Neonatology
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are neonatal deaths caused by?
poor husbandry practices
suboptimal management
poor monitoring
In utero vs at birth
Utero → lungs fluid filled, right side of the heart to the lungs, causes blood to shunt from the R side of the heart to the L. ductus arteriosus → blood goes from pulmonary artery to aorta. foramen ovale → blood goes from right atrium to left atrium
At birth → lungs fill with air, right side of the heart = low pressure system, no longer shunting from R - L, L side pressure is greater, ductus arteriosus closed, foramen ovale closes
What happens in neonates right before birth?
adrenal glands produce cortisol → cortisol released into the blood → goes to the lungs → stimulates type 2 pneumocytes to secrete surfactant → surfactant keeps alveoli open to facilitate breathing and reduce surface tension
Why is fetal hypoxia common?
newborns → dyspnea = reflex contraction of the chest with negative pressure/suction into the lungs → inability to inflate lungs → umbilical cord is cut → hypoxia → inc vascular resistance
Why are puppies more at risk of death at birth?
Not fully developed at birth. Have poor myocardial contractility and do not compensate well for hemorrhage, hyperthermia, acid/base imbalances. Not good blood pressure control
inc oxygen tension → ductus arteriosus narrows & pulmonary vessels dilate.
inc left sided pressure → closure of formen ovale
Why are puppies sensitive to temperature?
cannot shiver
cannot vasoconstrict
inc surface area
little body fat
poor blood flow
high water composition
unable to pant
Why are puppies more susceptible to bacterial infections?
they have a high stomach pH. they are born with sterile GI and get their microflora from mom, environment & diet
When is colostrum given to puppies?
available 2-3 days after birth, gut permeable closes 8 hrs after birth and none after 24 hrs
60-75% is IgG
What can we use to replace colostrum?
fresh/frozen plasma
pooled serum from healthy adults
can be given as 3 boluses or all at once
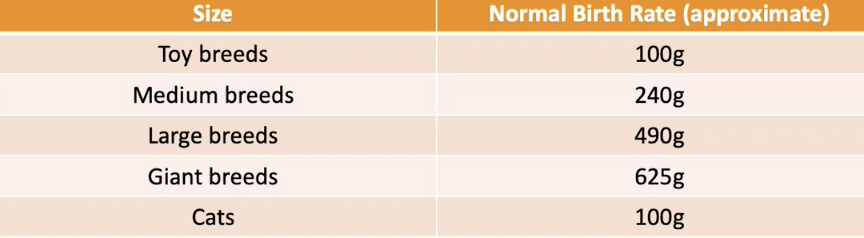
Normal puppy weights
normal weight loss in 24hrs (C-section)
gain 5-10% of body weight daily
should double their weight within 7-10 days of age
When do puppies have normal glomerular filtration rate?
6 weeks of age
Why are puppies prone to hypoglycemia?
born with limited glycogen stores
poor gluconeogenesis capability
inc demand for glucose, inc loss of glucose, dec ability to make glucose
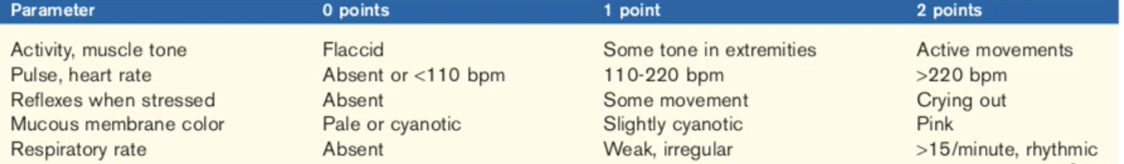
APGAR scoring
Appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, respiration
score of 0-2
HR
spontaneous breathing
response to an irritating stimulus
muscle tone
color of mm
score 10 → viable
score 6 or lower → mortality & need supportive care
rooting
righting reflex
suckle reflex
What causes dehydration?
not nursing
GI disturbances
skin tent and mm not reliable
look at urine color → very dilute, dark or brown is dehydrated
give fluid oral, sq, IV, or IO
What causes hypoglycemia?
diarrhea, vomiting, infection, dec intake
clinical sign: weakness, anorexia, tremors, crying, coma, seizures
Why do puppies get hypothermia? treatment?
cannot shiver or generate heat
should not be less than 35 C
when cold do not feed the puppy because their gut is slowed down → ileus
give fluids & warm them up very slow 1 C/hr
What causes sepsis?
wounds, tail docking, ear crops, umbilicus, respiratory infections, in utero
clinical signs: hypovolemia, vocalizing, reluctant to nurse, dec urine, inc lactate, cold, loss of hair
dx: culture
tx: warm fluids, plasma, antibiotics
Causes of fading puppy syndrome
infectious, sepsis, environment, genetics
sick at birth, weak, small, unable to nurse, dehydration, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, death
some can be appear healthy at birth but get sick in first weeks of life
What causes canine herpes virus?
in the environment → necrotizing disease in neonates
pups under 3 weeks
clinical signs: acute, stop nursing, vocalize continuously, death in 1-3 days
PM: petechial + ecchymotic hemorrhage on major organs
hard to diagnose and treat
What causes neonatal isoerythrolysis?
hemolytic disease of newborn kittens → type A blood have a dam with type B blood
anti-A antibodies attack own type A blood
clinical signs: anemia, icterus, tail tip necrosis, weakness, tachypnea, tachycardia, hemoglobinuria, sudden death
remove kitten from dam and if severe transfuse
avoid mating type B queens to type A toms
What are some congenital disorders?
excessive vit A → midline defects
lack of vit D → tooth & bone abnormalities
feline parvo → cerebellar hypoplasia
corticosteroids → cleft palate when given at certain stage of gestation
hare lip, umbilical hernia, anal atresia, skull disorders
How often do neonates need to be fed?
1 ml of milk/oz of body weight
6-8x daily or once every 2 hrs
food should be 38 C
4 tsp/lb
royal canin protech for the first week or 2 then switch to less expensive