Chapter 19 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is Homeostasis?
Homeostasis maintains optimal conditions for enzyme action and all cell functions.
What is a Stimulus?
They are changes in the environment
What are coordination centres?
They receive and process information from receptors
(such as the brain, spinal cord and pancreas)
Recepters
Information from receptors passes along cells (neurones) as electrical impulses to the central nervous system (CNS).
What are effectors?
They are muscles or glands, which bring about responses which restore optimum levels.
What is a CNS?
The CNS is the brain and spinal cord. The CNS coordinates the response of effectors which may be muscles contracting or glands secreting hormones.
What are reflexes?
They are automatic and rapid; they do not involve the conscious part of the brain
What does the nervous system do?
The nervous system enables humans to react to their surroundings and to coordinate their behaviour.
What is a Synapse?
The gap/connection between 2 neurones that don’t pysically touch
What is controlled the human body?
• blood glucose concentration
• body temperature
• water levels.
How are neurons adapted to their functions?
they have a long fibre (axon) so they can carry messages up and down the body over long distances
in a stimulated neuron, an electrical nerve impulse passes along the axon
the axon is insulated by a fatty (myelin) sheath - the fatty sheath increases the speed of the nerve impulses along the neuron
at each end of the neuron are tiny branches (dendrons), which branch even further into dendrites - the dendrites receive incoming nerve impulses from other neurons
What is a neurone?
They are adapted to carry electrical impulses from one place to another
What do all control systems include?
receptors
coordination centres
effectors
What is a sensory neurone?
The nerve cell that transmits electrical impulses from receptors in the sense organs to the CNS
What is a relay neurone?
They carry nerve impulses within the central nervous system
What is a motor neurone?
The nerve cell that carries electrical impulses from the CNS to effectors such as muscles or glands
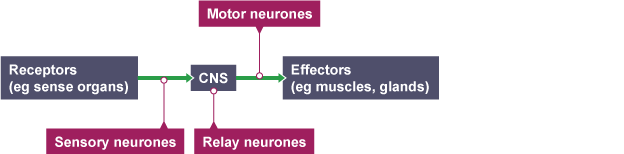
How do you get from a receptor to an effector?
Stimulus → receptor → coordinator → effector → response
How does a nerve impulse travel from one neurone to another
an electrical impulse travels along the first neurone.
when it reaches the end of the neurone, chemical transmitter molecules called neurotransmitters are released
the neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse and bind with receptor molecules on the membrane of the second neurone
this stimulates the second neurone to transmit the electrical impulse
What is a nerve?
A bundle of neurones
What does the the human nervous system consist of?
the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system