2.1 ESS Species and Populations
1/40
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Enviorment
A community of interdependent organisms and the physical environment they interact with.
Enviornments are made up of both ___ and ____ factors
abiotic biotic
biotic element
anything that is living and any interactions between the living components
Producers
plants that convert energy into matter
Consumers
animals that eat plants or other animals.
Decomposers
organisms that breakdown waste into component parts for reuse
Species
group of organisms with common characteristics that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring.
Population
is a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time
How to write species name?
Genus name first and capatalized. And species name after
The further apart the populations….
The less likely to interbreed
The biotic elements of the ecosystem interact with….
abiotic elements
temperature
abiotic
sunlight
abiotic
habitat
environment where species lives
niche
the smallest unit of the habitat and it refers to the way an organism fits into the ecosystem
fundamental niche
ALL the places where a species could live
realized niche
where the species actually lives
a habitat isnt always a…
geographical location
Limiting factors
resources in the environment that limit the growth
Limiting factors may be…..
abiotic or biotic
Density dependent
factors are ones that affect the population only when it reaches a certain density.
Density independent
factors will control populations no matter what the density of it is (often abiotic)
Carrying capacity
maximum number of individuals of a species that the environment can sustainably support in a given area
shows exponential population growth under ideal conditions with plenty of resources and limited competition
J-shaped curve
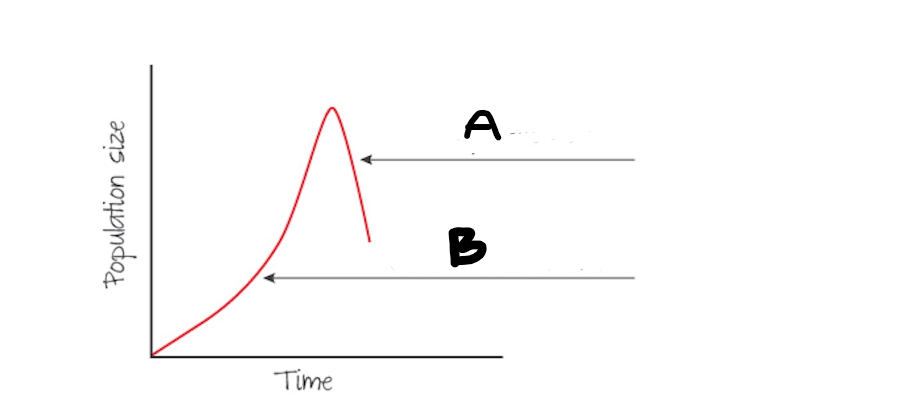
A
Population Crash
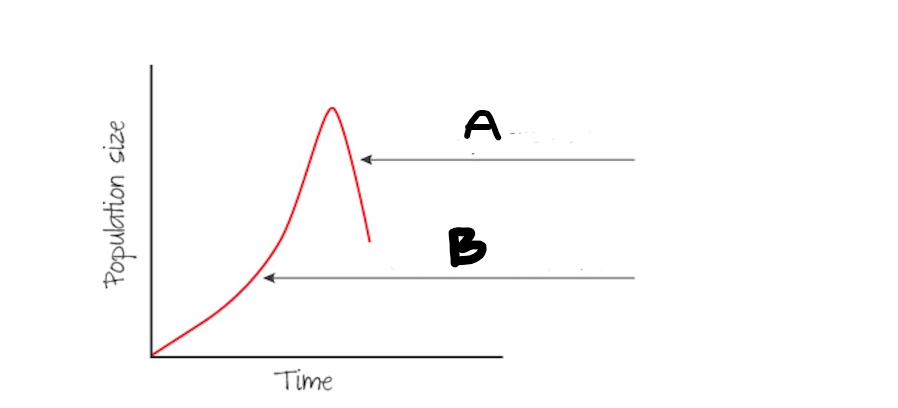
B
Initial growth phase is exponential bc of few limiting factors
S-shaped
more likely when resources are limited
Which graph is more likely to be used by k strategists
S curve
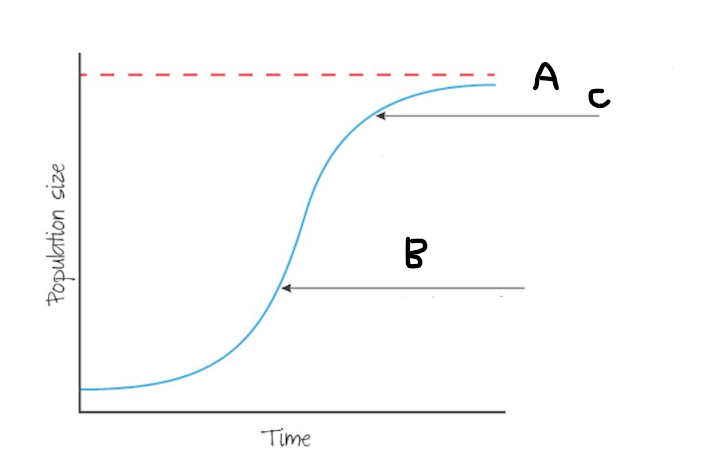
A
Carrying capacity
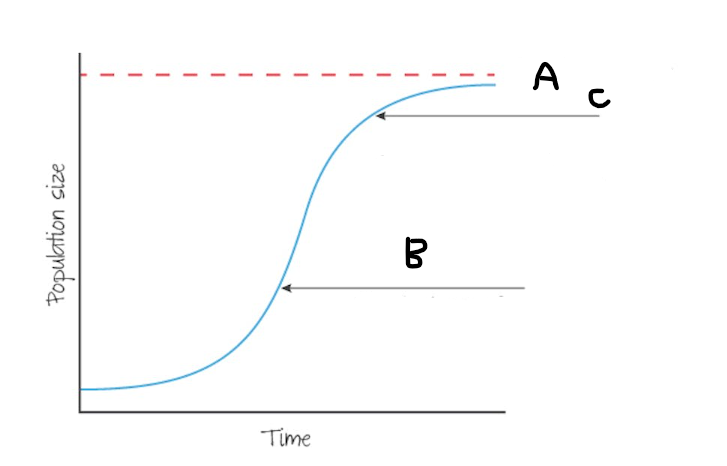
C
Growth rate slows as resources deplete
mutualism
benefit both individuals
predation
benefit one individual
Predation is a good example of……
evolution
Negative feedback
promotes stability in a system as it reverses the change and returns the system to the original state of equilibrium.
Positive feedback
amplifies the change in the system and keeps it going in the same direction
Parasitism
when an organism (the parasite) takes nutrients from another organism
ectoparasites
live outside host
endoparasites
live inside host
Intraspecific competition
when members of the same species compete for a limited resource
Interspecific competition
where members of different species compete for a resource that they both need.