MOD 10 - Inflammatory and Metabolic Disorders
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Types of Inflammatory Disorders
osteomyelitis
osteoarthritis
rheumatoid arthritis
gout
ankylosing spondylitis
Common causes of inflammation
infectious pathogens
allergens
cuts, scrapes, and fractures
immune reactions from antibody production
Common Inflammatory Symptoms
tissue swelling: increased plasma → increased pressure contributes to pain
joint swelling: direct result of the accumulation of fluid; also attributes to pain and decreased ROM
pus formation: causes an increase in necrotic tissue as pus composition is mainly dead/necrotic/destroyed cells
ulceration/scarring: a result of the tissue repair
Osteomyelitis (DERTC)
common in metaphyseal area, lower ext, children <5yr
MOI = a secondary infection caused by staphylococcal bacteria
internal bone is usually thickened with irregular patches of sclerosis (honeycomb effect of the internal bone)
good prognosis detected early and treated with antibiotics
bone necrosis, septic arthritis
Osteomyelitis - Pathogenesis
Formation of a sequestrum fragmented necrotic bone due to abscess
Formation of involucrum (new bone)
Reabsorption of sequestrum and formation of new irregular bone around the abscess
Migration of the staphylococcal bacteria via bloodstream
Brodie’s abscess
a chronic bone abscess in the metaphyseal area of the bone
common in children
Osteoarthritis (DERTC)
types of OA
primary: degenerative condition involving the cartilage of weight-bearing bones
secondary: orthopedic deformities or malunion
MOI + associated with continual stress to the joints; normal aging process (appears >40yrs)
narrowing of the joint spaces, osteophytes
pain killers, lifestyle changes, surgery
OA - Pathogenesis
eburnation
cause of osteophytes
bone becoming hard and glossy due to cartilage wear down
result of inflammation and irritation of the periosteum
Heberden’s nodes
a result of osteophyte formation of the bones, which give the hands a bumpy external appearance
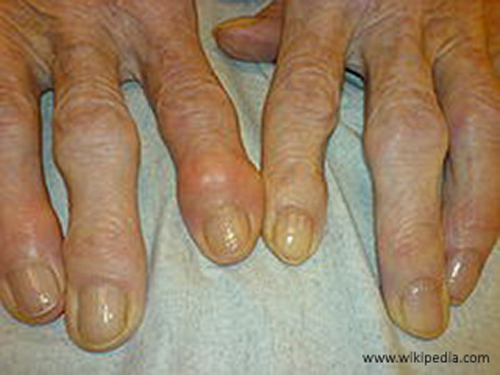
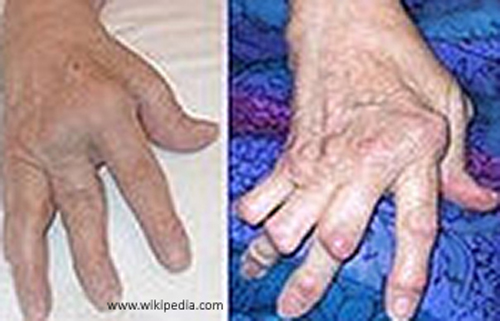
Rheumatoid Arthritis (DERTC)
occurs initially between 30-58 years old; seen most commonly in women 25-45 years old
an autoimmune systemic disease which affects both joints and soft tissue; non-bacterial inflammatory disease
Rarefaction = the distinct appearance of the dense cortex vs. less dense medullary cavity
no cure, but can alleviate symptoms: joint reconstruction, total joint arthroplasty, osteotomy, tendon repair, etc
RA - Pathogenesis
synovial membrane is thickened due to the inflammation process → the exudate results in pannus production (granulation of connective tissue) → which fills the joint space and erodes the articular cartilage → the bony ends erode and eventually fuse to adjacent bone structures = ankylosis
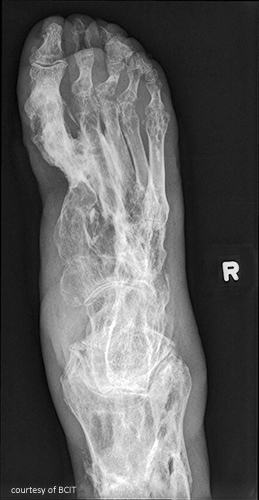
Gout (DERTC)
common in males (30-50yrs) and females post-menopausal; most common for males on diuretics (for CHF)
an inherited metabolic disorder that affects the joint and adjacent bone; polyarthritis
gout arthritis: lytic lesions, over-hanging edges of sclerosis
treatment is to reduce the production of uric acid or promote kidney excretion
uric acid kidney stones due to increased uric acid excretion by the kidneys
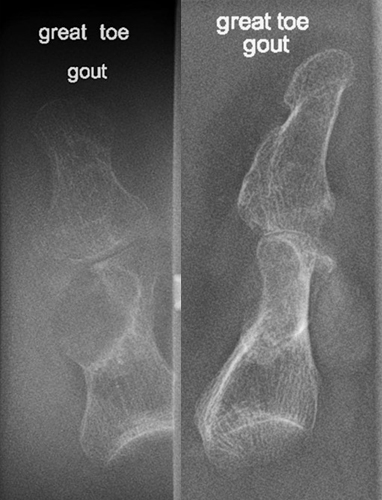
Gout - Pathogenesis
excess uric acid production causes a mass-like deposit in the joints, which then crystallize (tophi) and lead to an acute inflammatory process
symptoms are localized pain, erythema, swelling, and heat due to acute inflammation
Ankylosing Spondylitis (DERTC)
primarily affects the vertebral column; affects more male; begins in the SIJ
progressive inflammatory condition and is polyarthritic
blurred bony margins and narrowing/fusion of SIJ (bamboo like appearance)
no cure; given anti-inflammatory drugs and encouraged to exercise
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Pathogenesis
inflammation causes the SIJ to widen → new bone formation and eventual fusion of the SIJ → progresses sup. invading the vertebral column
bones become very brittle and pts are prone to osteoporosis
Osteoporosis and Osteopenia (DERTC)
osteoporosis = overall bony demineralization due to calcium reduction in the bones; metabolic disease
generalized = bone density is decreased overall; common in post-menopausal women
regional = confined to a specific area of the body due to immobilization (seen within 7-10 days of inactivity)
localized = affects only a small area of the bone due to local disease
osteopenia = the loss of bone density, more common in people >50yrs
MOI = unknown, but five known factors are: hormones, calcium intake, levels of activity, diet, age
rad appearance: bony cortex appears starkly white against the hazy grey trabecula "picture frame pattern"
treatment: supplementation of vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium, and patients are prescribed weight-bearing exercises
Osteoporosis - Pathogenesis
osteopenia has no signs or symptoms
loss of height (kyphosis in the thoracic spine) due to the anterior portion of the vertebra collapsing
back pain
localized or general bone pain
Spontaneous fractures may occur with minimal trauma. FOOSH injuries are commonplace
DEXA Usage
used as screening tools to assess bone quality for osteoporosis
T-score less than -1 = normal
T-score between -1 and -2.5 = osteopenia
T-score less than -2.5 = osteoporosis