Psychology 111: Exam Preparation for Exam #3 - University of Michigan
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Kelly's Attribution Theory
For behaviors that are consistent, people make personal attributions when consensus and distinctiveness are low.
Fundamental Attribution Error
Overestimate the role of personal (or dispositional) factors and underestimate role of situational factors.
Mere-exposure Effect
People tend to develop liking or disliking for things merely because they are familiar with them
Lake Wobegon Effect
A tendency for most people to believe that they are above average in intelligence, sense of humor, diving ability, and similar traits.
Self-serving Bias
The tendency to attribute our successes to internal, personal factors, and our failures to external, situational factors
Prisoner's Dilemma/Social Traps
A situation where two parties, separated and unable to communicate, must each choose between cooperating with the other or not.
Compliance
When an individual changes his or her behavior in response to an explicit or implicit request made by another person. Compliance is often referred to as an active form of social influence in that it is usually intentionally initiated by a person.
Conformity
The process whereby people change their beliefs, attitudes, actions, or perceptions to more closely match those held by groups to which they belong or want to belong or by groups whose approval they desire.
Foot-in-the-door Phenomenon
A compliance strategy that utilizes asking another person for small requests first, to make them comply with larger requests eventually.
Information Influence
A type of social influence in which individuals modify their behavior, opinions, or beliefs based on the information they receive from others
Normative Influence
Where a person conforms in order to be accepted and belong to a group.
Stanford Prison Study
The Stanford prison experiment (SPE) was a psychological experiment conducted in August 1971. It was a two-week simulation of a prison environment that examined the effects of situational variables on participants' reactions and behaviors.
Cognitive Dissonance
The discomfort a person feels when their behavior does not align with their values or beliefs
Social Facilitation
The theory that people perform better when in the presence of others, like a coworker or an audience.
Social Loafing
Where an individual exerts less effort to meet a goal when working in a group than they do working individually. It is often viewed as one of the main reasons that groups are less productive than the combined performance of the group members working independently.
Groupthink
A phenomenon that occurs when a group of individuals reaches a consensus without critical reasoning or evaluation of the consequences or alternatives.
Group Polarization
The idea that groups tend to make decisions that are more extreme compared to the original thoughts of individual group members
Deindividuation
Phenomenon in which people engage in seemingly impulsive, deviant, and sometimes violent acts in situations in which they believe they cannot be personally identified
Altruism
Acting to help someone else at some cost to oneself. It can include a vast range of behaviors, from sacrificing one's life to save others, to giving money to charity or volunteering at a soup kitchen, to simply waiting a few seconds to hold the door open for a stranger.
Bystander Effect
Occurs when the presence of others discourages an individual from intervening in an emergency situation, against a bully, or during an assault or other crime
Diffusion of Responsibility
As the number of bystanders increases, the personal responsibility that an individual bystander feels decreases
Attractive Bias
Individuals who are considered conventionally attractive are typically perceived more positively than their less attractive peers
Just-world Hypothesis
Our belief that the world is fair, and consequently, that the moral standings of our actions will determine our outcomes. This viewpoint causes us to believe that those who do good will be rewarded, and those who exhibit negative behaviors will be punished.
Attraction
The phenomenon of individuals taking interest in and liking another individual.
Baby Face Effect
Research has also found that people are more attracted to average faces. Finally, there is a tendency to find infant-like facial features attractive.
Jame-Lange Theory
Physical changes in the body happen first, which then leads to the experience of emotion. Essentially, emotions stem from your interpretation of your physical sensations. For example, your heart beating wildly would lead you to realize that you are afraid.
Cannon-Bard Theory
Stimulating events trigger feelings and physical reactions that occur at the same time. For example, seeing a snake might prompt both the feeling of fear (an emotional response) and a racing heartbeat (a physical reaction)
Two Factor Theory
Focuses on the interaction between physical arousal and how we cognitively label that arousal. In other words, simply feeling arousal is not enough; we also must identify the arousal in order to feel the emotion.
Sympathetic Nervous System
A network of nerves that helps your body activate its "fight-or-flight" response. This system's activity increases when you're stressed, in danger or physically active.
Role of Amygdala in Emotion
It's a major processing center for emotions. It also links your emotions to many other brain abilities, especially memories, learning and your senses. When it doesn't work as it should, it can cause or contribute to disruptive feelings and symptoms.
Ekmans Theory of Facial Expression
Paul Ekman theorized that some basic human emotions (happiness/enjoyment, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, disgust and contempt) are innate and shared by everyone, and that they are accompanied across cultures by universal facial expressions.
Facial Feedback Hypothesis
Individuals' emotional experiences are influenced by their facial expressions. For example, smiling should typically make individuals feel happier, and frowning should make them feel sadder.
Guilty Knowledge Test
The Guilty Knowledge Test (GKT) is a psychophysiological questioning technique that can be used as part of a polygraph examination which purports to assess whether suspects conceal "guilty knowledge" by measuring their physiological responses while responding to a series of multiple choice questions.
Misa
People try to make meaning of their experiences. In these reasonings they often attribute an event or behavior to something that actually has no relation/causation
Adaption-level Phenomenon
The tendency people have to quickly adapt to a new situation, until that situation becomes the norm.
Relative Deprivation
The belief that a person will feel deprived or entitled to something based on the comparison to someone else
Social Comparison
People coming to know themselves by evaluating their own attitudes, abilities, and traits in comparison with others. In most cases, we try to compare ourselves to those in our peer group or with whom we are similar.
Stress
A state if worry or mental tension caused by a difficult situation.
Micro Stressor
Brief bursts of stress caused by ordinary business or personal life events such as a client complaint, a teammate missing a deadline, or even unexpected traffic that happens so frequently that you do not even realize them.
Major Stressor
Major traumatic events, significant life changes, daily hassles, as well as other situations in which a person is regularly exposed to threat, challenge, or danger. The death of a loved one, excessive worrying, unemployment, and low self-esteem
Catastrophic Stressor
An overwhelming reaction to a traumatic event that is beyond the limits of normal life, such as rape, torture, genocide, or severe war-zone experiences.
General Adaption Syndrome
Describes the process your body goes through when you are exposed to any kind of stress, positive or negative. It has three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion. If you do not resolve the stress that has triggered GAS, it can lead to physical and mental health problems.
Type A Personality
A pattern of behavior and personality associated with high achievement, competitiveness, and impatience, among other characteristics.
Type B Personality
Often described as easygoing, relaxed, and highly flexible. The type B personality is basically the opposite of the type A. People with a type A personality are meticulous, whereas type B people tend to take a much more casual, carefree approach
Effects of Stress on Illness
Irritability or aggression, a feeling of loss of control, insomnia, fatigue or exhaustion, sadness or tears, concentration or memory problems, or more. Continued stress can lead to other problems, such as depression, anxiety or burnout.
Uplifts
Minor pleasant events, such as completing a rewarding task, occur in daily life.
Benefits of Relaxation, Exercise, Optimism
Slow down brain waves, which rejuvenates the brain's chemistry and gives rise to a calmer state of mind.
Psychological Disorder
A condition characterized bu distressing, impairing, and/or atypical thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
DSM-5
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, was the product of more than 10 years of effort by hundreds of international experts in all aspects of mental health.
Anxiety Disorders
Persistent and excessive worry that interferes with daily activities. This ongoing worry and tension may be accompanied by physical symptoms, such as restlessness, feeling on edge or easily fatigued, difficulty concentrating, muscle tension, or problems sleeping.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
A condition of excessive worry about everyday issues and situations. It lasts longer than 6 months. In addition to feeling worried you may also feel restlessness, fatigue, trouble concentrating, irritability, increased muscle tension, and trouble sleeping.
Phobias
A persistent, excessive, unrealistic fear of an object, person, animal, activity or situation.
Panic Disorder
An anxiety disorder characterized by unexpected and repeated episodes of intense fear accompanied by physical symptoms that may include chest pain, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, or abdominal stress.
Simple Phobias
Center around a particular object, animal, situation, or activity. They often develop during childhood and may become less severe as you get older. Common examples of simple phobias include: animal phobias-such as dogs, spiders, snakes or rodent.
Social Phobias
People experience extreme and persistent anxiety associated with social or performance situations, Some people with social phobia fear and avoid specific situations, while others may feel anxiety about certain social situations.
Causes of Phobias
A phobia may be associated with a particular incident or trauma. A phobia may be learned response that a person develops early in life from a parent or sibling.
PTSD(posttraumatic stress disorder)
A mental health condition that's triggered by a terrifying event experiencing or witnessing it. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety, as well as uncontrollable thoughts about the event.
OCD(obsessive-compulsive disorder)
A long-lasting disorder in which a person experiences uncontrollable and recurring thoughts (obsessions) engages in repetitive behaviors (compulsions), or both.
Obsessions
Repeated thoughts, urges, or mental images that are intrusive, unwanted, and make most people anxious. Common obsessions include: fear of germs or contamination.
Compulsions
Repetitive behaviors or mental acts that a person feels driven to perform in response to an obsession. The behaviors typically prevent or reduce a person's distress related to an obsession temporarily, and they are then more likely to do the same in the future.
Dissociative Disorders
Mental health conditions involve experiencing a loss of connection between thoughts, memories, feelings, surroundings, behavior, and identity. These conditions include escape from reality in ways that are not wanted and not healthy. This causes problems in managing everyday life.
Amnesia
Loss of memories, including facts, information and experiences.
Fugue State
A temporary state where a person has memory loss and ends up in an unexpected place. People with this symptom can't remember who they are or details about their past.
DID(diss
Someone with multiple, distinct personalities. The various identities control a person's behavior at different times. The condition can cause memory loss, delusions or depression. They are usually caused by past trauma.
Mood Disorders
Marked disruptions in emotions. These are common psychiatric disorders leading to an increase in morbidity and mortality.
Major Depression
A mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. It affects how much you feel, think, ad behave and can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems.
Minor Depression
Characterized by depressed mood or anhedonia and 1 to 3 of the following symptoms over 2 weeks: appetite disturbance, sleep disturbance, psychomotor agitation or retardation, loss of energy, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, difficulty concentrating, and recurrent thoughts of death.
Dysthymia
A milder, but longer-lasting form of depression.
Seasonal Affective disorder
Happens during certain seasons of the year often fall or winter. It is thought that shorter days and less daylight may trigger a chemical change in the brain leading to symptoms of depression.
Bipolar Depression
A mental illness that causes unusual shifts in a person's mood, energy, activity levels, and concentration tasks.
Vicious Cycle of Depression
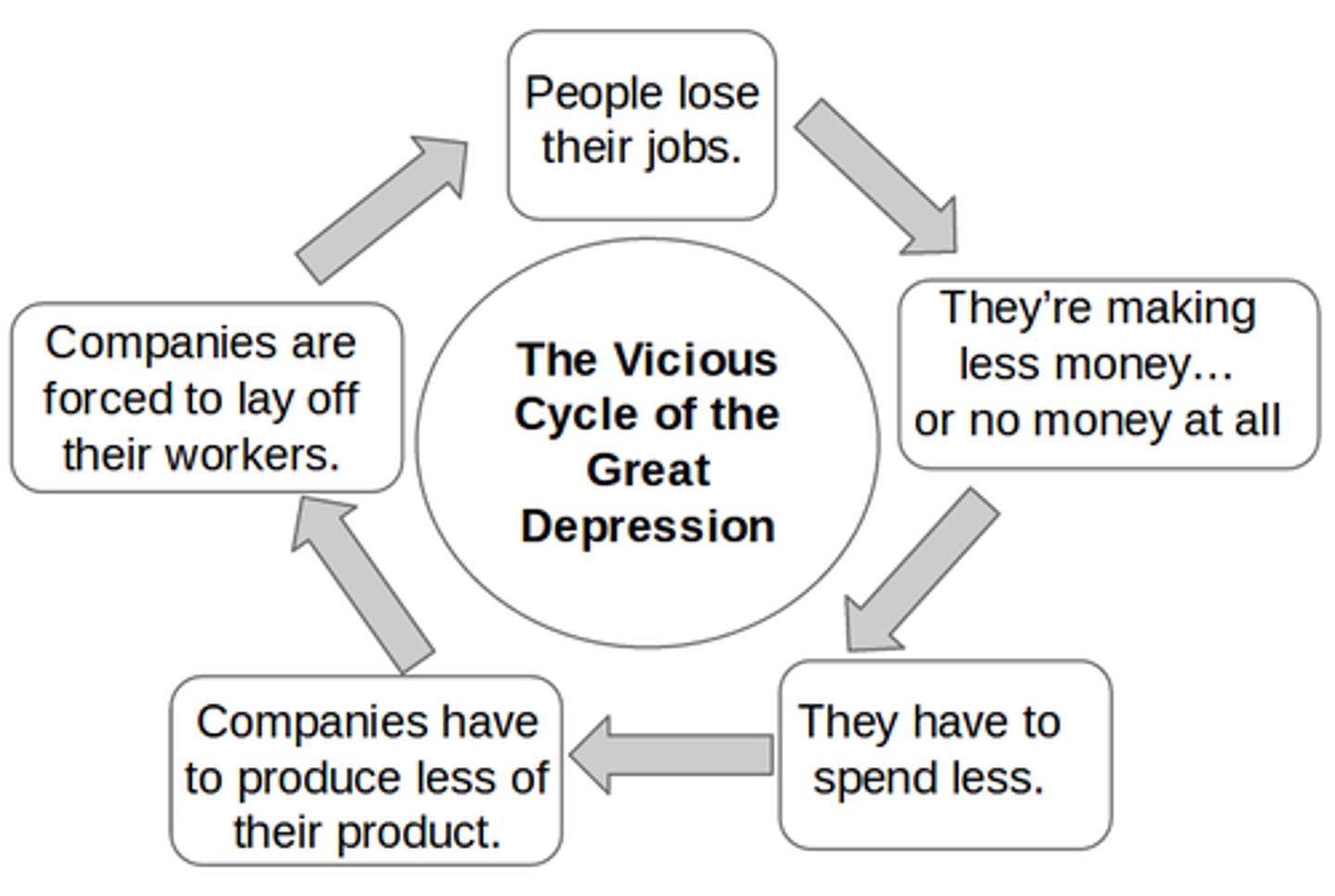
Learned Helplessness
When an individual continuously faces a negative, uncontrollable situation and stops trying to change their circumstances, even when they can do so. For Example, a smoker may repeatedly try and fail to quit.
Depressive Explanatory Style
People often attribute unwanted or adverse events to their lives as internal, global, and stable.
Schizophrenic Disorders
A serious mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally.
Delusions
A person with a delusion will hold firmly to the belief regardless of evidence to the contrary. Delusions can be difficult to distinguish from overvalued ideas, which are unreasonable ideas that a person holds, but the affected person has at least some level of doubt as to its truthfulness.
Hallucinations
A false sensory perception that has a compelling sense of reality despite the absence of an external stimulus. It may affect any of the senses, but auditory and visual are the most common.
Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Hallucinations, such as hearing voices or seeing things that do not exist, paranoia, and exaggerated or distorted perceptions, beliefs, and behaviors.
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Blunted affect, alogia (reduction in quantity of words spoken), avolition (reduced goal-directed activity due to decreased motivation), asociality, and anhedonia (reduced experience of pleasure)
Types of Schizophrenia
Paranoid schizophrenia, catatonic schizophrenia, disorganized or hebephrenic schizophrenia, residual schizophrenia, and undifferentiated schizophrenia
Borderline Personality Disorder
A mental health condition that affects the way people feel about themselves and others, making it hard to function in everyday life.
Antisocial Personality Disorder
A mental condition in which a person has a long-term pattern of manipulating, exploiting, or violating the rights of others without any remorse. This behavior may cause problems in relationships or at work and is often criminal.
Psychopharmacology
A field, which analyzes the impact of different drugs on the mental health of patients. It considers how different compounds alter people's behavior by changing the way that the person thinks or feels.
Trephination
A surgical procedure in which a disk of bone is removed from the skull with a circular instrument having a sawlike edge.
Lobotomies
A surgical procedure that involves severing the nerve pathways in the prefrontal cortex.
Antipsychotic Drugs
A type of drug used to treat symptoms of psychosis. These include hallucinations (sights, sounds, smells, tastes, or touches that a person believes to be real but are not real), delusions (false beliefs), and dementia (loss of the ability to think, remember, learn, make decisions, and solve problems).
Antidepressant Drugs
Antidepressants are psychiatric drugs which are licensed to treat depression.
Lithium for Bipolar Disorder
A mood stabilising medicine used to treat certain mental illnesses, such as: mania (feeling highly excited, overactive or distracted) hypomania (like mania, but less severe) bipolar disorder, where your mood changes between feeling very high (mania) and very low (depression)
Reuptake of Neurotransmitters
What happens after a signal is transmitted: The neurotransmitter, its "work" completed, is reabsorbed back into the cell that previously released it. Reuptake is essential for synaptic functioning. It allows neurotransmitters to be reused and helps regulate neurotransmitter levels present in the synapse.
ECT (electro
A treatment that involves sending an electric current through your brain. This causes a brief surge of electrical activity within your brain (also known as a seizure).
Psychotherapy
A variety of treatments that aim to help a person identify and change troubling emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. Most psychotherapy takes place one-on-one with a licensed mental health professional or with other patients in a group setting.
Free Association
Psychoanalytic patients are invited to relate whatever comes into their minds during the analytic session, and not to sensor their thoughts.
Resistance
The opposition to the therapy process in which a client refuses or rejects suggestions made by a psychologist.
Transference
When someone redirects their feelings about one person onto someone else. During a therapy session, it usually refers to a person transferring their feelings about someone else onto their therapist.
Repressed Memories
Occurs when trauma is too severe to be kept in conscious memory, and is removed by repression or dissociation or both.
Behavioral Therapy
A range of treatments and techniques which are used to change an individual's maladaptive responses to specific situations.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
A form of psychotherapy that focuses on modifying dysfunctional emotions, behaviors, and thoughts by interrogating and uprooting negative or irrational beliefs.
Dialectal Behavior Therapy (DBT)
An evidence-based model of therapy that helps people learn and use new skills and strategies so that they build lives they feel are worth living.
Mindfulness
Awareness of one's internal states and surroundings.
Group Therapy
The treatment of multiple patients at once by one or more healthcare providers.
Flooding
Flooding, sometimes referred to as in vivo exposure therapy, is a form of behavior therapy and desensitization—or exposure therapy—based on the principles of respondent conditioning.