phylogenetic trees
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
branch
a lineage evolving through time that connects successive speciation or other branching events
phylogeny
a visual representation of the evolutionary history of populations, genes, or species
speciation
when a population forms two populations that no longer can exchange genes, making it possible for them to diverge into two seperate species
node
a point in a phylogeny where a lineage splits( a speciation event or other branching event, such as the formation of subspecies)
internal nodes
a node that occurs within a phylogeny and represents ancestral populations or species
tip
the terminal end of an evolutionary tree, representing species, molecules, or populations being compared
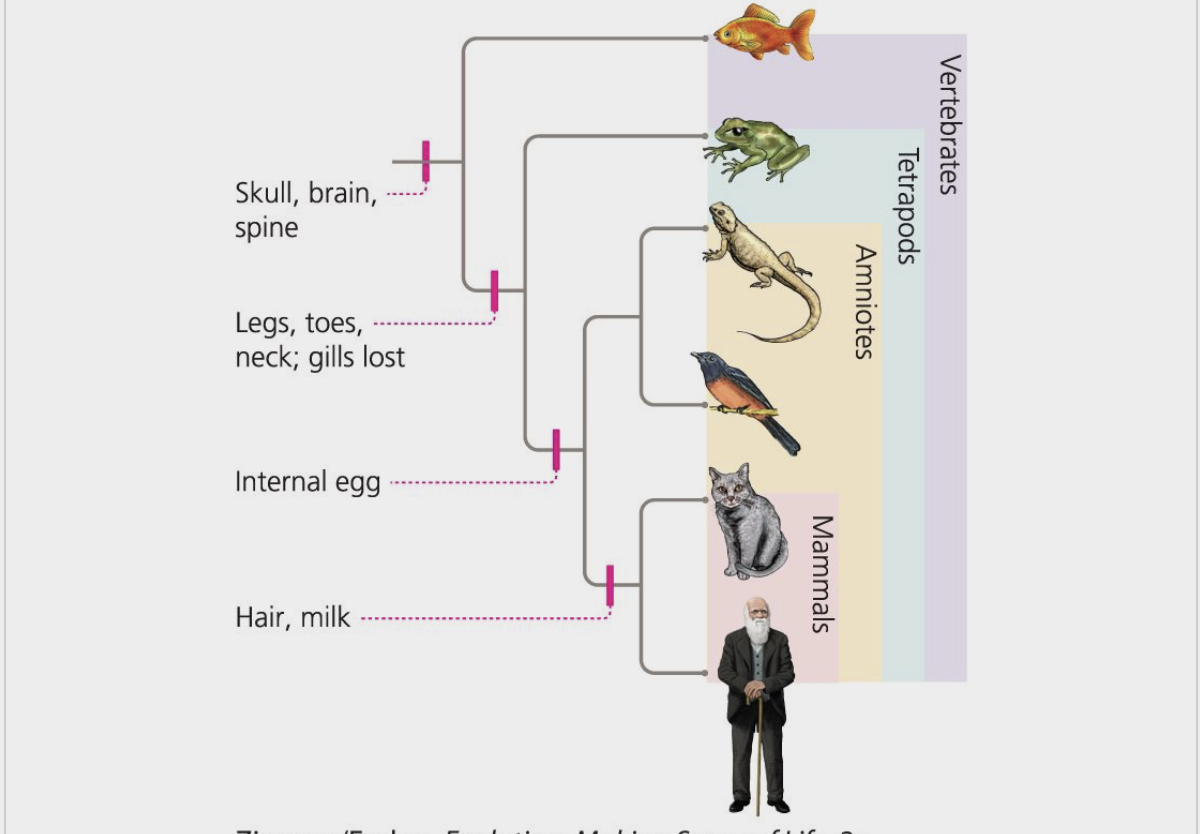
clade
a single “branch” in the tree of life; represents an organism and all of its descendants
cladogram
when a phylogenetic tree shows only the relationship among species; branches do not measure the period of time it took between speciation events
orientation of phylogenetic tree
there are many ways to represent the same relationships, can rotate branches around their nodes, can flip orientation, can leave out taxa and include clades, etc
nested hierarchy
is the result of traits evolving along different lineages with new traits appearing in some lineages
taxa
a group of organisms that a taxonomist judges to be cohesive taxonomic unit, such as a species or order
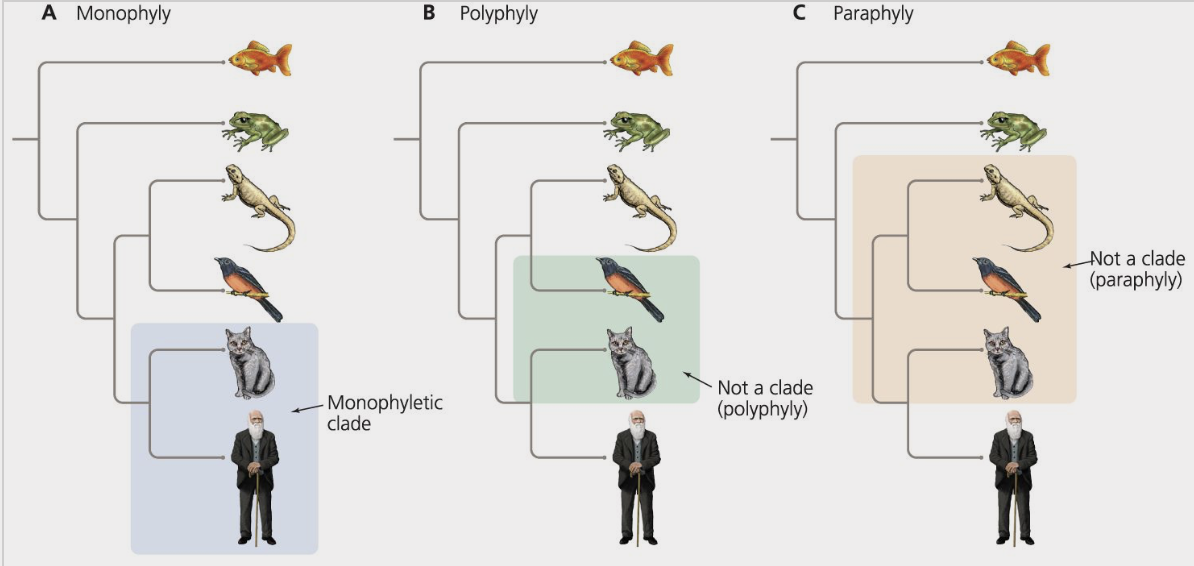
monophyletic
describes a group of organisms that form a clade
ex) mammals
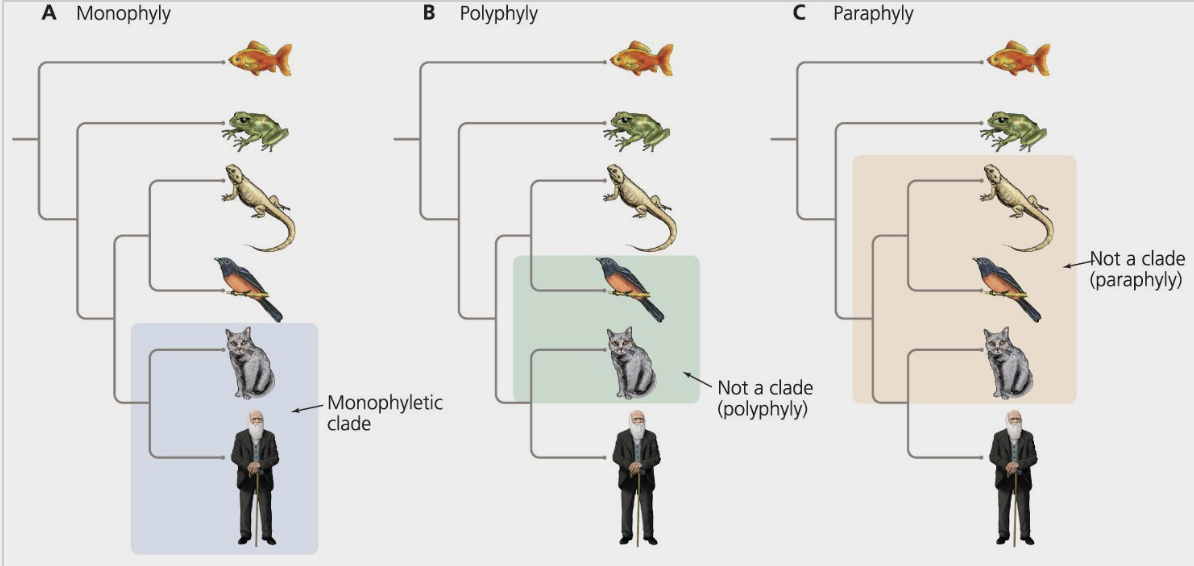
polyphyletic
describes a taxonomic group that does not share an immediate common ancestor and therefore does not form a clade
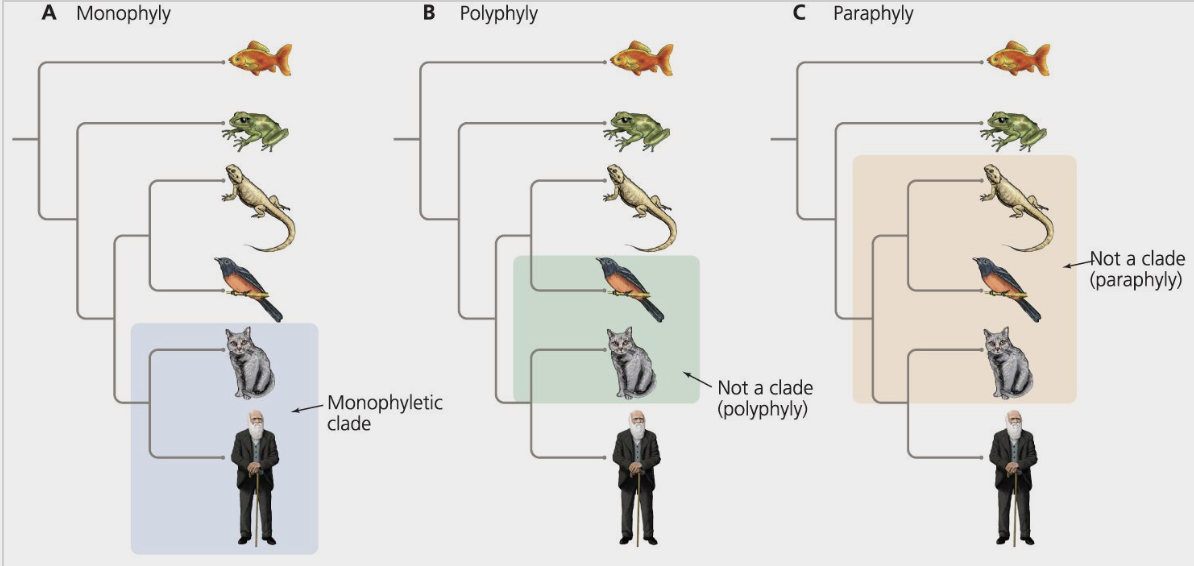
paraphyletic
describers a group of organisms that share a common ancestor, although the group does not include all the descendants of that common ancestor
ex) reptilia because it does not include birds
character
a heritable aspect of organisms that can be compared across taxa
synapomorphies
a derived form of a trait that is shared by a group of related species(that is, one that evolved in the immediate common ancestor of the group and was inherited by all of its descendants)
outgroup
a group of organisms that is outside of the monophyletic group being considered
be be used to infer the ancestral states of characters
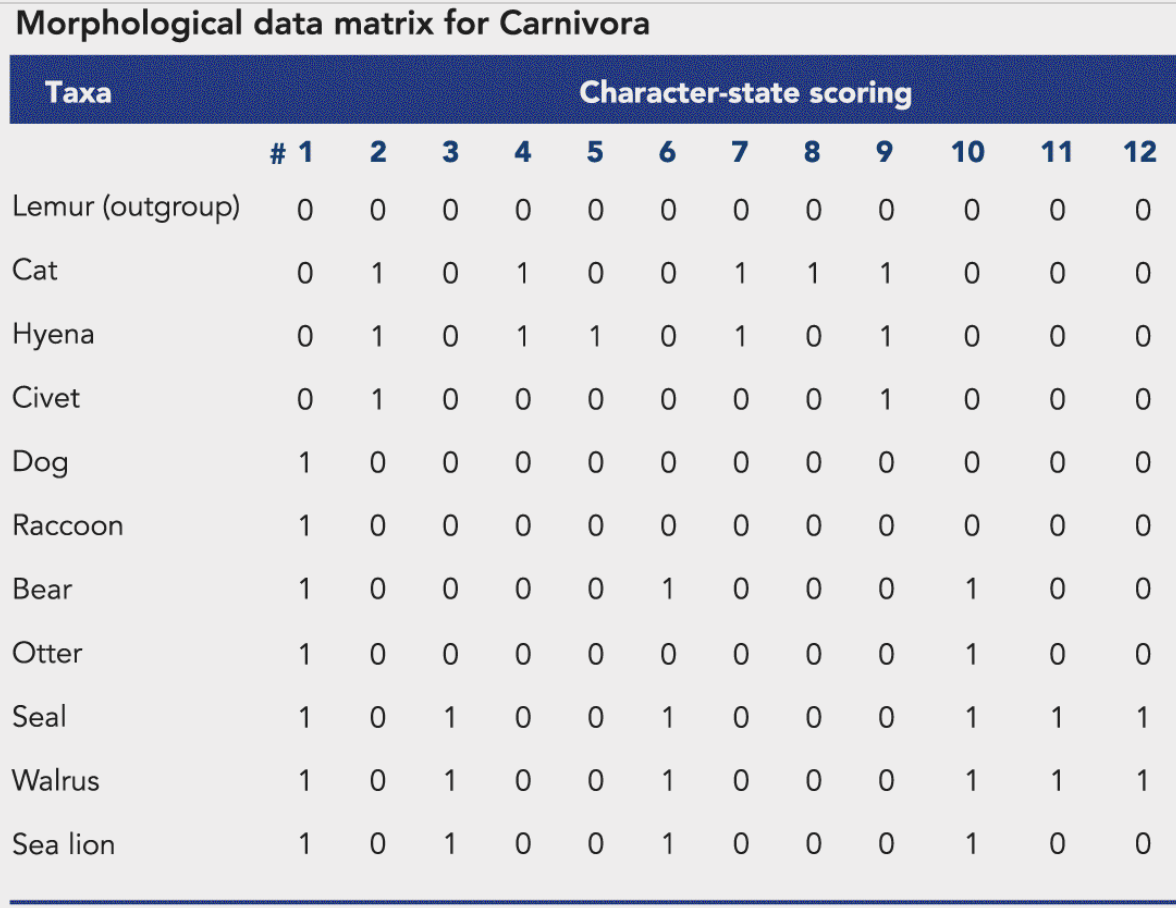
data matrix
a spreadsheet-like display of data
a primitive state is denoted as a zero in the table; the derived state is denoted as an one
homoplasy
describes a character state similarity not due to shared descent
for example produced by convergent evolution or evolutionary reversal
convergent evolution
the independent origin of similar traits in separate evolutionary lineages
evolutionary reversal
describes the reversion of a derived character state to a form resembling its ancestral state
parsimony
a principle that guides the selection of the most compelling hypothesis among several choices; the hypothesis requiring the fewest assumptions or steps is usually the best
consensus tree
when multiple tree options are combined to represent both the resolved(monophyletic) and unresolved portions of the phylogeny
polytomy
describes an internal node of phylogeny with more than two branches( the order in which the branching occurred is not resolved)
fossils and phylogenys
incorporating fossils of extinct species allow to extract info about phylogenies and and allow to determine timing of evolution
if several fossils from same clade can provide constraints to clade’s history
horizontal gene transfer
describes the transfer of genetic material to another organism, sometimes a distantly related one, without reproduction; once material added to recipient’s genome, it can be inherited by decsent
monotremes
mammals that secrete milk through a network of glands instead of nipples; they also lay eggs; ex) platypus and echidna
therians
all mammals other than monotremes which bear live young; split into two branches: marsupials and eutherian mammals
marsupials
young crawl into a pouch on the mother’s belly after they’re born until they are big enough to survive
ex) opossums, kangaroos, and koalas
eutherian mammals
mammals that develop a placenta to feed embryos in the uterus
ex) humans and all other mammals
exaptations
a trait that initially carries out one function and is later co-opyed for a new function; the original function may or may not be retained
BRCA1
a tumor-suppressor gene that when mutations occur can dramatically increase a women’s risk of developing breast cancer
shows that alleles have their own genealogies
genealogy
a line of descent traced continuously from an ancestor
gene tree
the branched genealogical lineage of homologous alleles that traces their evolution back to an ancestral allele
coalescence
the process by which the genealogies of alleles merge together as you trace them back in time to their common ancestor.
determine is population has experienced major changes in size or natural selection
the rate of branches coalesce depends on the size of the population
ex) positive selection=shorter coalesce
ortholog
one of two or more homologous genes separated by a speciation event
ex)BRCA1
paralogs
a homologous gene that arise by gene duplication; together form a gene family
introgression
describes the movement of alleles from one species or population to another.
occurs when two species interbreed and the hybrid offspring survive to mate with the original species, introducing new genes back into their genomes
ex) neanderthals and homo sapiens interbreeding
incomplete lineage sorting
occurs when a genetic polymorphism persists through several speciation events.
when fixation of alternative alleles eventually occurs in the descendant species, the pattern of retention of alleles may yield a gene tree that differs from the true phylogeny of the species
tiktaalik
375 million year old bone that taught use that after an organism dies the DNA degrades and ancient DNA rarely survives more than 100,000 years
molecular homoplasy
more common than morphological homoplasy because each DNA based has only 4 states( A,T,G,C) and separate lineages may arrive at the same character state
maximum parsimony
a statistical method for reconstructing phylogenies that identifies the tree topology that minimizes the total amount of change, or the number of steps, required to fit the data to the tree
purifying/negative selection
removes deleterious alleles from a population; a common form of stabilizing selection
bootstrapping
a statistical method that allows for assigning measures of accuracy to sample estimates;used for estimating the strength of evidence that a particular nose in a phylogeny exists
distance-matrix method
a procedure for constructing phylogenetic trees by clustering taxa based on the proximity(or distance) between their DNA or protein sequences
places closely related sequences under the same internal branch, and estimate branch lengths from the observed distances between sequences
predicts closely related species will have more similarities than more distantly related ones
neighbor joining
a distance-matrix method in which scientists pair together the two least-distance species by joining their branches at a node; repeated until tree with smallest possible distances and branch length is found
maximum likelihood
an approach used to estimate paramater values for a statistical model
used in phylogeny reconstruction to find the tree topologies that are most likely given model for molecular evolution and particular data
bayesian methods
refer to tests that are similar to maximum likelihood; use statistical model to determine the probability of data given an evolutionary model and phylogenetic tree
microsatellite
a noncoding stretch of DNA containing a string of short( 1-6bp), repeated segments
the number of repetitive segments can be highly polymorphic, helping them compare populations and assigning relatedness among individuals