2.2 HL, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
not done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Photosynthetic autotroph
Autotrophic energy from carbon dioxide, processed through photosynthesis e.g. plants, algae, some bacteria
Chemosynthetic autotroph
autotrophic energy from chemicals, processed through chemosynthesis e.g. some bacteria
Productivity
production of biomass per unit area per unit time
Primary productivity
gain by producers (autotrophs) in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time
Units: kg carbon/m^2/yr
Depends on:
amount of sunlight
ability of producers to convert energy into biomass
The availability of other factors needed for growth e.g. minerals and nutrients
Secondary productivity
biomass gained in heterotrophic organisms, through feeding and absorption, measured in units of mass or energy per unit area per unit time
Gross primary productivity (GPP
the mass of glucose created by photosynthesis per unit area per unit time in primary producers GPP=NPP+R
Net primary productivity equation
NPP= GPP - R
What is NPP?
represents the amount of energy converted to new biomass that becomes available to the next trophic level
Gross secondary productivity (GSP)
the gain in biomass by consumers using carbon compounds that are absorbed and assimilated from ingested food GSP= food eaten - faecal loss
note: Not considering respiration and other bodily functions
Net secondary productivity equation
NSP= GSP - R
Sustainable yield
the rate of increase in natural capital (i.e. natural income) that can be exploited without depleting the original stock or its potential for replenishment
Maximum sustainable yield equation
MSY= NPP or NSP
Ecological efficiency
The percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next
Ecological efficiency equation
(energy used for growth (new biomass)/ energy supplied)x 100
Entropy
the disorder of energy in a system
Entropy in a system increases as biomass passes through ecosystems
Increase in entropy reduces the energy available to do work
Entropy in an isolated system where there is no new input of energy
tends to increase spontaneously
Second law of thermodynamics
In an isolated system entropy tends to increase spontaneously/ in any transformation there is a net increase in entropy/ dissipation of energy
Nutrients are circulated and re-used frequently
Unlike energy which flows through ecosystems (enters as light energy and leaves as heat), matter (nutrients) cycles between the biotic and abiotic environment
Stores (storages)
remain in equilibrium with the environment
Sinks
indicate a net accumulation of the element
Sources
indicate a net release of the element
Carbon cycle
natural process where carbon moves between different stores and flows
Carbon cycle before the industrial revolution
Pre-industrialisation carbon cycle was in a dynamic equilibrium; amount of carbon absorbed into the stores is balanced by the amount of carbon released
residence time
The length of time that one atom of carbon remains in a specific store
Affect of humans on residence time
Humans have affected residence time in many ecosystems, we release carbon into the atmosphere that would have otherwise remained locked away through our production of energy
Organic stores of carbon
organisms
crude oil
natural gas
coal
Inorganic carbon stores
oceans
soils
atmosphere
Sequestration
natural capture and storage of CO2 from the atmosphere by physical/ chemical processes
Ecosystem as a sink
Young forest acts as a sink because they are actively absorbing carbon
Ecosystem as a store
Mature forests act more as stores because their growth rates are slower but they hold the carbon they absorbed in the past
Ecosystem as a source
If deforestation or fires are occurring, forests can be sources of carbon
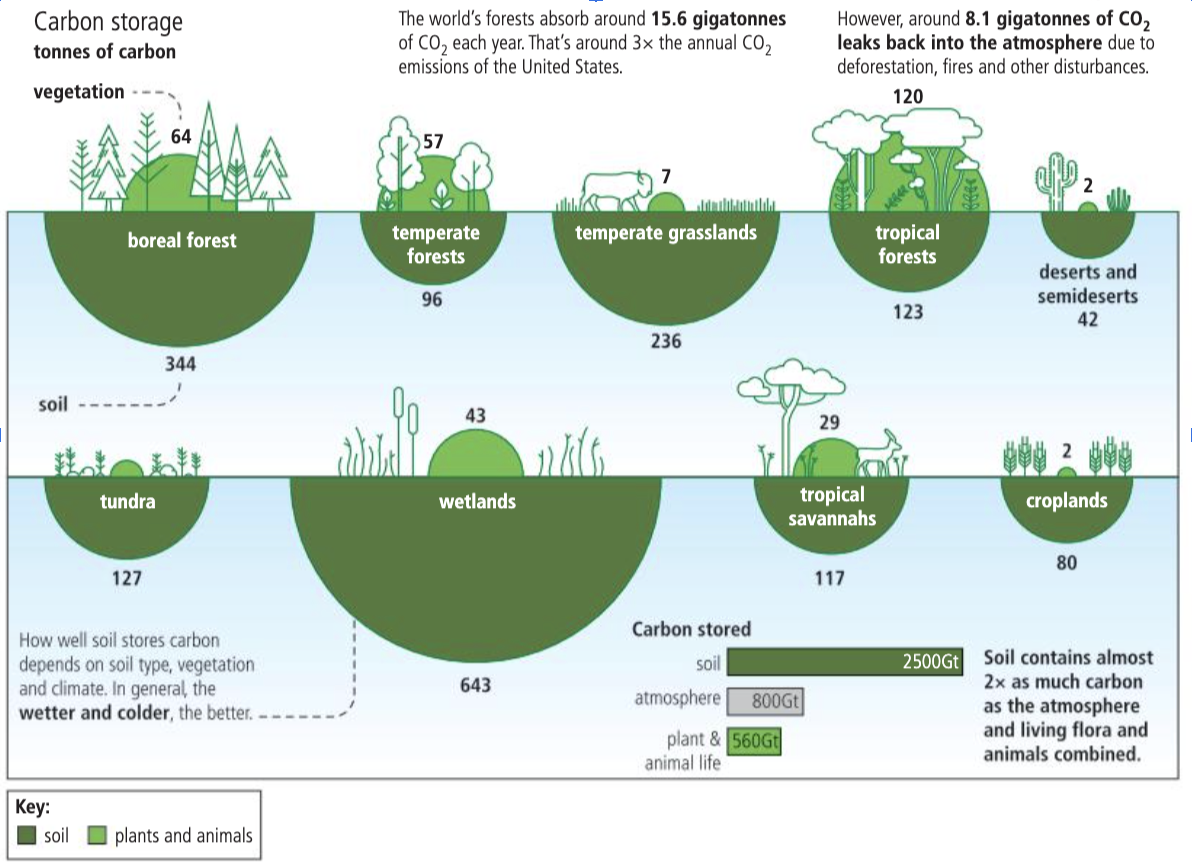
Rules about storage in ecosystems
Wet, colder soil stores carbon better
Plants cannot have greater storage than soil
fossil fuel formation
formed from organic material that has been preserved for millions of years
Fossil fuel residence time
Very long residence time: they continue functioning as storages for many thousands or millions of years naturally
Atmospheric concentration of CO2
atmosphere is currently at nearly 412 parts per million (ppm) and rising -> 47% increase since the beginning of the Industrial Age(280 ppm)
11% increase since 2000, when it was near 370 ppm
Regenerative agricultural practices
practices that aim to promote soil health and carbon sequestration by imitating natural ecosystems
Examples of regenerative agricultural practices
Crop rotation, cover crop, no till periods
Length of time that a crop is grown can also influence soil carbon dynamics
Short-term cropping: Growing crops for short periods, such as annual grains, often leads to increased soil erosion and carbon loss
Long-term cropping (e.g., timber production): Growing perennial crops, such as trees, provides extended cover and reduces soil disturbance, promoting carbon sequestration over a longer period
Physical dissolution
when CO2 molecules in the atmosphere dissolve in seawater, forming carbonic acid
Biological uptake
marine organisms such as phytoplankton and algae use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, incorporating it into their biomass