PT-5 Asthma LOIL: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Why does asthma have such a high mortality rate?
- Misdiagnosis/underdiagnosis.
- Annual reviews missed.
- Long wait for referrals (up to 18m).
- Poor adherence w/treatment.
- Environmental factors eg smoking/dampness.

What are the key symptoms of asthma?
- Cough.
- Wheeze.
- Chest tightness.
- SOB.
Vary over time with triggers.
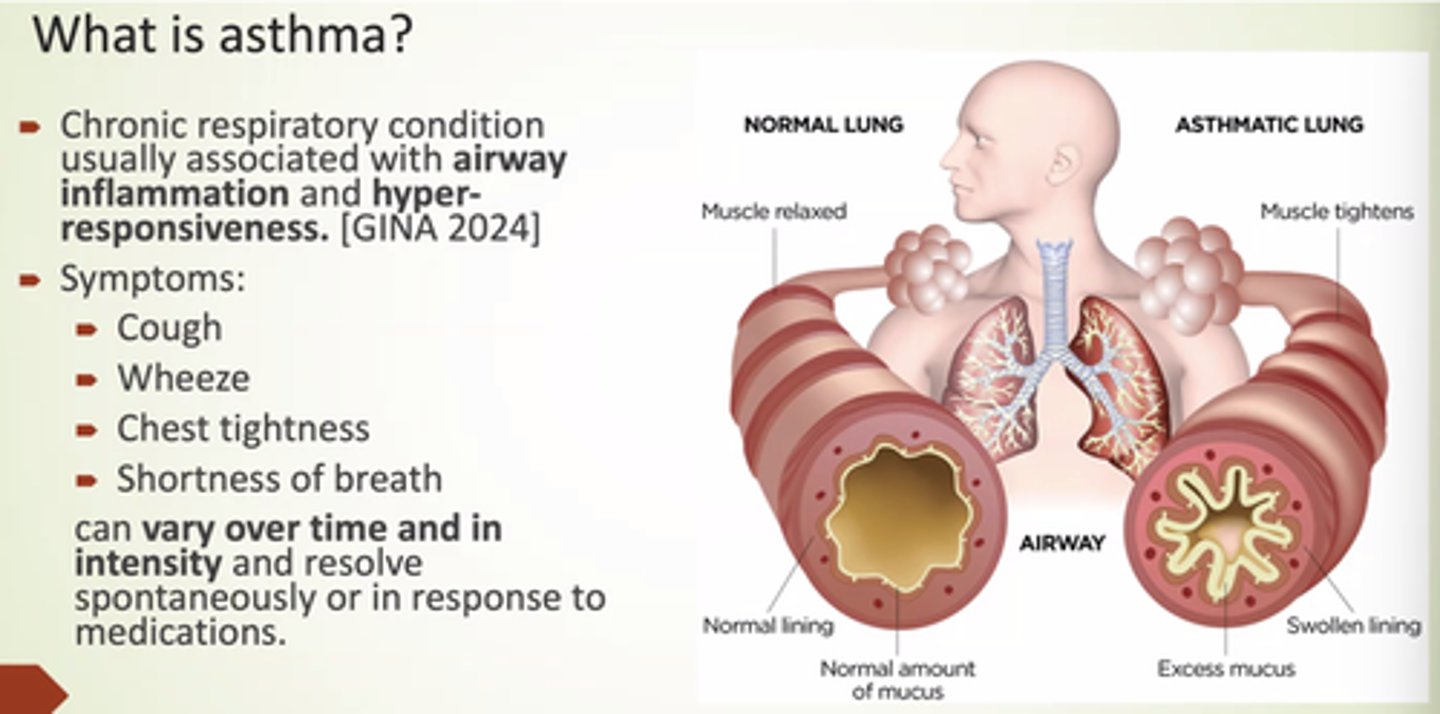
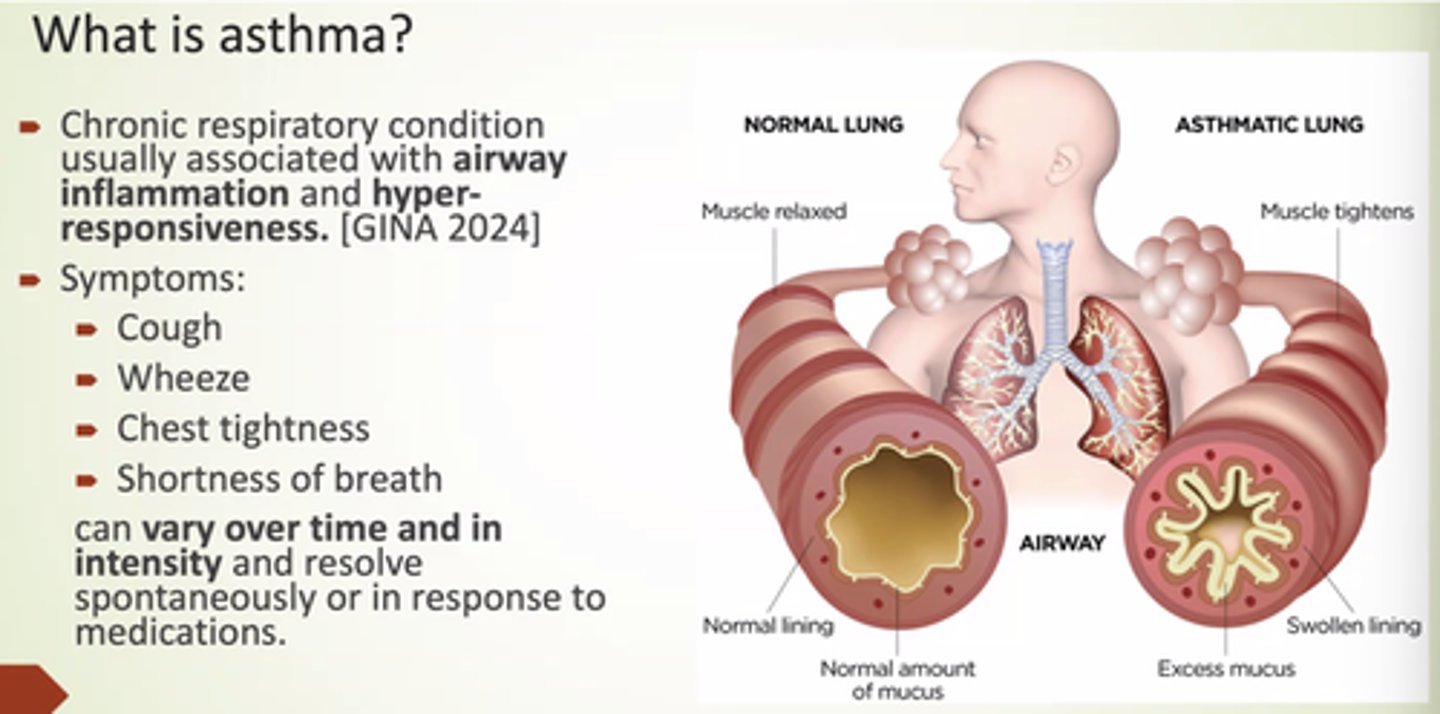
What is asthma?
Chronic respiratory condition usually associated w/airway inflammation and hyper-responsiveness.
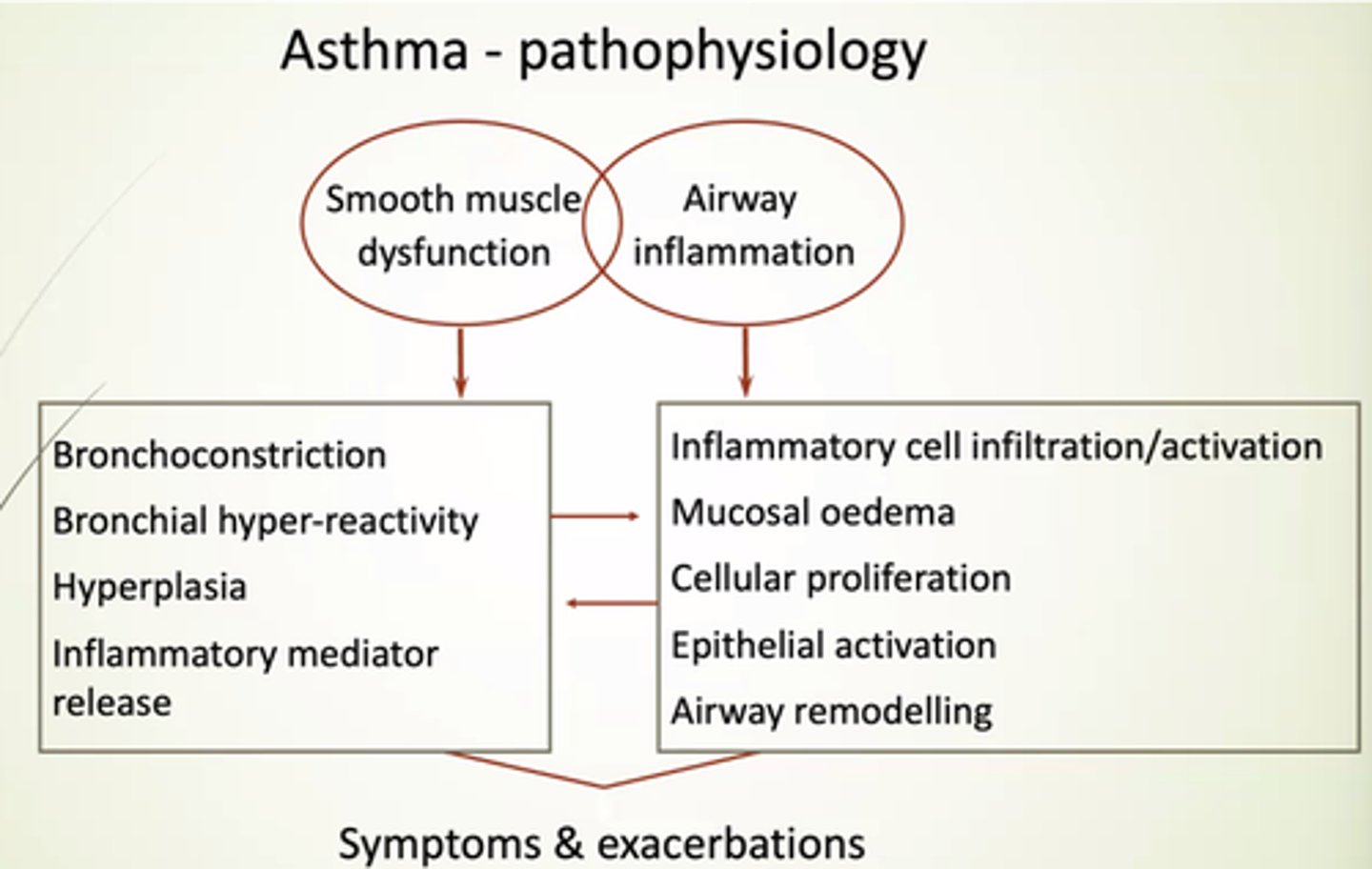
What does SM dysfunction in asthma lead to?
- Bronchoconstriction.
- Bronchial hyper-reactivity.
- Hyperplasia.
- Inflammatory mediator release.
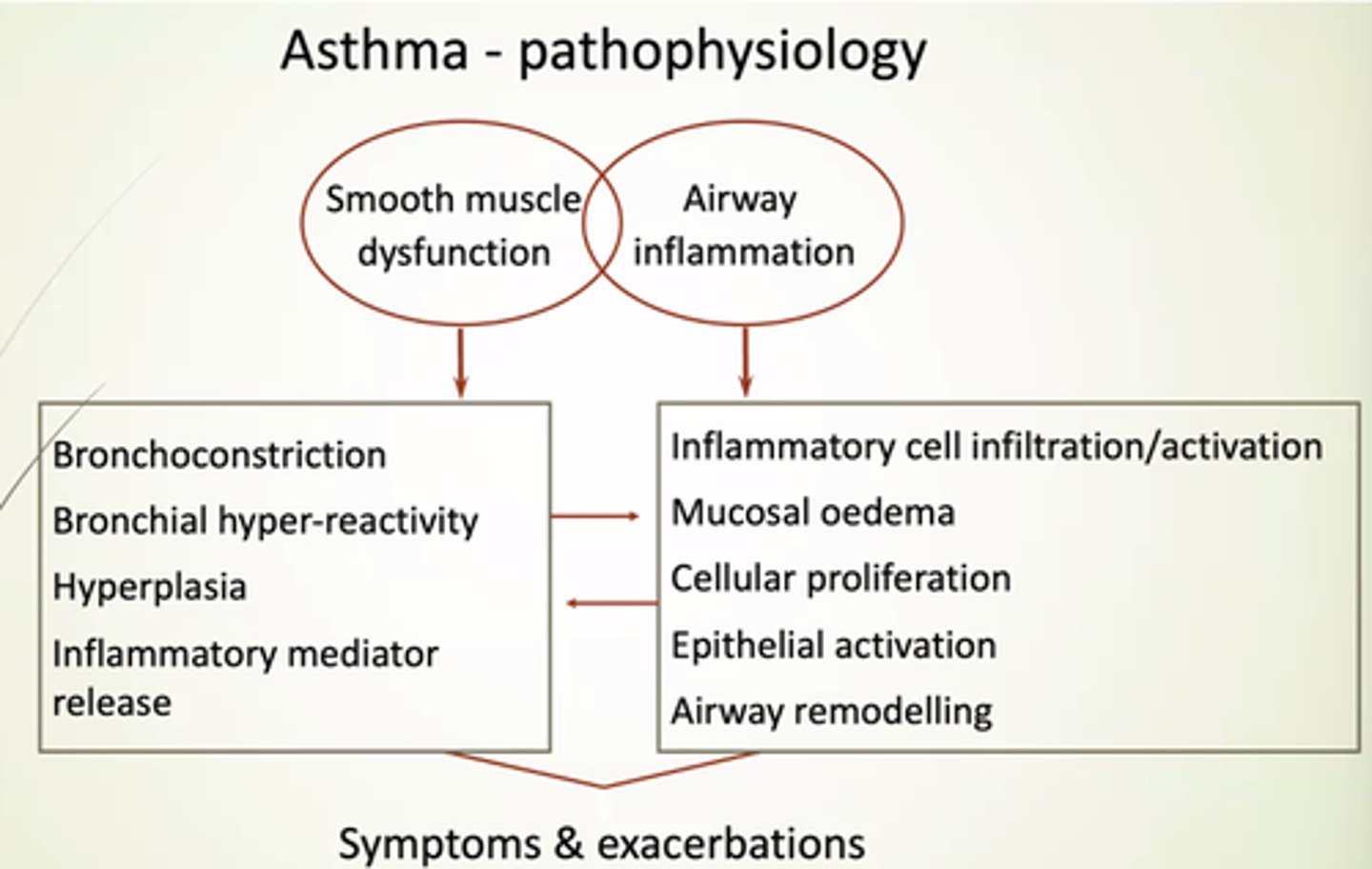
What does airway inflammation in asthma lead to?
- Inflammatory cell infiltration/activation.
- Mucosal oedema.
- Cellular proliferation.
- Epithelial activation.
- Airway remodelling.
List some asthma phenotypes.
- Allergic.
- Non-allergic.
- Cough variant.
- Late onset.
- Obesity driven.
- Persistent airflow limitation.

Define asthma exacerbation
Flare up - acute worsening in symptoms and lung function from usual.

Define uncontrolled asthma
Where symptoms affect pt's lifestyle or restrict their usual activities.
May wake pts up at night.
(including flare ups needing OCS).

Define severe asthma
Uncontrolled asthma despite optimised treatment w/ high dose ICS/LABA or OCS.
OR that requires high-dose ICS/LABA or OCS to prevent it becoming uncontrolled.
ie if they've just presented, it can still be severe.

What are some genetic risk factors for asthma?
Personal or family Hx of atopic diseases.
Eg asthma, eczema, allergic rhinitis.

What does atopy mean?
Genetic predisposition/tendency to develop disease.
What are some environmental risk factors for asthma?
- Air pollution.
- Cold, damp housing.
- Allergens.
- Exposure to tobacco.
- Workplace exposure.

What are some health and lifestyle risk factors for asthma?
- Obesity.
- Respiratory infections in infancy.
- Premature birth and low birth weight.

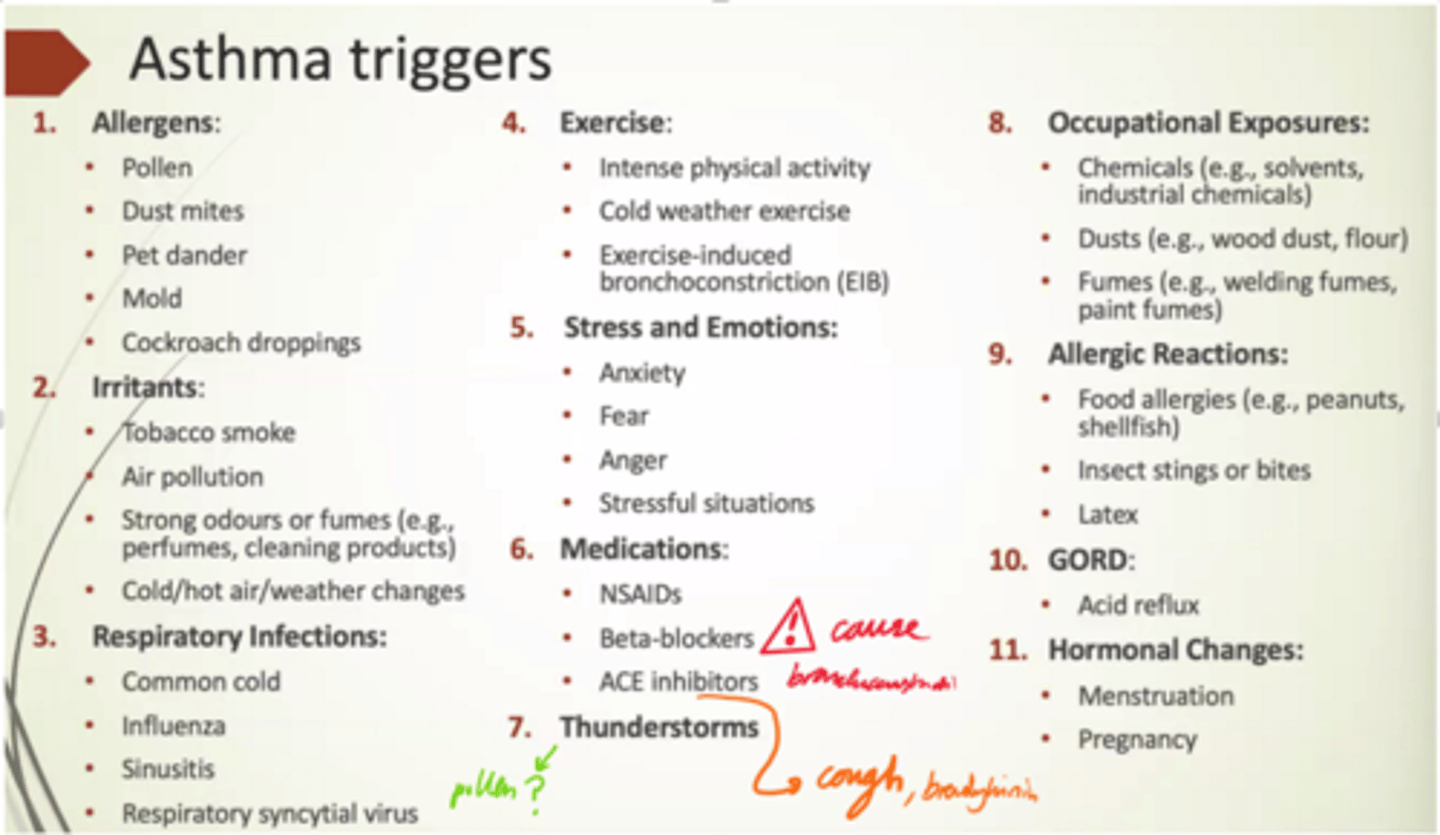
List some triggers for asthma
- Allergens.
- Irritants.
- Respiratory infections.
- Exercise.
- Stress and emotions.
- Medications.
- Thunderstorms.
- Occupational exposures.
- Allergic rxns.
- GORD.
- Hormonal changes.
What national guidelines are used for asthma treatment?
BTS + SIGN + NICE joint guidelines.
BTS = British Thoracic Society.

How is asthma diagnosed in adults?
- Hx taking, including symptoms, triggers, family Hx.
- Physical examination for signs of asthma incl wheeze.
- Objective tests!
What differential diagnoses can we have for asthma symptoms?
Anxiety, psychological causes, upper airway dysfunction (when breathlessness comes from throat rather than lungs).
When is a wheeze considered life-threatening?
When the pitch of the wheeze gets higher and higher until it stops.
The higher the pitch, the narrower the tubes
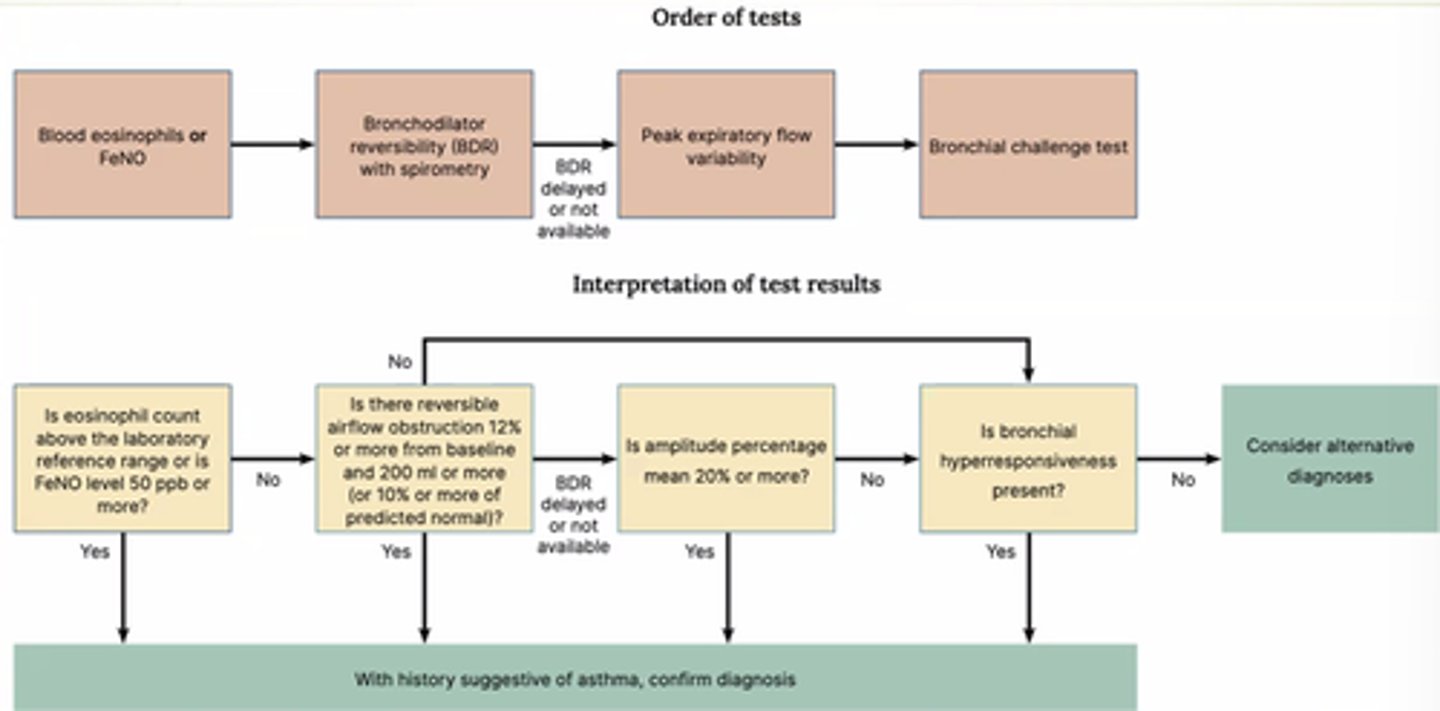
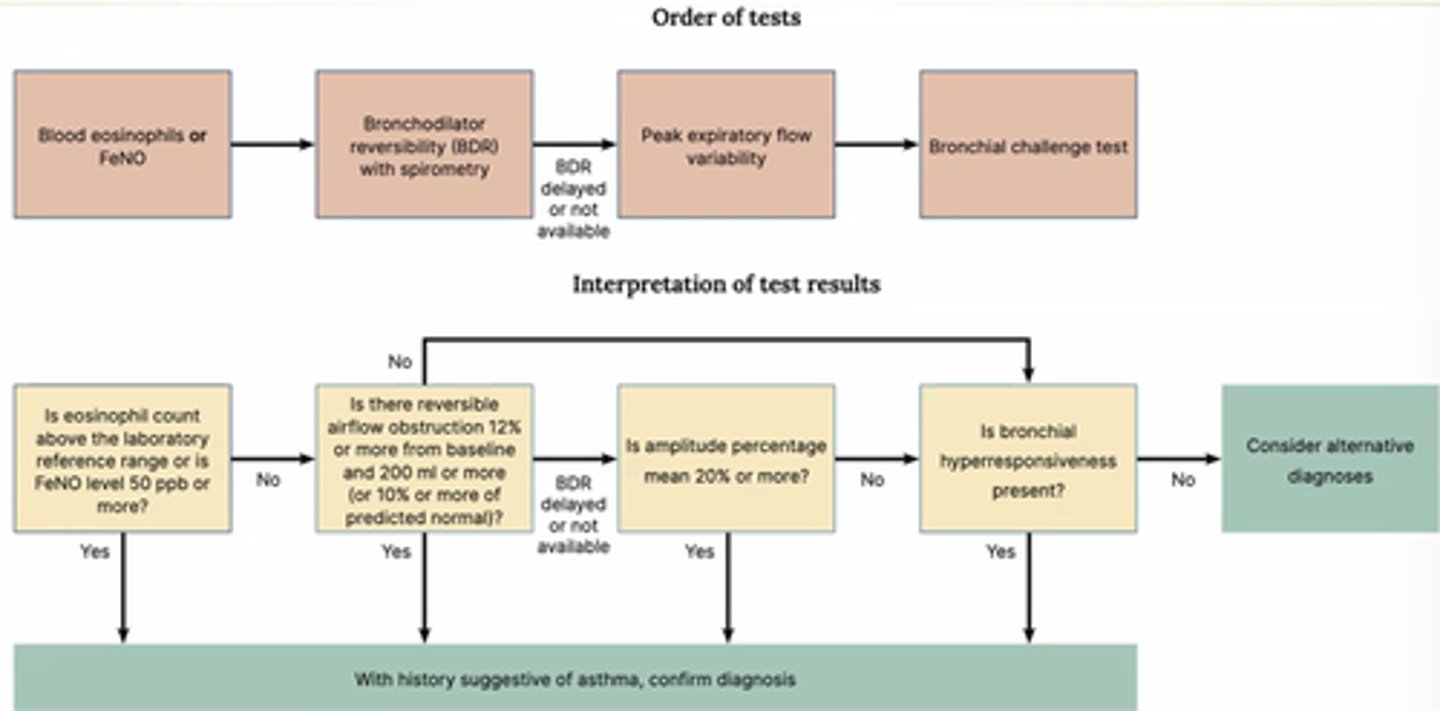
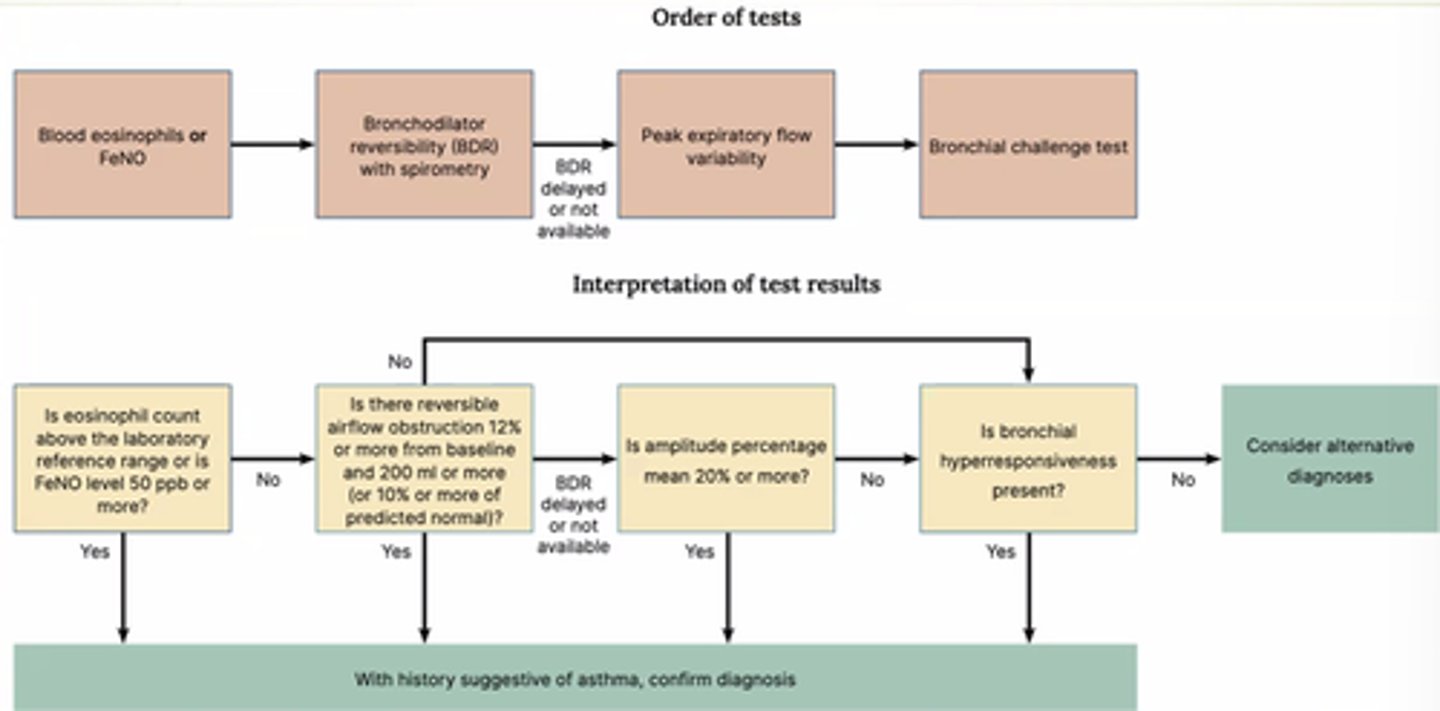
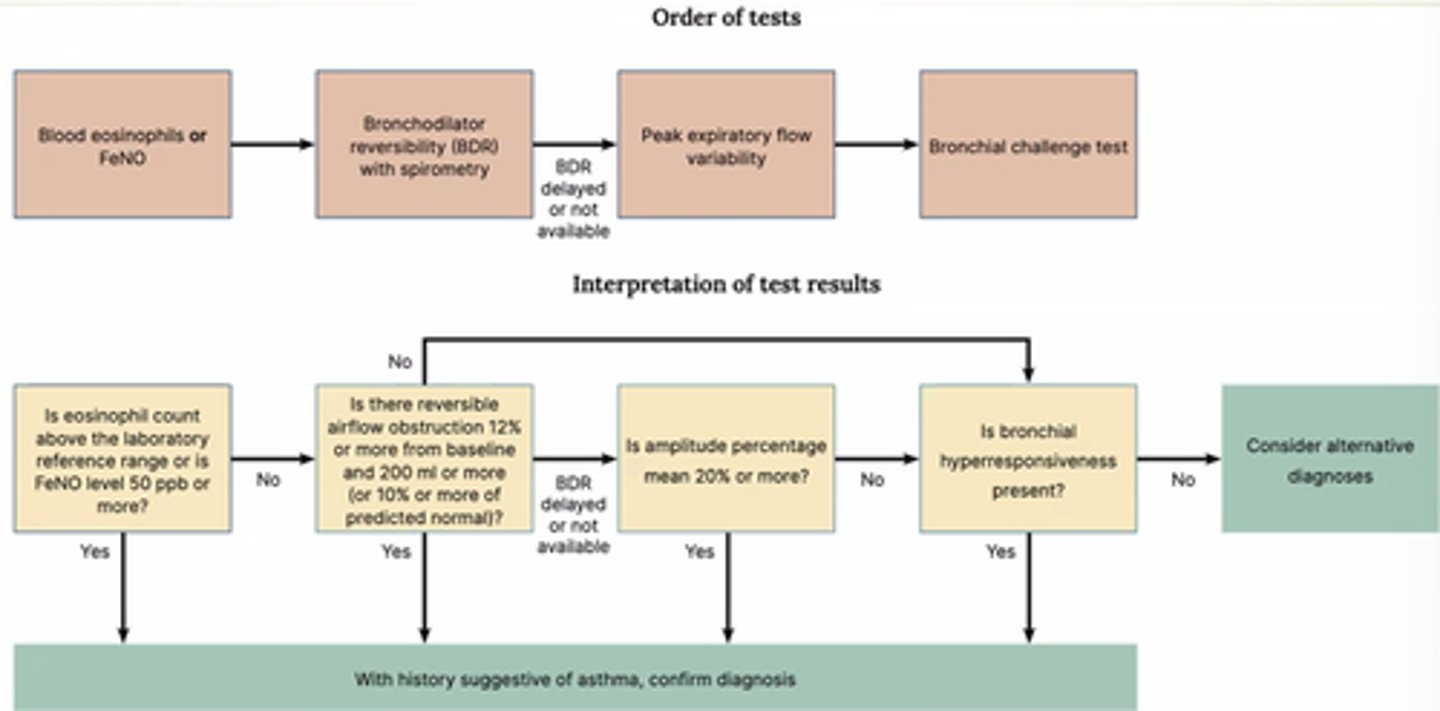
What objective tests are used for age 5+ to diagnose asthma?
- FeNO or blood eosinophils.
- Bronchodilator Reversibility (BDR) with spirometry.
- Peak Flow.
- Bronchial challenge test.
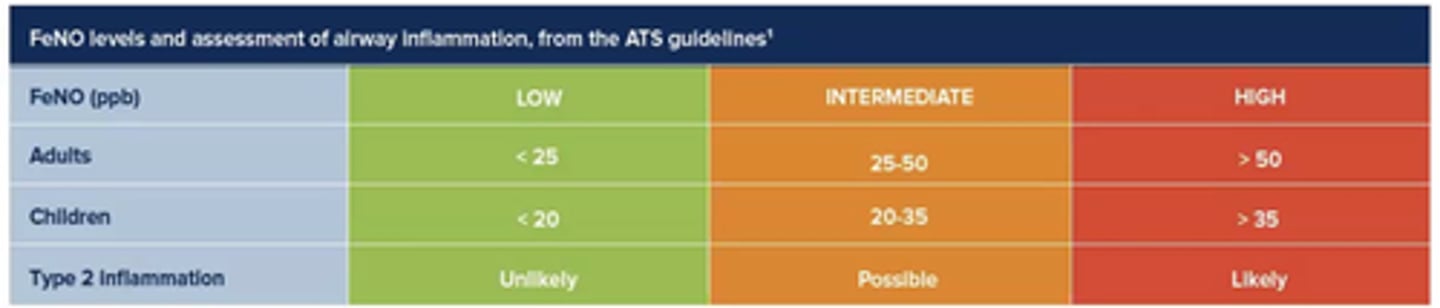
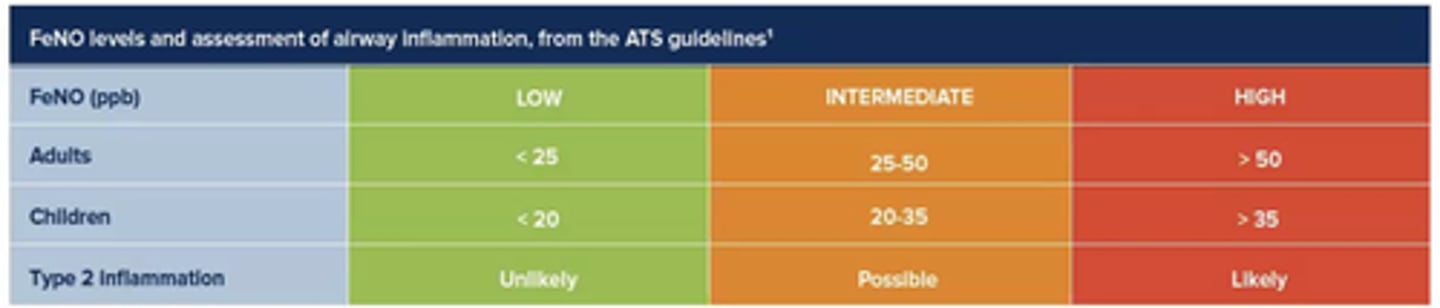
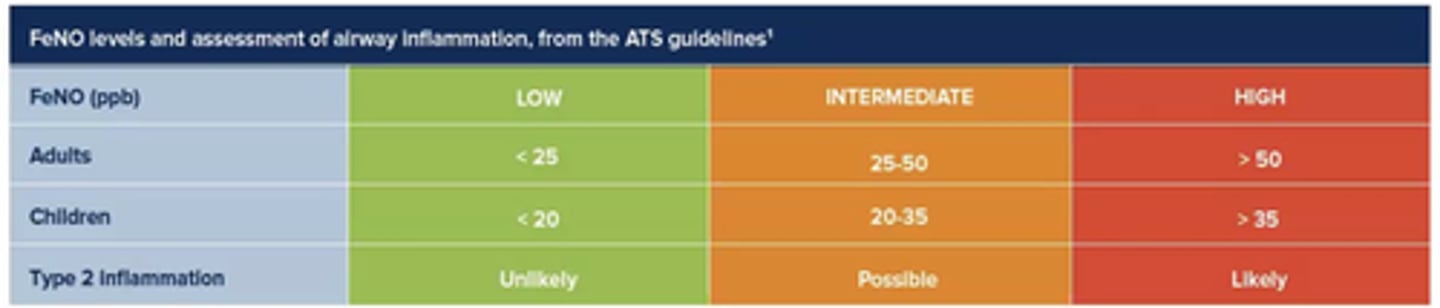
What does FeNO testing measure?
Amount of NO in exhaled breath.
Indication of eosinophilic inflammation in lungs.
(NO is excreted from eosinophils).
(Picks up eosinophilic asthma).
What do we look for in a FBC with asthma diagnosis queried?
Eosinophils!
What is the Bronchial challenge test?
Inhale offensive substance and measure what the lungs do in response.
What are some advantages to FeNO testing?
- Simple.
- Non-invasive.
- Non-aerosol generating.
Why should you not carry out FeNO testing in a bout of allergic rhinitis?
Bc it can mimic asthma
How does smoking affect FeNO test?
Smokers/ex-smokers - smoking reduces amount of NO that can be picked up by FeNO testing.
How should patients prepare for FeNO testing?
- Avoid exertion and smoking >1hr.
- Avoid nitrate-rich foods >3hr.
- Avoid hot drinks, caffeine, alcohol (>1hr).
What are some limitations of FeNO testing?
- Some pts won't perform: breathing through nose/insufficient expiratory effort.
- OCS/ICS use.
- Allergic rhinitis.
- More reliable when it is high.
How do nitrate-rich foods affect FeNO levels?
Decrease FeNO levels.
How does taking OCS affect FeNO?
OCS suppresses eosinophilic inflammation and masks the results.
How does taking ICS affect FeNO?
If good ICS technique/control, FeNO should be normal.
- If not, then inhaler technique is incorrect, OR asthma is severe and ICS isn't enough
What does spirometry assess?
Airflow and lung volume.

What 3x key parameters are measured in spirometry?
- FEV1.
- FVC.
- FEV1/FVC ration (%).

What is FEV1?
Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second.
After deep inhalation and forced exhalation.

What is FVC?
Forced Vital Capacity: total vol of air in one forced exhalation.
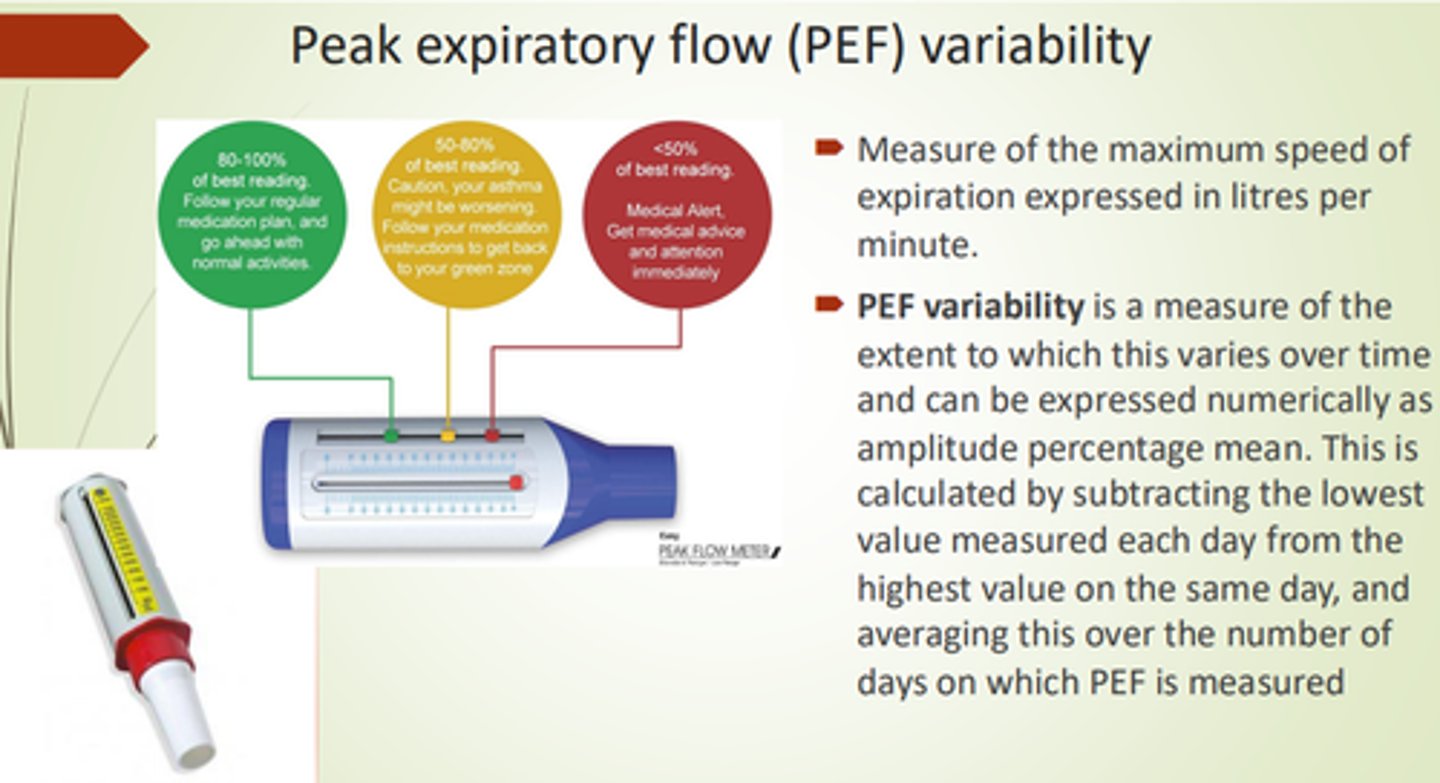
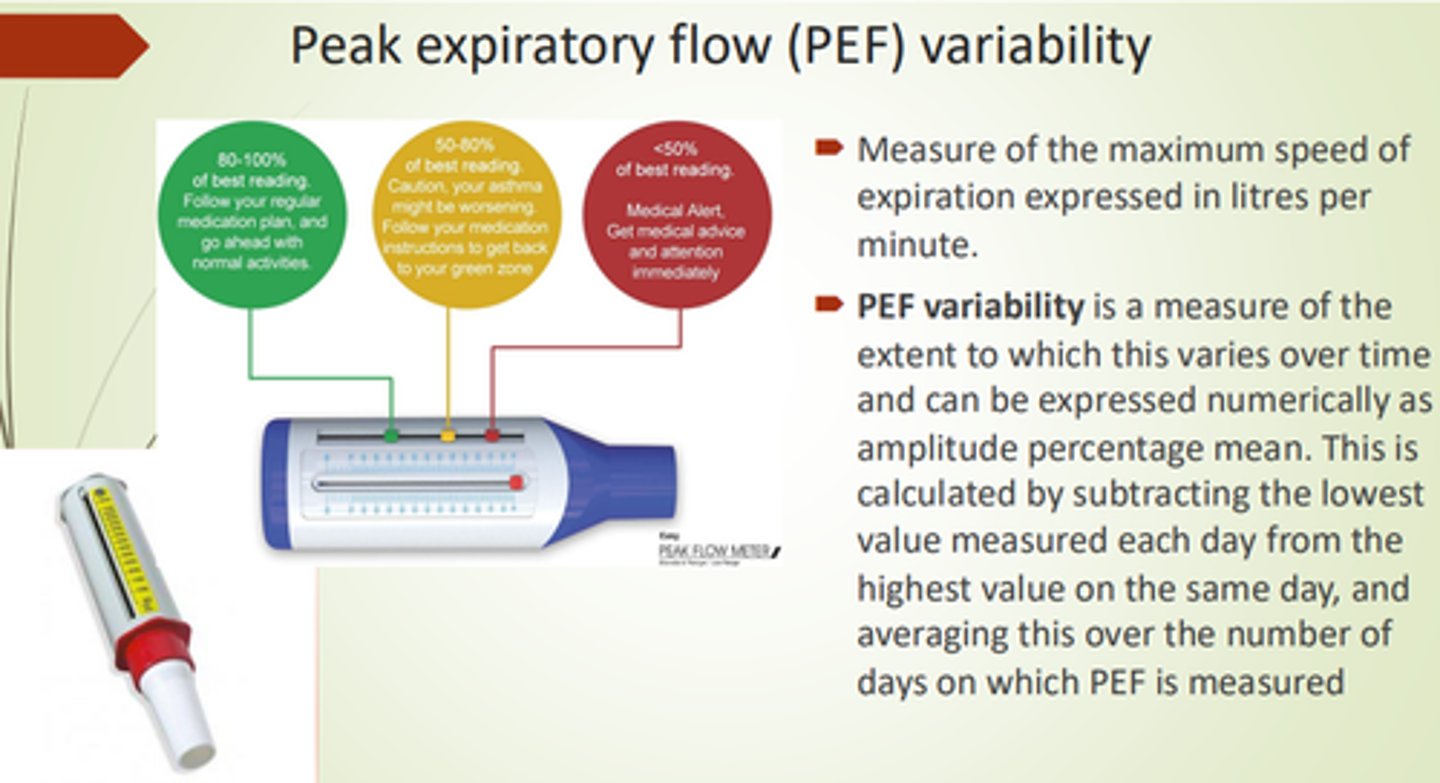
What is PEF Variability?
Peak Expiratory Flow variability - a measure of peak flow variety over time (% mean).
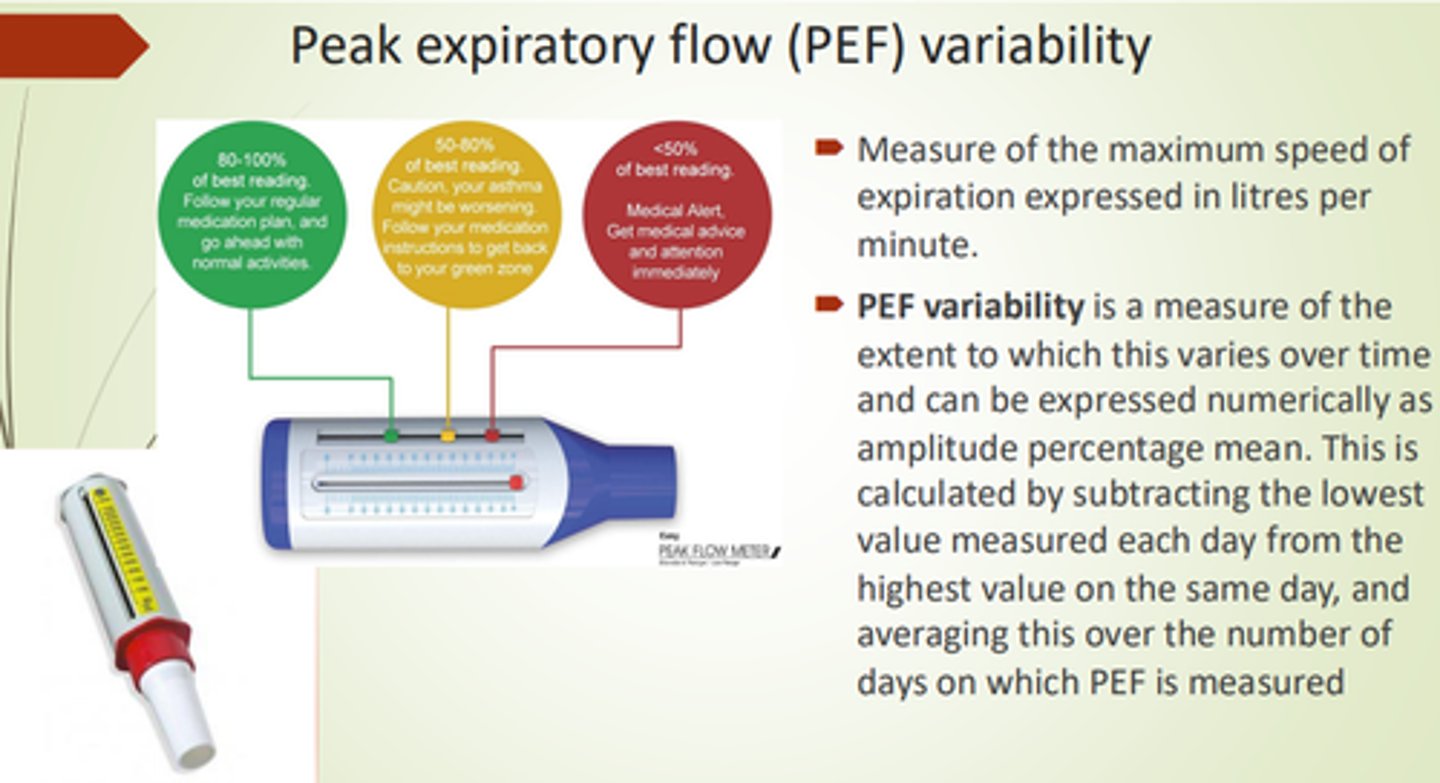
What are some advantages to using peak flow?
- Pt can do at home.
- Easy monitoring.
What's a downside to peak flow meters?
Pts could falsify results to what you want to hear
What does the Bronchial Challenge Test measure?
Bronchial responsiveness.
- Measures FEV1 at baseline and after each dose of irritant.

How is the Bronchial Challenge Test performed?
- Small increments of bronchoconstrictor given.
- Until drop in FEV1 is 20% from baseline, or until highest bronchoconstrictor dose is reached.
What is Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness?
A measure of how easily bronchospasm can be induced in the airways

What are AIR and MART?
AIR = Anti-Inflammatory Reliever.
MART = Maintenance and Reliever Therapy
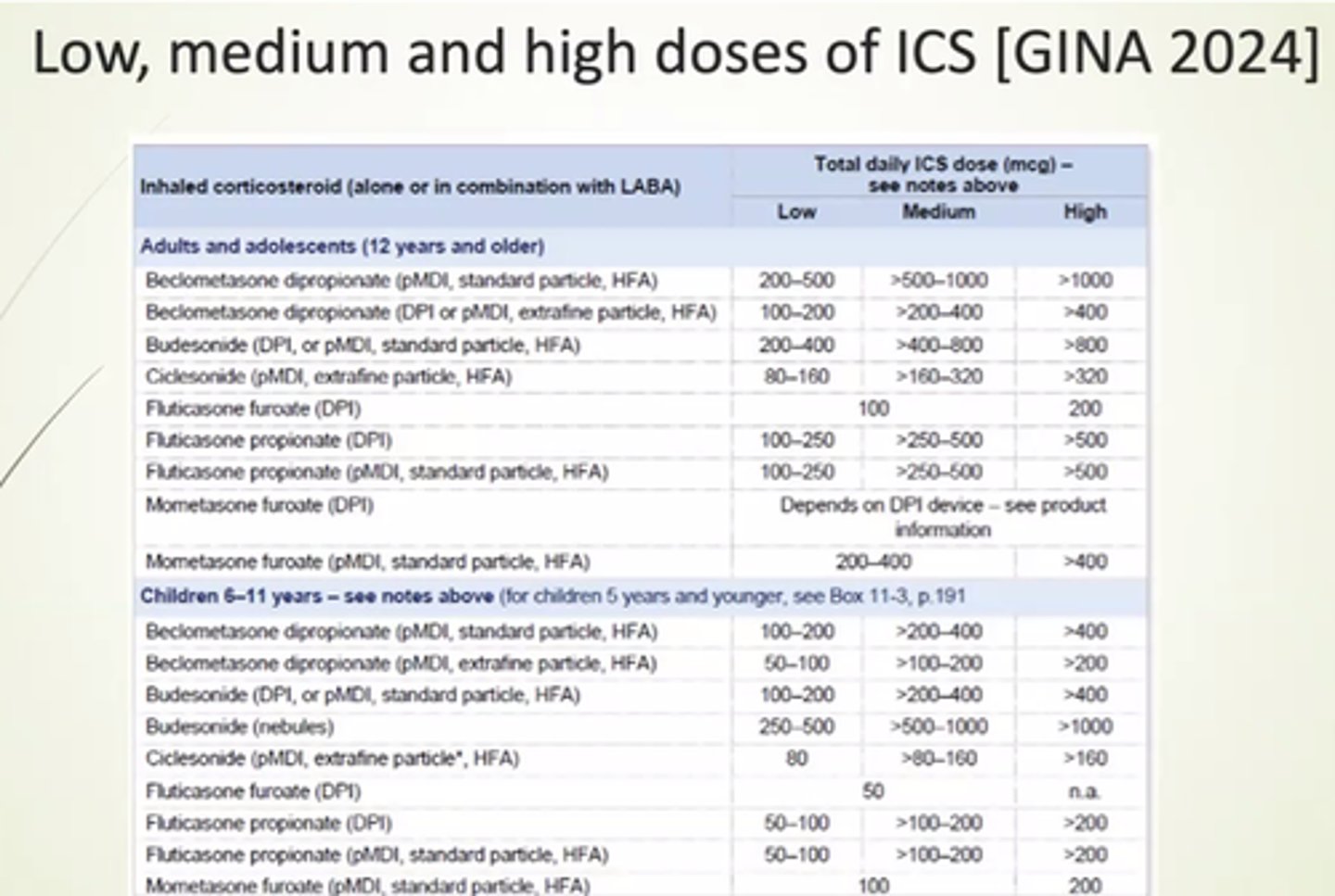
What's 1st line asthma treatment for adults and children aged 12+?
AIR therapy - low dose inhaled ICS/formoterol inhaler as needed.
What's 2nd line asthma treatment for adults and children aged 12+?
Low dose MART - ICS/Formoterol inhaler regularly AND prn
Why is Formoterol now the 1st line bronchodilator?
Bc it's the quickest bronchodilator - onset of action is in minutes.
Best option if acutely unwell pts.
Need to relax bronchial SM ASAP!
Why do we use combined ICS and Bronchodilators in MART?
= MART produces regular anti-inflammatory action, regular and quick acting relaxation of bronchial SM, and relief for breathlessness.
- Use same inhaler to relieve and maintain for ease.
Why are SABAs now not recommended in initial asthma treatment?
SABAs increase risk of exacerbations and asthma-related mortality if used without ICS.
UK approach is now not to use SABAs without concomitant ICS.

What are some advantages to using MART?
- Improved preventer adherence.
- Reduced exacerbations.
- Single inhaler.
- Easy to step up/down.
- Reduced cost for pts.

When should we NOT use MART?
- Children unable to use inhalers without spacers.
- Mainly exercise-induced asthma.
- High risk of CS side fx.
- With non-formoterol LABA.
How should we escalate asthma treatment is it remains uncontrolled, despite good adherence?
- Add Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist eg Montelukast.
- Increase ICS dose.
- Use ICS + LABA.
- Try LAMA.

How often should you review asthma treatment?
- Every 2-3 months when trialling new treatments.
- Annually for stable long-term asthma.
What are some potential reasons for uncontrolled asthma?
- Differential diagnoses.
- Poor adherence.
- Poor inhaler technique.
- Smoking + vaping.
- Occupational Exposure.
- Seasonal factors.
- Environmental factors (mould/air pollution).
- Psychological Factors.
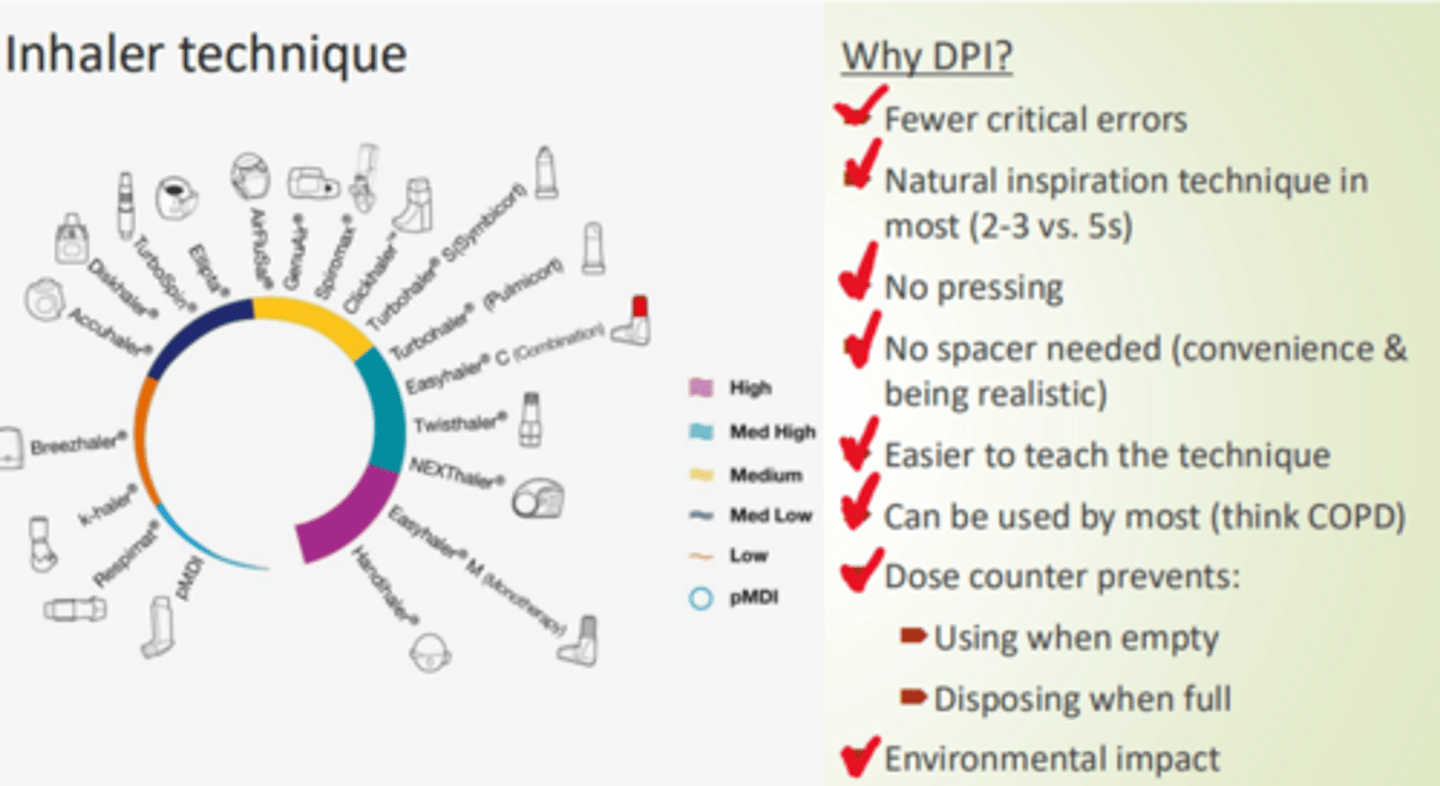
What is choice of inhaler type based on?
- Assessment of correct technique.
- Pt preference.
- Lowest environmental impact.
- Presence of integral dose counter.

When might FeNO levels be decreased?
In pts who smoke, or who have recently finished a course of prednisolone.
What are some advantages to using DPIs?
- Fewer critical errors.
- More natural inspiration technique.
- No pressing/coordination.
- No spacer needed.
- Better for environment.
What are the main treatment goals for asthma?
- Symptom control.
- Risk reduction.
- Minimise environmental impact of medication.

What are ACT and ACQ?
Asthma Control Test and Asthma Control Questionnaire

What are some common side fx of OCS?
- Opportunistic infections.
- Cushings.
- Moon face.
- Hypokalaemia, Na retention.
- Fluid retention and oedema.
- Thinning skin.
- Sleep disturbances.

What should be checked before prescribing OCS?
- Check inflammatory markers (elevated eosinophils and/or FeNO).
- If had previously, check the time it took them to respond to OCS.
- Risk vs Benefit.

What's included in a PAAP? (Personalised Asthma Action Plan)
- How to recognise signs of worsening asthma.
- How to respond.
- How to monitor response to treatment.
- Contact details for asthma nurses.

How can we identify uncontrolled asthma?
Frequent exacerbations:
- Req OCS 2+ times a year.
- 1+ hospitalisations.
- Despite max ICS.
Poor symptom control (frequent wheezing/coughing/night waking).
6+ SABAs in 12 months.
