Membrane Proteins
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are two main functions of biological membranes?
Define boundaries
Sequester reactions
What are the three main functions of membrane proteins?
Signal transmission
Transport of polar molecules
Tissue organization
What are the three structural types of membrane proteins?
1) Integral
2) Lipid-anchored
3) Peripheral
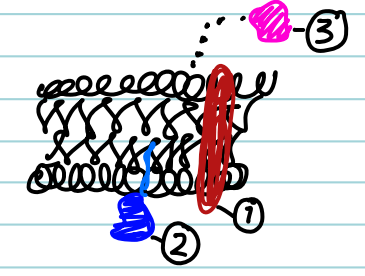
What defines an integral membrane protein?
It spans the phospholipid bilayer
What defines a peripheral membrane protein?
It associates loosely with the membrane surface via non-covalent interactions
What defines a lipid-anchored membrane protein?
It is covalently attached to a lipid that embeds in the membrane
What disrupts peripheral membrane proteins?
pH change
What disrupts integral membrane proteins?
Detergents
What disrupts lipid-anchored membrane proteins?
Phospholipase
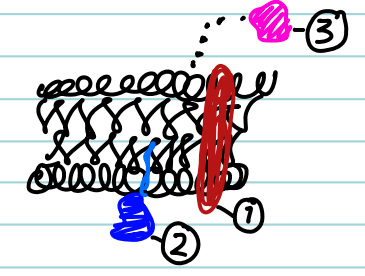
Identify the different types of membrane proteins
1) Integral
2) Lipid-anchored
3) Peripheral
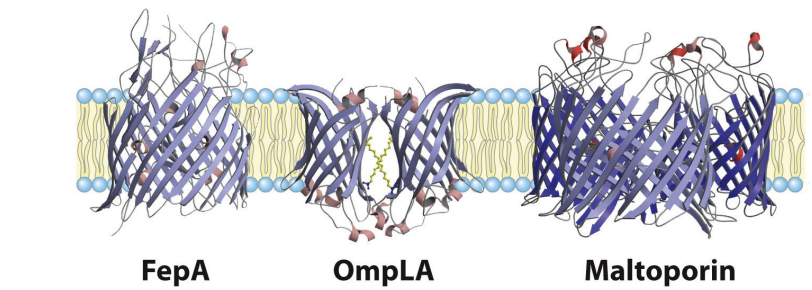
What secondary structures are common in membrane-spanning domains?
Alpha helices and beta barrels
How long is a typical membrane-spanning alpha helix?
20–25 amino acids
What is a beta barrel?
A tube-like structure made of beta sheets forming a channel
Why are alpha helices and beta barrels used in membrane proteins?
They allow all polar backbone atoms to form internal hydrogen bonds, stabilizing them in the hydrophobic membrane
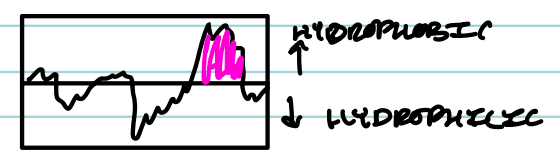
What tool predicts membrane-spanning alpha helices?
A hydropathy plot
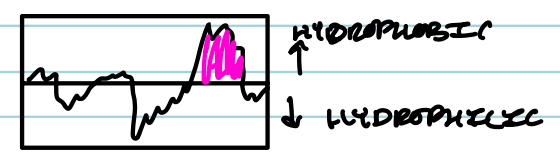
How does a hydropathy plot work?
It shows hydrophobicity of amino acid stretches; high peaks suggest transmembrane regions