Year 11 Human Biology ATAR reproduction
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Somatic Cell
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells; 2n
Gamete
a mature haploid male or female germ cell that is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote; n
Gonad
female or male reproductive organ that produces sex cells and hormones; ovary or testis
Fertilisation
Fusing of a male gamete with a female gamete.
Testis
male reproductive organ that produces sperm and hormones
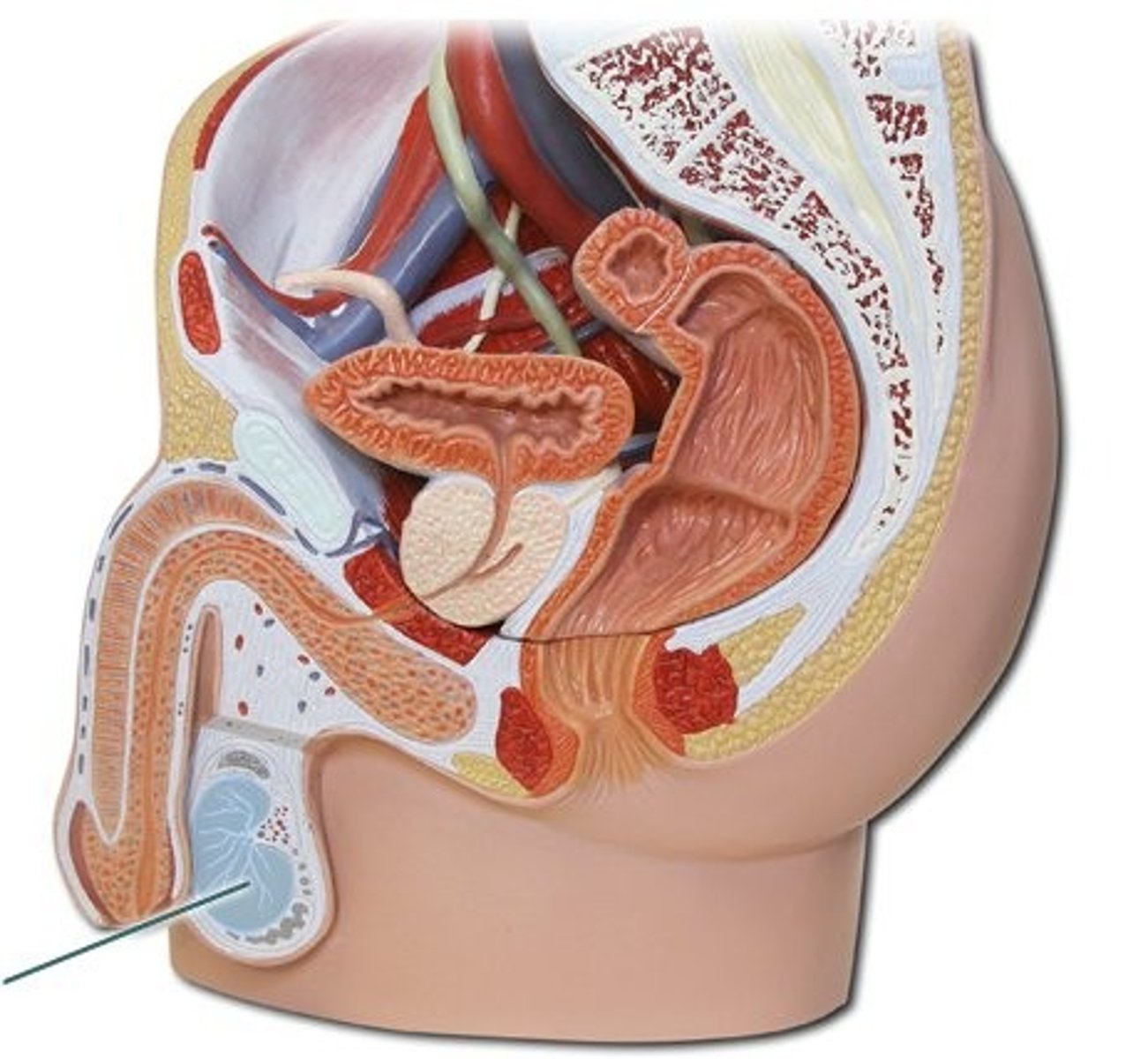
Scrotum
External sac that contains the testes
Bulbo-Urethral Glands
aka Cowper's Glands; secretes a fluid that becomes part of the semen
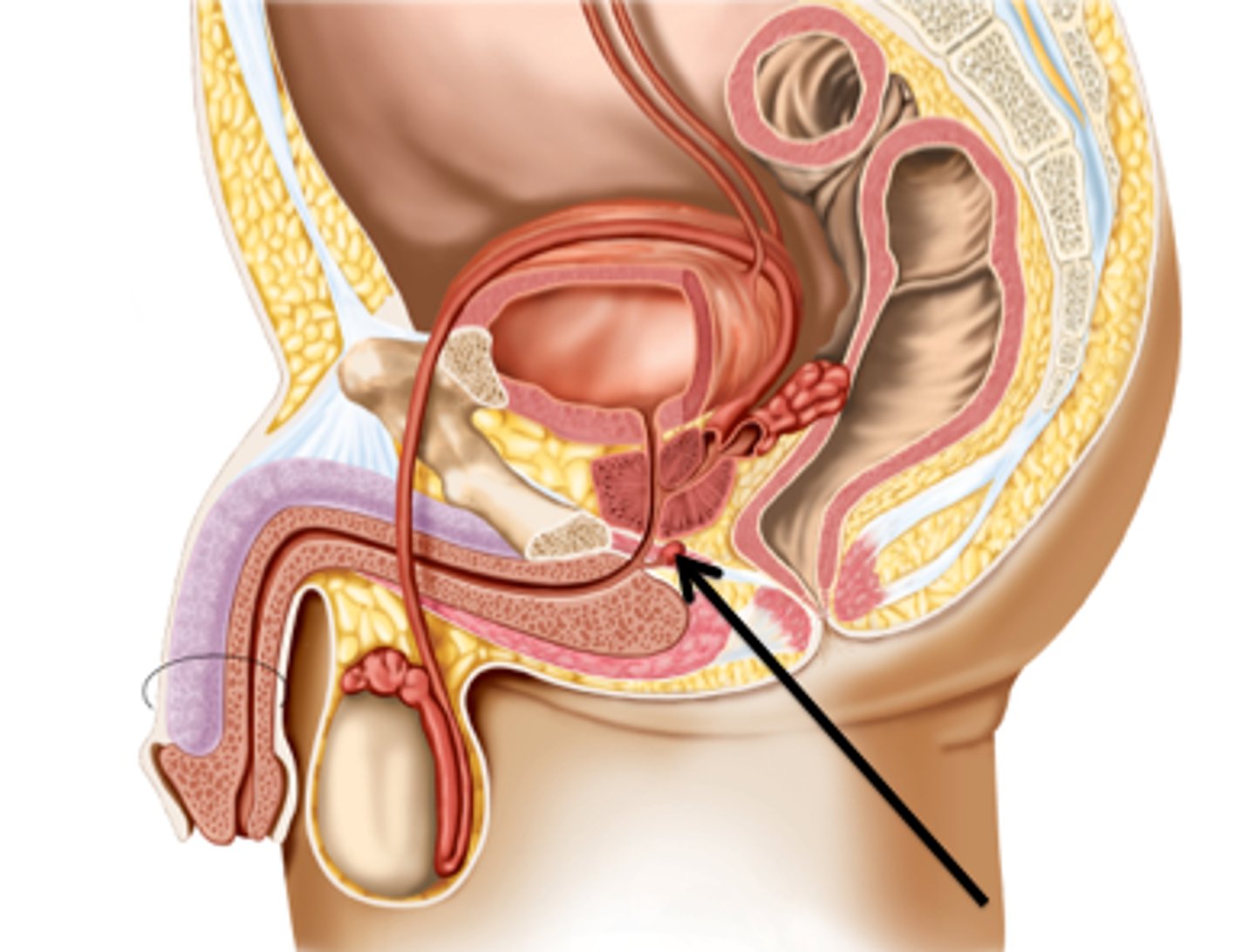
Epididymis
A long, coiled duct on the outside of the testis in which sperm mature.
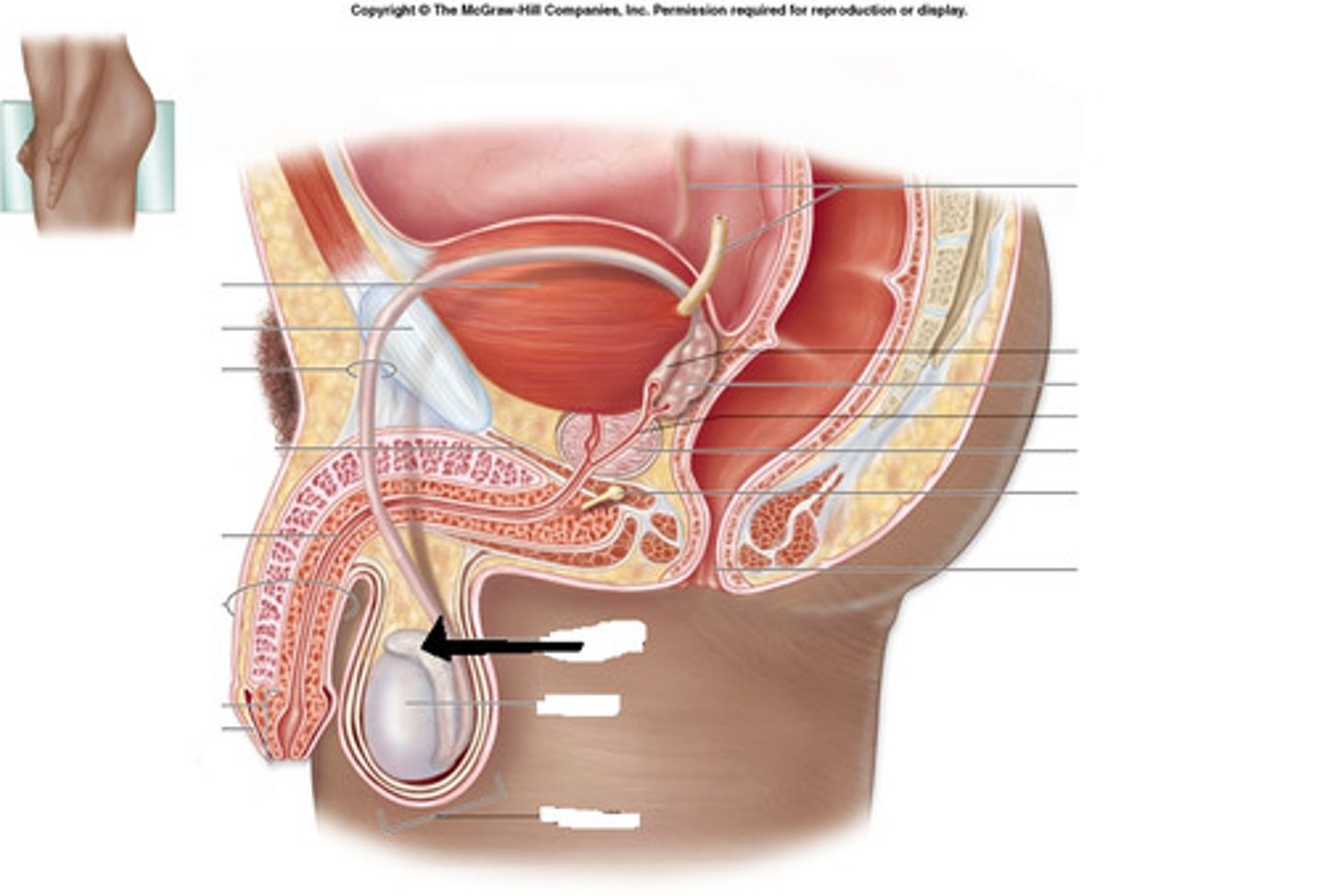
Seminal Vesicles
paired sac-like exocrine glands that secrete fluid into the vas deferens; this fluid is the main component of semen
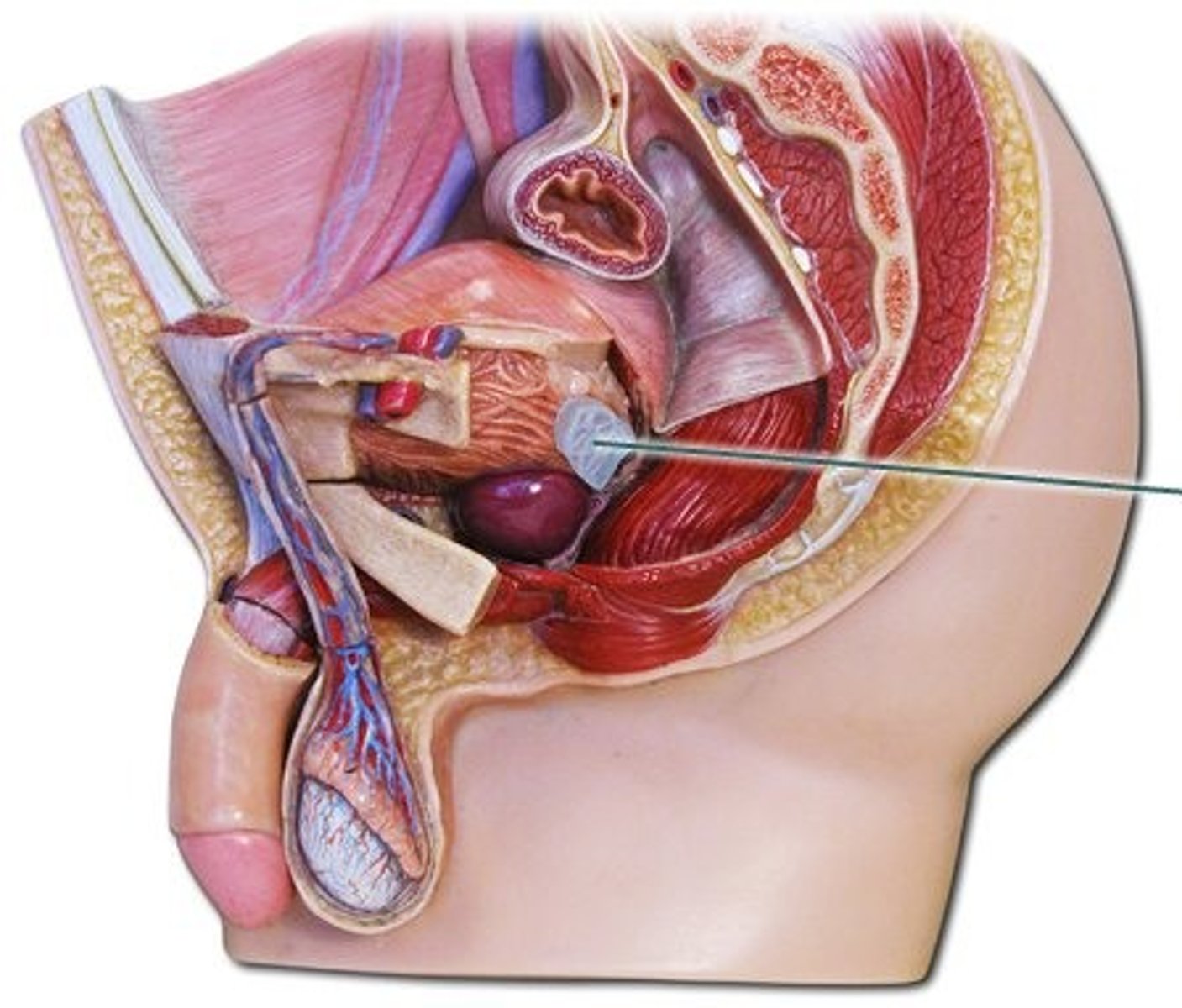
Vas Deferens
Tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra
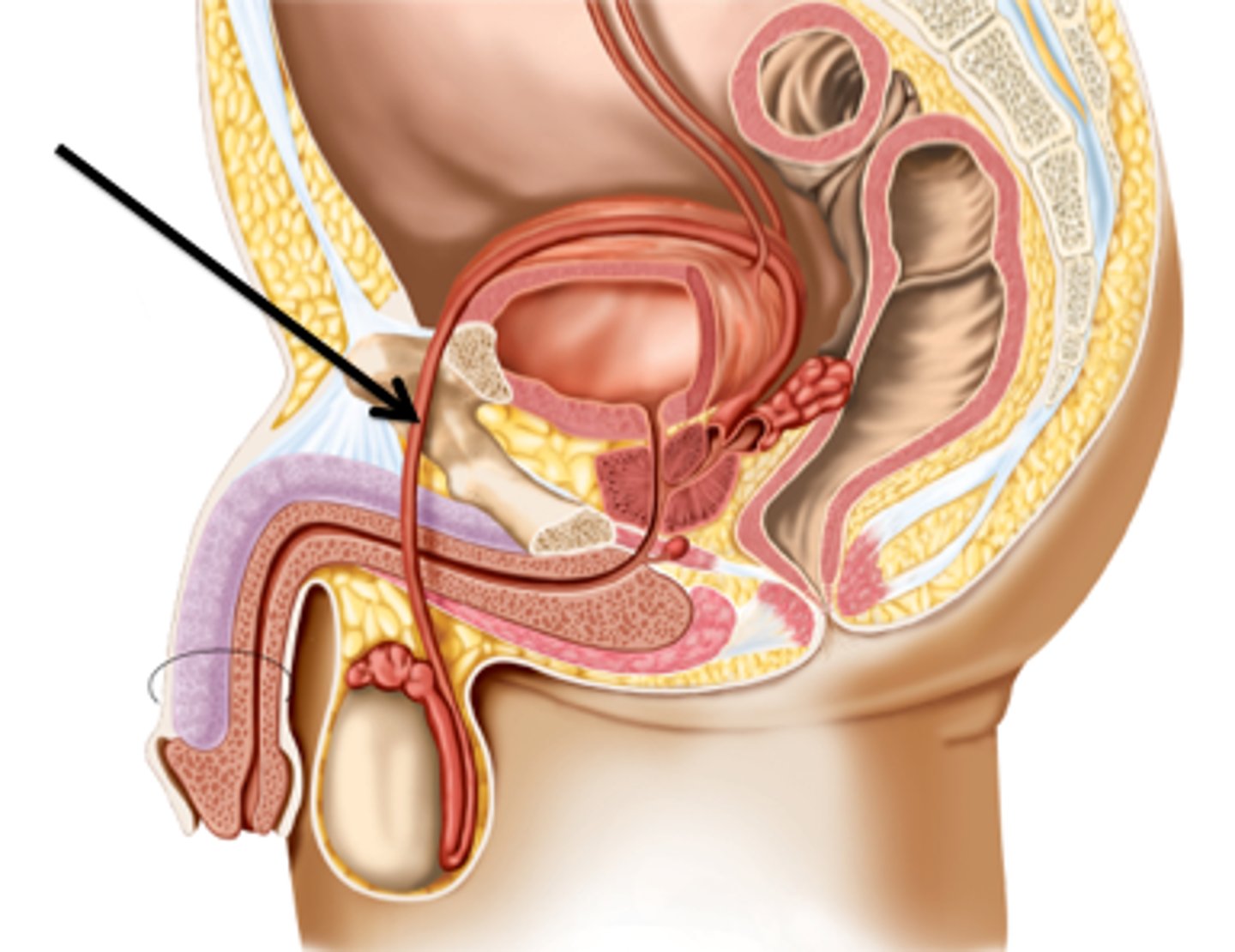
Prostate Gland
Secretes an alkaline fluid that helps activate sperm
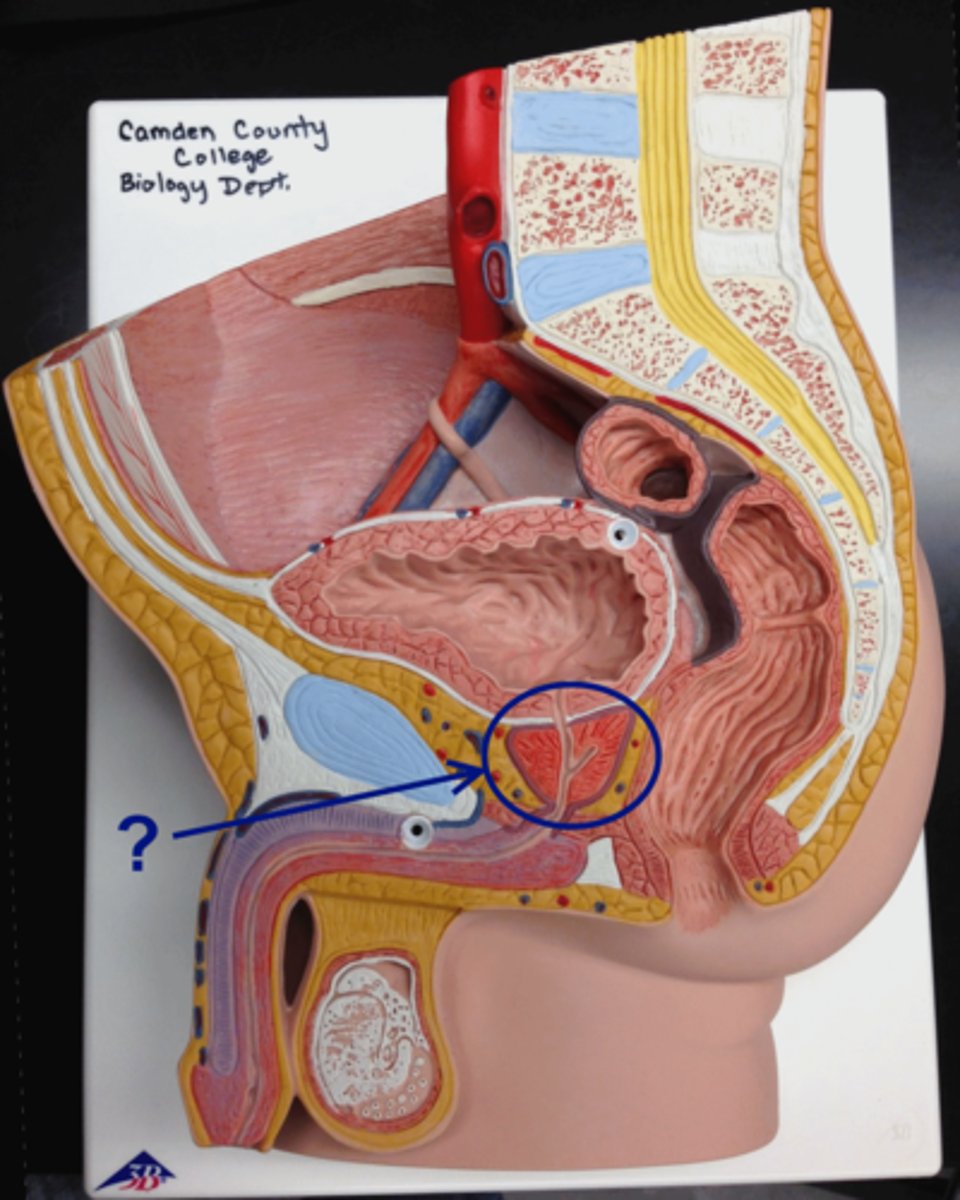
Penis
the male reproductive organ that removes urine from the body and that can deliver sperm to the female reproductive system
Uterus
Female organ of reproduction used to house the developing fetus.
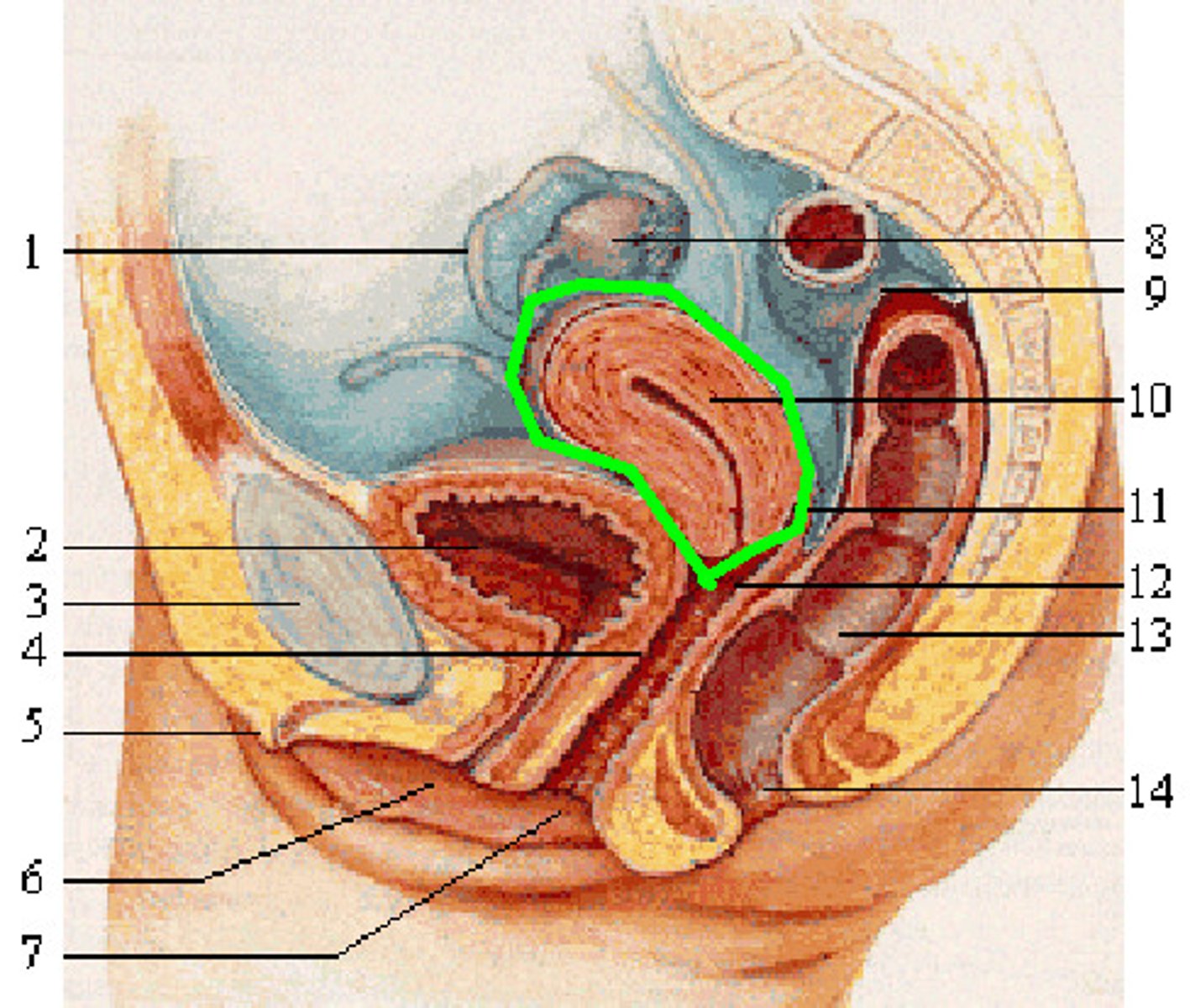
Uterine Tube
aka fallopian tube;The organ that transports the ovum to the uterus is the
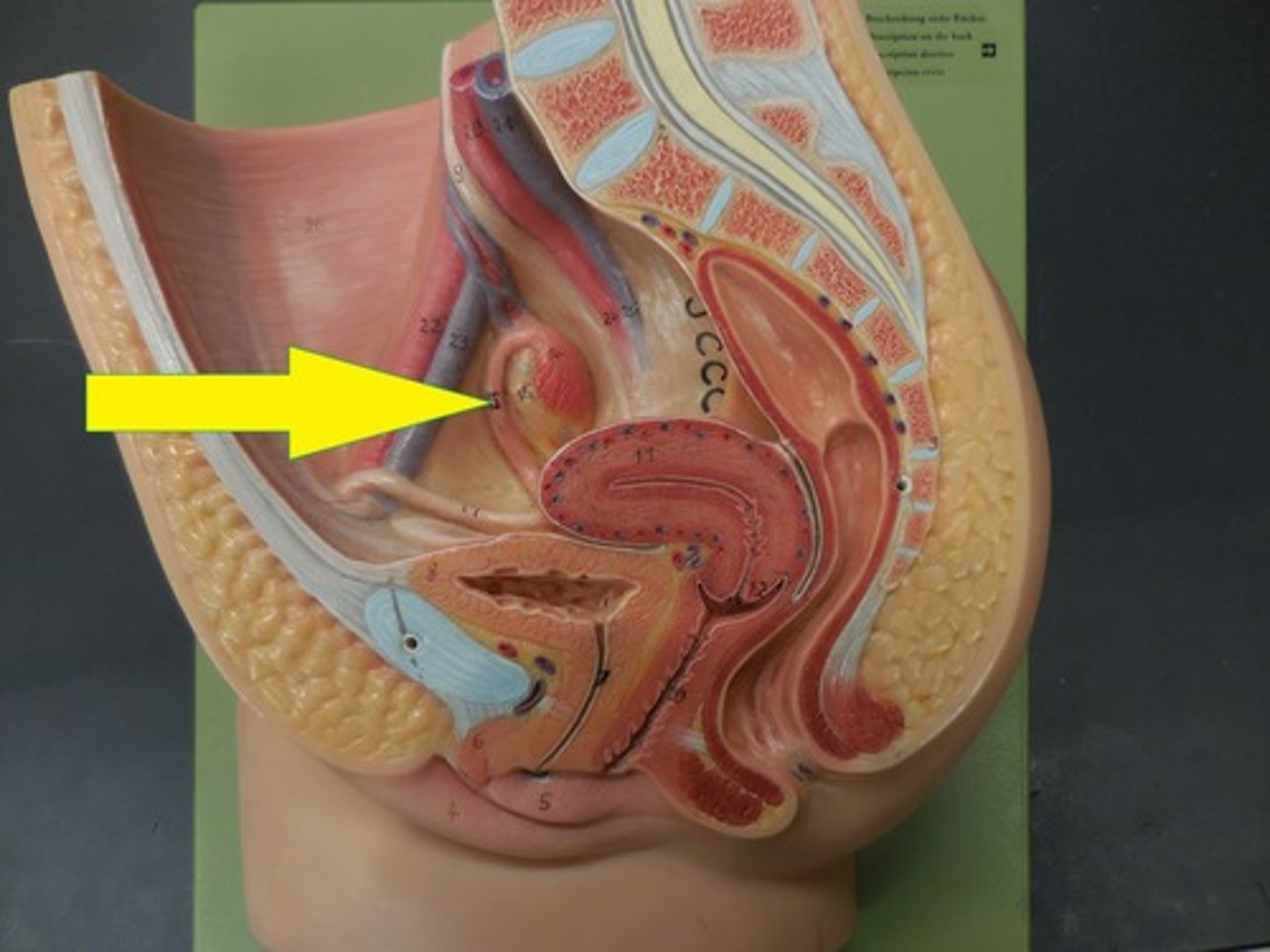
Cervix
The opening to the uterus
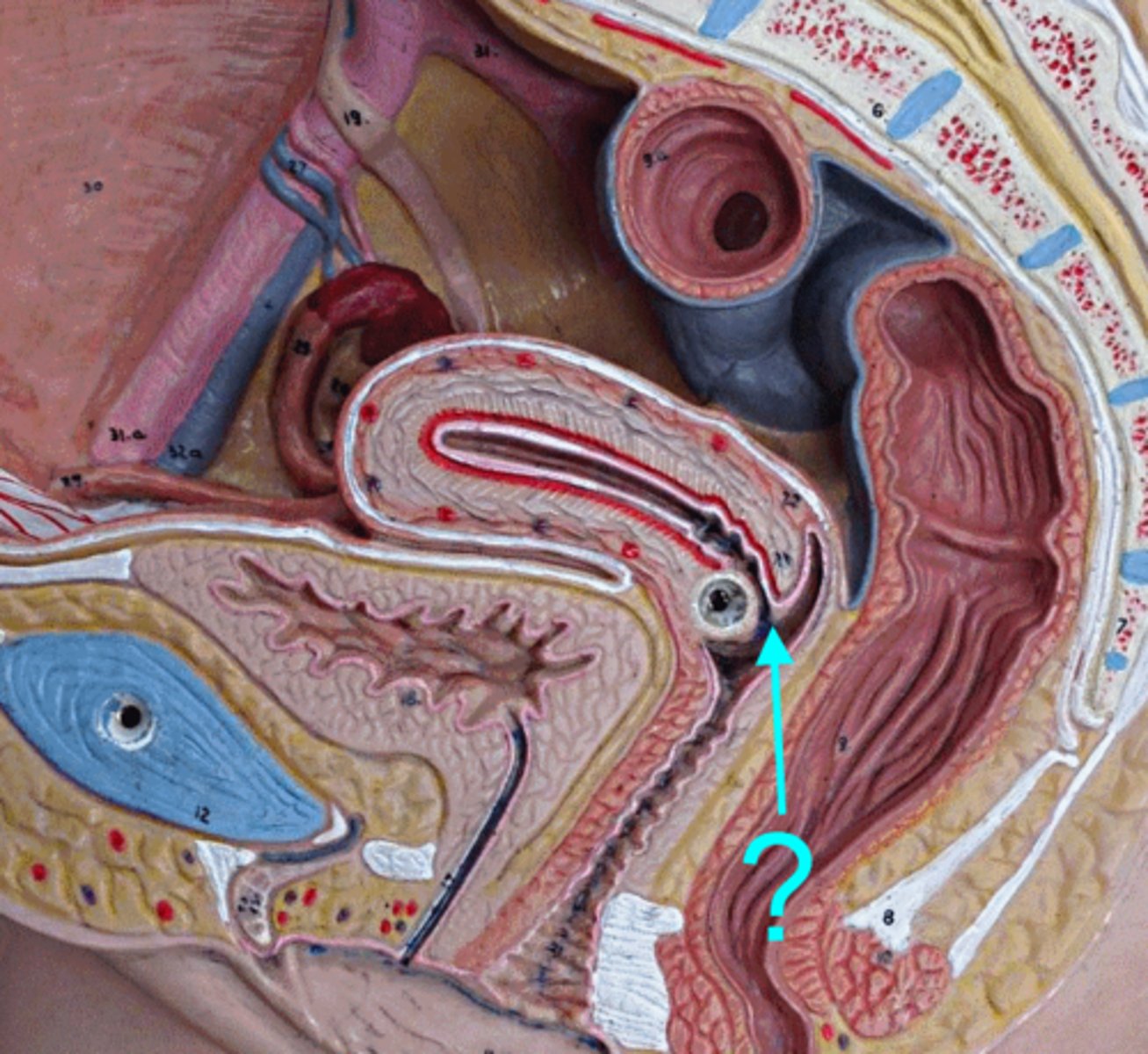
Ovary
a female reproductive organ in which ova or eggs are produced
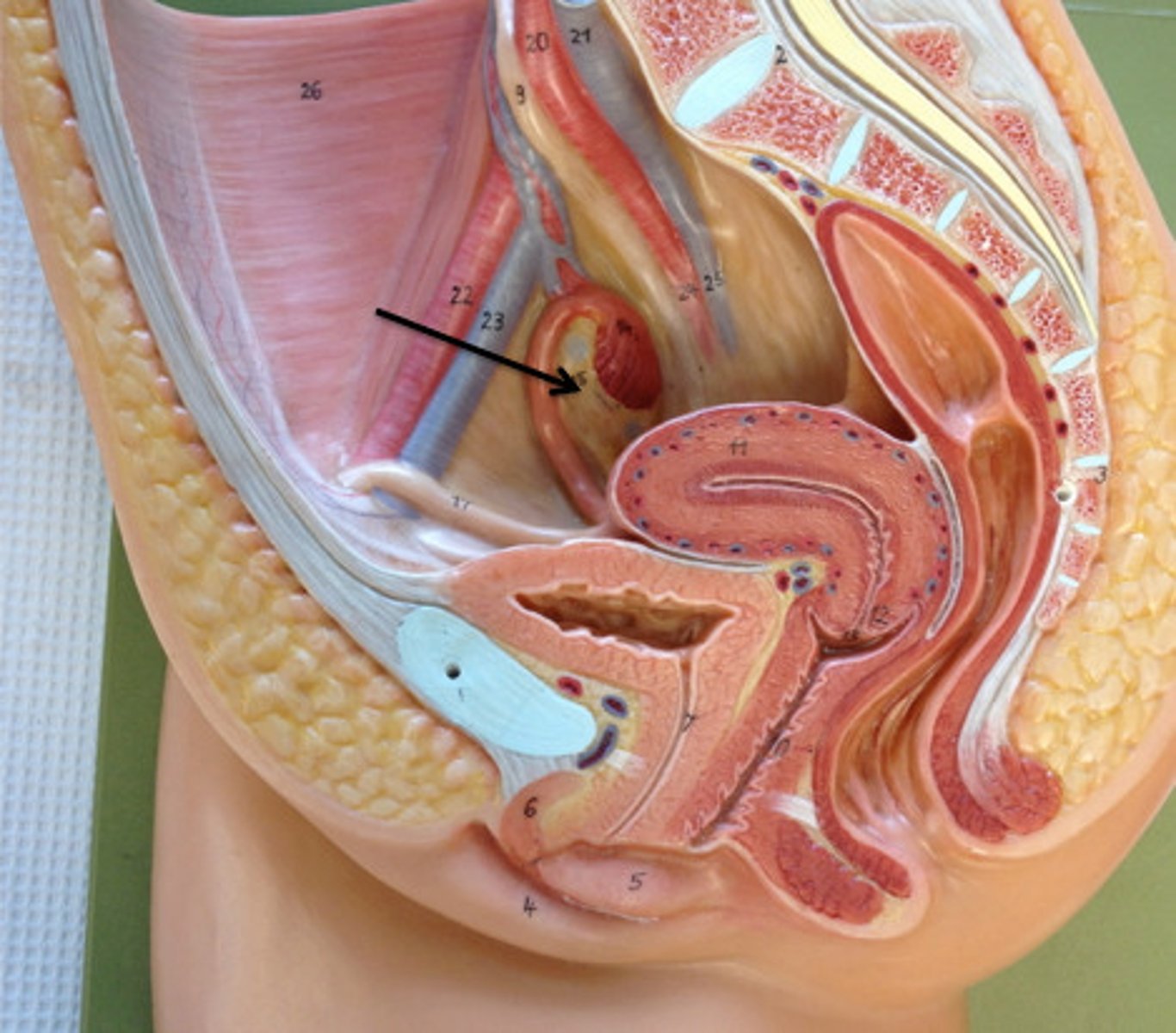
Vagina
Female organ of intercourse; birth canal
Endometrium
inner, mucous membrane lining of the uterus
Fimbriae
Fingerlike projection of the uterin (fallopian) tubes that drape over the ovary.
Mitosis
Cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
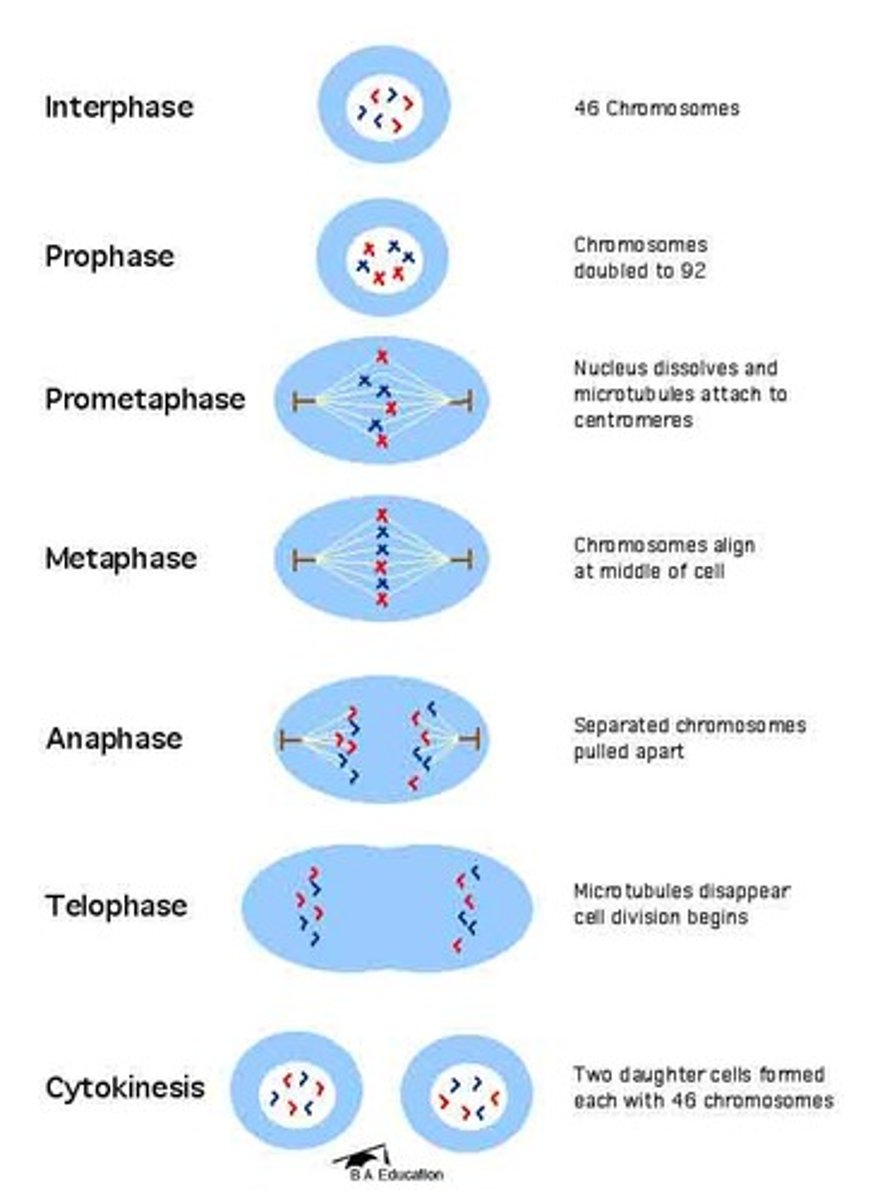
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases; DNA replication takes place
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
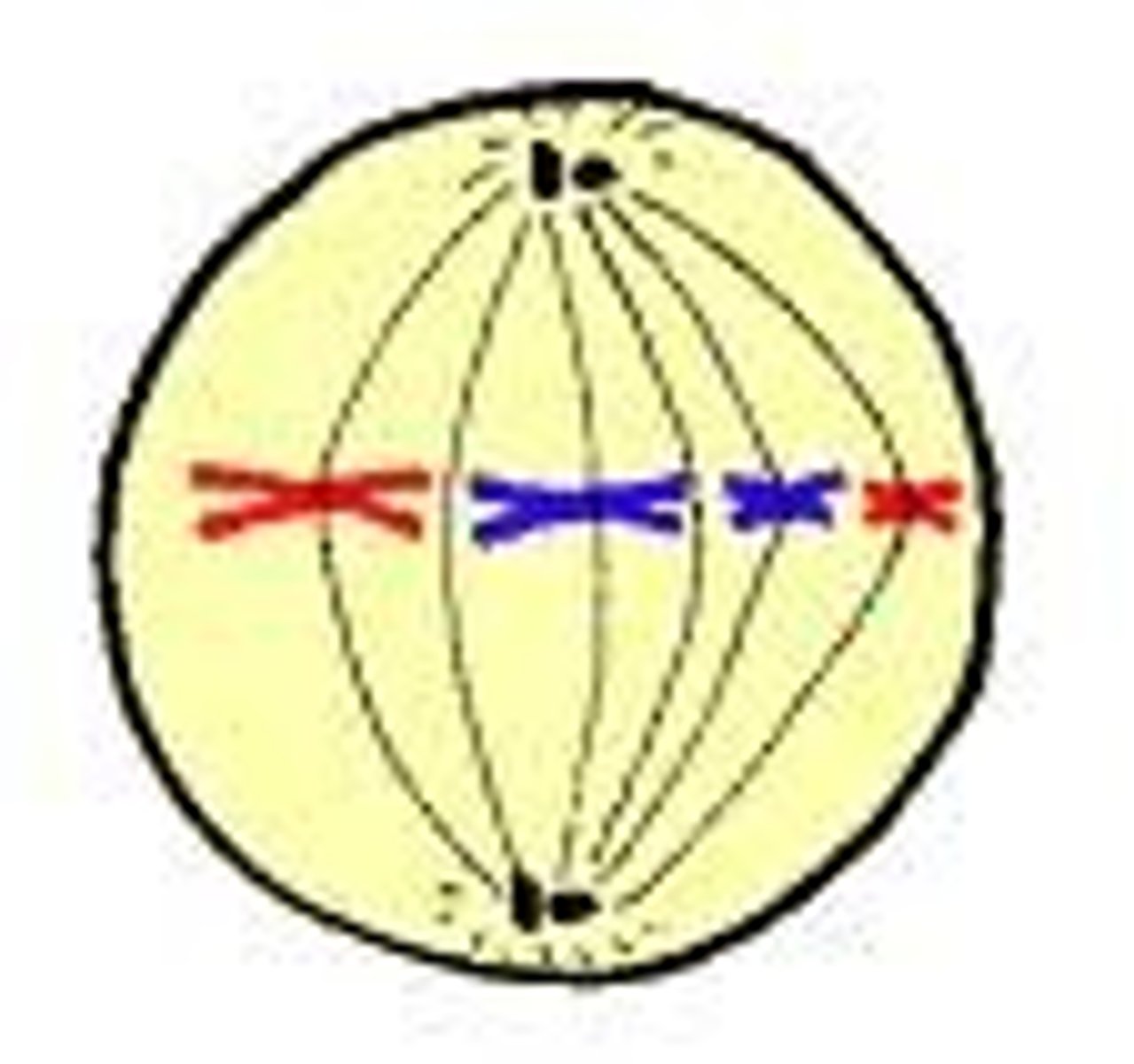
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
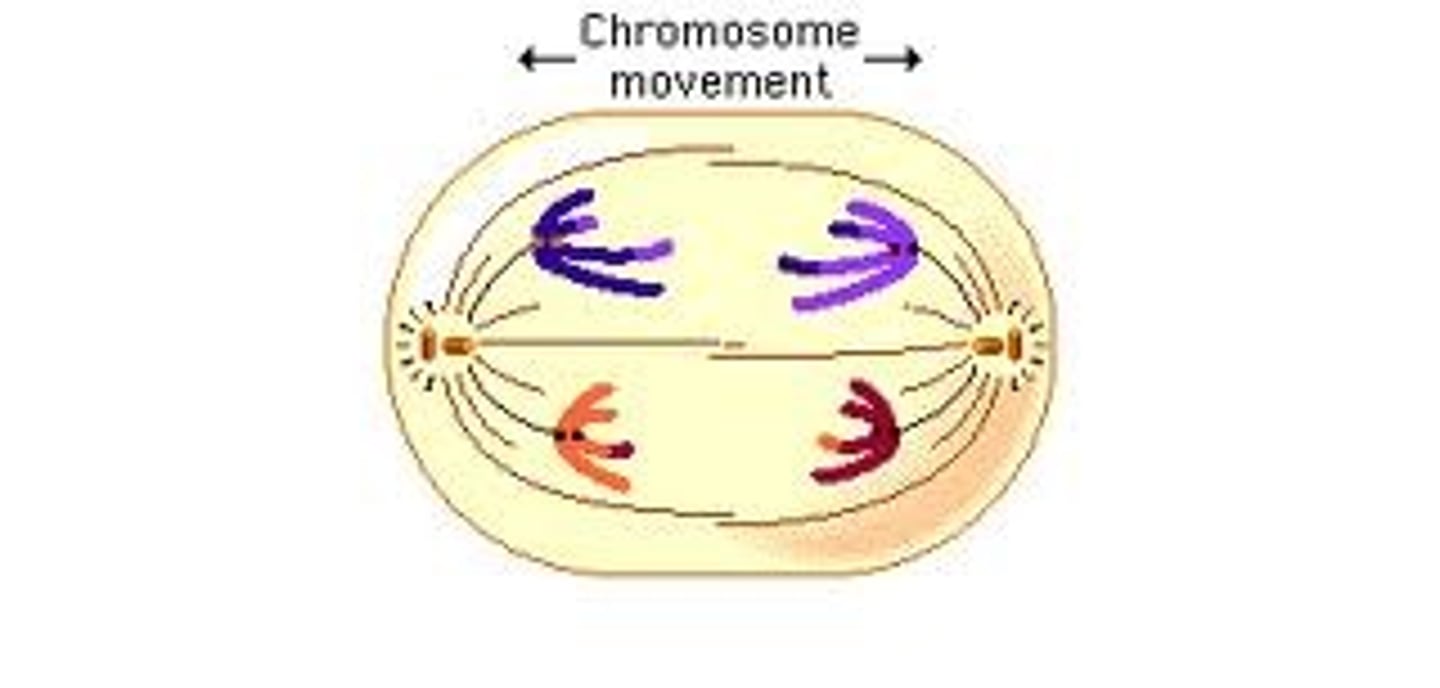
Telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
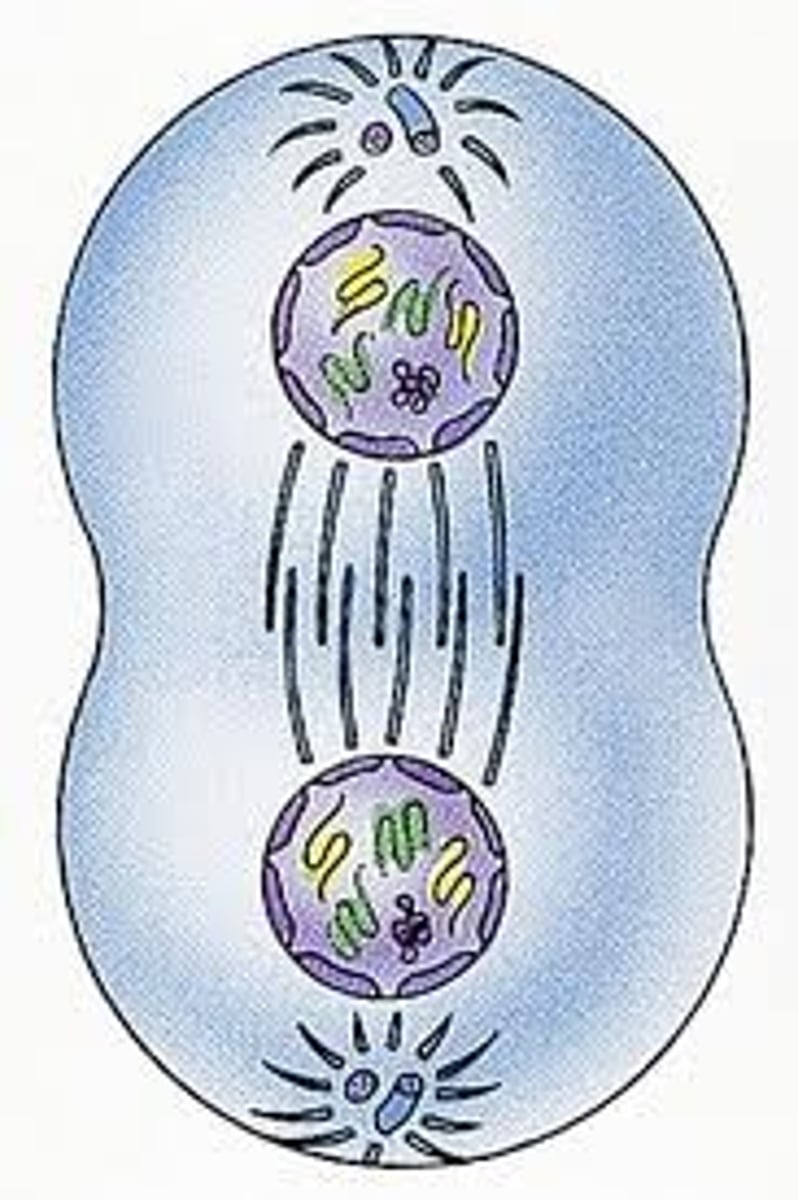
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells
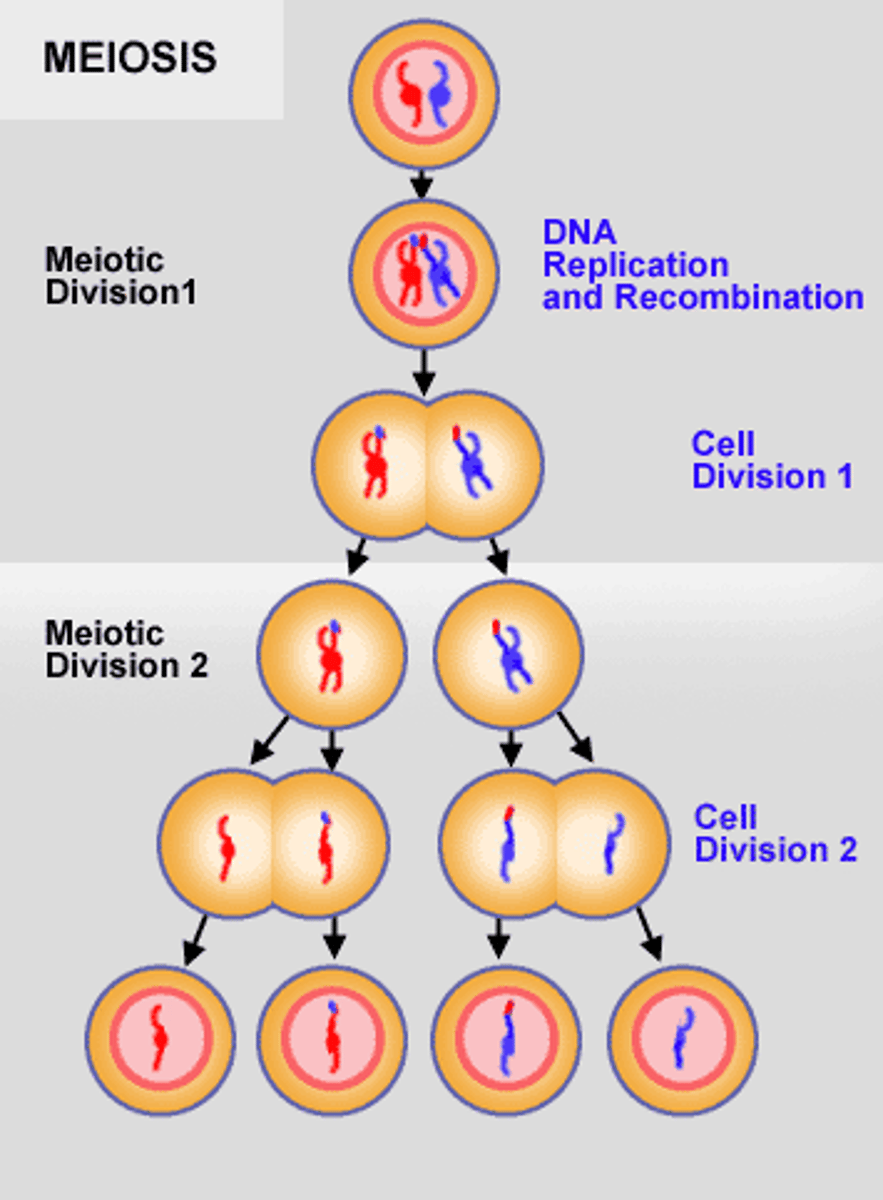
Meiosis I
first phase of meiosis; Homologous chromosomes separate
Meiosis II
the second phase of meiosis consisting of chromatids separating, along with the two diploid cells splitting in two
Diploid Cell
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set inherited from each parent.
Haploid Cell
A cell containing only one set of chromosomes (n).
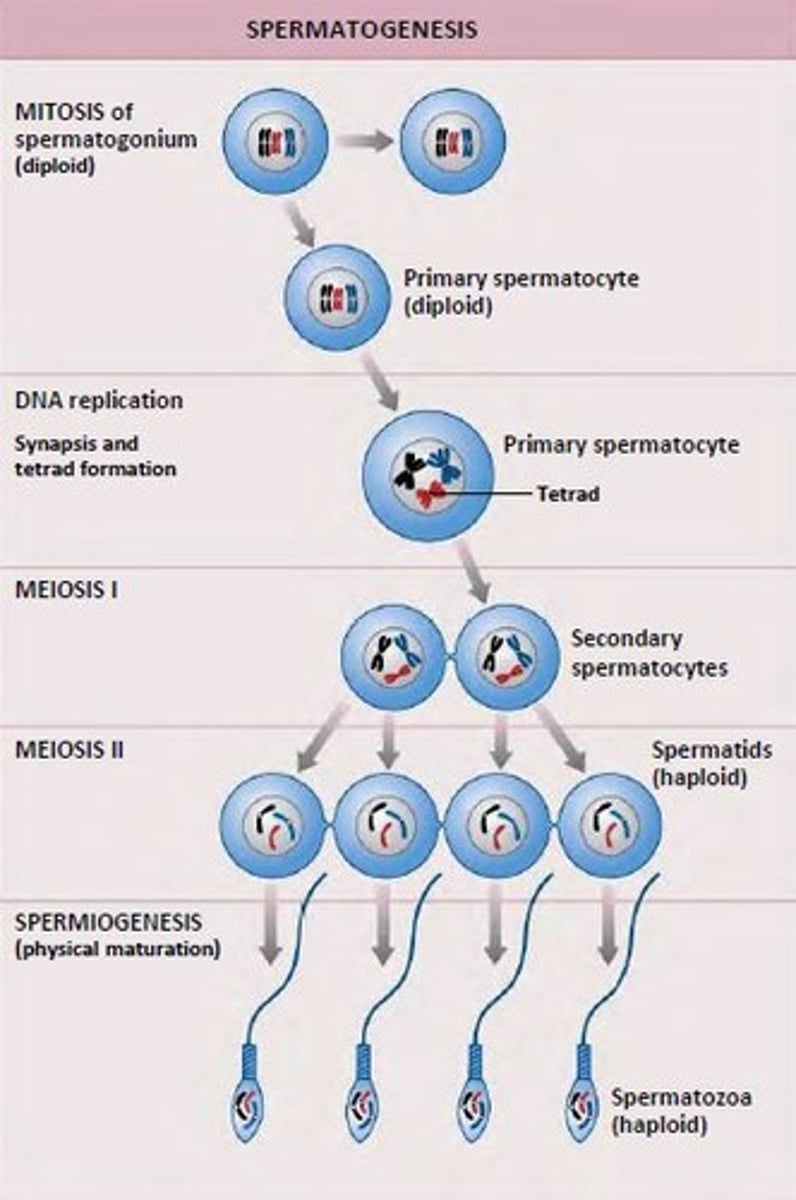
Spermatogenesis
Formation of sperm; Occurs in seminiferous tubules of testis; starts during puberty
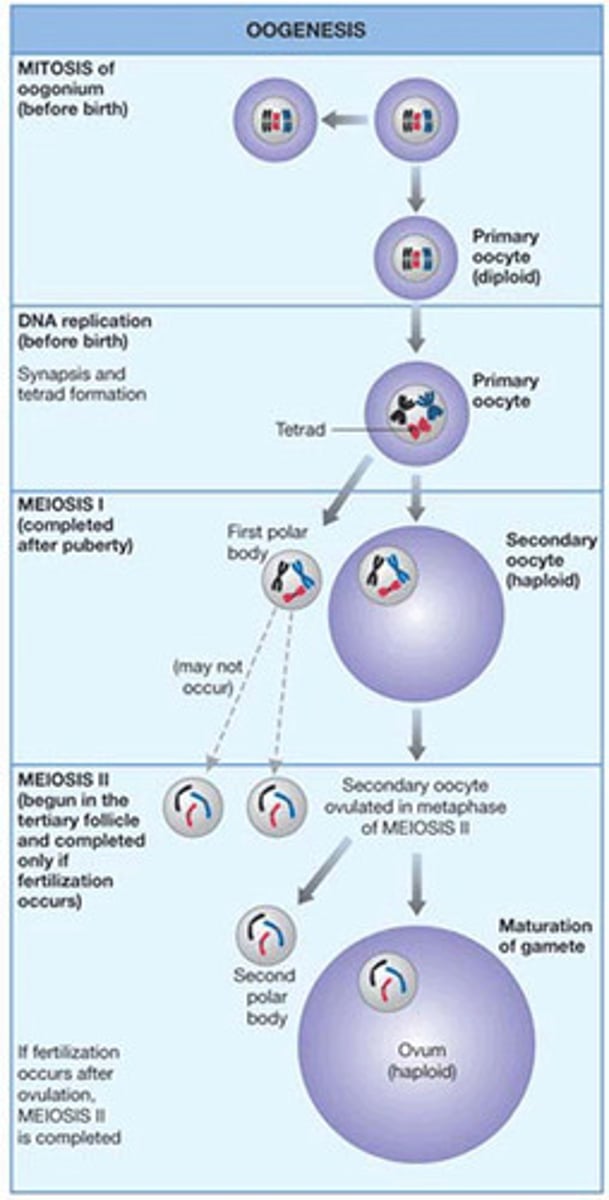
Oogenesis
the production, growth, and maturation of an egg, or ovum
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
a hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that promotes the formation of ova or sperm
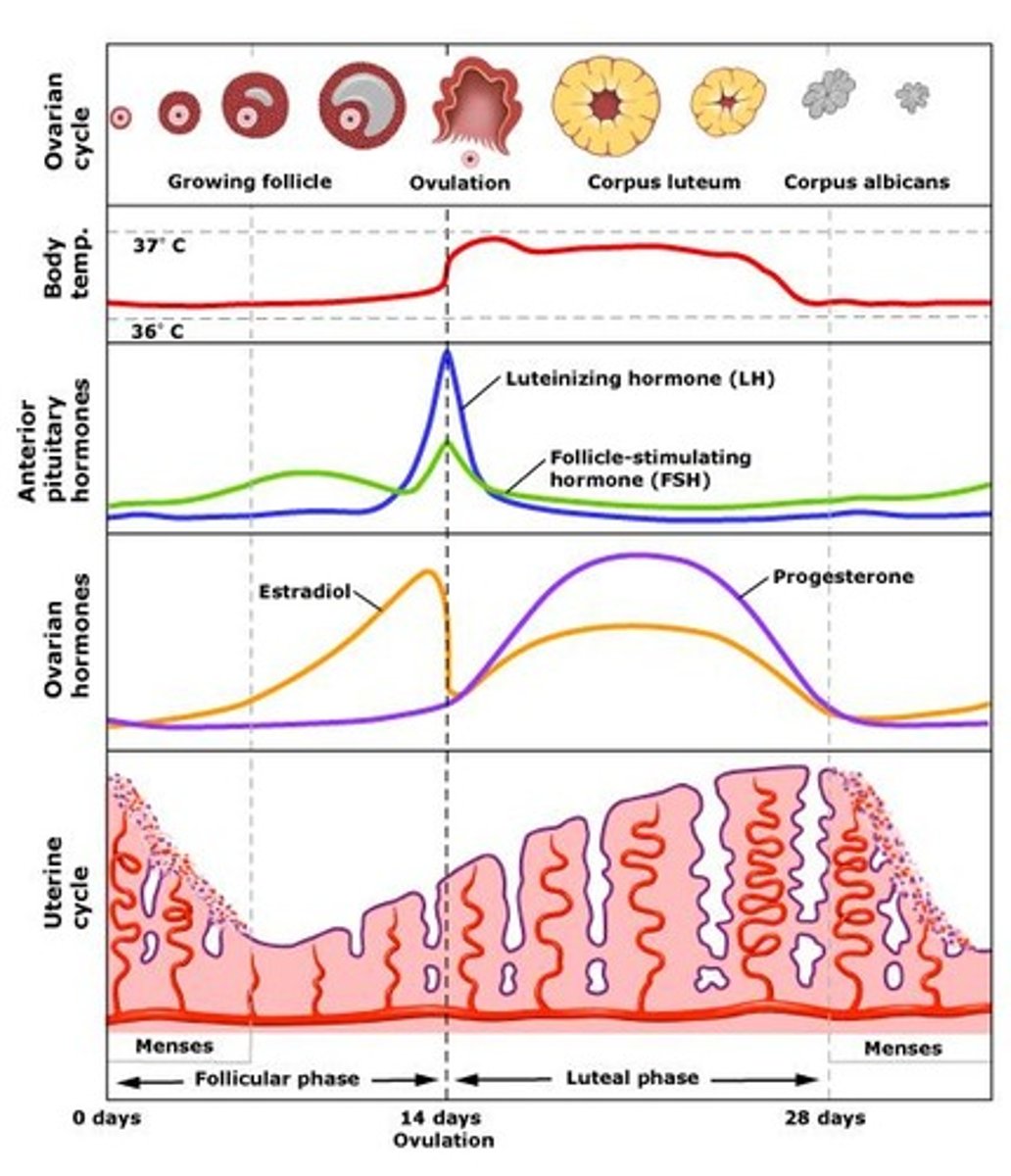
Oestrogen
Female sex hormone which stimulates the lining of the womb to build up in preparation for a pregnancy.
Luteinizing Hormone
A protein hormone secreted by the pituitary that stimulates ovulation in females and promotes secretion of testosterone in testes
Progesterone
A hormone produced by the ovaries which prevents endometrium shedding
Menstruation
The shedding of the uterine lining; days 1-4
Pre-ovulation
Endometrium thickens & softens; Increase in blood vessels and mucus-secreting glands; Development of follicle (FSH released); Days 5-12;
Ovulation
Rupture of mature follicle - egg released; Day 13 -15
Secretory Phase
the phase of the menstrual cycle during which the corpus luteum develops and secretes progesterone; Days 16-20
Premenstruation
Endometrium begins to deteriorate; Degeneration of corpus luteum; Days 21-28
Corpus Luteum
Empty ovarian follicle that secretes progesterone after release of the egg cell
Corpus Albicans
The scar tissue that replaces the corpus luteum. it is caused by the drop of LH levels in the blood at the end of the 28 day-cycle
Testosterone
develops of immature sperm into spermatozoa, causes maintenance of male reproductive organs,
Zygote
the fertilized egg; it enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo
Embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month
Blastocyte
an undifferentiated embryonic cell
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
hormone produced by the placenta to sustain pregnancy by stimulating the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone