HEAL 2045: NUTRITION EXAM 1
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What are the typical american food choices?
low in fruits, veggies, whole grains, dairy, and oils, and high in refined grains, processed foods, added sugars and sodium, and saturated fats.
What is adequate intake (AI)?
Dietary reference value used to estimate the nutrient intake level that is sufficient to meet the nutritional needs of most healthy individuals based on their life stage and gender.
what are recommended dietary allowances (RDA)?
Nutrient intake goal that defines the amount of a specific nutrient that most healthy individuals in a certain demographic need to consume daily to meet nutritional requirements.
what are dietary guidelines for americans (DGA)?
Evidence-based recommendations issued by the US department of health and human services and USDA to promote health and prevent diet- related chronic illness
What is Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)?
Highest daily intake of a nutrient that is unlikely to pose adverse health effects in the general population
What are processed foods and an example?
any food that has been altered from its original state (cooking, canning, freezing, mixing)
frozen vegetables, canned peaches, whole wheat bread
what are refined foods and an example?
a type of processed food where parts of the original food have been removed. sometimes they're chemically altered to have added nutritional benefits but it isn't the same as the natural version.
removing germ and bran from white bread, sugary cereal, potato chips
what are natural/unprocessed foods and an example?
foods as they are found in nature, directly from a plant or animal, with no alteration or treatment beyond harvest
fresh veggies, whole grains, herbs and spices, fresh cuts of meat
What are characteristics healthy eating patterns?
1. variety
2. balance
3. moderation
4. individually appropriate
What are the three different healthy eating patterns?
1. U.S. Style (aligns with DASH diet)
2. Mediterranean
3. Vegetarian
What are MyPlate Concepts?
Graphic illustration of DGA that was created to help consumers achieve healthy eating patterns
What are the MyPlate DGA distributions?
1. 1/2 fruits and vegggies
2. 1/4 protein
3. 1/4 grains
What are the macronutrient distributions/AMDRs?
1. 45-60% daily calories from carbs
2. 20-35% daily calories from fat
3. 10-35 daily calories from protein
What do experts recommend regarding supplements - are they needed for most of the average population?
Food and nutrient needs should be met through food and beverages, not supplements. Most people don't need supplements if they have a balanced diet.
What is the aim of the DGA's?
DGA's provide evidence-based advice that is focused on providing nutritional health promotion. Updated every 5 years, contains four broad guidelines and key recommendations for food/beverage intake.
what are the 4 guidelines of the DGA?
1. Follow a healthy dietary pattern at every stage of life
2. customize and enjoy nutrient-dense food/beverage to reflect personal preferences, cultural traditions, and budgetary considerations
3. Focus on meeting food group needs with nutrient-dense foods and beverages, and stay within calorie limits
4. Limit food and beverages high in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and limit alcoholic beverages.
What is another name for dextrose?
Glucose
What is the primary site of digestion for CHO (carbohydrates)?
Small intestine
What is soluble fiber?
Dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, which slows digestion and provides food for beneficial gut bacteria.
What are health benefits of soluble fiber?
Main health benefit is lowering LDL and blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
What is insoluble fiber?
Doesn't dissolve in water, adds bulk to stool, and helps move food through the digestive system and relieve constipation.
What are health benefits of insoluble fiber?
Promotes regular bowel movements, potentially reducing risk of hemorrhoids, diverticular disease, and colorectal cancer.
What are whole grains?
all components of grain kernel present
-endosperm
-bran
-germ
What are refined grains?
foods processed to remove course parts such as the bran and germ which removes the fiber and some vitamins and minerals
What are the differences between whole and refined grains?
Whole grains contain the bran, endosperm, and germ, and provide a good source of vitamins, fiber, minerals, and antioxidants.
Refined grains have the pran and germ removed during processing, leaving only the endosperm.
What is glycogen storage?
complex polysaccharide carb storage in muscles and liver, human version of starch. Releases glucose into the bloodstream to maintain blood sugar between meals and during activity. No dietary source.
What is the glycemic index?
Ranks food from 1-100 based on their effect on blood-sugar levels. Not a reliable guide for choosing healthy foods.
What is the glycemic response of certain foods?
describes how quickly food-derived glucose enters the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
How does the glycemic response of certain foods affect BG levels?
foods with high GR are digested rapidly, causing a sharp spike in BG levels. low GR foods are digested slowly, leading to a gradual increase in BG levels.
What impacts Glycemic Responses?
fiber content, processing, fat, and physical form of food affects rate BG levels rise.
How does the pancreas regulate/manage blood-glucose levels?
When BG levels are high, the pancreas releases insulin to remove glucose from the blood.
when BG levels are low (postprandial state), pancreas releases glucagon to stimulate glucose release from liver.
What is the difference in structure of proteins compared to CHO and lipids?
Proteins contain nitrogen-amino groups, where CHO and lipids don't have nitrogen
What is the RDA for healthy adults when consuming protein?
0.8g/kg of bw, 10-35% of total calories
Who requires additional protein in their diet, and what kind of patients/people are they?
1. When kcal intake is low resulting in protein being used for energy
- starvation, extreme anorexia
2. When the body needs to heal itself
- thermal injuries, sepsis, post-surgical, skin breakdown
3. When excessive protein losses need replacement
- malabsorption syndromes, dialysis patients
4. When periods of normal tissue growth occur
- pregnancy, strength training, childhood
What is the basic process of protein metabolism?
1. Digestion, HCI converts pepsinogen to pepsin and breaks proteins down to amino acids
2. Absorption, absorbed through small intestine mucosa cells
3. Amino Acid Pool, liver retains amino acids and makes proteins needed in metabolic pool.
4. Metabolism, anabolic or catabolic reactions based on what's needed
5. Release, liver regulates their release into bloodstream for practical use
What are the types of vegetarianism?
Vegan: excludes animal products and byproducts
Raw Vegan: Same as above + 75-100% of foods are raw and/or uncooked
Lacto-ovo Vegetarian: Includes dairy and egg products
Lacto-vegetarian: Includes dairy products
Pesco-Vegetarian: Includes fish products
Semi-Vegetarian: Doesn't eat red meat
Flexitarian: Eats chicken and fish, and occasionally red meat
What nutrients should vegetarians watch out for?
Iron, Zinc, Calcium, vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, iodine, vitamin B12, sometimes protein
What is nitrogen balance?
Reflects the state of balance between protein catabolism and anabolism, determined by comparing the amount of nitrogen consumed (intake) versus amount excreted (output)
What is positive nitrogen balance?
Anabolic state, when protein synthesis exceeds protein breakdown
eg. athletes, pregnant women
What is negative nitrogen balance?
Catabolic state, when protein breakdown exceeds protein synthesis
eg. starvation, fad/low calorie diets
What is protein complementing?
combining various plant based protein sources to consume all essential amino acids
What is marasmus syndrome?
deficiency of protein and energy over long periods of time (chronic malnutrition). Normal albumin levels
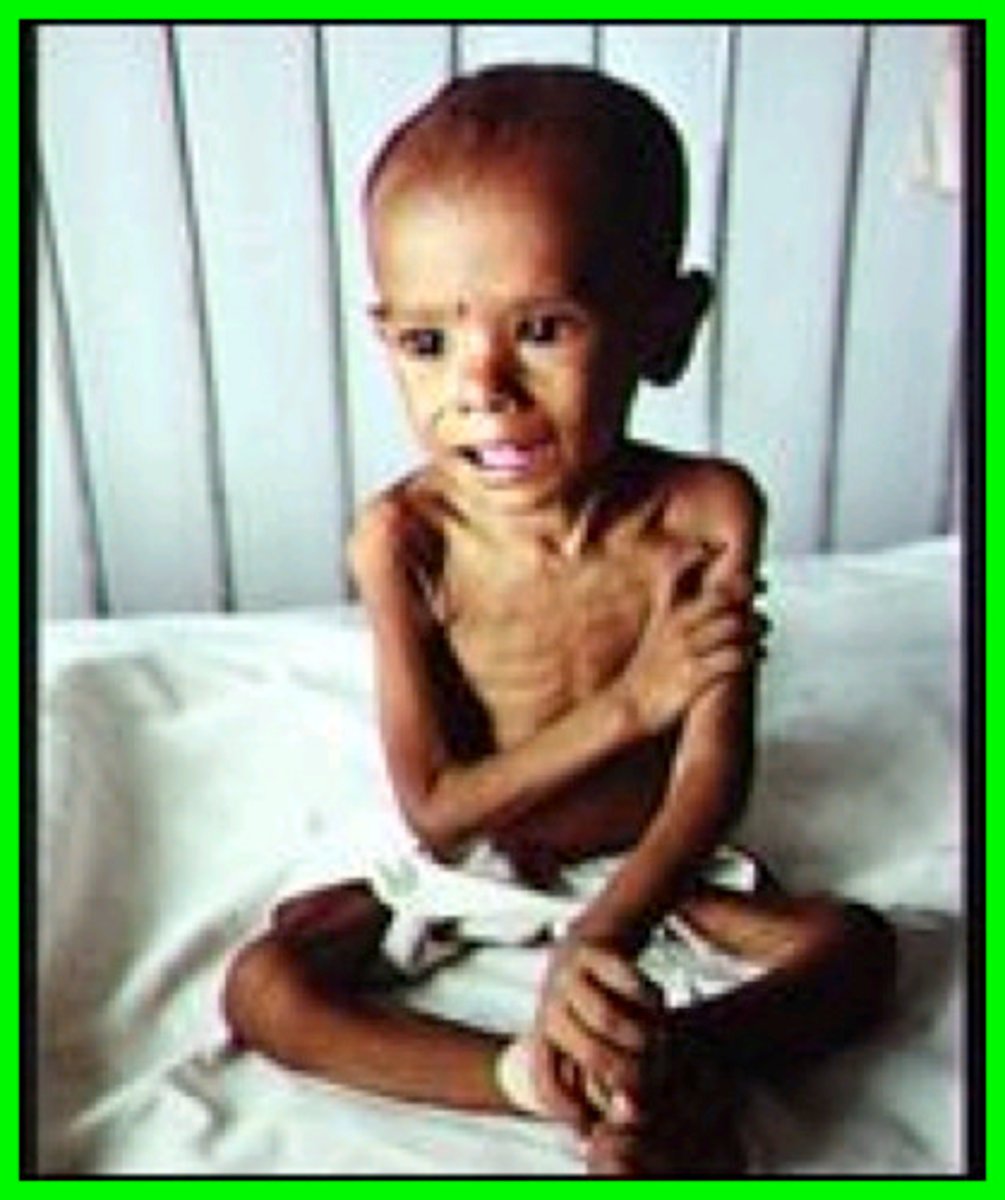
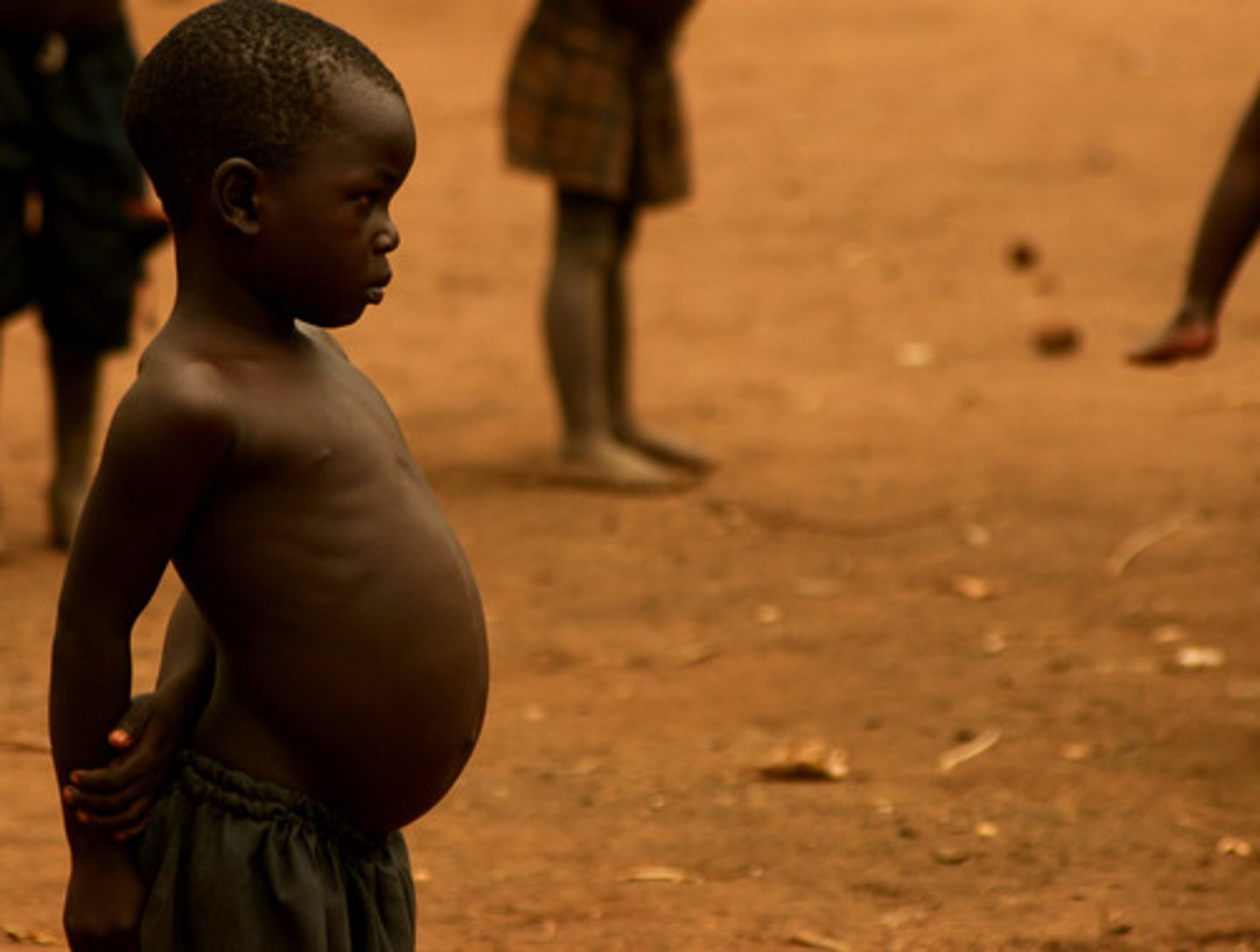
What is kwashiorkor syndrome?
Protein deficiency with adequate or near adequate calories for a short period of time (acute malnutrition). Low albumin levels leads to edema

What is refeeding syndrome?
when nutrition is reintroduced too quickly to a person who has been severely malnourished or starved
What are the 3 classes of lipids?
triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats: unhealthy fats, solid at room temperature, contribute to a rise in LDL and overall cholesterol. Linked to heart disease
Unsaturated fats: Healthy fats, liquid at room temperature, can lower LDL and raise HDL. Can reduce symptoms of heart disease
What are omega-3 fatty acids (n-3) and their source?
Essential fatty acid containing alpha linoleic acid, promotes cardiovascular health
- flaxseed oil, canola oil, soybeen oil, walnut oil, fatty fish
what are omega-6 fatty acids and their sources?
Essential fatty acid containing linoleic acid, human body can't produce them and are needed for various physiological processes.
- mainly plant oils like corn, soybean, safflower, cottonseed
What do trans fats do, and why are they unhealthy?
Mostly synthetic fats with hydrogen atoms added to the double bond in unsaturated fatty acids in vegetable oils.
Raise LDL and lower HDL, increases risk of CVD, has no known health benefits. Best to avoid consumption completely.
What are ways to minimize saturated fats in the diet?
1. eat less meat or choose leaner meat options
2. choose low-fat options of food
3. bake, grill, or steam foods instead of frying in butter/lard
4. reduced trans fat intake
5. replace fatty foods with fruits and vegetables
6. increase consumption of unsaturated oils instead of solid fats
What do the DGAs recommend regarding saturated fat intake?
- recommended saturated fat intake is less than 10% of total calories for those aged 2 and older
- encourages replacing with unsaturated fats
- avoid trans fats entirely
What is cholesterol?
sterol non-essential lipid found in cell membranes and brain tissues.
What is cholesterol's role in the body?
- Structural component of cell membranes
- Used to make bile acids, steroid hormones, and vitamin D
- transported in blood as part of lipoproteins
What foods is cholesterol found in?
Found only in animal foods
- egg yolks
- liver/other organ meats
- meat, poultry, fish, shellfish,
- full-fat dairy products
what do DGA's say about cholesterol intake?
DGAs removed strict cholesterol limit, but still recommend minimizing intake as part of healthy eating patterns
What is the molecular structure of triglycerides?
glycerol (3-carbon backbone) bound to 3 fatty acids with an ester bond
what is the process of hydrogenation and its benefit to food manufacturing companies/consumers?
hydrogenation is the process of adding h+ atoms to unsaturated fatty acids making fats more saturated
increases shelf life and stability of foods, allows for high temp cooking like frying, improves texture and mouthfeel for baked goods and spreads, makes liquid oils more solid
What's the difference between saturated and unsaturated versions of oils?
saturated oils are solid bad fats, raising LDL and total cholesterol, 10% or less recommended for daily kcals
unsaturated oils are liquid good fats, lower LDL raise HDL
all oils contain a mix of both types, but are categorized by which type is more abundant
What is linoleic acid (n-6)?
omega 6 polyunsaturated fat, essential nutrient.
maintains various physiological processes (immune response, skin and hair growth, cell membrane integrity)
what are food sources of linoleic (n-6)?
vegetable oils, nuts and seeds, some animal products
what is alpha linoleic acid (n-3)?
omega 3 polyunsaturated fat, essential nutrient. Precursor to DHA and EPA.
important for cardiovascular, neurological, and immune health
What are food sources of alpha linoleic acid (n-3)?
flaxseed, chia, walnuts, fish products
what types of fat are "healthy fats" and what do they do for the body?
Monounsaturated fats, lower LDL and may raise HDL, antioxidant (vitamin E), reduces risk of CVD
polyunsaturated fats, omega 3's (n-3) and 6's (n-6).
n-3 anti-inflammatory, cv health, neuro health, optical health
n-6 skin and hair growth, cell membrane health, growth
what are phospholipids?
fat and water soluble lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule
What is the role of phospholipids in the body?
1. maintains cell membrane structure
2. emulsifies fats during digestion for absorption
3. act as chemical messengers between cells
4. part of lipoproteins which transport fats
5. nervous system function as part of myelin sheath
What does a typical food label include?
1. serving size + servings per container
2. calories per serving
3. macronutrient density (fat, carbs, protein, sodium, cholesterol)
4. micronutrient density (vitamins and minerals)
how many calories per gram of carbohydrates?
4 kcal/g
how many calories per gram of protein?
4 kcal/g
how many calories per gram of fat?
9 kcal/g
what is %DV based on?
based on a 2,000 kcal/day diet
5% DVor less of a nutrient = low dv
20% DV or more of a nutrient = high dv
helps compare foods quickly
What is the serving size update that occured on nutrition labels?
FDA updated serving sizes to better reflect what people actually eat and drink instead of what they should eat or drink
Calorie and nutrient amounts may appear higher
What role does the FDA play in regulating supplements?
1. sups are not FDA approved, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring their products are safe and accurately labeled. FDA only intervenes after a sup is found unsafe
2. FDA requires truthful labeling and can't make disease-treatment claims, only can say "may help ______" and needs FDA disclaimer saying it hasn't been evaluated
3. FDA enforces good manufacturing practices
4. FDA monitors adverse effects and can issue warnings, recalls, or remove unsafe sups
Are health claims verified by the FDA on supplement labels? review?
Health claims describe the relationship between a nutrient or ingredient + ability to reduce risk of a disease or health condition. Health claims must be pre-approved by the FDA, they require scientific evidence before being used on a label
eg. calcium may reduce risk of osteoperosis
Structure/function claims are or are NOT subject to FDA
Structure/function claims describe how a nutrient or sup affects the body's structure and function. They aren't subject to FDA pre approval and manufacturer is responsible for ensuring the claim is truthful
eg. supports heart health
what does the term "Very Low" mean?
minimal amount per serving
what does the term "reduced/less" mean?
25% or less than reference food
what does the term "lean" mean?
less than 10g fat, 4.5g sat fat, 95 mg cholesterol per serving
what does the term "extra lean" mean?
less than 5g fat, 2g sat fat, 95 mg cholesterol per serving
what does the term "good source" mean?
10-19% dv per serving
How to interpret a food label?
1. check serving size
2. check calories
3. check macros
4. check micros
5. look at % DV
6. Check Ingredients
7. Understand claims
Which allergens are required to be on food labels?
1. milk
2. eggs
3. tree nuts
4. Shellfish
5.Peanuts
6. Fish
7. Wheat
8. Soy
9. Sesame
"METS P F W S S" menumonic
What are all essential amino acids?
PVT TIM HALL
1. Phenylalanine
2. Valine
3. Tryptophan
4. Threonine
5. Isoleucine
6. Methionine
7. Histidine
8. Arginine
9. Leucine
10. Lysine
The number of double bonds present in the fatty acid chain determines the?
Saturation level, melting point, state at room temperature, chemical reactivity
Olive oil is mostly what type of fat?
monounsaturated fat