Dimensions of globalisation (2)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
types of capital
FDI
Aid
remittance payments
repatriation of profits
loans
FDI
foreign direct investment
= money invested into a foreign company from another company
intention of making interest
investors have a lot of influence over the operations of the company
Aid
money sent from a country/global institute to help another country in a time of need
bilateral = from another company with intention of helping other country, i.e., disaster relief
can also come from world bank/IMF
Remittance payments
= payments sent to home countries by migrants working in a foreign country
vital source of income for LICs
workers send money back to families in their home country, helping origin countries economy rather than worker's country (typically a HIC)
Repatriation of profits
= sending money back to the HQ of a TNC company from an operating branch in a foreign country
money is sent back to a typically developed HIC country of the TNC rather than contributing to the economy of the operating country
e.g., coca-cola HQ in USA, primark HQ in Ireland
Loans
money borrowed that must be repaid with interest
can be given by a country, but usually from the world bank or IMF
e.g., Greece 2008 financial emergency, received a loan from the world bank
World Bank
a group of global institutions that give loans for development and relief
IMF
international monetary fund
aim = to secure financial stability and facilitate international trade
Core - Periphery Model + Wallerstein's world systems theory
a model that represents the flows of capital between core, periphery, and semi-periphery regions (+ world bank/IMF)
builds upon dependency theory
... the idea is that countries are interdependent, but periphery regions are more dependent on core regions and are therefore disadvantaged as their development relies on the actions and decision of core regions
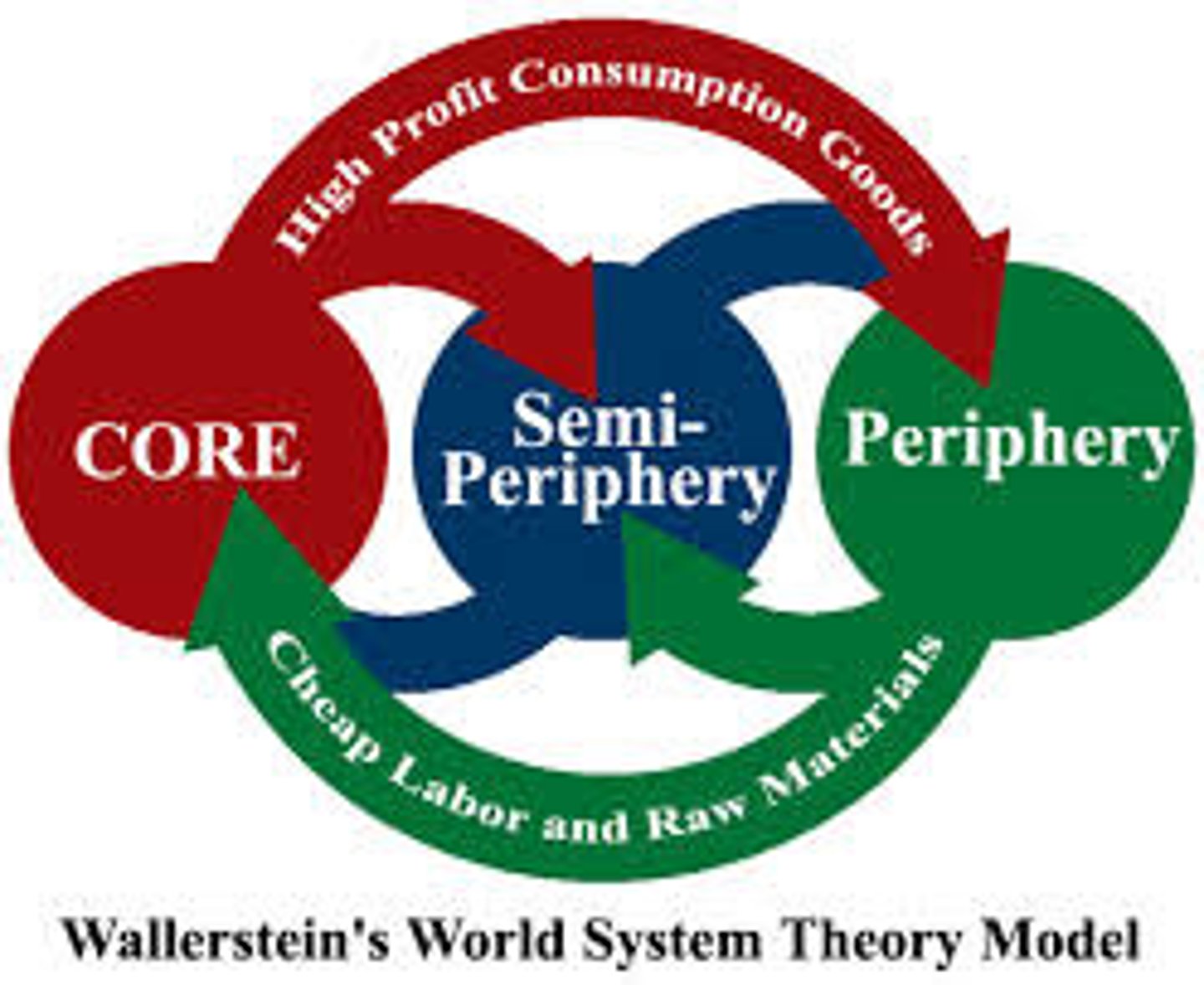
core regions
developed, HIC countries
send FDI, loans, and bilateral aid to periphery regions
receive repayments, interest and repatriations from periphery regions
Tiger economies
Trade blocs (NAFTA(replaced by usmca) , EU)
G7
BRICs
Hong Kong, London, New York, Paris
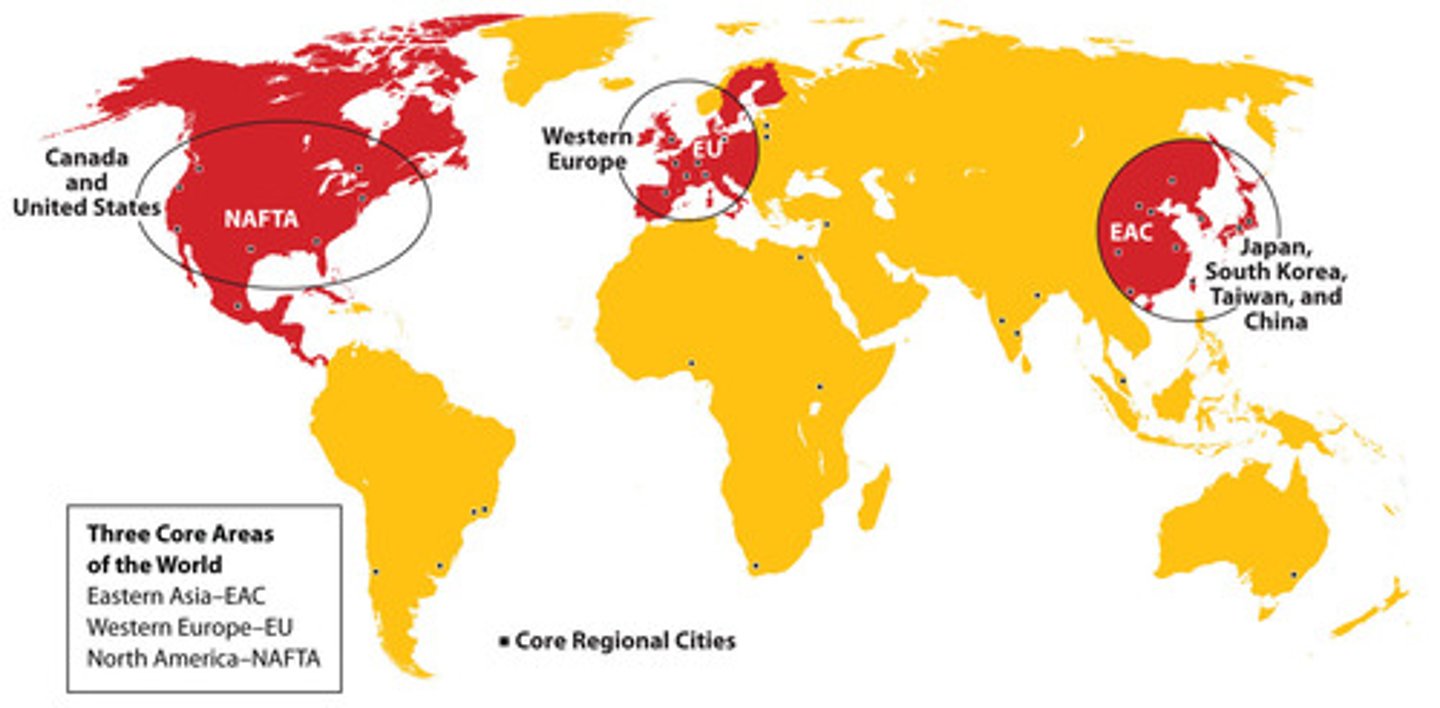
Tiger economies
the most globalised countries
Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore
"tiger cubs" = emerging globalised countries e.g., Thailand
Periphery regions
typically underdeveloped regions, LIC's
send repayments back to IMF/World Bank and core regions
receive loans, aid, repatriations, and (sometimes) investments from IMF/world bank and core regions
LIC's and LDC
sub-saharan Africa, Caribbean countries
Semi-periphery regions
developed, newly emerging regions
typically receive the most investments and FDI from core regions
may have outstanding loans from development
MINT and some BRICs
MINTs
Mexico, Indonesia, Niger, Turkey
newly emerging countries
developing economies
BRICs
Brazil, Russia, India, China
developing countries that are gaining in economic status, stability, and power
How has flows of capital contributed to globalisation
FDI = HIC influence over foreign countries, interdependence for development and interest
Repatriation of profits = allows expansion of TNCs into foreign markets (e.g., China has 2nd most pizza hut stores in the world after USA), contributes to flow of products + services
Loans = dependency of LICs and NEEs on HICs and global institutions, build relations and progresses development
Aid = builds relationships between countries which may in turn lead to trade agreements, or beneficial geopolitical arrangements, contributes to flow of ideas + goods
Remittances = enable migrants to send money home, can move to HICs for better jobs, contributes to flow of people, ideas and culture
Flows of labour - movement of people
flows of labour is essentially migration, the movement of humans
could be political, social, economical or environmental
political conflict, environmental refugees, asylum seekers, economic migrants seeking jobs + labour, better Q of L
Flows of Labour
labour is the main motivator for migration
people in LICs typically migrate to HICs for better job opportunities that have higher wages
can be highly skilled jobs or low skilled jobs
... profits can be remitted back to home country
highly skilled jobs benefit the country and the person
i.e., NHS, 38% of its workforce are trained abroad
low skilled jobs often lead to the exploitation of workers and overpopulation in the country
i.e., moving to the UK for better jobs, but having to do the jobs that no one wants as are unqualified, low wages
can also lead to brain drain in origin country
HIC's + flows of labour
the majority of international migration is migration to a HIC
14.1% of HICs populations are made up of international migrants
LIC's + flows of labour
only 1.6% of LICs populations are made up of international migrants
typically move to HICs
highly skilled jobs
= require qualifications and specialised training
can be in finance sectors, science, computer science or medicine
have to be carried out be qualified people
highly paid
e.g., NHS, 38% of workforce are trained abroad (Pakistan and India)
low skilled jobs
= don't necessary require qualifications or intense training
customer services, factory production jobs, call centres
can lead to overpopulation and exploitation as workers are underpaid and employed in illegal work
often low paid jobs
Migration in Asia (Labour)
63 million = internal migration
... mainly from SE Asia to West Asia
more high paid jobs, better Q of L and less overpopulation
e.g., UAE, Saudi Arabia
20 million to Europe
...Germany, UK, Spain and France
(Germany = highest)
=> England has a high pop. of Indian migrants that contribute to workforce
17 million to North America
... mainly to California and New York
majority = Chinese, followed by Indian and Philippine migrants
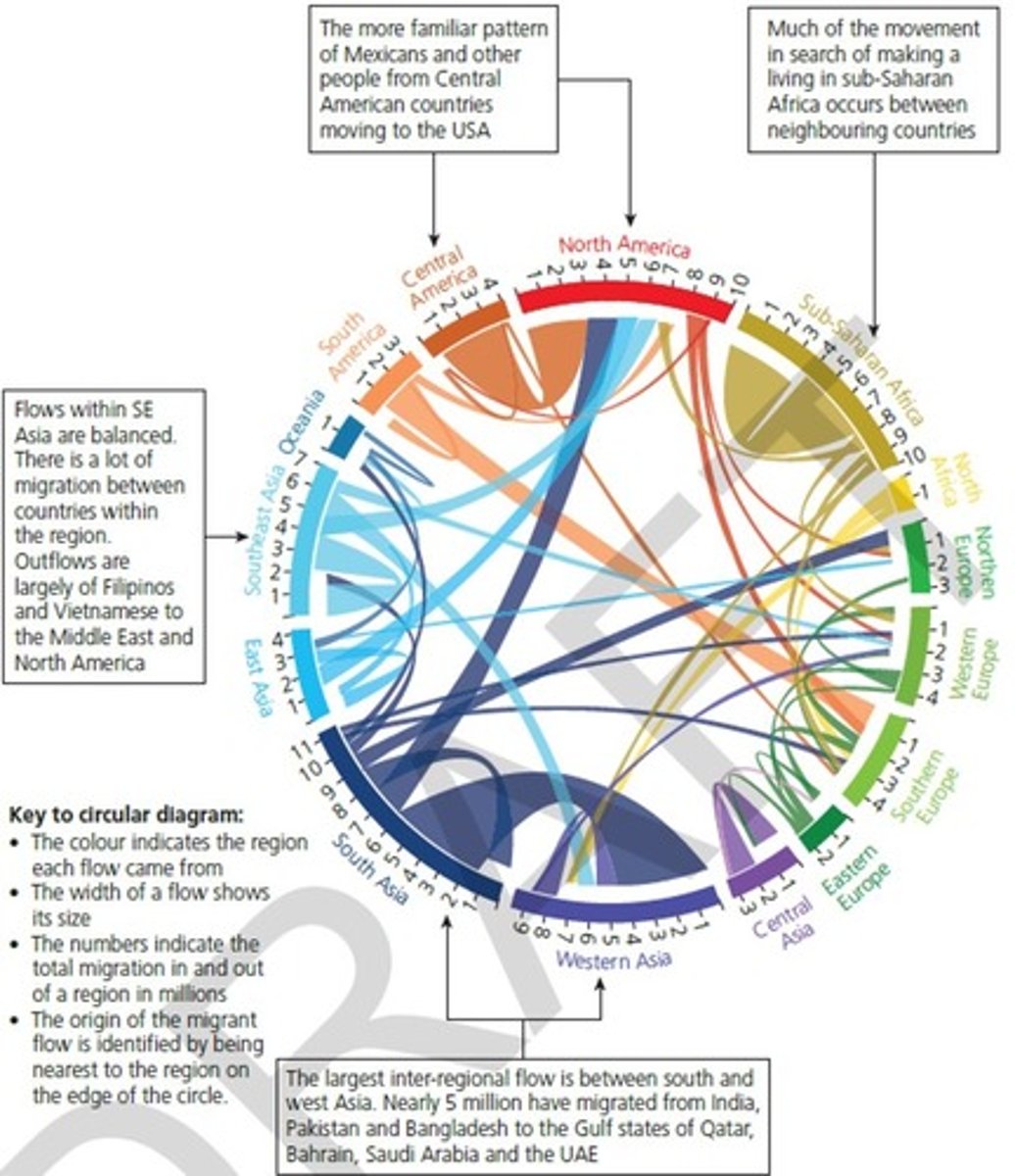
Migration in Europe (Labour)
43 million = internal migrants
Western Europe to Eastern Europe
e.g., Polish, Romanian and Czech republic migrants move to England, France and Germany
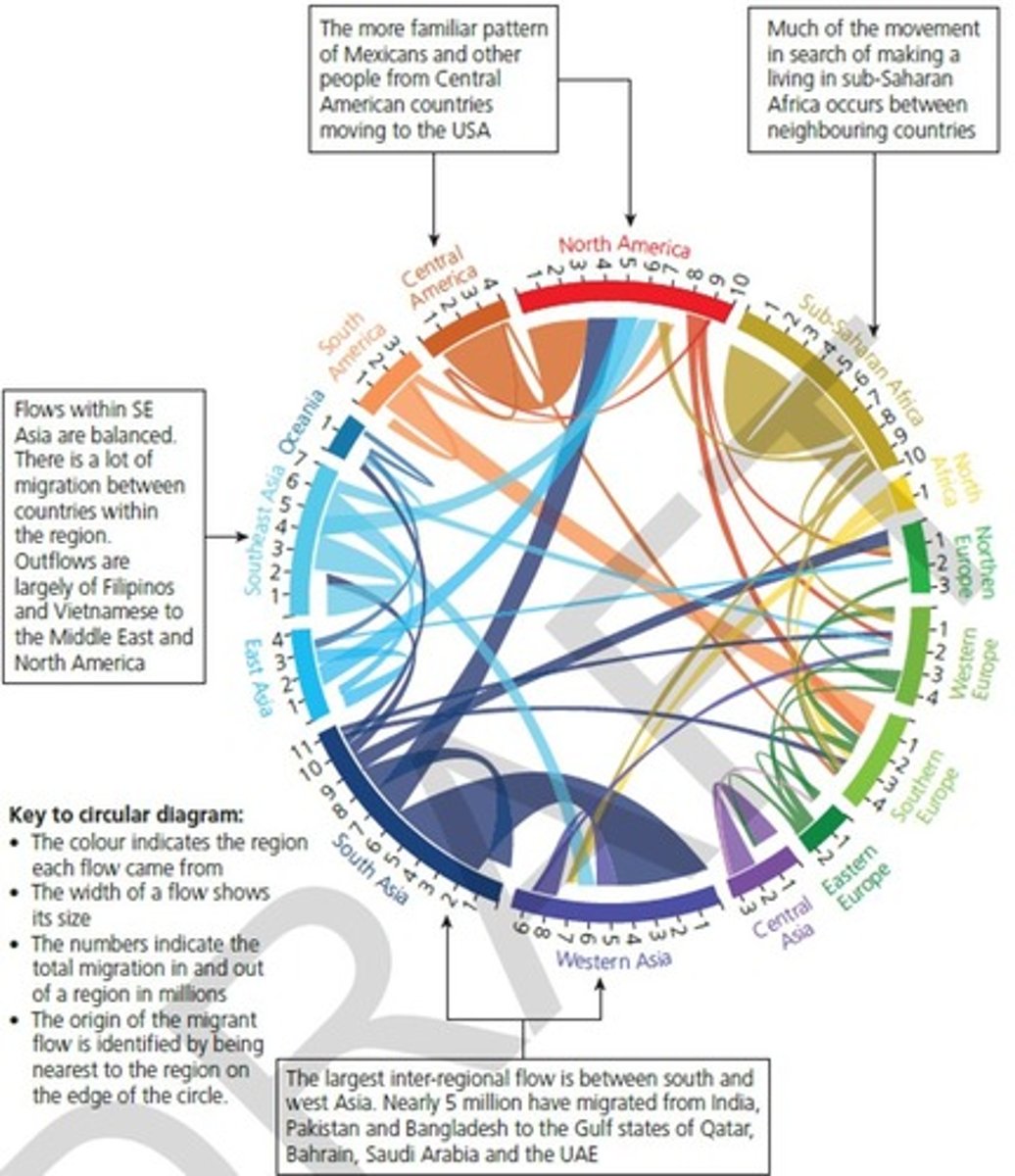
Migration in Africa (Labour)
19 million = internal migration
(majority of migrants are from sub-saharan african countries, and move to higher income countries like South Africa and Nigeria)
migrants in north Africa moving to European Mediterranean countries (Spain, Italy, Malta)
... seek better QofL, jobs, and flee from political unrest
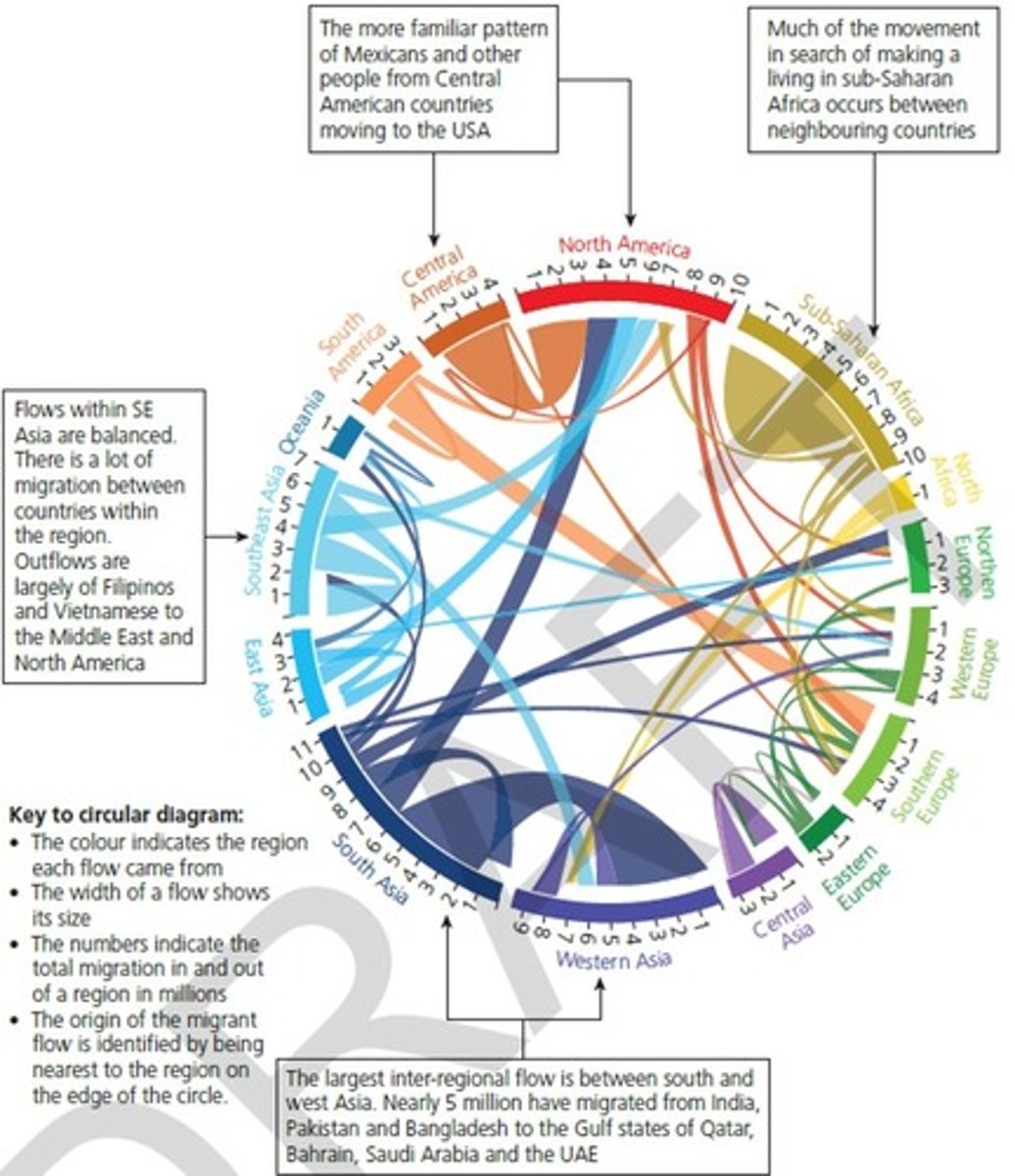
Migration from Latin America and Caribbean to America (Labour)
26 million migrants
most of the migrants are from Mexico and Cuba and move to east coast of USA
22 million migrants are Latin American
4 million migrants are Caribbean
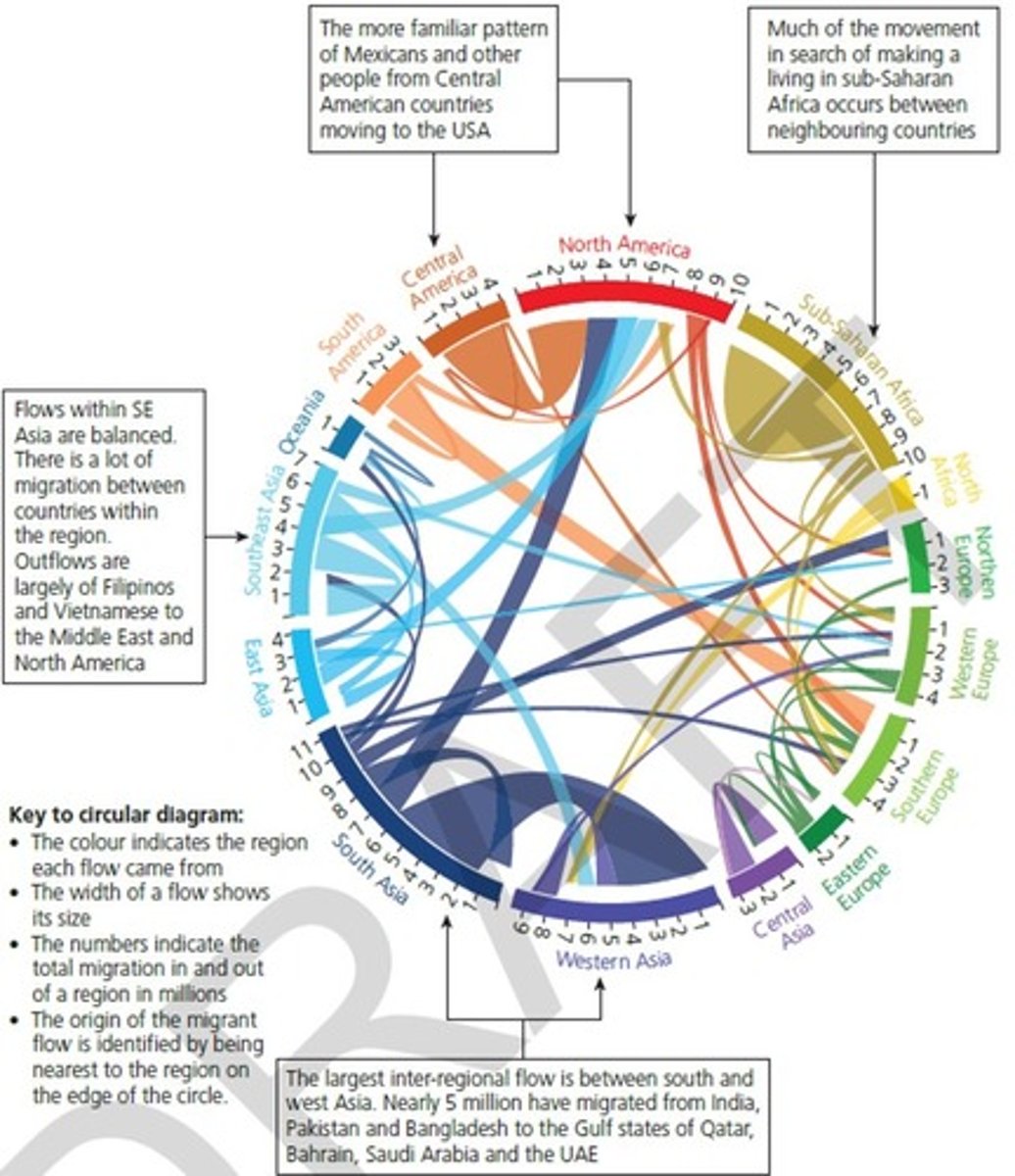
how does the flow of labour contribute to globalisation
Migrants = contributes to flows of people, culture and ideas
Economical: ... HICs have high skilled workforce, LICs have the remittances of profits
Social: ... interconnected + communication between countries, better QofL in HICs due to higher wages + remittances benefit economy and lives in origin country
Cultural: ... religion, diverse communities (St Paul's carnival + Afro-Caribbean community in Bristol), ideas + share of values
...global culture and community
Political: ... can benefit geopolitical relations, strengthen economies
... EU migration, can travel between countries within the EU with ease
... India and UK free trade agreement (2022), UK has a high pop. of Indian migrants
Flows of Products
= the movement of produced goods from area of production to area of consumption
increased globalisation has caused flow of products to become international
last 200 years, trade grown and transformed global economy
today, 1/4 of global production is exported
... generated gains but has distributional consequences
e.g., 2015, value of world trade of food and manufactured commodities was $25 trillion
Past patterns of production
produced goods were manufactured by high income countries due to them having access to resources (factories and ability to buy materials)
products were usually sold within they country they were produced in
Deregulation and the change in patterns of production
= a shift in product flows from internal (within the country) to international
- international trade has now created major product flows between LICs and HICs
- technological advancements
- decrease in manufacturing in HICs + higher prices of products in HICs due to transportation cost
e.g., employment in manufacturing in UK has decreased by over 3.4 million jobs since 1985
Globalisation
"the process by which people, their cultures, ideas, money, goods and services can be transferred between countries with few or no barriers"
Dimensions of globalisation
Capital, Labour, Products, Services, Information
Flows of Capital
the movement of currency and money
capital = all the money that moves between countries that's used for investment, trade, or production
i.e., stock market
2022 daily volume of foreign exchange = $6.6 trillion (40% lower than pre-pandemic)
technological advancements and flows of products
technological advancements (transportation and communication) mean that products can now be produced in LICs
.... beneficial to manufactures
1. lower labour costs
2. less restrictions
3. lower materials costs
=> offshoring
factors increasing the flows of products
Transport:
- reduction in transaction costs
- reduction in transport cost and time
e.g., containerisation
Communications:
- trade agreements and relationships
Technology:
- faster air travel
- repatriation of profits
- online transactions
- stock market
Containerisation
Movement of goods using ships/transport using standard containers
able to move large volumes of products at cheaper prices
e.g., HMM Algeciras, 24,000 containers

Changes in flows of products - NEEs
as emerging economies grow, so does the amount of wealthier middle class civilians (Newly Emerging Middle Class - NEMC)
... leads to an increasing demand for materials and manufactured products in growing consumerist societies
e.g., first apple shop opened in china (2008), now there are 57 stores open in 2024
= shows demand for consumerist products
how do flows of products contribute to globalisation
Economical: repatriation of products due to offshoring and increased flows of capital, investments and FDI in LICs
... unequal power relations due to influence of TNCs
Social: jobs for people in LICs, wages to support family, NEMC
... low wages, exploitation and poor working conditions, health
Cultural: share of global products, westernisation e.g., Apple stores in China
Political: increased coordination between countries
... trade agreements, trade blocs, geopolitical relations
e.g., banana trade wars
developments in transportation and technology have aided the increase in flows of products
Flows of Products - trade
trade has grown over the last century
... exports in 2014 were 40x larger than in 1913
- up until 1870, worldwide exports were less than 10% of global output
- 2014, value of exported goods was near 25%
trade is a fundamental part of economic activity
... countries exchange final products and intermediate inputs, creating networks of economic interactions
why has trade grown?
Higher levels of communication, transport and capital make it possible to exchange products
increased integration of economies
trade is a fundamental part of economic activity
... countries exchange final products and intermediate inputs, creating networks of economic interactions
WTO
world trade organisation
theory of comparitive advantage
Ricardo's theory
= a country can specialise in manufacturing one product
specialisation and free trade will benefit all trading parties
impacts of covid on world trade (Products)
2020: global trade reduced by 20%
2023:
- Trade between US and china shrunk by 15% from 2019 levels
- Trade between US and EU will grow but lower than $135 billion surge in 2015-19
- Trade between EU and china shrunk by $30 billion from 201
Flows of Services
= the transfer of economic activities which are traded without production of material goods
- high level of service to businesses
- low level services to consumers
grown due to ability to transfer information globally
... no longer has to be tied down to exact location due to internet
High level services - Flows of Services
= activities that generally require a higher skill level, usually important and complicated, meaning the person delivering the service should be qualified and trained so that they can deliver the best service possible
e.g., financial services
... those who give financial services are usually trained and fully qualified as they should be well-informed to make decisions about money
e.g., finance, investment, advertising
Low level services - Flows of Services
= services that require less training and are not as important to consumers
... usually customer service based
e.g., call centres
... workers only need basic training to offer advice or sell products
e.g., banking, travel, tourism, call centres, communication services
Distribution of high and low level services
high level services = usually concentrated within HICs
... increasingly locating to global hubs within cities
(can also be cities in NEEs)
e.g., London, Paris, Moscow, Hong Kong, Singapore, Rio de Janeiro
low level services = outsourcing in order to take advantage
... HICs can utilise lower labour costs for less vital tasks
e.g., calling up a customer service centre in India
=> has developed global connections and accelerated globalisation
How do flows of services contribute to globalisation
Economical: outsourcing of TNC's, capital, expansion into global markets
Social: migration and flows of labour
... economic migrants, seeking high skilled + high paying jobs in HICs
... can communicate with people in different countries, technology
(may lead to brain drain)
... jobs for people in LICs (low wages, low skilled)
Flows of Information
= governed by the movement of people through migration and by speed of data and communication transfers
... digitalised and satellite tech transformed flows
e.g., phones, internet, live media coverage, on-demand tv, online platform
... becoming increasingly significant, especially in the expansion of knowledge based economy
different types of information flows
- fast broadband and connections
- social media
- real time data
- large databases and archives
fast broadband and connections - flows of information
= allows news and financial information to be transferred almost instantly, allowing people to be more informed about global current events
social media - flows of information
= has allowed people to communication across countries and allows people to experience other cultures, making people across the world more interconnected
e.g., 400 million tweets a day
real time data and data transfers - flows of information
= contribute to the "knowledge economy" (quaternary industry)
... is essentially the industry that requires information to develop rather than products
=> the ability to transfer information has created developments in stock markets, high tech products, the education sector, and many areas of society
large databases and archives - flows of information
can be used for research and education
... the ability to research allows people to seek better employment opportunities
=> creates more global connections and allows online working from home jobs
How do flows of information contribute to globalisation
economical: stock market (real time data), FDI, TNC info based off of databases and archives, cryptocurrency and finance, operation of TNCs in foreign countries (offshoring)
Social: communication, share of ideas via social media, education, NGOs operate based off of databases in LICs, 400 million tweets a day
Cultural: share of ideas and values via the internet and social media, knowledge of current events and news (broadband and connections), research and knowledge of other cultures (databases and archives)
Political: increased communication between countries, news and and current affairs to base geopolitical ideas off of,