COPY Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Solar energy is converted into chemical potential energy and stored in the bonds of glucose through carbon fixation
Relationship between 2 Phases of Photosynthesis
Reciprocal relationship
Products of light dependent are the reactants of light independent and vice versa
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Rxns
Example of rxn coupling
Requires reduction and oxidation of 2 reactants at the same time
Relied on in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration to shuttle electrons between the endergonic and exergonic parts
Oxidation
Lose/give up e-
Compound gains positive charge
Reduction
Gain/receive e-
Compounds lose positive charge
Electron Carriers (photosynthesis)
Can be both oxidized and reduced
Shuttle high energy e- from light dependent rxns to light independent rxns
The e- can be from the e- that were excited from photons of light
Ex. NADP+/NADPH
NAD+/NADH
FADH/FADH2
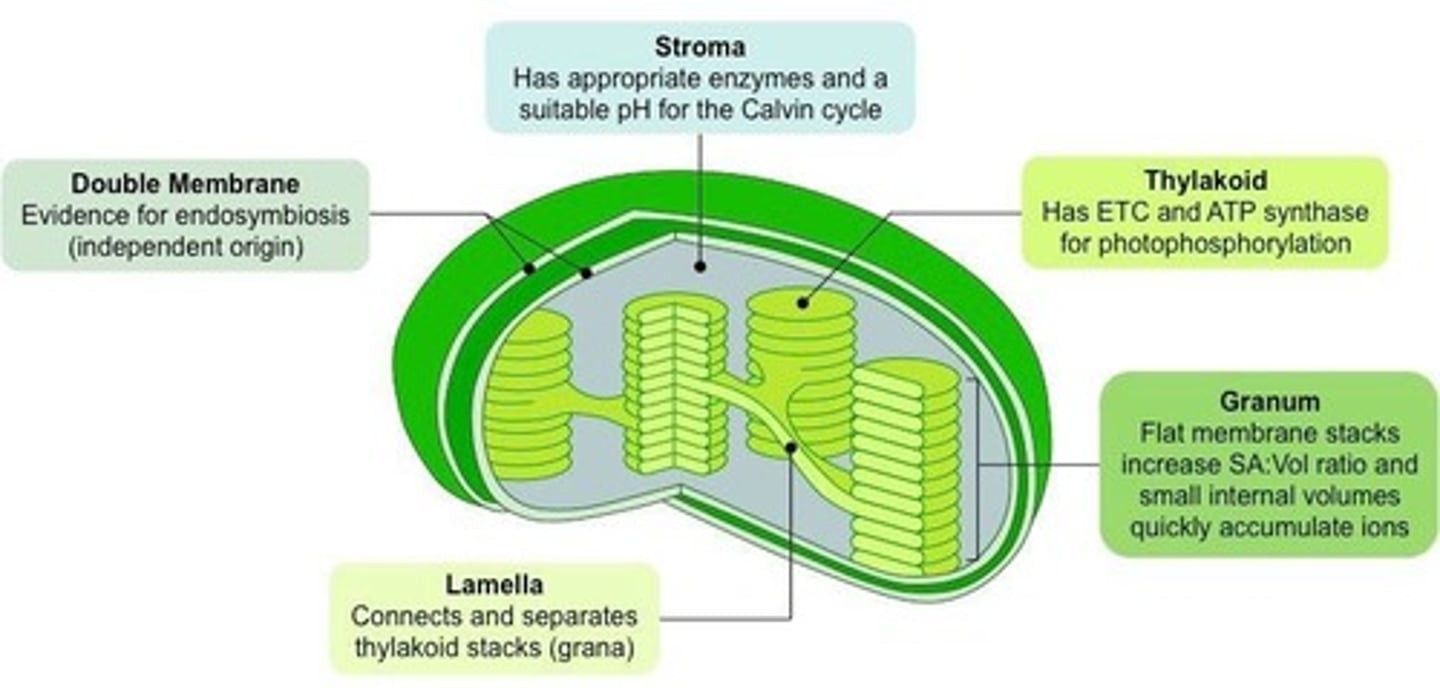
Chloroplast Anatomy
Stroma - has enzymes and suitable pH for Calvin Cycle
Double Membrane - evidence for endosymbiosis
Thylakoid - ETC and ATP synthase
Granum - flat membrane stacks --> increase SA:Vol ratio and small internal volumes quickly accumulate ions
Lamella - connects and separates grana (thylakoid stacks)
What rxns occur in the stroma?
Light independent rxns
What rxns occur in the thylakoid membrane?
Light dependent rxns
Thylakoid Membrane
1. Contains photosystem proteins (have chlorophyll)
2. ATP synthase
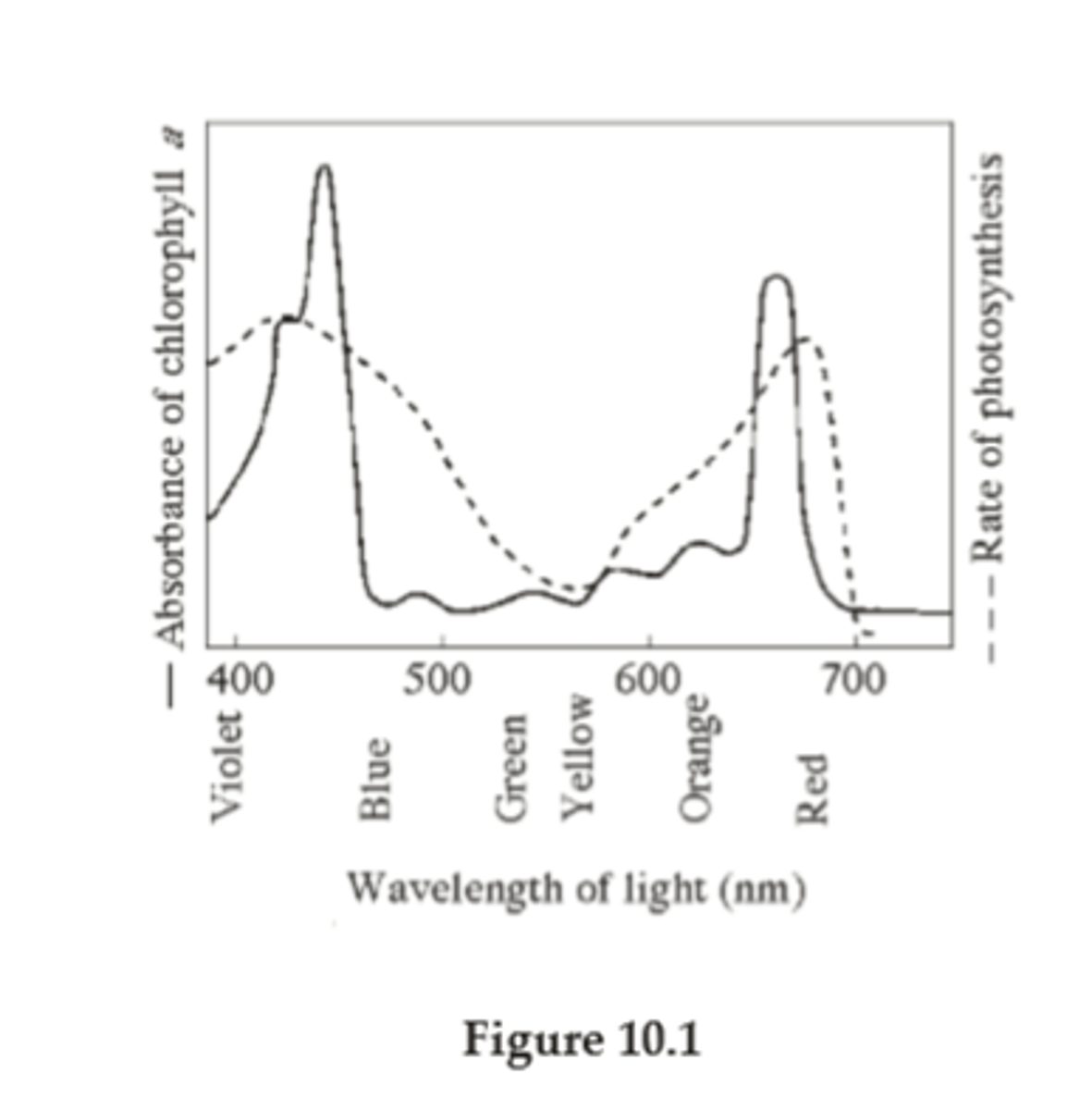
Chlorophyll
Light absorbing pigment in photosystem proteins
Absorb all wavelengths except for green - green is reflected
Absorbance Spectra
Peaks = absorbed light used for photosynthesis
Valley = reflected light that is seen by eye but not used for photosynthesis
Exclusion Statement
Memorization of the steps in the Calvin cycle, the structure of the molecules, and the names of enzymes (except ATP synthase)
Origin of Photosynthesis
Ancestral prokaryotes were the first to develop photosynthesis
Evolution of photosynthesis introduced oxygen into early Earth's atmosphere
Eukaryotic cells became capable of performing photosynthesis after evolving (endosymbiosis)
Light Dependent Rxns
Thylakoid membrane
3 parts - ETC, photolysis, and chemiosmosis
Inputs - NADP+, ADP, H2O
Outputs - NADPH, ATP, O2
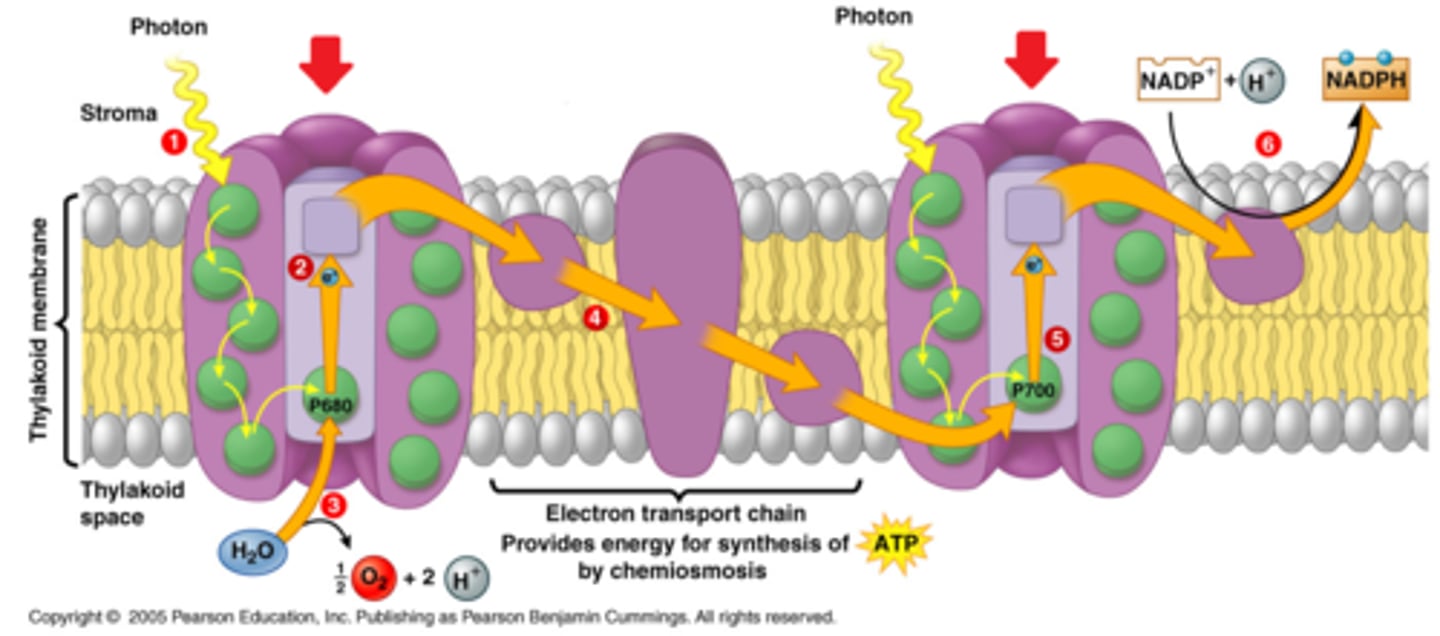
Electron Transport Chain (photosynthesis)
1. Light strikes an e- in chlorophyll in Photosystem II
2. e- is excited to a high energy state
3. High energy e- moves through a series of proteins until it reaches Photosystem I
4. Energy from moving e- is used to actively transport H+ ions from stroma into the lumen --> creating and maintaining an H+ ion gradient across the thylakoid membrane
5. e- is out of energy when it reaches Photosystem I
6. Another photon of light hits and excites the e-
7. e- is captured by NADP+ and H+ to reduce NADP+ into NADPH
8. NADPH is transported to the stroma and used in light-independent rxns
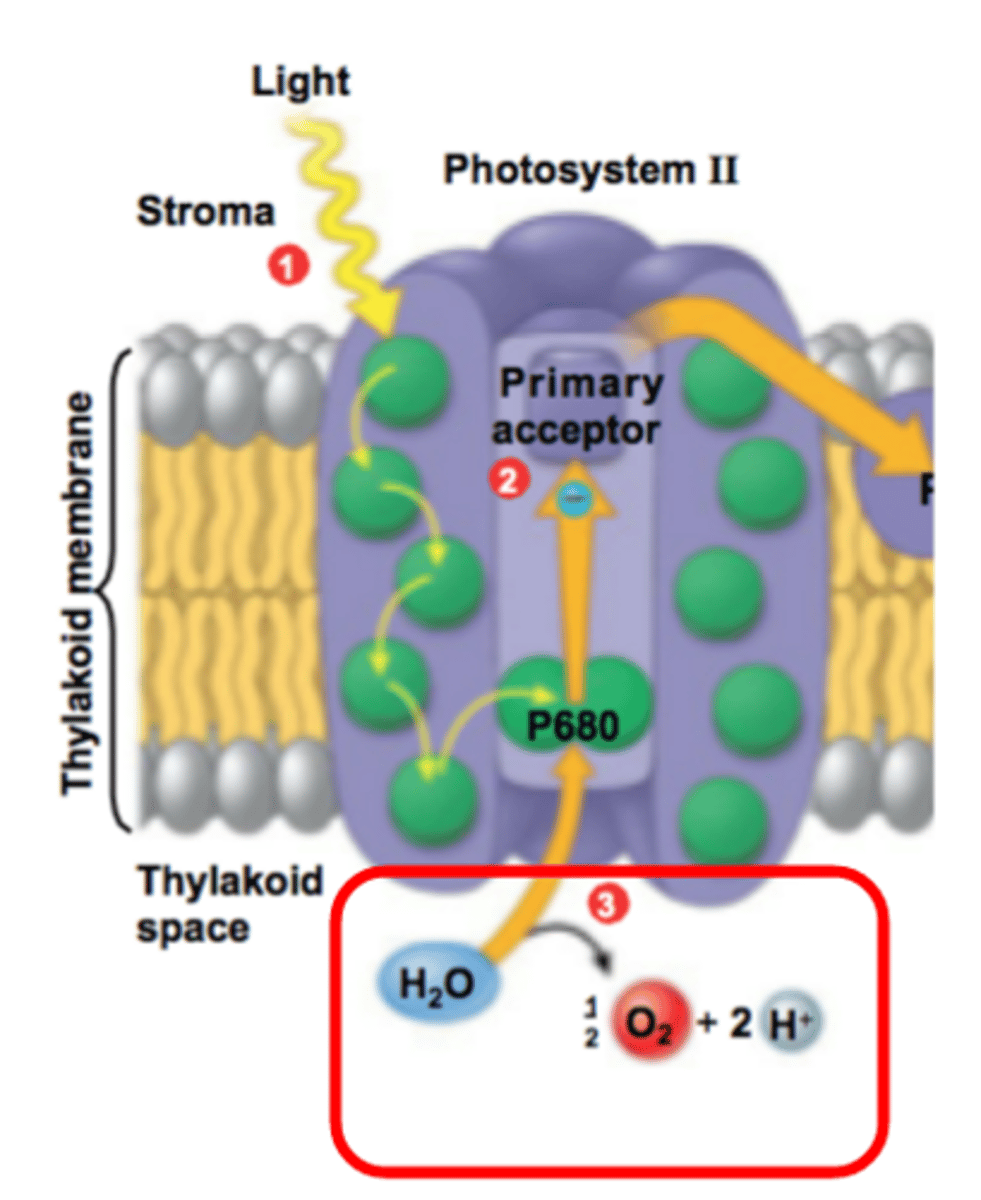
Photolysis
Water is struck by photon of light and broken into O2, H+, and e-
E- --> replenish photosystem II
O2 --> waste product
H+ --> maintain concentration gradient
Chemiosmosis
1. ETC generated a H+ ion gradient across thylakoid membrane
2. H+ ions diffuse through a channel in ATP synthase
3. Energy of diffusion allows ATP synthase to phosphorylate (add phosphate) to ADP to make ATP
4. ATP is transported and used to power light independent rxns
Light Independent Rxns
Aka Calvin Cycle
Stroma
Inputs - CO2, NADPH, and ATP
Outputs - Glucose, NADP+, ADP
Gist of Calvin Cycle
1. NADPH and ATP are oxidized and energy is released
2. The energy is used by enzyme RuBisCo to reduce and fix inorganic carbon from CO2 into an organic form in glucose
3. NADP+ and ADP are regenerated and recycled back to light dependent rxns
Must occur TWICE before 1 glucose molecule is produced
How to Experimentally Measure the Rate of Photosynthesis
Measure the change in concentration of the substrate or product over time
1. Variable to Measure - oxygen production over time; part of photosynthesis - light dependent rxns; lab applications - submerge a plant/photosynthetic organisms in water and measure rate of bubble production and or change in concentration of oxygen over time
2. Variable to Measure - CO2 consumption over time; Part of photosynthesis - light independent rxns; Lab applications - put plant/photosynthetic organism in an enclosed space and measure the change in concentration of CO2 over time
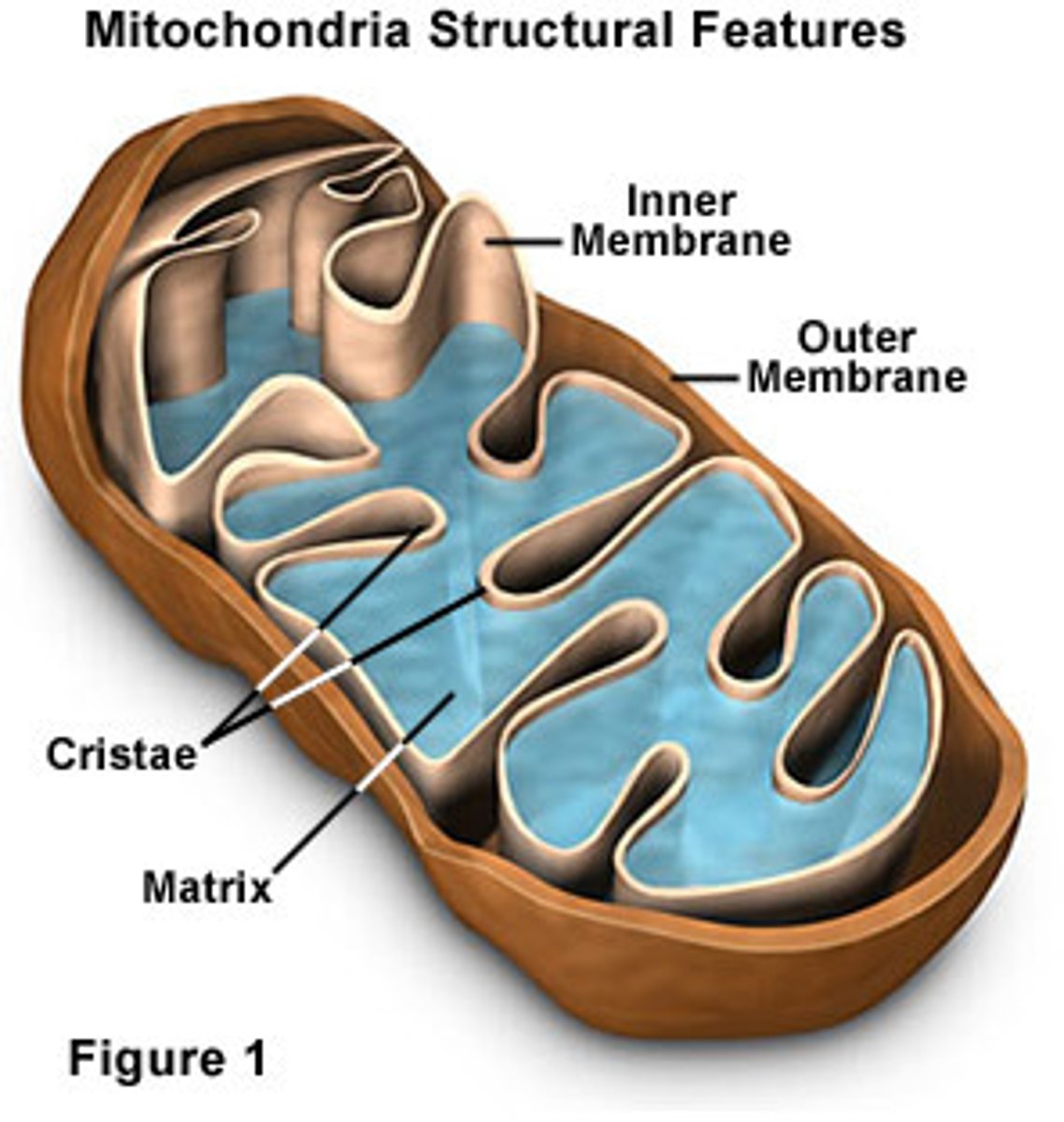
Mitochondrion Anatomy
Inner Membrane - ETC and oxidative phosphorylation
Outer Membrane - linking step (pyruvate oxidation)
Matrix - citric acid cycle
Cristae - highly folded so as to increase SA:Vol ratio
Origins of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Exact same theory regarding photosynthesis applies to cellular respiration
Early prokaryotes capable of respirating formed a symbiotic relationship with ancient cells
Cellular Respiration
Process that organisms use to turn glucose into ATP
All living organisms utilize respiration
2 types - aerobic and anaerobic
Anaerobic Respiration
Aka fermentation - alcohol fermentation (plants, bacteria, yeast) and lactic acid fermentation (animals)
No oxygen needed
Purpose - breaking down ATP to oxidize NADH to regenerate NAD+ for glycolysis to occur
Aerobic Respiration
Aka respiration
Purpose - generate ATP for use in cellular processes that maintain homeostasis
1. Glycolysis (anaerobic)
2. Pyruvate oxidation (aka linking step)
3. Krebs cycle
4. ETC and Oxidative phosphorylation
Potential chemical energy in the bonds of glucose is converted into usable chemical energy in the bonds between the phosphates in ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O
Glycolysis
Anaerobic
Cytoplasm
1. Oxidizes glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvate
2. Requires reduction of 2 NAD+ to NADH --> NADH carries high energy e- to later parts of aerobic respiration
3. Needs 2 ATP but makes 4 ATP so net gain is 2 ATP
4. Must occur before any form of respiration can occur bc pyruvate is NEEDED
All living organisms utilize glycolysis, which is a major evidence for common ancestry
Pyruvate Oxidation aka The Linking Step
Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-coA as it is transported from the cytoplasm, across the mitochondrial membranes, and into the matrix
Krebs Cycle
Acetyl-CoA goes through a series of exergonic chemical rxns that reduce NAD+ to NADH and FADH to FADH2
Electron Transport Chain (Cellular Respiration)
Inner mitochondrial membrane
NADH and FADH2 are oxidized releasing e- and energy --> NAD+ and FADH are recycled back into the cell environment
e- move through the ETC, losing energy until they combine with O2 and H+ ions to form water as a waste product
Energy released is used to maintain an H+ ion gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Coupled with the ETC
Similar to chemiosmosis
1. H+ ions diffuse through ATP synthase from the matrix to the intermembrane space
2. Energy from this diffusion is captured and used to phosphorylate ADP into ATP
3. Generates 32-34 ATP
Oxidative Efficiency
Cells are not 100% efficient at capturing all of the energy released from oxidation of NADH during the ETC
Energy not captured is given off as heat
Homeothermic organisms will decouple the ETC and oxidative phosphorylation to generate more heat and regulate body temp
How to Experimentally Measure the Rate of Aerobic Respiration?
Measure the change in concentration of the substrate or product over time
1. Variable to Measure --> oxygen consumption over time; part of aerobic respiration --> oxidative phosphorylation
2. Variable to Measure --> CO2 production over time; Part of Aerobic Respiration --> glycolysis and the citric acid cycle