 1999
What was the Labor movement?
Labor unions
Things to help to workers in factories - shorter working hours
What was the Chartist Movement?
A petition to parliament (The People's Charter 1838) wanted to extend the right to vote for all men
After 1884 most adult males in Britain had the right to vote
Before the movements, how much of the population could vote?
Only 5% of the population could vote - limited to men who owned a lot of land
What was women's suffrage?
Women's right to vote
What date do women get suffrage in England?
1928
What date do women get suffrage in the US?
1919
Who was James Hargreaves?
Invented the Spinning Jenny
Made creating yarn easier and textiles more affordable
Who was James Watt?
Invented the Steam Engine
Used to pump water out of mines and to power blast bellows
Who was Eli Whitnery?
Invented the Cotton Gin
Machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from seeds
Who was Henry Bessemer?
Invented the Steel Process
Used to make steel from iron ore
Who was Edward Jenner?
Invented the Smallpox Vaccine
Vaccine that helped humans develop immunity from smallpox
Who was Guglielmo Marconi?
Invented the Radio
Purpose was to convey information from one place to another
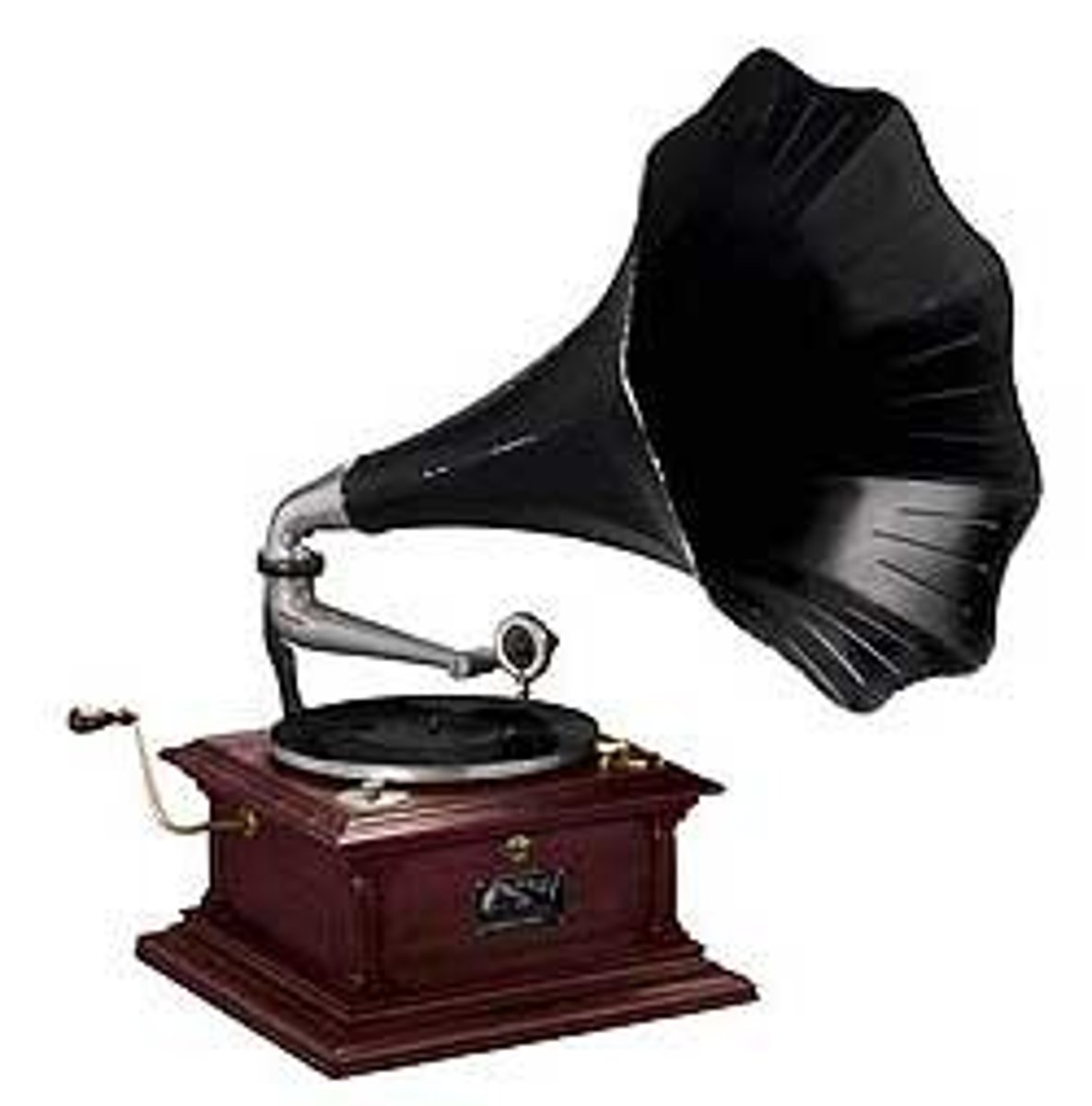
Who was Thomas Edison?
Invented the Phonograph
Purpose was to transcribe telegraphic messages through indentations on paper

Who was Henry Ford?
Invented the Model Ford T
First car that's affordable for the majority of the lower class
Who was Louis Pasteaur?
Invented the Germ Theory
He proved food spoiled from bacteria and humans became sick from germs not smell of animal carcasses
Who was Alexander Graham Bell?
Invented the telephone
Allowed people to communicate by voice over long distances
Who were the Wright Brothers?
Invented the Airplane
Used for transportation, recreation, military, etc
Who was Milicent Fawcett?
She focused on the importance of women's education
Founded the Suffragist movement
Leaded peaceful protests
Who was Emily Davison?
Gave her life for the suffrage movement when she was wounded after being stepped on by King's horse
Who was Caroline Norton?
Married to an abusive husband
Published eloquent works about stopping child labor and her time with her husband
Helped pass the Divorce Act and the Infant Custody Bill after her husband refused to allow her to see her children
Who was Emmeline Pankhurst?
Founded WSPU (Women's social and political union)
Helped employ military tactics - more violent than millicent
Arrested twice for protesting in front of Parliament
Who was Constance Markievicz?
Irish Nationalist
First women elected into British House of Commons - denied the seat
Ensured that Winston Churchill would be defeated in Manchester by election
Second women to hold a cabinet position as Minister for Labour in Irish government
What was the WSPU (Women's Social and Political Union) 1903?
It was a militant organization for women's rights
What is child labor?
The use of children in industry or business, especially when illegal or considered inhumane
What was the middle class like?
A larger middle class - neither rich or poor
Smaller family sizes
Cult of Domesticity
What methods did women's right activists use?
They refused to eat in prison, they smashed windows, destroyed property, and caused scenes in front of government offices
What was class identity?
It was the rise of the classes realizing what class they belonged to - the rise of the middle class (feeling that they're upper class but upper class disagrees)
Allows people to move upwards in classes through jobs
First Industrial Revolution vs. Second Industrial Revolution
First - basic necessities
Second - higher inventions - cars, planes, etc
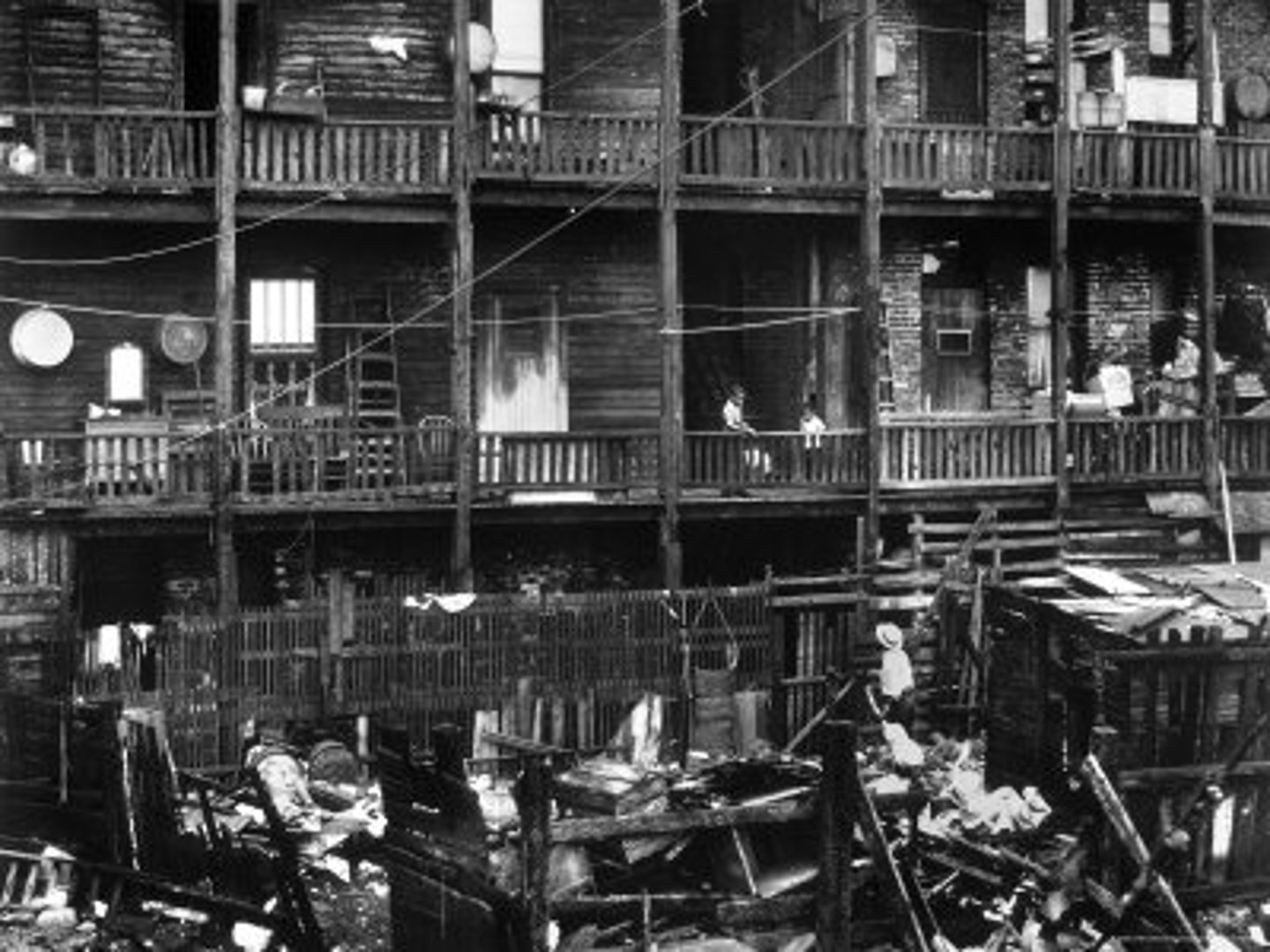
What were tenements?
Small cramped multi-family apartment in city

In the 1800s, was the method of selecting the British Government a democracy?
No because only 5% of the population could vote which was mainly rich men
Upper class also rules the government
What is an example of an artifact shown at the Great Exhibition?
The Koh-i-Nour diamond which killed all the men who held it
In the late 1600s, what does Britain become?
A constitutional monarchy
Monarch serves as head of state but Parliament holds the real power
Parliament (House of Lords and House of Commons)