mass spectrometery
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Define mass spectrometry
An analytical technique used to identify different isotopes + find the overall relative atomic mass of an element → the mass spectrometer measures the relative mass of isotopes
What are some different uses of mass spectrometry
In environmental analysis
In pharmaceutical / clinical analysis
In forensic analysis
What are the different stages of mass spectrometry
Ionisation
Acceleration
Ion drift
Ion detection
Data analysis
Why is a vacuum required for during mass spectrometry
So there’s no interference from particles in the air
Explain what happens in Stage 1 - electrospray ionisation method
Sample is dissolved in a volatile polar solvent
Injected through a needle at a high voltage
Each particle gains a proton (H⁺) to form 1+ ions
What is the equation for the electrospray method
X(g) + H⁺→ XH⁺ (g)
What are the XH⁺ ions attracted to?
A negatively charged electric plate
Explain the electron impact method for Stage 1
High energy electrons are fired from an electron gun
These knock off an electron from each particle to form 1+ ions
What is the equation for the electron impact method
X(g) → X⁺(g) + e⁻
Explain Stage 2 - acceleration
Positive ions are accelerated by an electric field to a constant kinetic energy
Velocity of the ions depend on the mass of the ion → mass + velocity are inversely proportional
What happens in Stage 3 - ion drift
Ions separate → all have a constant kinetic energy but different velocities - ions with a lower mass take a shorter time to reach detector
Ions drift in a flight tube of a known distance + time it takes for ions to reach detector is measure → time of flight
What does the time of flight depend on?
The ion’s velocity which depend on its mass
What happens in stage 4 - ion detection
Positive ions hit detector (negatively charged plate) + pick up an electron → causes a current to flow
The current produced in ion detection depends on what?
The abundance of ions hitting the detector → greater the abundance, the bigger the current - current is directly proportional to abundance
What happens in Stage 5 - data analysis
Detector is linked to an amplifier + then to a recorder which converts the current into a peak which is shown in a mass spectrum
Height of peak is proportional to size of current generated, and therefore proportional to the abundance of that ion
Peaks are displayed on a plot of mass / charge (m/z)
Why is it necessary to ionise molecules when measuring their mass in a mass spectrometer
Ions are accelerated by an electric field
Only ions will create a current when hitting a detector → can be detected
What are the units for ‘time of flight’ calculations
time of flight
length of flight tube / distance
velocity of particle
mass of particle
kinetic energy of particle

How do you convert the mass number into kg
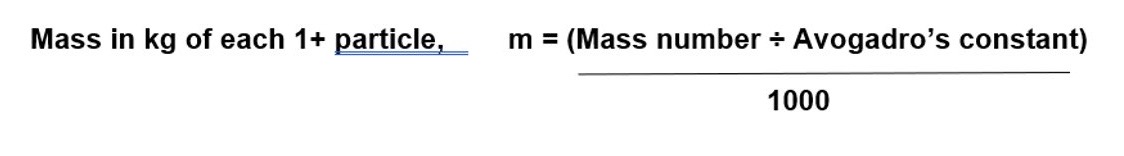
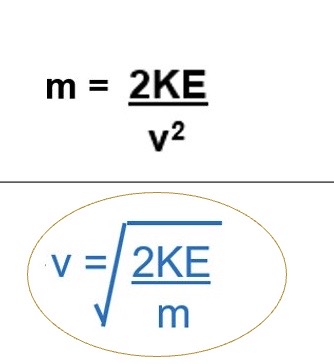
What is the equation for kinetic energy
½ x mass x (velocity)²
Rearrange the kinetic energy formula to make:
m the subject
v the subject
What is the equation for velocity
velocity = distance / time


Explain how to find the mass of an ion
Multiply the number of protons by its mass
Do the same for neutrons + electrons
Sum of all (mass x no.)
What is the formula you use if you’re calculating time or mass of an isotope and are only given the time and mass of another isotope

What are mass spectra
Graphs which give the following information about the positive ions produced from a sample in the mass spectrometer
m/z of each ion → gives mass of each isotope as ion has a single positive charge
abundance of each ion → shown above each peak
What do we use as the standard when measuring relative atomic mass of all other elements?
Carbon - 12 → its relative mass is given 12 exactly
What is the equation for calculating relative atomic mass, using data from mass spectrometer?
Relative atomic mass should always be rounded to..
1 d.p → just like in the periodic table unless specifically asked
Masses of individual isotopes should always be to the nearest…
whole number


During electron impact ionisation, what can happen to covalently bonded molecules?
They can have their bonds broken + break into fragments → this is called fragmentation
True or false? Fragmentation occurs to all molecules
False → only occurs to some
So because fragmentation only occurs to some molecules, what does this mean for the molecules that it doesn’t occur to?
They will remain intact + just gain a positive charge → these unfragmented + positively charged molecules give us the peak with the greatest m/z value which is called the molecular ion peak
What does the peak with the greatest m/z value tell us about the sample during electron impact ionisation
The sample’s Mr
What is the fragmentation like during electro spray ionisation?
Very little occurs so there are a lot less peaks in a mass spectrum
With electrospray ionisation, what is the Mr of the sample equal to + why?
To the peak with the greatest m/z value minus one because during electrospray ionisation, a proton is gained which has a mass of 1
Both ___ and ___ exist as a pair of isotopes
Bromine
Chlorine
Bromine contains what isotopes + in what ratio?
79Br and 81Br → 1 : 1
Chlorine contains what isotopes?
35Cl and 37Cl → 3 : 1
The existence of these isotopes can be seen in…
the mass spectrum of any molecules that contain these atoms → their presence results in multiple molecular ion peaks
Use probability to calculate the ratio of the abundances for these peaks
Use probability to calculate the ratio of the abundances for these peaks
What are the number of molecular ion peak + the ratio of peaks for :
1 chlorine atom
2 chlorine atoms
1 bromine atom
2 bromine atoms