OLI AP Unit 3 Module 5 Macromolecules
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
macromolecules
at least 1000 atoms
made of monomers
basis of complex cellular life
not intrinsically stable
polymer
very large molecule made of smaller units joined by covalent bonds using a common set of chemical reactions
4 major macromolecules
nucleic acids
proteins
lipids
carbohydrates
monomers of macromolecules
protein- amino acids joined by peptide bonds
polysaccharides- monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds
nucleic acids- nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds
carbohydrates general formula
(C(H2O))n
2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen all attached to carbon backbone
carbohydrate functions
energy storage
structure
cell recognition and signaling
monosaccharides
simple sugars
glucose, fructose
3-7 carbon atoms
used for energy
polysaccharides
long polymers covalently bonded
store energy of monosaccharide
starch, glycogen
structure in plants
component in DNA backbone
glycosylations
carbohydrate modifications
on lipid membranes and proteins for specialized function and recognition
glucose
most common carbohydrate in nature
(C(H2O))6
common source of energy
protein
linear molecule comprised of amino acids
20 dif amino acids
protein structures
primary structure- sequence of amino acids
secondary structure- sequence folds to form a shape
tertiary structure- functional form
quaternary structure- several separate proteins combine
a protein’s size, shape and reactive properties depend on the
number, type and sequence of amino acids
protein functions
enzymes- rate of reactions
cell signaling and recognition
support
amino acids
monomers of proteins
sequence of amino acids in a protein is encoded in
the DNA of the cell
amino acid backbone structure
amino group
carboxyl group
alpha-hydrogen
functional/R-group
all amino acids have same main chain atoms but differ in
side chains
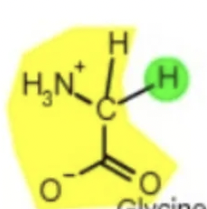
glycine gly
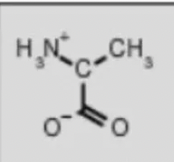
alanine ala
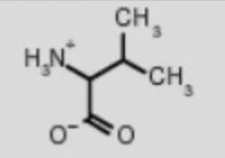
valine val
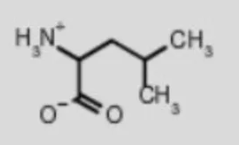
leucine leu
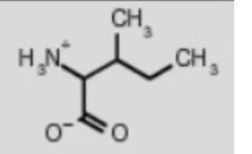
isoleucine ile
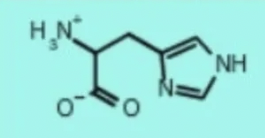
histidine his
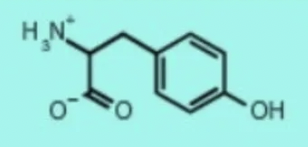
tyrosine tyr
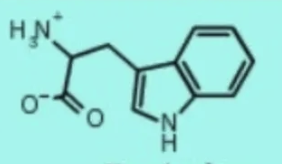
tryptophan trp
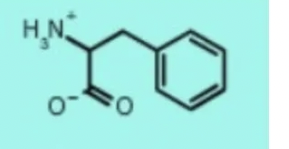
phenylalanine phe
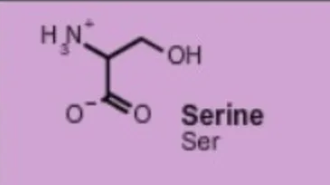
serine ser
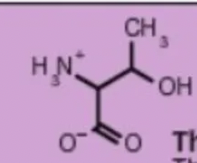
threonine thr
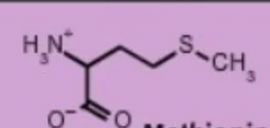
methionine met
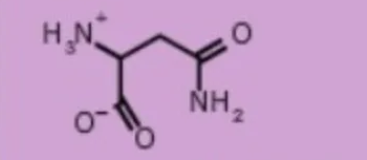
asparagine asn
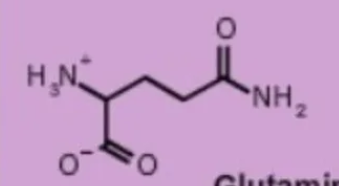
glutamine gln
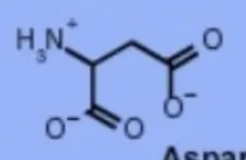
aspartic acid asp
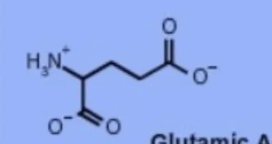
glutamic acid glu
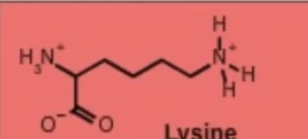
lysine lys
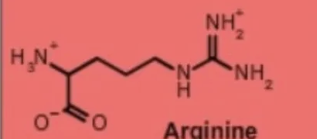
arginine arg
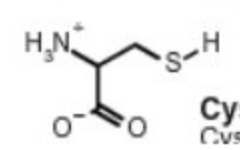
cysteine cys
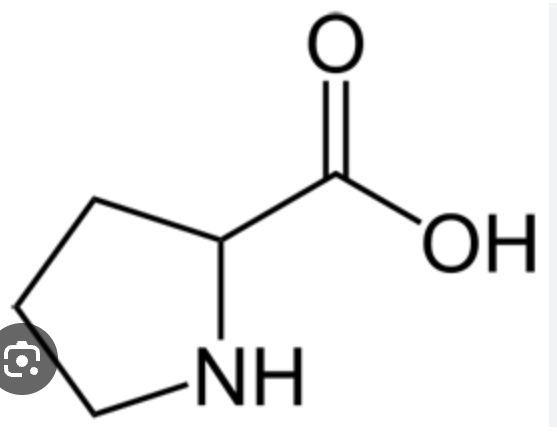
proline pro
functional groups
groups of atoms in a side-chain of amino acids
commonly polar
can be neutral or charged
can be acidic, neutral or base
bond between amino acids
peptide bonds
covalent
amino acids are joined together by a
condensation reaction that yields a molecule of water
nitrogen of an amino group joins with carbonyl carbon of a carboxyl group
each amino acid in polymer is known as a
residue
peptide chains
linear with defined ends
peptide
short polymer- less than 50 residues
polypeptide
longer polymer- more than 50 residues
main chain atoms are
polar functional groups
primary sequence of a protein
N-terminus on left
C-terminus on right
name of N-terminal residue is always first amino acid
nucleic acid
replicating macromolecule
in cell nucleus
DNA and RNA are most important
nucleic acid code is made of sequences of 4 bases
adenine
cytosine
guanine
thymine or uracil
bases are arranged in sets
of 3 called triplets
each triplet specifies an amino acid
chromosomes
structures of organized nucleic acids
DNA is organized into a
linear polymer in a double helix
nucleotide
DNA monomer
phosphate group
5-sided sugar
nitrogenous base
nucleotides are linked
by bridging phosphate molecules btwn 2 hydroxyl groups
by phosphodiester bonds
main difference in polymer backbone between DNA and RNA is
sugar used in formation of polymer
DNA sugar
2’ position of furanose has a hydrogen
RNA sugar
2’ position of furanose has an OH and sugar is ribose in furanose conformation
DNA/RNA polymer backbone sequence
phosphate
ribose/deoxyribose
phosphate
ribose/deoxyribose
DNA double helix is held in place with
hydrogen bonding of purines to pyrimidines
when cell divides
all DNA of genome is duplicated
protein production sequence
DNA replication
DNA transcription
RNA translation
DNA transcription
DNA is transcribed into RNA to make a protein
RNA translation
RNA is translated from a nucleic acid code into amino acid sequence of a protein
lipids
fats and waxes
form membranes of cells and organelles
enable isolation and control of chemical processes
long-term energy storage
cell signaling
lipids accumulate in
adipose cells
excess carbohydrates can be
converted into lipids which are stored in fatty tissue
lipid soluble vitamins
A, D, E, K
lipid structure
hydrophilic head
hydrophobic tail
membrane interior is
hydrophobic and attracts hydrophobic materials in it
proteins with hydrophobic regions
float inside lipid bilayer
transport charged or lipophobic molecules in and out of cell
carbohydrates attached to lipids jutting out of membrane are important for
cell recognition