Sister Taxa and Homologous Structures
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Sister taxa
Groups of organisms sharing a common ancestor
Shared ancestral character
Character originated in ancestor of two taxa
Homologous structures
Bones in bat wing and human forelimb
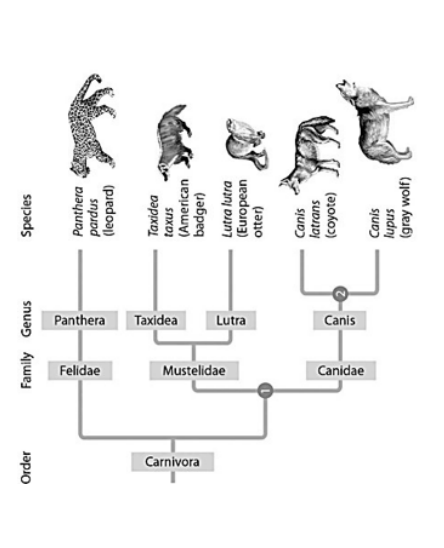
In Figure 20.6 below, which similarly inclusive taxon descended from the same common ancestor as Canidae?
Mustelidae
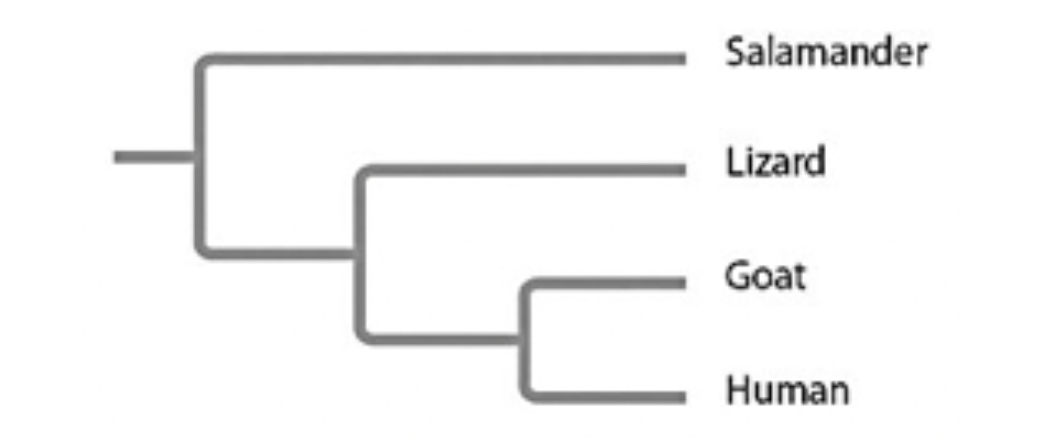
Based on the tree below, which statement is not correct?
Lizards are more closely related to salamanders than to humans.
Evolution is best defined as which of the following?
a change in genetic composition of a population from generation to generation
During a study session about evolution, one of your fellow students' remarks, "The giraffe stretched its neck while reaching for higher leaves; its offspring inherited longer necks as a result." Which statement is most likely to be helpful in correcting this student's misconception?
Characteristics acquired during an organism's life are not passed on through genes.
Which of the following is an example of artificial selection?
a farmer cultivating sweet watermelons
What are adaptations?
inherited characteristics of organisms that enhance their survival and reproduction in specific environments
Two plant species live in the same biome but on different continents. Although the two species are not at all closely related, they may appear quite similar because of
convergent evolution
Natural selection changes allele frequencies because some ________________ survive and reproduce better than others
individuals
Analogous features share ________ function but not ________ ancestry.
similar; common
Which of the following is NOT TRUE about viruses?
They are comprised of cells.
Which situation is not an example of a prezygotic barrier?
Two species of insects produce infertile offspring
A lion and tiger will produce hybrids ___________.
when members of closely related species reproduce
Which of the following is a mechanism of evolution?
Genetic flow
.Which following associated with random changes in the allele frequencies of a population?
Genetic drift
"Organisms evolve on purpose" is:
An inaccurate statement because variation that selection acts on is already in a population and doesn't arise in response to the environmental change.
Genes are_______________.
Basic units of heredity, DNA, Units that determine phenotype.
A animal that is heterozygous for a trait will have
Two different alleles for the same trait
Which of the following descriptions correctly identifies a main structural difference between viruses with envelopes and viruses without envelopes?
Only viruses with envelopes have their contents enclosed by a layer containing lipids
.Which of the following statements best supports the argument that viruses are nonliving?
They do not carry out metabolic processes.
The host range of a virus is determined by whether ________.
the proteins on virus surface can bind with proteins on the host surface
Which of the following characteristics, structures, or processes is common to both bacteria and viruses?
genetic material composed of nucleic acid
Which of the following statements best describes evolution?
Natural selection favors the most abundant trait.
Schooling by fishes is what time of adaptation.
Behavioral
Mimicry of leaves by insects is what kind of adaptation.
Structural
Which is true about microevolution?
Adaptations lead to variation in the same species
Hybrid in viability
Is a post-zygotic isolating mechanism where hybrids fail to reach reproductive maturity
A key difference between acclimation and adaptation is:
Acclimations are reversible changes in phenotype, adaptations are not reversible.
Genetic Drift
Changes in allele frequencies due to the chance events
Random events; not based on characteristics
More likely to impact small populations
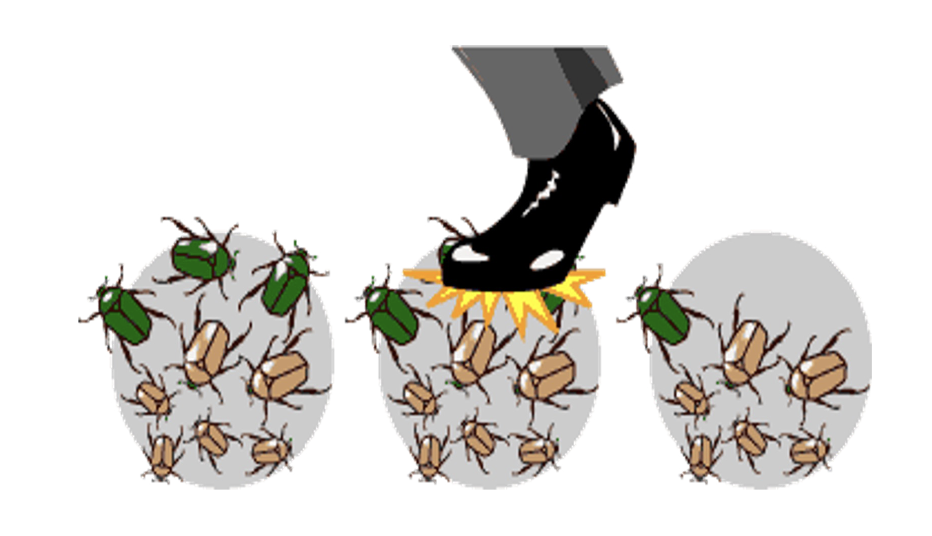
Natural Selection
More adapted individuals survive and pass genes
The more prolific reproduction of individuals with favorable traits that have survived environmental change because of those traits
Increase in frequency of a particular allele
Resulting in decrease of other alleles because individuals with the FAVORABLE allele are more likely to survive and reproduce
Allowing the passing of allele on to their offspring in a particular environment
Variation in a trait
Fitness difference relationship between trait and some aspect od reproduction or survivorship
Heritability of trait must be at least
Gene Flow
The movement of different alleles into or out of a population
Such a movement may be due to the migration of individual organisms that can reproduce in their new population
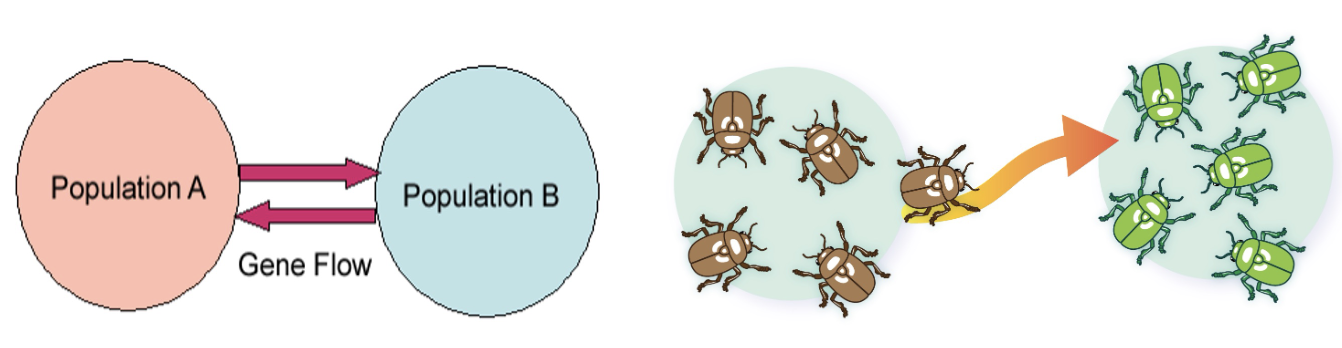
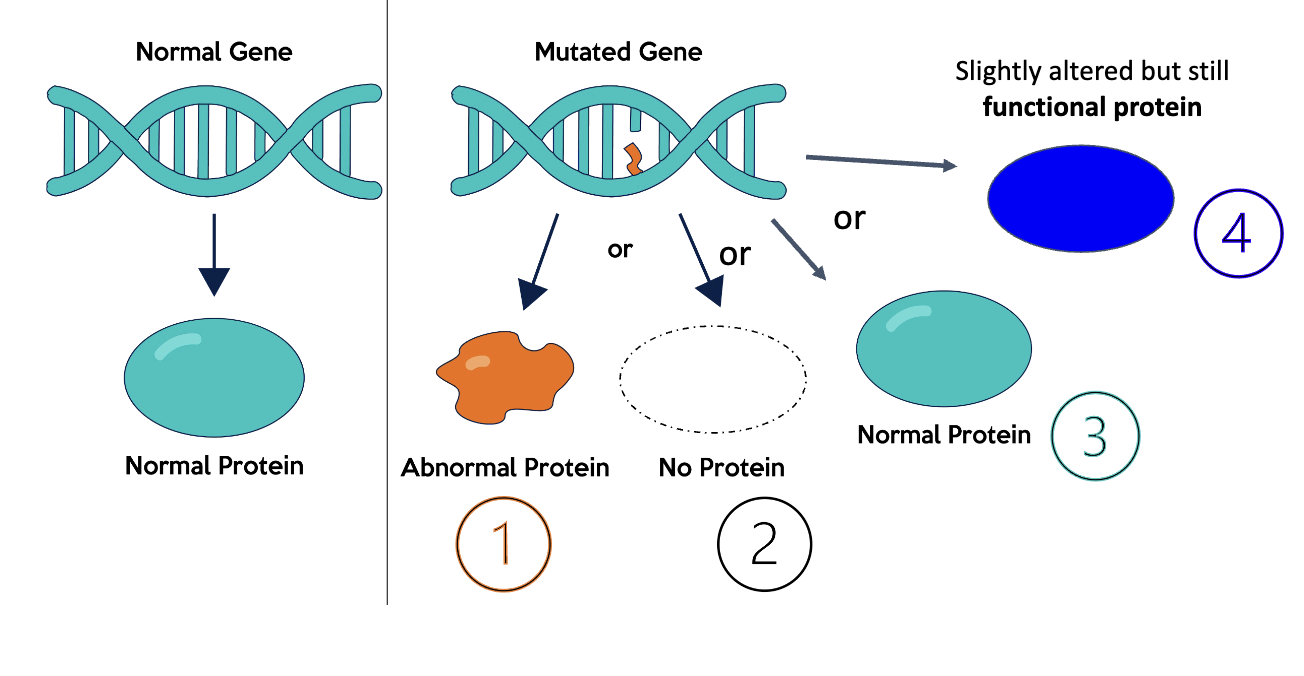
Mutation
A change in DNA; change in the DNA sequence
The ultimate source of new alleles
most common way to introduce genotypic and. Phenotypic variability
Harmful/ unfavorable and will eventually be eliminated
Beneficial and will eventually spread
Neutral- no effect
The usefulness of a mutation is dependent on whether it helps the organism survive and reproduce
Heterozygosity
Heterozygous refers to having different alleles for a particular trait
Gene diversity(heterozygosity), defined as the chance that two DNA segments drawn randomly from a group are different.