Male and Female Reproduction
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
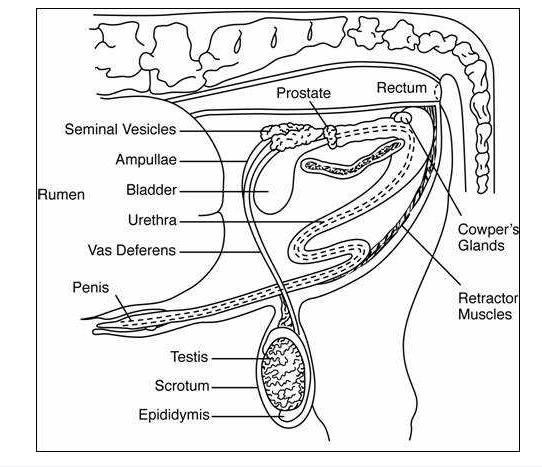
Testes
Produce sperm and testosterone
Epididymis
Passageway of sperm from testes to vas deferens
3 parts: head, body, tail
Vas deferens
Transport sperm from testes to penis (during ejaculation)
Accessory sex glands
Secrete components of seminal fluid
Penis
Fibroelastic or vascular type
Overall functions of the male
Produce and maintain supply of sperm (spermatogenesis)
Detect females in estrus (pheromones, visual cues)
Inseminate females and fertilize the female gamete)
Spermatic cord
Contains vas deferens, pampiniform plexus, and external cremaster muscle nerves
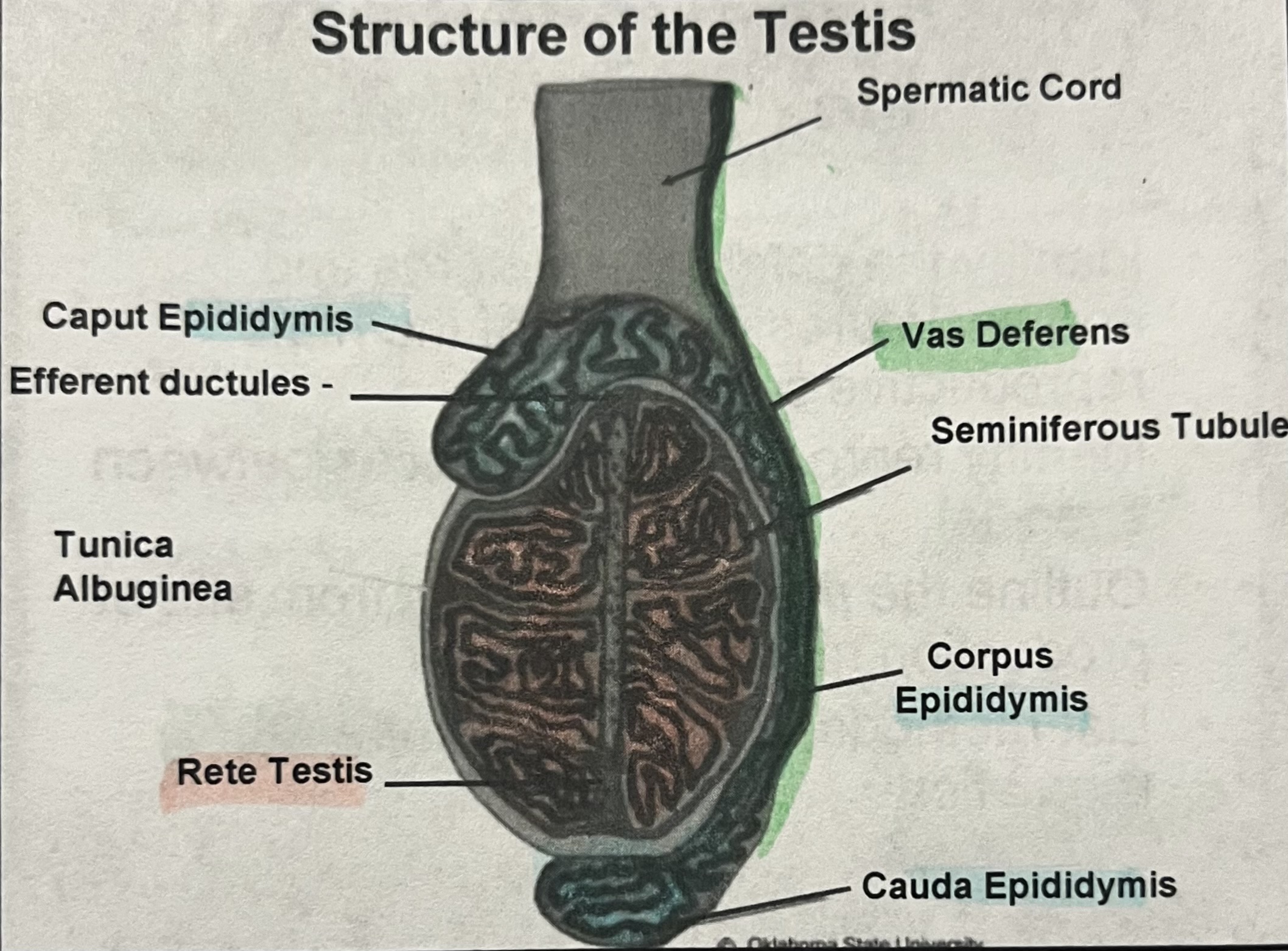
Tunica albuginea
Connective tissue which holds testis together
Seminiferous tubule
Sperm producing cells— true germinal epithelium
Rete testis
Function in sperm transport from seminiferous tubules- 100 tubules
Caput epididymis
Function in maturation of spermatozoa, fluid absorption
Corpus epididymis
Maturation of spermatozoa
Cauda epididymis
Final maturation and storage, only sperm capable of fertilization
Efferent ducts
6-12 tubules absorb fluid
Scrotum
Protection and temperature regulation
Leydig cells (LC)
Source of testosterone
Mitosis (proliferation)
Spermatogonia undergo multiple divisions to generate a larger number of spermatocytes
Meiosis 1 and 2
Replication of DNA to produce haploid spermatids
Differentiation
No further cell divisions, resulting in a fully differentiated immature sperm (spermatids) that is released into the lumen
Mediastinum
In center of testes, transport spermatozoa from lobules within testes to epididymis
Transport from epididymis to penis
Exit epididymis and enter vas deferens
Vas deferens becomes urethra once past bladder
Pass accessory glands that secrete components of seminal fluid
Accessory glands examples (in chronological order)
Ampullae
Seminal vesicles
Prostate
Cowper’s gland
Penile configuration in body
Retained in body until excitation/ejaculation
Compressed into sigmoid flexure (s-shaped curve) by the retractor penis muscle
Horses do not have sigmoid flexure
At excitation, the retractor penis muscle relaxes to extend penis for mating
Fibroelastic penis
Fibrous, hard sheath of connective tissue all the way through the penis
Penis does not expand in diameter during erection, it becomes rigid and extends
Boar, bull, ram
Vascular penis
Penis increases in diameter and length when aroused
“Bells out” to plug cervix of female during ejaculation
Stallion and men
Flehmen response
Scent driven stimulation
Exposure of vomernasal gland
Visual/auditory/tactile stimulation
Animal can be trained to mount live animals or (simulation animal— SA) dummies for breeding and/or collection of semen
Volume and sperm concentration
Inversely related
Concentration of semen depends in whether specie is a multiple ovulatory, as well as the complexity of the cervix
Pendulous testes
Fibroelastic penis with pointed glans in bull and a small projection (filiform appendage) in sheep
Horizontal testes
Vascular penis with belling glans in stallion
Inverted testes
Fibroelastic penis with spiral shaped glans that will lock into sow cervix
Cryptorchidism
Lack of testis descent into scrotum and thus thermoregulation is absent
Common in boars and stallions
Bilateral cryptorchidism
Sterile
No spermatogenesis
Testosterone is produced
Unilateral cryptorchidism
Fertile
Reduced sperm producing capacity
Temperature of testis for spermatogenesis
3-6 degrees Fahrenheit less than body temperature
5 factors for testis temp regulation
Location: testis are outside and away from the body for air circulation
Insulation: thin scrotal skin with subcutaneous fat
Sweat glands: For evaporative cooling
Tunica dartos muscle: smooth muscle under scrotum that can contract to move testis closer or relax to help testis move away from the body
Body supply to testis: warm arterial blood is cooled before entering testis by crossing over cooler veins that are leaving testis
Importance of keeping testis cool
Protect sperm
The farther from the body, the cooler
The tail of the epididymis is the coolest
Elevated temperatures will kill sperm cells
Typically lower sperm count and motility in very high temperatures
Estrous
The reproductive cycle in females that are of an estrual species (bovine, ovine, caprine, porcine, caprine, feline)
Generally calculate from the period of estrus and ovulation to the next period of estrus and ovulation
Estrus (Heat)
The period of time where a female is sexually receptive to the male for purposes of mating
Anestrous period
When a female is not in estrus. Non-breeding season
Estrus synchronization
Controlling the estrous cycle so that a high percentage of females in the herd express estrus at the same time
Clone
An individual grown from a single somatic cell of its parent and genetically identical to it
AI
Abbreviation for artificial insemination, a common technique where semen is placed into the reproductive tract of the female by artificial techniques rather than natural mating
ET
Abbreviation for embryo transfer, a procedure used to transfer embryos from a donor female to a group of recipient females
Haploid
Half the normal number of chromosomes, found in sperm and ova
Open
Refers to non-pregnant females
Fertility
The capacity to initiate, sustain, and support reproduction
Dystocia
Difficult birth, intervention required
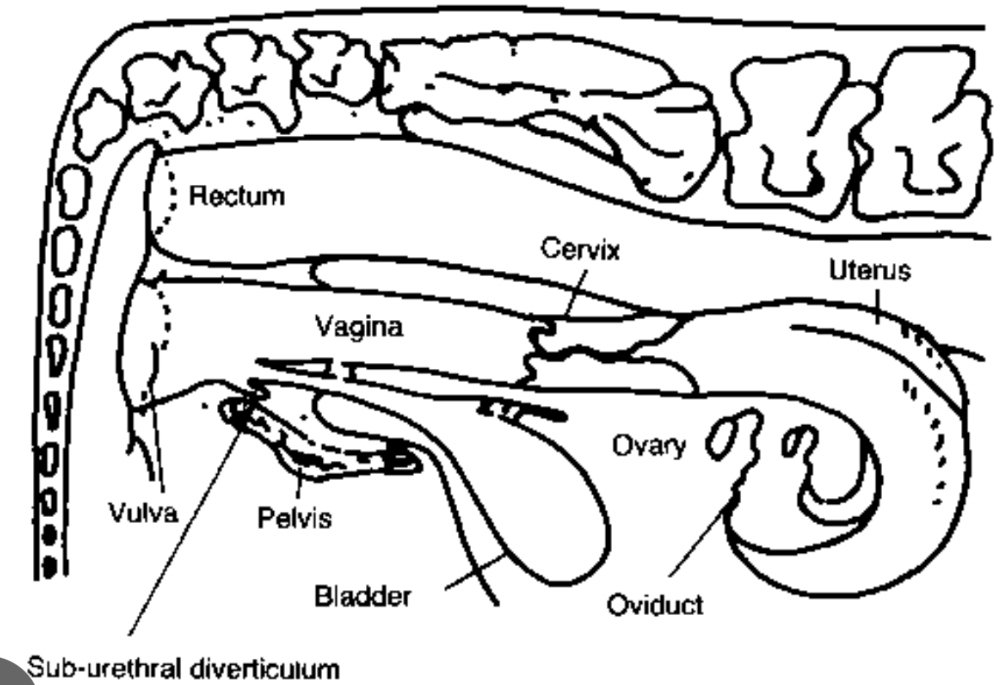
Vulva/vagina
Female organ of copulation; birth canal for parturition
Cervix
Passageway for sperm following breeding; seals off uterus during pregnancy
Uterus
Secretory organ; incubator for embryo and placenta; control of cyclicity (leuteolysis which destruction of the corpus luteum); contraction for parturition
Oviduct
Passageway for ovum and sperm; site of fertilization
Ovary
Produces female gamete and female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
Vulva
Passageway for urine
Receptor for penis during copulation
Expands at parturition for delivery of fetus
Not to be confused with the anus
Interior protective structures of the female reproductive tract
Vagina and cervix: tissue is keratinized to protect against abrasion, secretory, provides barriers
Functions of vagina
Copulatory organ
Fornix vagina is site of semen deposition (cow, ewe)
No glands— secretions come from passageway of plasma components as well as cervix
Provides lubrication
pH us acidic (5.7)— bacteriostatic
Birth canal
Dilates for fetus during parturition
Functions of the cervix
Composed of cartilage surrounded by soft tissue
Openings are the external or internal Os
Passageway for sperm following breeding
Secretes mucous, seals off uterus during pregnancy
Passageway of fetus
Species specific configuration (rings, spiral, or folds)
Cow cervix
Hard and rigid during estrus
Composed of thick connective tissue
Contain crypts which provide surface area for sperm reservoir
4-5 annular rings
Tightly closed except during estrus
Mucus characteristics change during estrous cycle
Estrus: clear, watery parallel strands (estrogen)
Diestrus: little mucus, jelly-like mucus cross-linked by disulfide bonds (progesterone)
Fornix vagina
Present in mare, ewe, and cow
Recess in the anterior vagina that surrounds the protruding cervix
Mare cervix
There are no obstacles in the body after the fornix vagina
Opposite of other species, it has a soft and pliable cervix during estrus and flattens on floor of vagina
During pregnancy, cervix is tight and closed
Sow cervix
Many interdigitating pads
Does not have fornix vagina
Uterus (womb)
Incubator for fertilized ovum, nutrients to ovum
Aids travel of sperm
Secretory organ
Has two horns or branches and a single body
Shape differs between species
Sperm related uterine functions
Transport sperm
estrogen stimulates myometrial contractions so that sperm move to site of fertilization
Sperm motility
Viable sperm (motile) are important so that they are not absorbed
Partially prepares sperm for fertilization
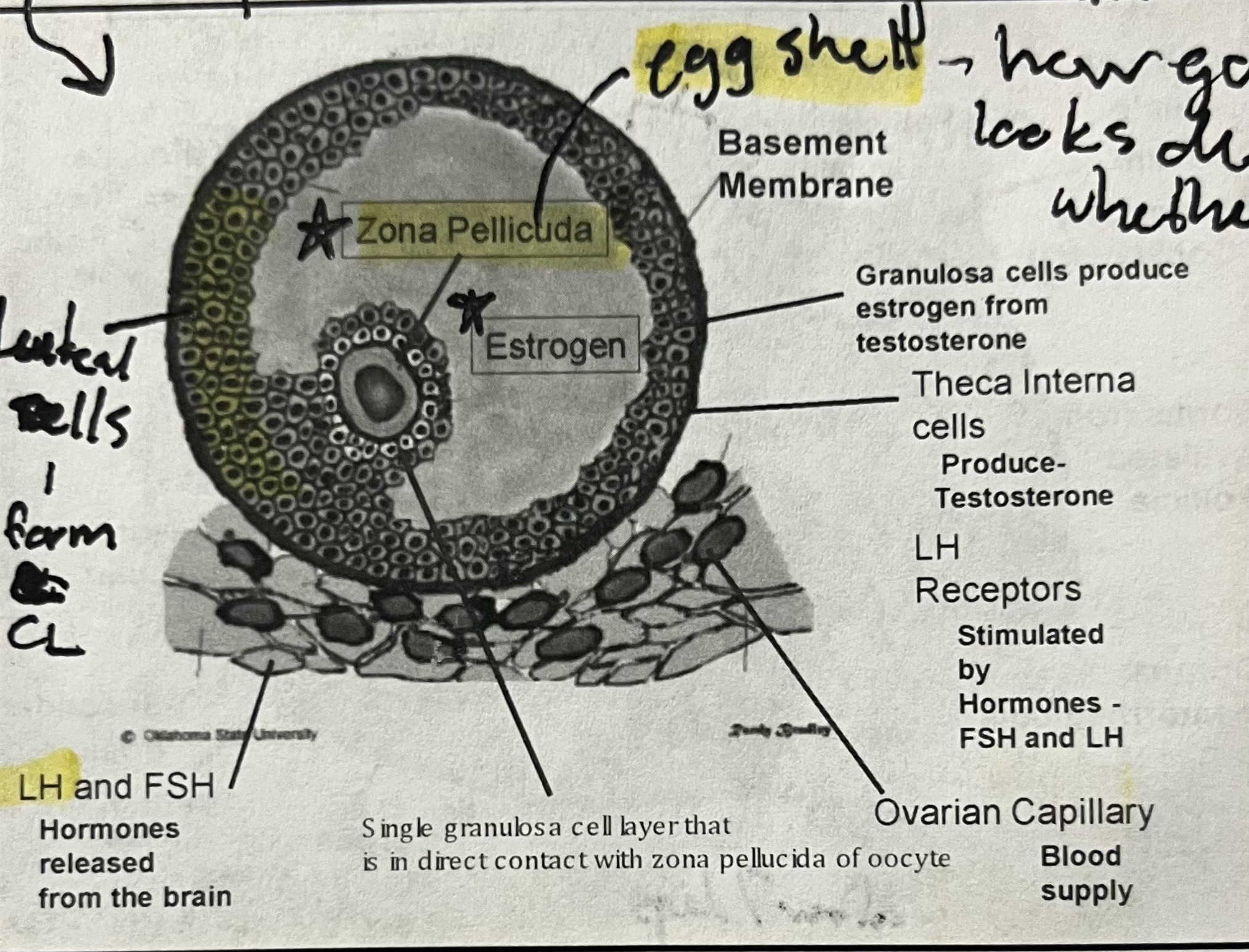
Estrogen stimulates uterine secretions which capacitate sperm (zona pelucida)
Protective uterine functions
Absorption and phagocytosis
Occurs by uterine epithelium and leukocytes which fight infection
Recovers from pregnancy
Uterine involution— myometrial contractions and enzymatic activity shrink uterus back to normal size
Muscle contractions (kinda different)
Towards oviduct during estrus (heat), but following ovulation are towards cervix until progesterone increases from CL
If not pregnant
Uterine endometrium releases prostaglandin (PGF_{2a}) to cause the CL to regress
Fetus related uterine functions
Provides environment for embryo
Uterine secretions stimulated by estrogen and progesterone
Proper timing of embryo and uterus is important for embryo transfer
Supports development of fetus
Quiescent myometrium— progesterone
Immunological protection from rejection by maternal immune system
Expels fetus at birth
Strong rhythmic myometrial contractions (progesterone low)
If pregnant
Embryo provides a chemical signal (interferon tau) which allows the CL to be maintained
Oviduct
Tube that connects the ovary to the uterus
Has 3 distinct regions
Infundibulum
Ampulla
Isthmus
Ampulla-Isthmus Junction (AIJ)
Infundibulum
Surrounds ovary with finger-like projections
Ampulla
Transports oocyte
Isthmus
Transports sperm
Ampulla-Isthmus Junction (AIJ)
Site of fertilization
Ovary regions
Comprised of two main regions
Cortex (outer on all— except mare)
Produce the female gamete (ovum or oocyte)
Released from follicle
Includes ovarian structures
Produce hormones
Medulla (inner in all— except mare)
Support tissue including blood vessels and immune cells
Function of the ovary
Farm animals have TWO ovaries
Surrounded by connective tissue called tunica albuginea
Produces female gamete (the ovum) — largest single cell in the body
Produces female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
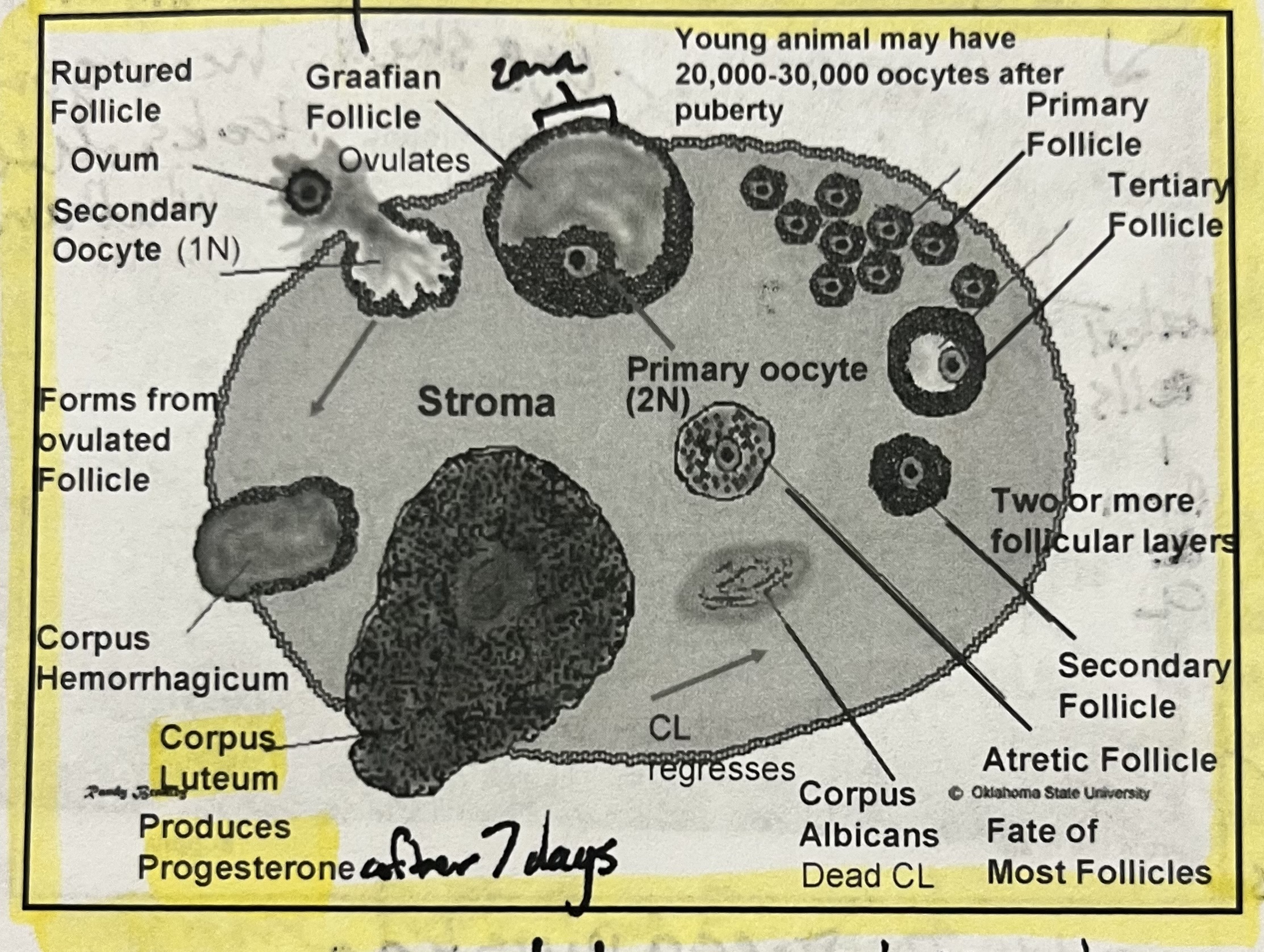
Follicle
Blister-like structure on the ovary that contains ovum and hormone-rich fluid (liquor folliculi)
3 types
Graafian
Mature folicle
Atretic
Deteriorated follicle
Cystic
Continuous corpus luteum, graafian, or atretic structure (may or may not cause clinical signs)
Corpus luteum
“Yellow body” forms after ovulation
Produces progesterone which is important for maintaining pregnancy
Composed of luteal cells that originate from granulosa and theca cells of the Graafian follicle
Function of the corpus luteum
Produce progesterone to:
Inhibit estrus and parturition
Block myometrial contractions
Stimulate stimulate endometrial secretion of nutrients
Stimulate the production of luteolytic agent to kill the CL if no embryo is present
Prostaglandin (PGF_2a)
Structures on the ovary
Follicles develop on the ovary and mature until one becomes a Graafian follicle
Follicles not selected for ovulation become atritic and regress
When oocyte is released from the follicle, follicles will transition through the corpus hemorrhagicum, corpus luteum, and the corpus albicans
Diagram of bull reproductive system (draw)
Structure of the testis (draw)
Testes anterior/posterior halves
Cow reproductive system
Ovarian process diagram
Graafian follicle diagram
Bicorunate
Sow reproductive tract
Bipartite
Cow, ewe, doe reproductive tract
Modified bipartite
Mare reproductive tract
ovulation fossa
Specialized structure on mare ovary to funnel a single ovulation