Unit 3 - Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What did John Dalton propose about atoms of the same element? and was he correct?
No, only 21 elements are composed of atoms that are exactly alike in their makeup.
the majority of the elements have some subtle variations in their atoms that compose them, which are called isotopes
What did John Dalton propose in his Atomic Theory about atoms being divided?
He believed that atoms cannot be divided into anything smaller.
this is incorrect because atoms are actually made up of smaller particlels within themselves called subatomic particles (protons, electrons, and neutrons).
What did John Dalton propose about an atom’s destructibility?
He believed that atoms are indestructible
this is in fact incorrect because atoms can be destroyed and are the bases for nuclear weapons and energy.
What did John Dalton propose about atoms when they chemically combine with other atoms?
He was correct about the idea that atoms can only combine with other atoms as whole particles, which is seen in chemical formulas.
ex. H20, can never be H1/2O
Law of Definite Composition
applies to ALL compounds
same elements chemically combine
same atomic ratio each time the compound is formed
Law of Multiple Proportions
Only applies to a few compounds
Stipulations:
must have 2 elements that can form a pair of compounds with each other
one of the element’s atomic ratio does not CHANGE (stays constant in both compounds) the other elements atomic ratio does change by some small number
DO EXAMPLES
What are atoms?
atoms are exceedingly small, cannot see a singular atom
make up matter
Mass of atoms
cannot use balance, a mass spectrometer is used
atomic mass units are used
1g = avogadros number (amu)
Which subatomic particle was found first, and info about it?
Protons were
Symbol: p+
Charge: +
Location: found inside the atom’s nucleus (center of atom)
Purpose: they are responsible for the atom’s Atomic Number
Mass of a proton: = 1.0073amu
Need to know, called “assigned mass” when rounded to 1amu
Atomic Number: #p+ = Atomic Number
Information about Electrons
Symbol: e-
Charge: -1
Location: found outside of the nucleus
Purpose:
responsible for the atom’s properties and behavior
responsible for chemical reactions
responsible for chemical bonding
Mass: 0.0005486amu (more important: assigned mass is 0amu)
the mass of an electron is considered to be negligible
Information about Neutrons
Symbol: no
Charge: are neutral, no charge
Location:
found inside the nucleus along with the protons
Neutrons are nucleons, also “live” in the nucleus
Mass: 1.0087 amu (more important: assigned mass = 1amu)
Purpose:
contribute to the heftiness or massiveness of the atom (Most Massive Subatomic Particle)
along with protons, are responsible for the atom’s Mass Number
Atomic Mass
found on Periodic Table of Elements
has units of amu or u
atomic mass: is not used in atomic notation
Mass Number
does not have units
#p+ + #no = mass number
Mass Number has a symbol: “A”
Information about Charges
single atoms are loaded with charge!
(+) protons
(-) electrons
single atom
charge is neutral
quantity of p+ and e- must be equal!
ex. phosphorus (+15 - protons) + (-15 - electrons) = 0
Charges of atoms when they chemically combine
when atoms chemically combine, they become charged
charged atoms are called “Ions”
Cations
(+) charged ion
atom loses some of its electrons
means p+ > e-
Anions
(-) charged ion
atom keeps all of its electrons and gains a few more
means p+ < e-
Coulomb’s Law
attraction/repulsion is inversely related to the distance between the particles
opposite charges attract when (+) & (-), when they are close to one another
Like charges repel (-) & (-) or (+) & (+), when they are close to one another
Atomic Notation
the superscript is the mass number (symbol : A)
the subscript is the atomic number (symbol : Z)
A = p+ + n0
Z = p+
A - Z = n0
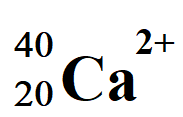
What is a nuclide?
An atom written in atomic notation
verbalized as “a nuclide of Sodium 23(mass number)”
written as Na(symbol) - 23 (mass number)
What charges mean in atomic notation
Na - 23+1
That atomic number(Z) is 11, means that protons are 11 and electrons are 11. The +1 means that the atom has a positive charge, meaning 1 electron was lost.
If it were -2, then it is a negative charge, with the atom gaining 2 electrons
only electrons can be gained or lost because the protons are trapped in the nucleus.
What did John Dalton believe about the similarity between all atoms that compose an element for all elements?
He believed that the atoms are all exactly alike in every capacity for the atoms that compose that element.
This is only true for 21 elements, the 97 other elements display subtle variation in their atomic form.
Isotopes
ex. Carbon has 3 different forms. C-12, C-13, C-14, all have protons of 6, but different neutrons
the percent abundances is how much of each isotope composes that element
98.0% is C-12, 1.9% is C-13, 0.1% is C-14.
All 3 forms of carbon exhibit same properties + behavior, same identity
Only difference, attains to how heavy because of different amount of neutrons
Information about isotopes part 2.
Iso = same or identical
P = protons
Nuclides with the same or identical number of protons in their nuclei
several atomic forms or nuclides, meaning different amount of neutrons
Radioactive Elements
some radioactive elements can also be composed of several nuclides(isotopes). They are called Radionuclides or collectively called radioisotopes
Mass numbers used to distinguish what?
The mass numbers of the most stable nuclide were once used on the periodic table to distinguish the radioactive elements from the “normal” elements.
Isobar
Iso - same or identical
bar - pertains to “heaviness” or weight.
nuclides that share in common the same mass number
can be different elements that have different atomic mass(A), but different protons.
these different elements, when you add up the protons and neutrons will equal the same mass number
ex. U -235, Np-235, P4 - 23
Isotone
Nuclides that share the same quantity of neutrons
tone has N, meaning same neutrons