Chapter 17: Sex
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
Genetic Sex
Genotype based on chromosomes
2
New cards
Gender Identity
Self-perception of gender
3
New cards
Sexual Orientation
the sex of whom one is physically attracted
4
New cards
Concepts of biological sex and gender
– Biological characteristics and qualities
– Gender-specific behaviors
– Gender identity
– Gender-specific behaviors
– Gender identity
5
New cards
def 4 Gender-specific behaviors
1. Introspection
1. Upbringing
2. Societal expectations
3. Genetics, hormones
6
New cards
X chromosome _____ than Y
larger
7
New cards
X contains ___ genes, and Y contains __ genes.
800, 50
8
New cards
male and female genotype
male: XY
female: XX
female: XX
9
New cards
X-linked diseases occur more often in… than…
men, women
10
New cards
What makes fetus develop as male
SRY: gene on Y chromosome
* Encodes testis-determining factor (TDF)
* Causes the development of testes and testicular hormones
* Encodes testis-determining factor (TDF)
* Causes the development of testes and testicular hormones
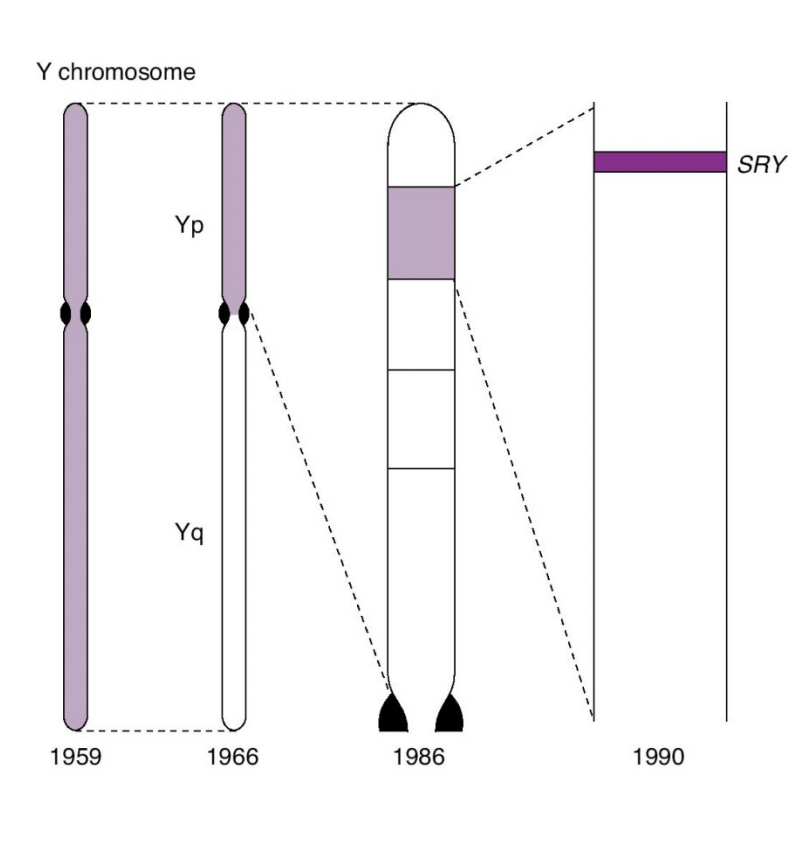
11
New cards
what causes Sex Chromosome Abnormalities
Rarely, too few, or too many sex chromosomes
12
New cards
def turner syndrome
Partial or complete absence of one X chromosome in a female (XO genotype)
13
New cards
def Klinefelter syndrome
Extra X chromosome in a male (XXY genotype)
14
New cards
Differentiation of Fetus and Development of Gonads
male: wolffian duct
female: Mullerian duct
female: Mullerian duct
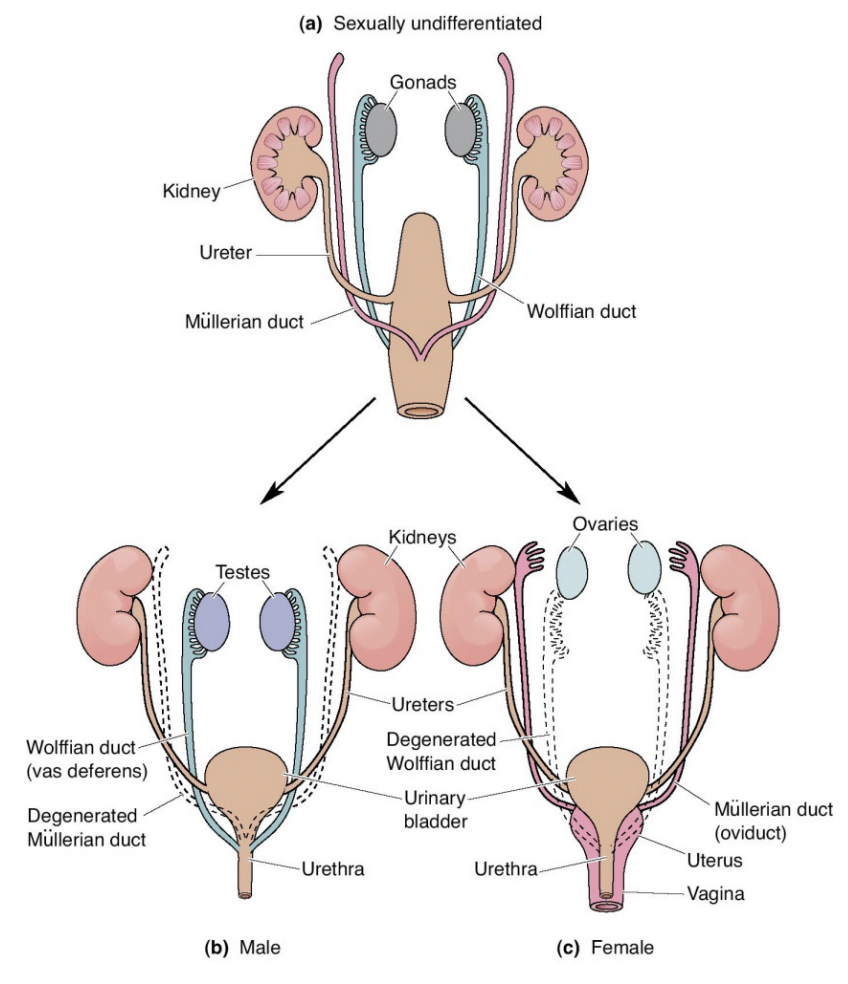
15
New cards
def sex hormones
steroids
* develop from cholestoral
* made of fatty tissue
* develop from cholestoral
* made of fatty tissue
16
New cards
male and female sex hormones
male: testosterone
female: estradiol
female: estradiol
17
New cards
what releases sex hormones
endocrine glands
18
New cards
what regulates the endocrine glands
Pituitary gland
19
New cards
high concentration of androgens
men
20
New cards
high concentration of estrogens
women
21
New cards
how is estrogen made
Testosterone (androgen) + aromatase → estradiol (estrogen)
22
New cards
what don’t pass through cell membranes,
bind surface receptors.
bind surface receptors.
protein hormones
23
New cards
what do pass through cell membrane, bind to
cytoplasmic receptors.
cytoplasmic receptors.
steroid hormones
24
New cards
Receptor concentrations ___ in different brain regions.
vary
25
New cards
what do testes release
androgen
26
New cards
Testosterone increase at puberty leads to development of…
secondary sex characteristics.
27
New cards
what do ovaries secrete
estradiol (estrogen) and progesterone (progestin)
28
New cards
Estrogen increase at puberty leads to maturation of… and development of…
maturation of female reproductive system and development of breasts.
29
New cards
Blood concentrations of sex hormones vary b/t male and female
male: levels fluctuate rapidly each day
female: levels fluctuate in 28-day cycle
female: levels fluctuate in 28-day cycle
30
New cards
Gonadotropins
LH and FSH
31
New cards
LH and FSH funct. in males
LH stimulates testosterone production; FSH aids sperm maturation
32
New cards
LH and FSH funct. in females
LH and FSH cause estrogen secretion.
33
New cards
def 2 phases of Menstrual cycle
1. follicular phase
2. luteal phase
34
New cards
Sexual response cycle
Arousal, plateau, orgasm, resolution
35
New cards
Cerebral cortex ctr Reproductive Organs
– Neural control of sexual response
36
New cards
Spinal cord ctr Reproductive Organs
– Mediates sexual response of genitals
37
New cards
External genitals
males: penis
females: labia and clitoris
females: labia and clitoris
38
New cards
what kind of muscles make up genitals
smooth muscle
39
New cards
what relaxes smooth muscle in penis and
clitoris
clitoris
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), and nitric oxide (NO)
40
New cards
Activity from the sympathetic division of the ANS
Male orgasm: muscular contractions → ejaculation
females orgasm: muscular contraction
females orgasm: muscular contraction
41
New cards
Polygyny
Male mates with many females.
42
New cards
Polyandry
Female mates with many males.
43
New cards
Monogamy
Male and female mate exclusively.
44
New cards
why are prairie voles social and monogamous
more oxytocin (female) and vasopressin (male)
45
New cards
what are montane voles asocial and promiscuous
fewer receptors for oxytocin and vasopressin
46
New cards
what do human plasma oxytocin levels increase
* During breastfeeding in mothers
* During sexual intercourse in men and women
* During sexual intercourse in men and women
47
New cards
Brain activation demonstrates…
strong reinforcing nature of partner and parental relationships.
48
New cards
what do fMRI studies show
Oxytocin and vasopressin play roles in human bonding.
49
New cards
who is more verbal and who is more spacial
women, men
\*Larger differences between individuals than between sexes\*
\*Larger differences between individuals than between sexes\*
50
New cards
Steroids funct
* Alter membrane excitability, sensitivity to neurotransmitters, neurotransmitter release
* Modulate functions of various enzymes, channels, and transmitter receptors
* Diffuse across outer cell membrane
* Bind to specific steroid receptors in cytoplasm and nucleus
* Modulate functions of various enzymes, channels, and transmitter receptors
* Diffuse across outer cell membrane
* Bind to specific steroid receptors in cytoplasm and nucleus
51
New cards
Organizational effects of hormones
* Development, anatomy
* Tend to be irreversible
* Tend to be irreversible
52
New cards
Activational effects of hormones
* Behaviors
* Tend to be temporary
* Tend to be temporary
53
New cards
what normally determines hormonal funct.
genetic sex
54
New cards
Treatment with testosterone in early development of mammals leads to
reduced female reproductive behaviors
55
New cards
what causes an Androgen-insensitive genetic males
defective androgen gene on X chromosome
56
New cards
what causes Congenital adrenal hyperplasia in genetic females
abnormally large adrenals overproduce androgens → External genitals intermediate between normal clitoris and penis
57
New cards
def Gynandromorph
having both male and female tissues
58
New cards
Gynandromorphic zebra finch - brain differences
Female left side
Male right side
Male right side
59
New cards
Role of genes in complex sex behaviors in fruit flies
* Sexual behaviors encoded in genes
* The fru and dsx genes
* The fru and dsx genes
60
New cards
what causes increased sexual interest - male vs female
* male: rise in testosterone
* Women: rise in estrogen
* Women: rise in estrogen
61
New cards
what rises during pregnancy
Rise in leptin levels
62
New cards
how does interaction with offspring may alter male brain structure
* increase density of dendritic spines
* Increased vasopressin receptors
* Increased vasopressin receptors
63
New cards
what has dramatic effects on hippocampal neuronal dendrites
Estradiol treatment
64
New cards
what coincides with female rat’s peak fertility
Increase in hippocampal spine numbers
* May play a role in changing reproductive needs
* Estradiol’s protective effect on neurons (in culture)
* May play a role in changing reproductive needs
* Estradiol’s protective effect on neurons (in culture)
65
New cards
def 2 benefits of estrogen
* May protect against stroke
* May benefit women with multiple sclerosis
* May benefit women with multiple sclerosis
66
New cards
Interstitial nucleus of the anterior hypothalamus (INAH); INAH-3 is Twice as large in… than…
men, women
67
New cards
• INAH-3 in… similar to that in…
gay men, women
68
New cards
Spinal nucleus of the bulbocavernosus (SNB) larger in… during…
men, erections
69
New cards
Corpus callosum: splenium larger in… than…
females, males
70
New cards
dimorphisms are
subtle, few, and functions unknown.