5. pigmented lesions part 3
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what are the seven developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesions?
McCune Albright syndrome
Neurofibromatosis I
Carney complex
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Leopard syndrome
dyskeratosis congenita
Laugier Hunziker syndrome
which developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesion?
variant of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia: developmental condition resulting from GNAS1 mutation
associated w café au lait (light brown) macules and endocrinopathies
McCune-Albright
GNAS1 mutation which developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesion?
McCune-Albright syndrome
what is the triad of McCune-Albright syndrome?
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia affecting several bones (not just maxilla and mandible)
endocrine dysfunction: hyperthyroidism and/or sexual precocity, the latter predominantly identified in female
cutaneous hyperpigmentation (café au lait)
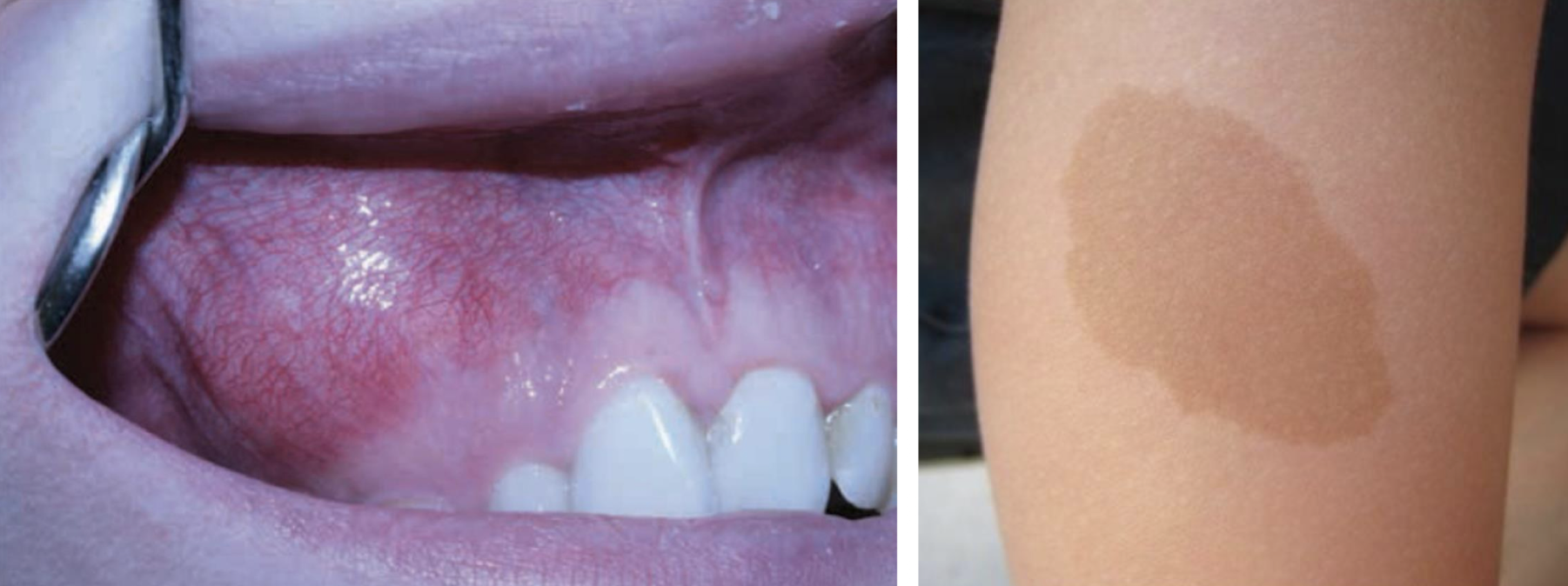
fibrous dysplasia affecting maxilla
GNAS1 gene mutation
what is neurofibromatosis?
autosomal dominant NF1 gene mutation mapped to chromosome 17
aka Von Recklinghausen disease
specific diagnostic criteria
neurofibromas are benign tumors that grow on nerves (MAS does not have)
NF1 gene mutation
neurofibromatosis
what are the diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis?
two or more of the following:
6+ café au lait spots
>5mm prepubertal pts
>15 mm in postpubertal pts
2+ neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma
axillary and/or inguinal freckling
optic nerve glioma
distinctive osseous lesion like dysplasia of sphenoid wing, thinning of long bone cortex w or w/o pseudoarthritis
first-degree relative (parent, sibling, offspring) w NF1 according to above criteria
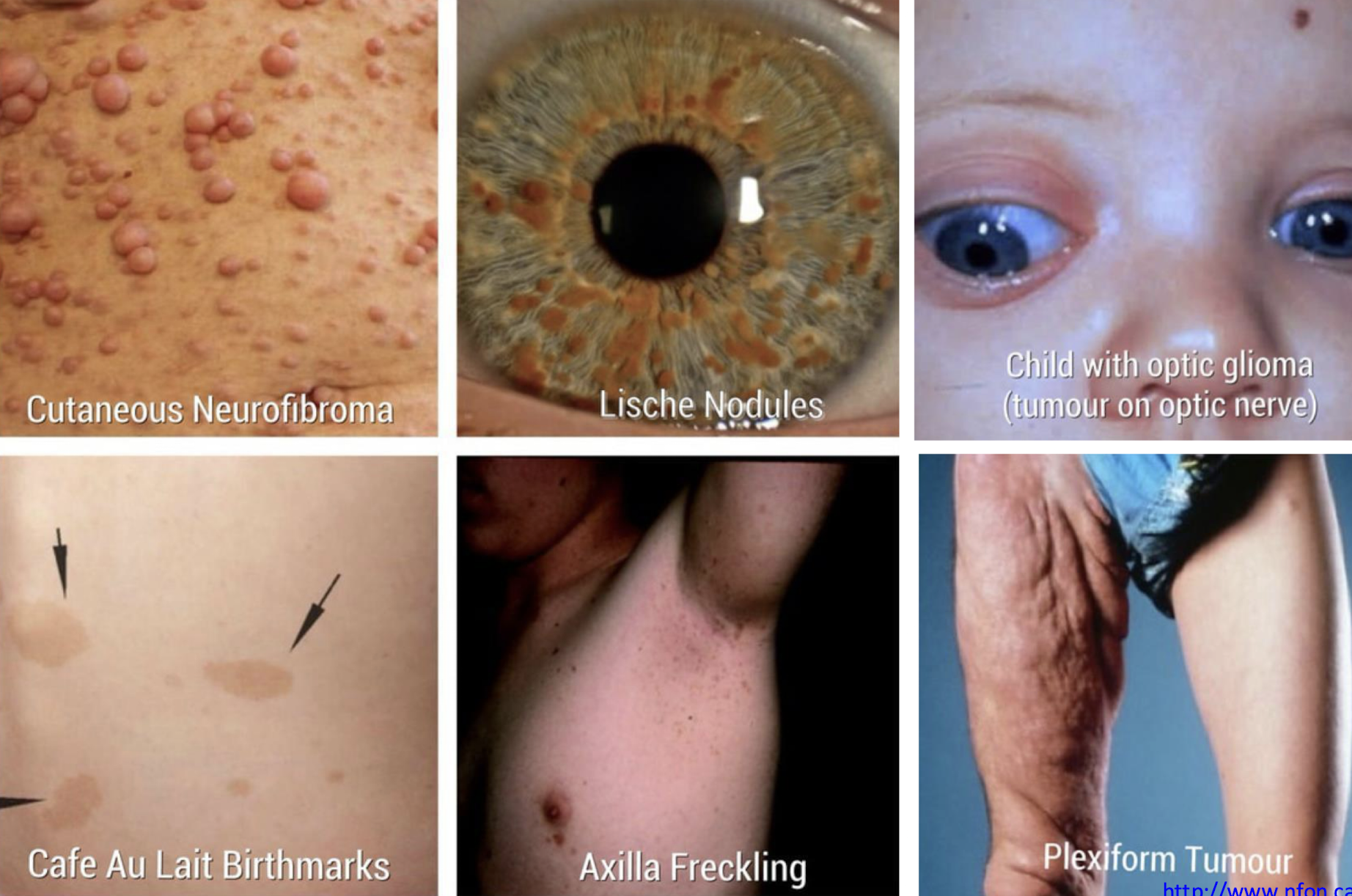
neurofibromatosis I
neurofibromatosis neurofibromas have propensity to turn into what type of cancer?
soft tissue cancer (vs someone w sporadic neurofibroma)
what’s the dermatological/geographical difference between neurofibromatosis and McCune Albright?
McCune-Albright café au lait has irregular edges like coast of Maine while neurofibromatosis café au lait has smooth border like coast of cali
which of the following is not characteristic of neurofibromatosis?
A. Unilateral enlargement of tongue
B. Lisch nodules
C. Café au lait macules
D. Autosomal recessive
E. Optic glioma
D. autosomal recessuve
which developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesion?
autosomal dominant
cardiac myxomas
cutaneous myxomas
spotty pigmentation: lentigines on face and vermillion border, blue nevi including epithelioid blue nevi
carney complex
myxomas
benign, non-cancerous tumor made of gelatinous connective tissue, most commonly found in the heart, but also in other soft tissues
Carney complex
lentigines
small, flat, pigmented spots on the skin that are a result of excess melanin production and are commonly known as age spots, sunspots, or liver spots
Carney complex
nevus
mole, a small, typically benign skin growth
Carney complex
autosomal dominant developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesion? (hint)
neurofibromatosis, carney complex, and peutz-jegher
PRKAR1A gene located at 17q22-24 but no targeted Tx yet
Carney complex

carney complex (C = lentigines)
a biopsy of this would look like melanotic macule
which developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesion?
autosomal dominant
mutation of STK11/LKB1 gene
Freckle-like lesions of the hands, peri-oral region, and/or oral mucosa
Intestinal polyposis with predisposition to adenocarcinoma (super young adults)
Peutz-Jegher
mutation of STK11/LKB1 gene
Peutz-Jegher
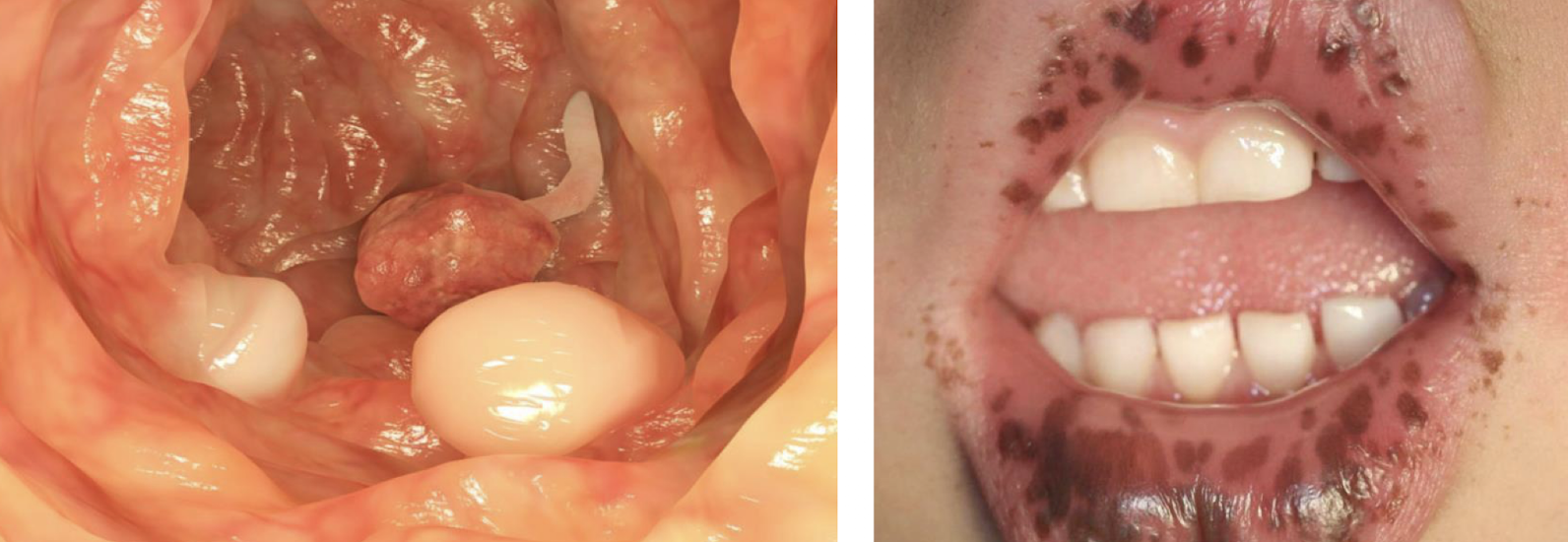
Peutz-Jeghers
what are the four diagnostic criteria for Peutz-Jeghers?
3+ histologically confirmed Peutz Jeghers polyps
any number of Peutz-Jeghers polyps w a family history of the syndrome
characteristic prominent mucocutaneous pigmentation w a family history
any number of Peutz-Jeghers polyps and characteristic prominent mucocutaneous pigmentation
Peutz-Jegher
mutation of PTPN11 gene
leopard syndrome
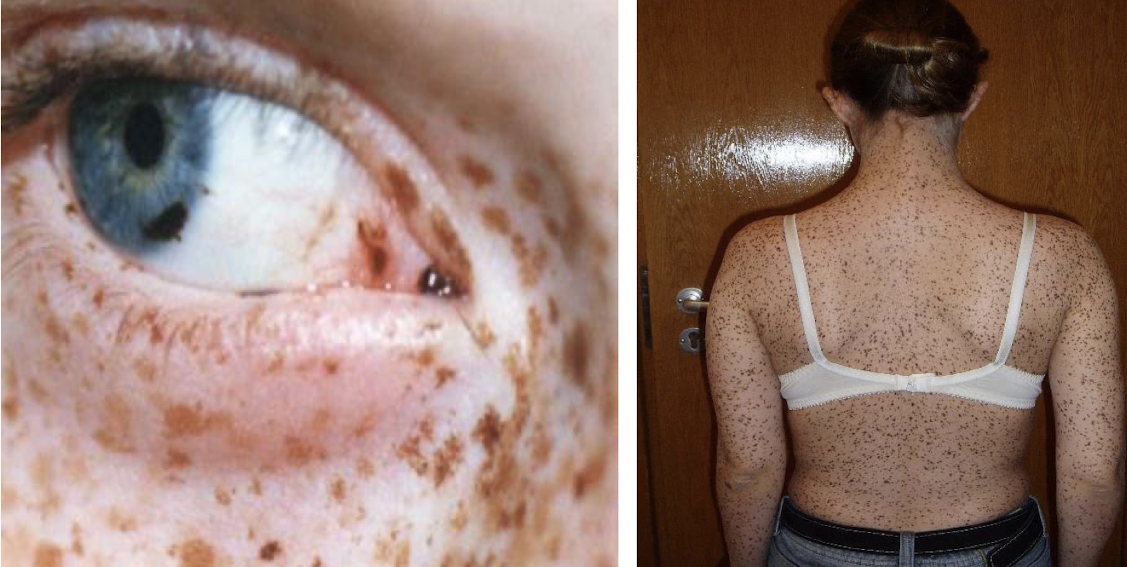
leopard syndrome
what does leopard of leopard syndrome stand for?
Lentigines
ECG conduction abnormalities
Ocular hypertelorism
Pulmonic stenosis
Abnormal genitalia
Retardation of growth
Deafness
DKC1 gene mutation
dyskeratosis congenita
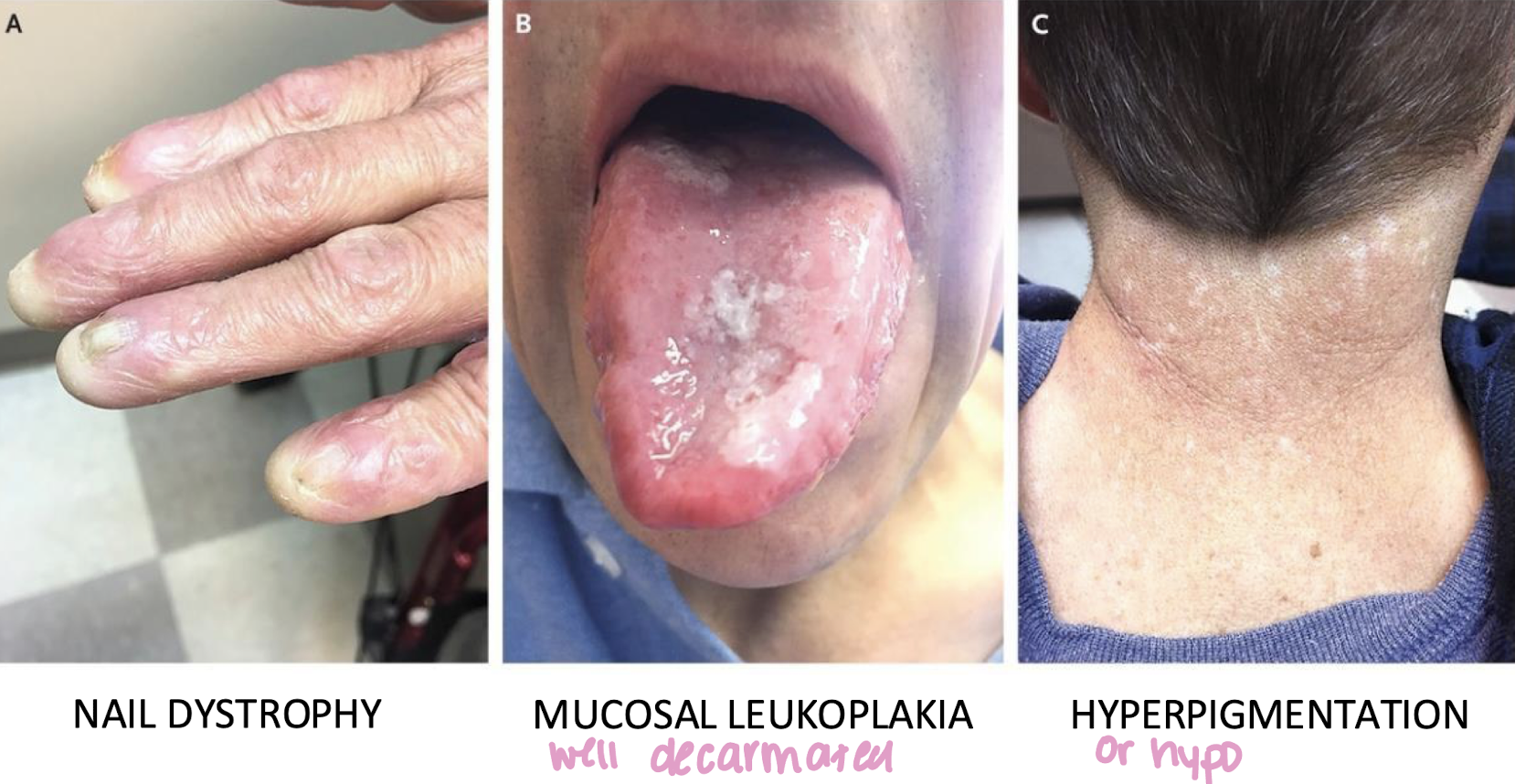
relevant to white lesion lecture, 30 yo w (pre)cancer diagnosis
dyskeratosis congenita
which developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesion: rare inherited disorder characterized by premature aging of certain tissues and organs?
dyskeratosis congenita
which developmental melanin-associated pigmented lesion?
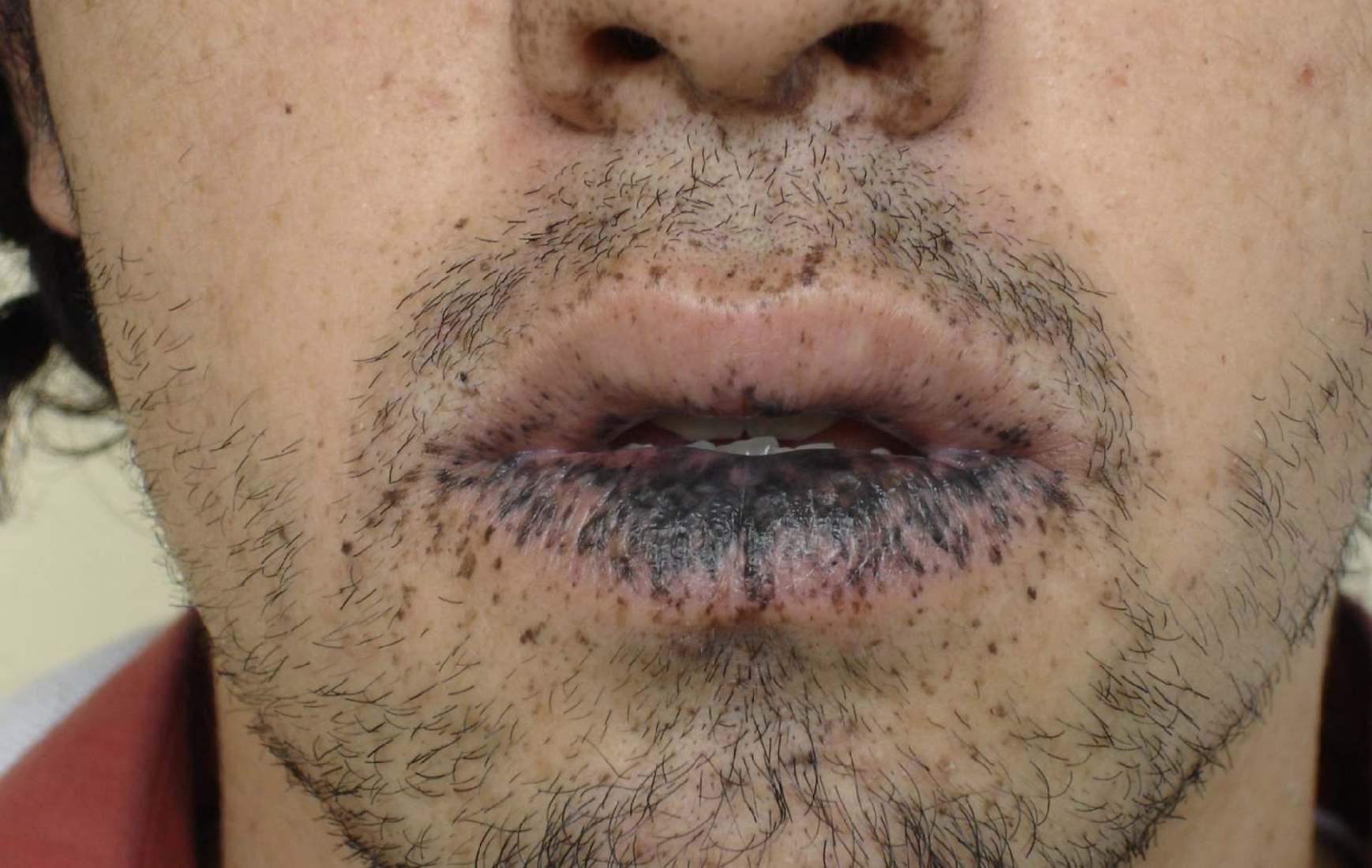
Rare acquired, diagnosis of exclusion
Macules of the labial and/or buccal mucosa
Longitudinal streaks in fingernails (melanonychia)
Laugier Hunziker
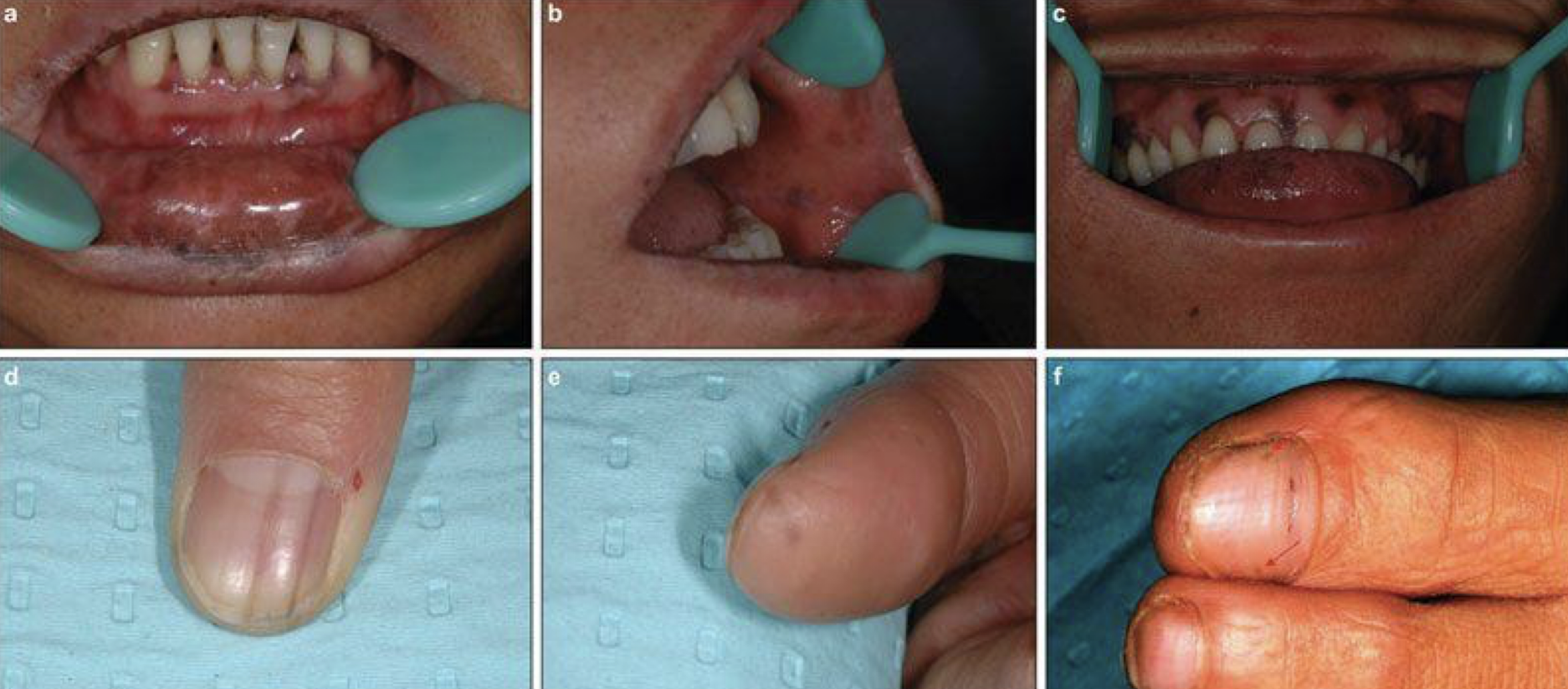
Laugier-Hunziker syndrome

Laugier Hunziker syndrome
Which of the following conditions does an individual appear to have with oral melanotic macules and gastrointestinal polyps?
A. Addison disease
B. Laugier Hunziker syndrome
C. Peutz-Jegher syndrome
D. McCune-Albright syndrome
C. Peutz-Jegher syndrome