Lecture 1
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Parasitology
Study of symbiosis
Germen scholar A. de Bary, 1879 definition of Parasitology
Any two organisms living in close association, commonly one living in or on the body of the other, are symbiotic, as contrasted with free living. usually the symbionts are of different species but not necessarily
Animal association
Homogenetic
Heterogenetic
Homogenetic association
Between individuals of the same genotype
Heterogenetic association
between individuals of different genotype
Interactions of Symbionts
No physiological or biochemical dependence
Physiological or biochemical dependence
Types of No physiological or biochemical dependence
Phoresis and Commensalism
Phoresis
“Traveling together” no physiological or biochemical dependence on either side
Commensalism
“Eating on the same table” One benefits from the other while the host is not harmed nor helped
Types of Physiological or biochemical dependence
Mutualism and Parastism
Mutualism
both partners benefit from the association ( Usually obligatory)
Parasitism
the parasite harms its host
Metabolic Dependence
Developmental Stimuli
Nutritional Materials
Digestive Enzymes
Control of Maturation
Typical characteristics of parasitism
higher reproductive potential
unique morphological or physiological specialization
special site specificity
usually non-lethal
generally more numerous and much smaller than the host
have evolved methods of evading the immune system
change host behavior
Types of parasites (A)
Ectoparasite and Endoparasite
Types of parasites (B)
Facultative and Obligate
Facultative Parasites
not normally parasites but can become so when they are accidentally eaten or enter a wound
Example of Facultative Parasites
freeliving amebas
Obligate Parasites
cannot complete their life cycle without spending at least part of the time as a parasite
Types of Obligate Parasites
Temporary or intermittent
Permanent
Incidental
Erratic
Temporary or intermittent parasite
Only Reeds on the host and then leaves
Example of temporary parasite
Mosquito / bed bugs
Permanent parasite
Live their entire adult lives within or on their host
Example of permanent parasite
Ascaris / hard ticks
Incidental parasite
Enters or attaches to the body of a species of host different from its normal one.
Example of incidental parasite
Dipylidium caninum
Erratic parasite
Wanders in to an organ in which it is not usually found
Example of erratic parasite
Entamoeba histolytica in the liver or lung
How to differentiate among various types of hosts
According to the role the host plays in the life cycle of the parasite
Types of hosts
Definitive host
Intermediate host
Paretenic or transport host
Reservoir host
Definitive host
The parasite reaches sexual maturity
Intermediate host
Require for parasite development but on in which the parasite doesn’t reach sexual maturity
Paratenic / Transport host
Parasite does not undergo any development but in which it remains alive and infective to another host
Reservoir host
Animal that harbors an infection but shows no il effects and serves as a source of parasite
Image of definitive host
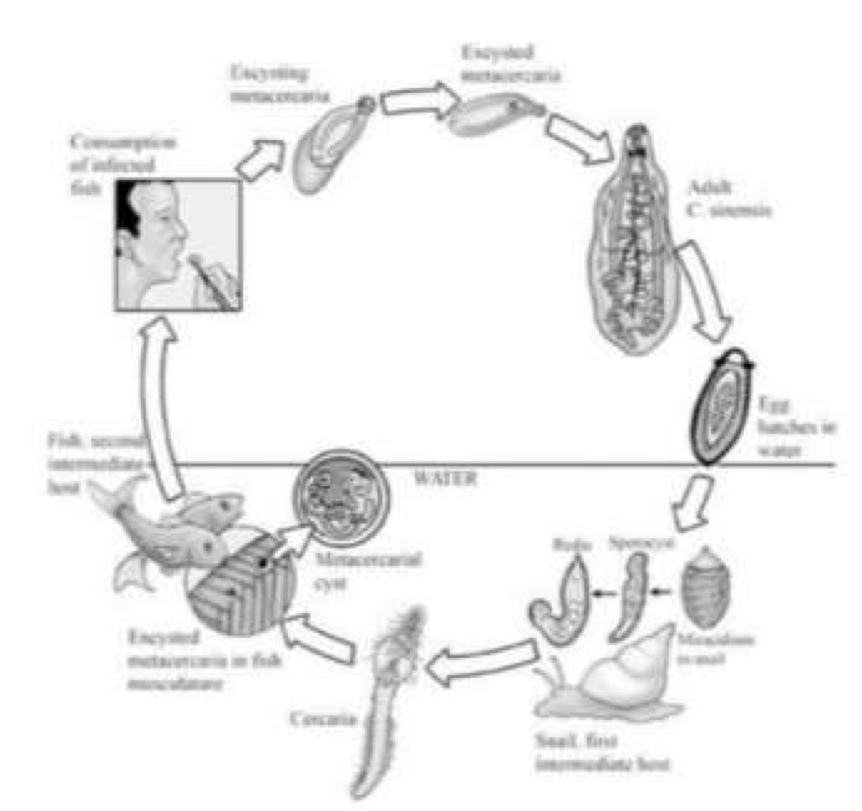
Image of Intermediate host
Life cycle of parasites
Single or direct life cycle
Complex or indirect life cycle
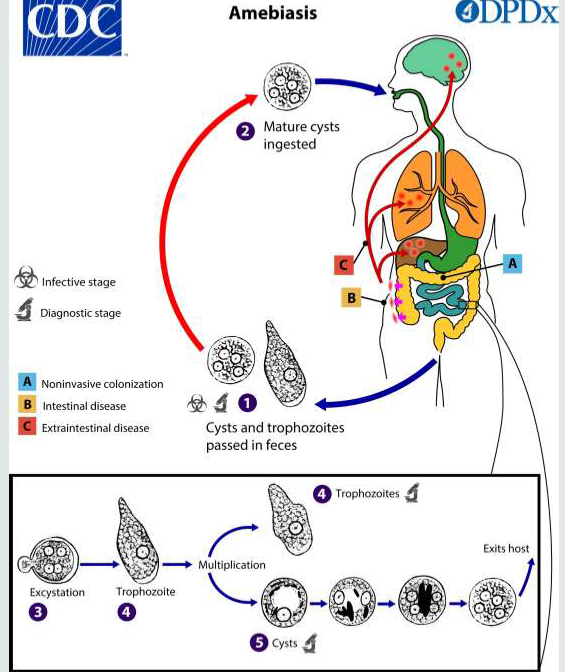
Single or direct life cycle
Complex or indirect life cycle
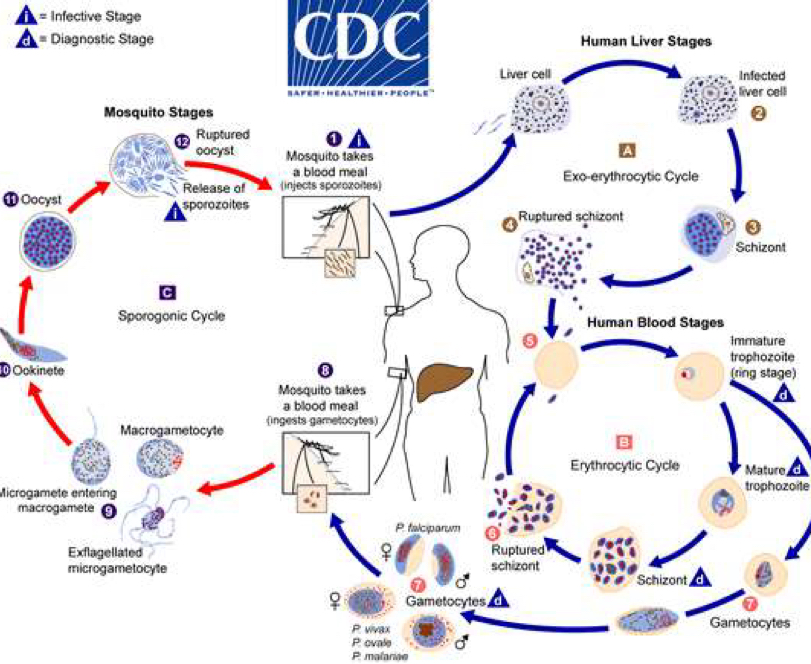
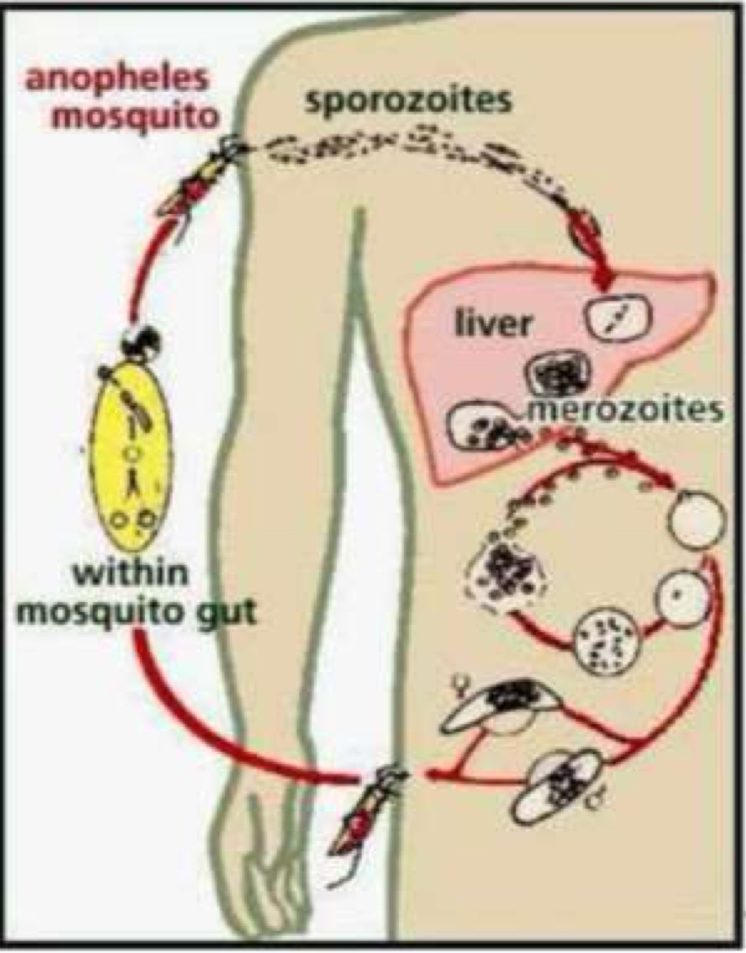
Source of parasite names
The name of the individual who originally named the parasite
Named after their host
Named after the organ where they were discovered
The geographical location or the place they were discovered
Based on their morphology
Example of a parasite that was named after the person who originally named it
Giardia parasite
Example of a parasite that was named after their host
Emeria Bovis
What does the scientific name of a parasite consist of
Genus and species
Example of a parasite that was named after the organ was discovered in
Fasciola Hepatica
Example of a parasite that was named after the location it was found
Leishmania braziliansis
Example of a parasite that was named after thier morphology
Fasciola gigantica
Parasites are divided into major divisions, including
Protozoa
Platyhelminthes
Acanthocephala
Nematoda
Arthropoda
Example of Protozoa
Amoebae, Flagellates, Ciliates
Example of Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
Cestodes, trematodes
Another name for Acanthocephala
Thornyheaded worms
Another name for Nematoda
Roundworms
Example of Arthropoda
Insect, Spiders, Mites, Ticks
Methods of infection
Oral (eggs or larvae swallowed)
Vector (a blood feeding arthropod)
Penetration (specialized mouthpart that can pierce through skin)
Methods of escape
Sputum
Vector ( removes parasites while feeding)
Urine / Faeces
What the most common method of escape
Urine / Faeces
Direct effect of parasite on host
The parasites are undoubtedly the reason for its state
They can be discussed under the heading of trauma, nutrition robbing , toxin production, etc
Indirect effect of parasite on hosts
Exposing the host to concomitant infectious diseases
Impact on physical and mental development
Impact on production rates
Pathogen
As parasite which injures the host
Infection
The penetration of a parasite within the host
Infestation
The presence of arthropods on the skin of the host
Epidemic
The sudden appearance of an infection which spreads rapidly found in a large population
Endemic
An infection which has always existed in a region
Incubation
The time between the entrance of the parasite and the begin of the disease
Habitat
The natural abode of a parasite species
carrier
A person who carries a certain parasite without displaying any signs of disease
Zoonoses
The diseases of animal which are transmissible to man
Incidence
The rate part which a disease or a certain event occurs
Prevalence
The total number of cases of a disease at a certain time in a designated area