ECON Chapter 5
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Elasticity and its application
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
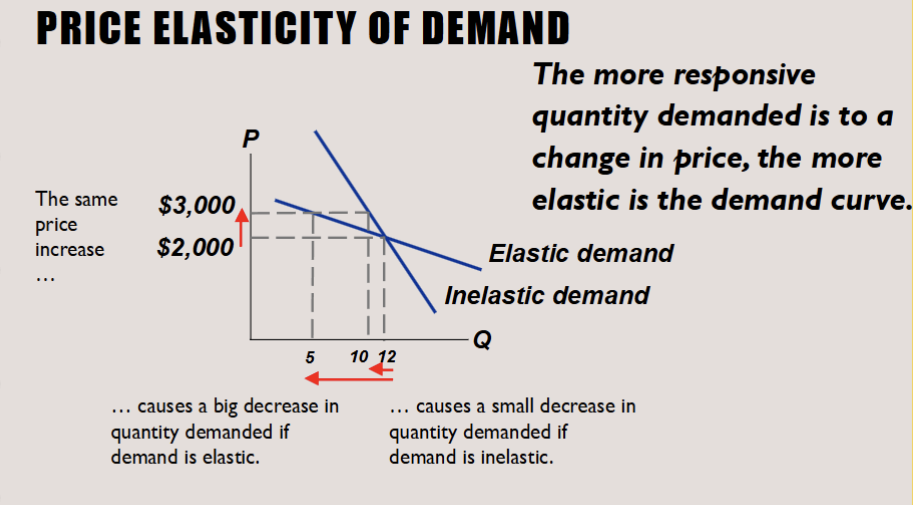
Demand is elastic
How quantity is sensitive to a change in a price
Elastic demand (PED > 1): Quantity demanded changes by a larger percentage than the price (consumers are very responsive to price changes).
Example:
Luxury items: Designer handbags, sports cars, or high-end electronics.
If the price of a luxury car increases 10%, many buyers will just not buy it → demand drops significantly.
Fast food vs. home cooking: If the price of McDonald’s burgers rises, people can easily switch to other restaurants or cook at home.
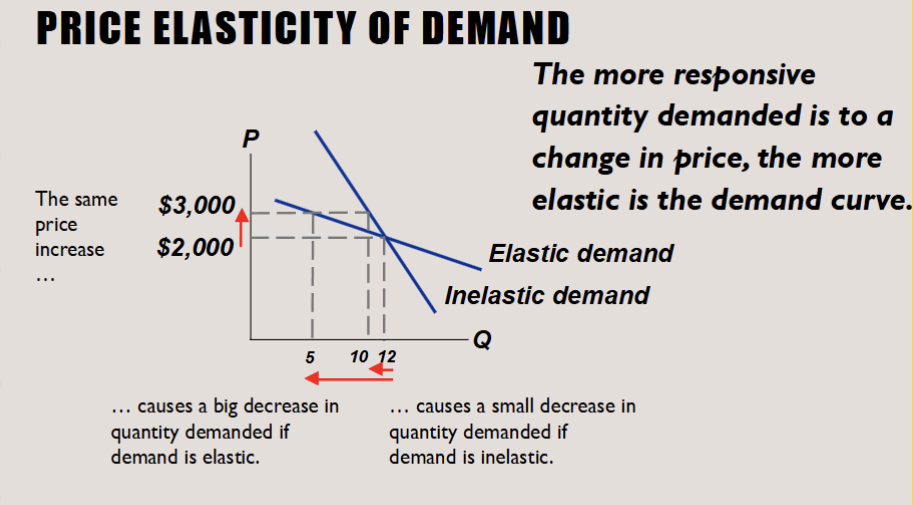
Demand is inelastic
Inelastic demand (PED < 1): Quantity demanded changes by a smaller percentage than the price (consumers are not very responsive to price changes).
Example:
Necessities: Gasoline, electricity, basic medicines (like insulin).
Even if gas prices go up 20%, most people still need to drive to work or school, so demand doesn’t drop much.
Basic groceries: Salt, bread, milk.
If salt’s price doubles, people still buy nearly the same amount because they don’t use very much anyway.
Demand has unit elasticity
Unit elasticity= 1
Example:
Suppose movie tickets cost $10, and 100 tickets are sold → total revenue = $1000.
If price rises to $11 (+10%), and ticket sales fall to 90 (–10%), total revenue = $990.
If price falls to $9 (–10%), and sales rise to 110 (+10%), total revenue = $990.
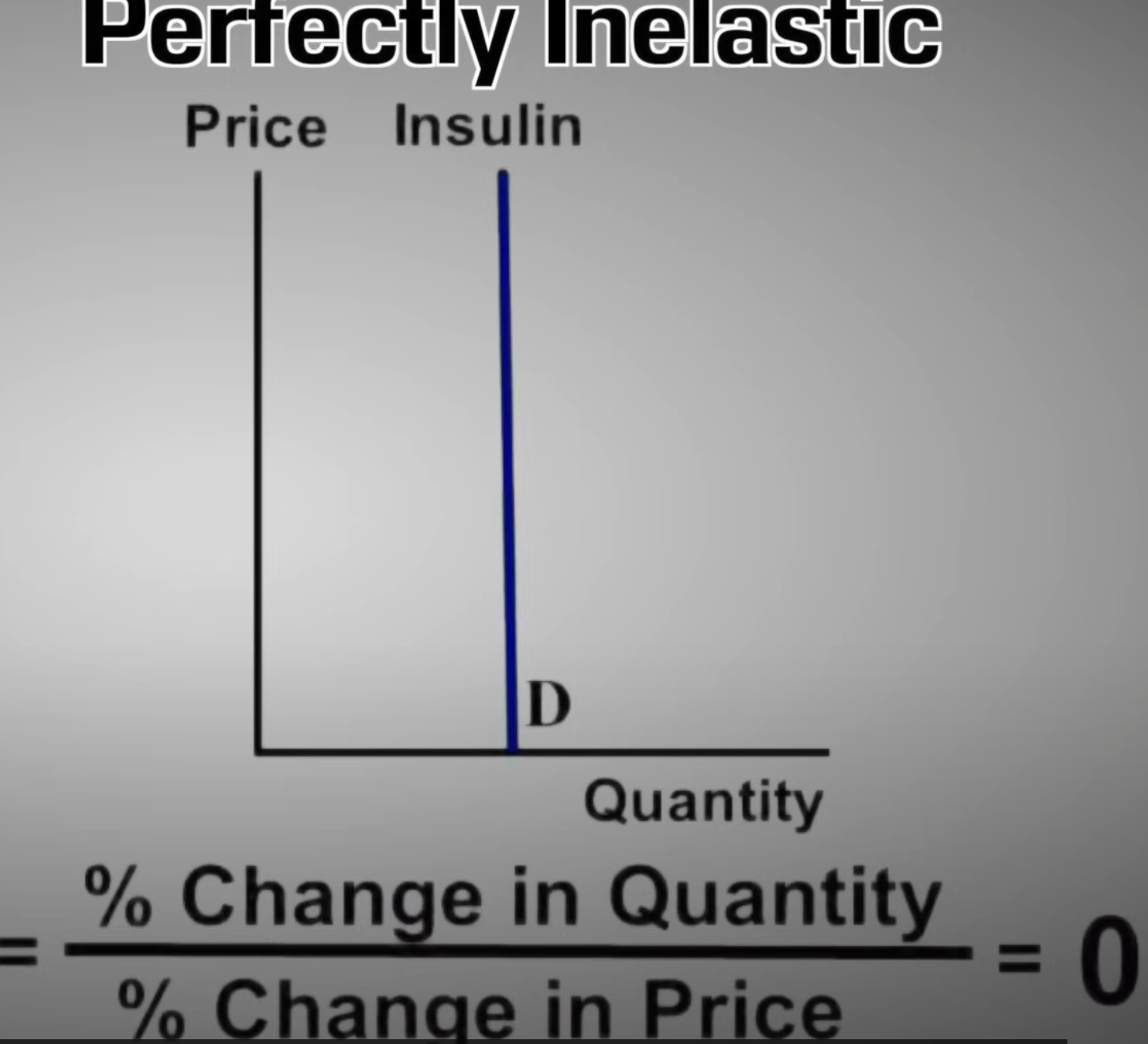
Perfectly Inelastic
increase in price has no effect on quantity
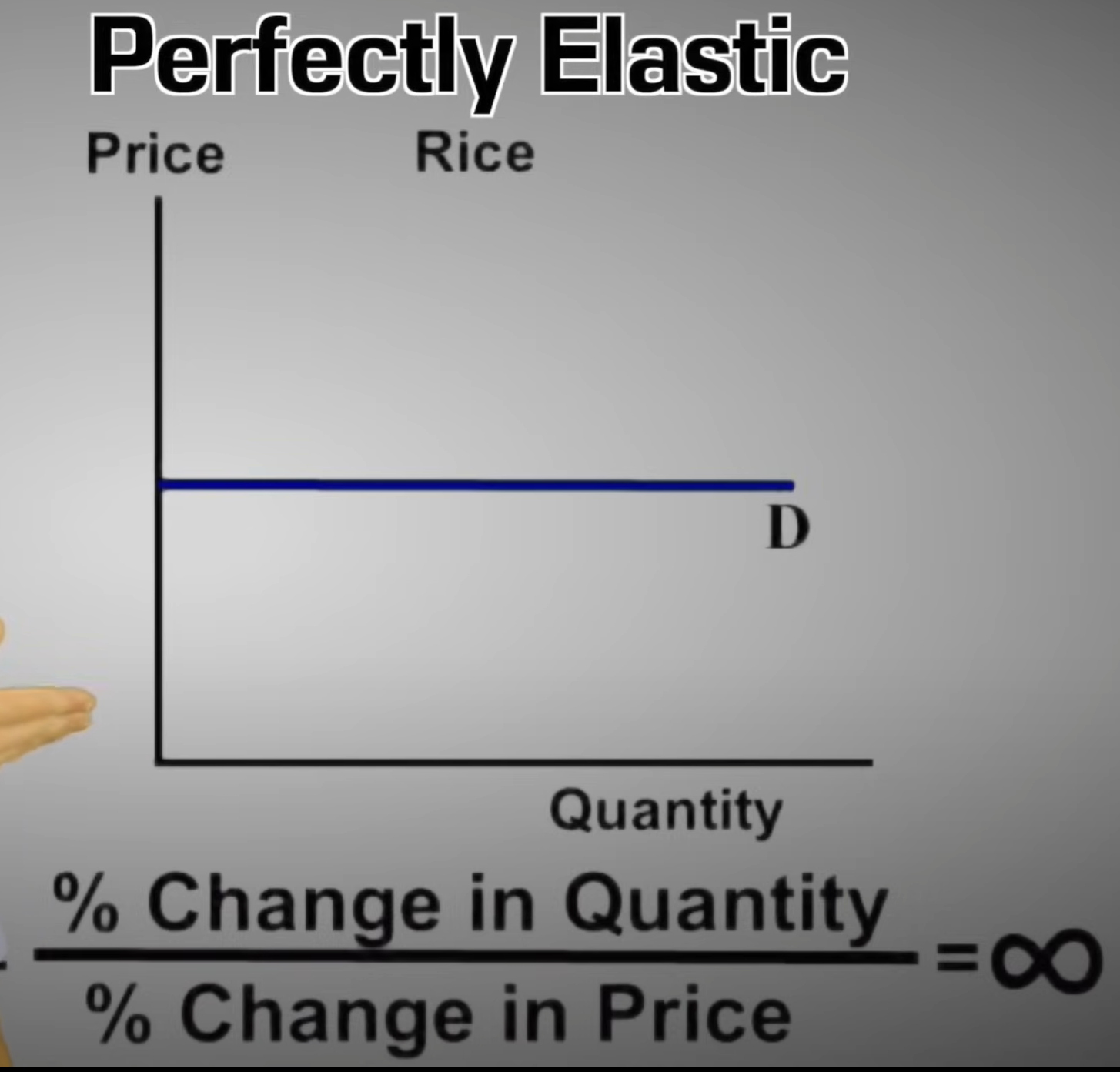
Perfectly Elastic
a quantity demanded or supplied changes infinitely in response to even the smallest change in price
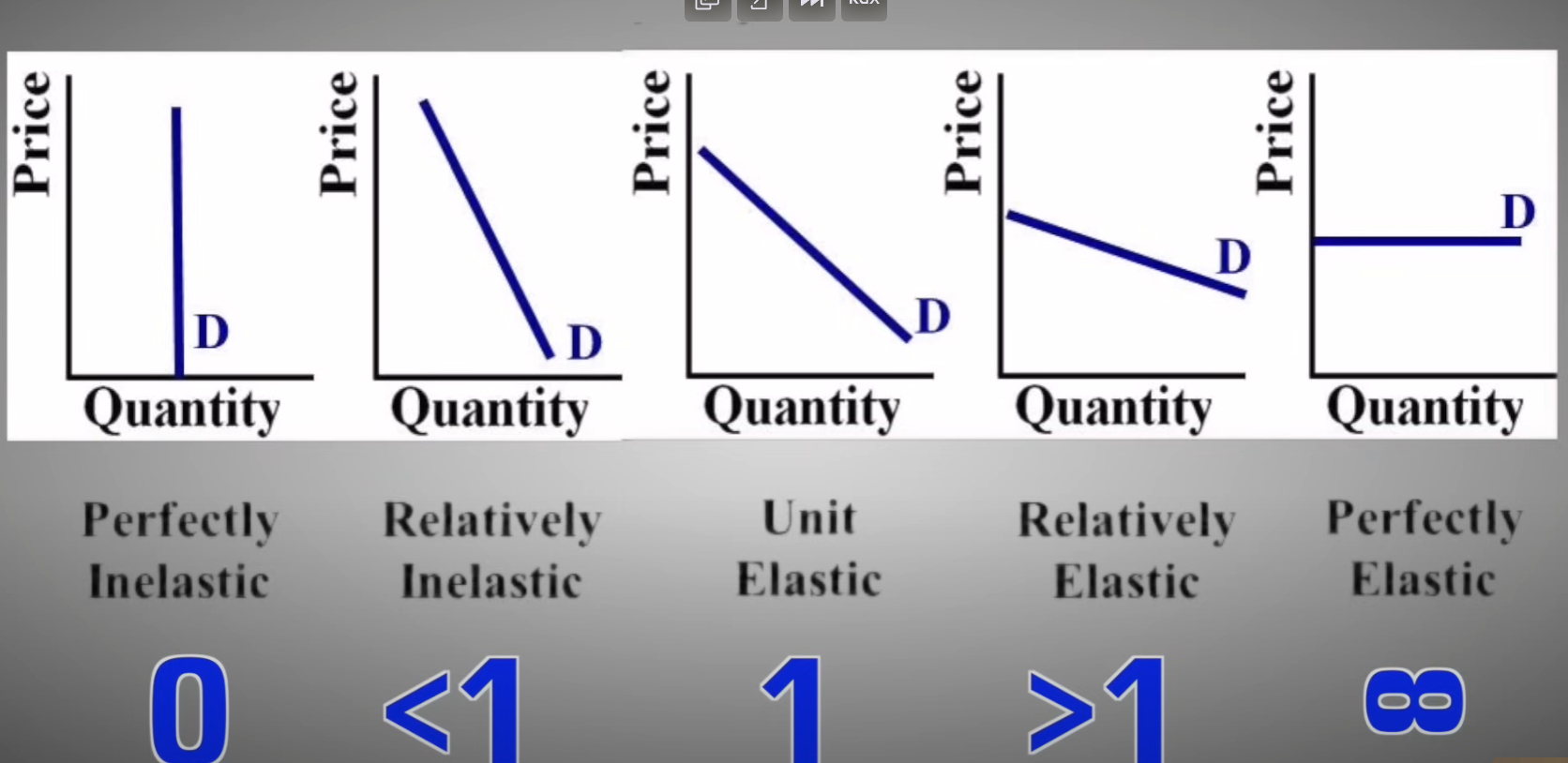
summary
,
Elasticity Rule
Slope ≠ Elasticity
Slope of a demand curve: Measures the change in price relative to the change in quantity. It depends on the units (e.g., dollars vs. cents, gallons vs. liters).
Elasticity: Measures percentage changes (relative responsiveness), so it’s unit-free
The rule:
If two demand curves pass through the same point (say they both cross at the same price and quantity), the one that is flatter (less steep) is more elastic.
Why?
A flatter curve means that for the same percentage change in price, there’s a larger percentage change in quantity demanded.
A steeper curve means quantity doesn’t change much when price changes → more inelastic.

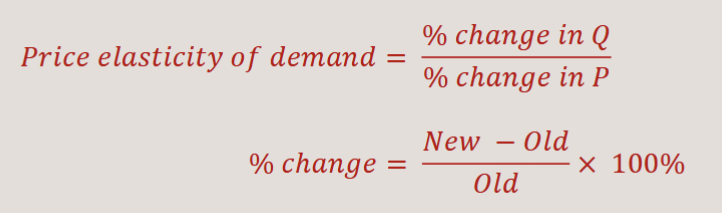
Formula of Price Elasticity of Demand
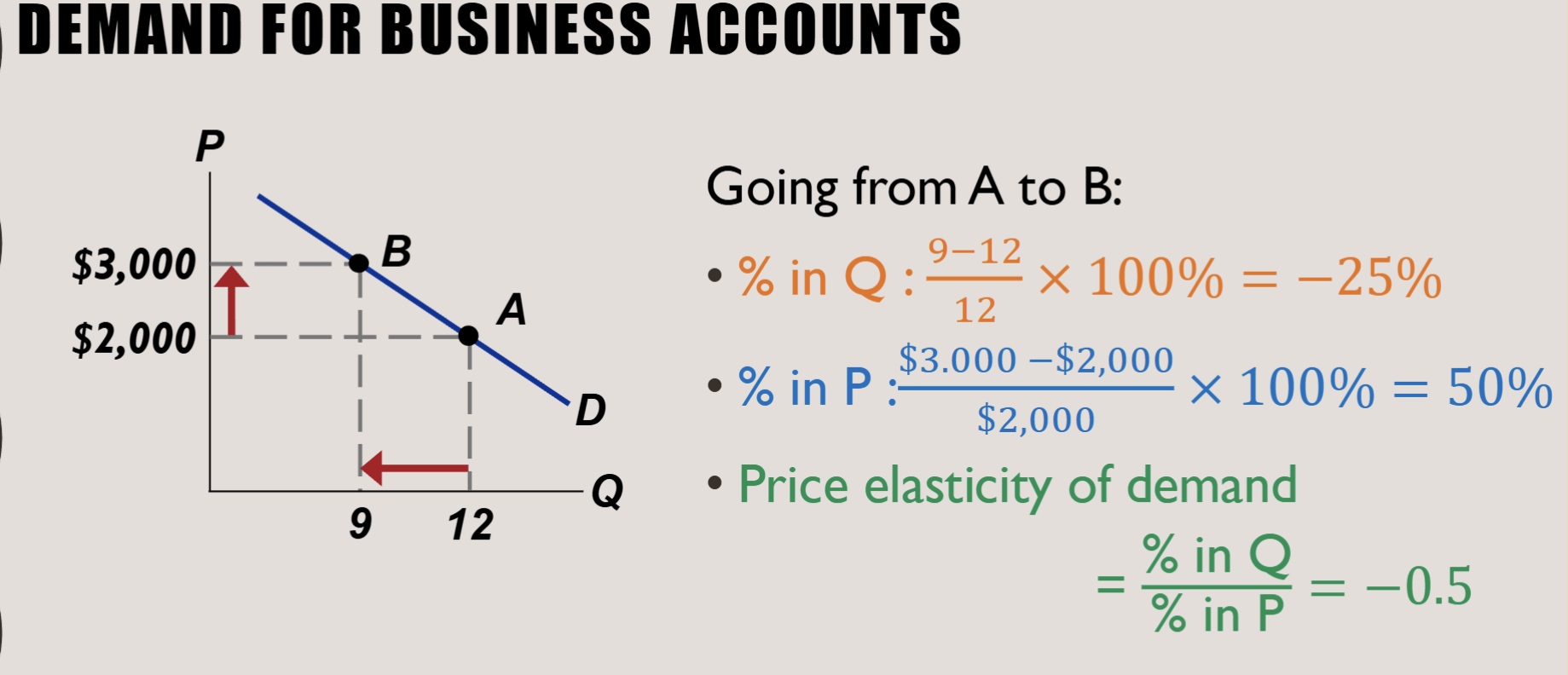
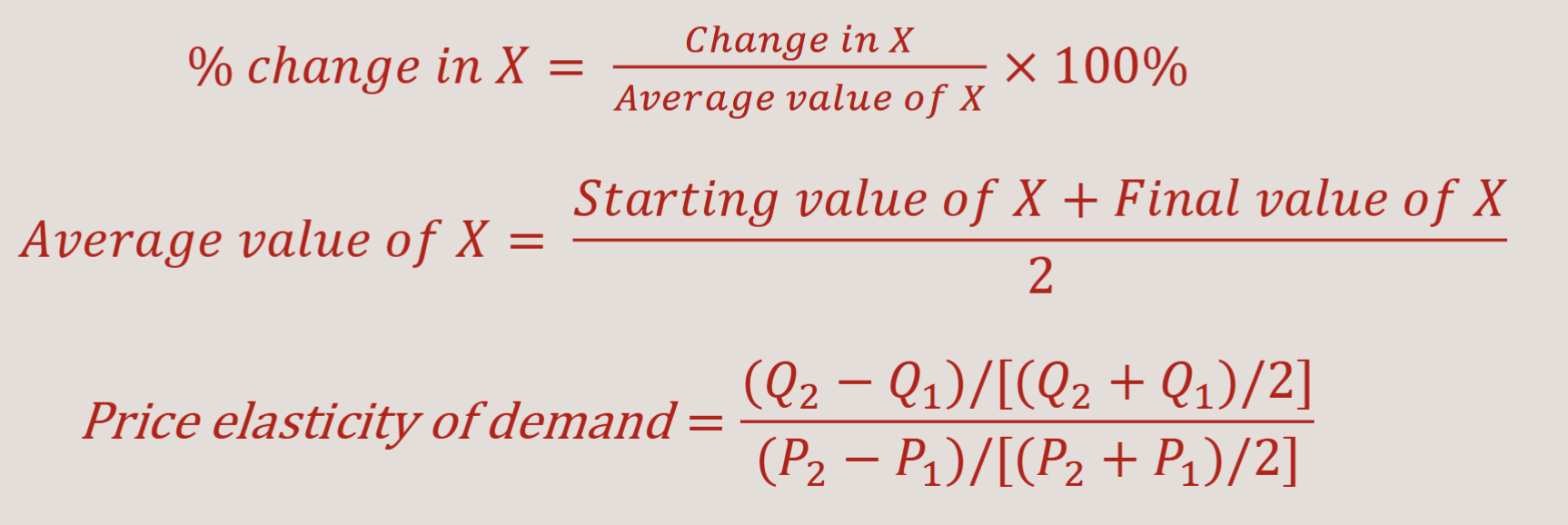
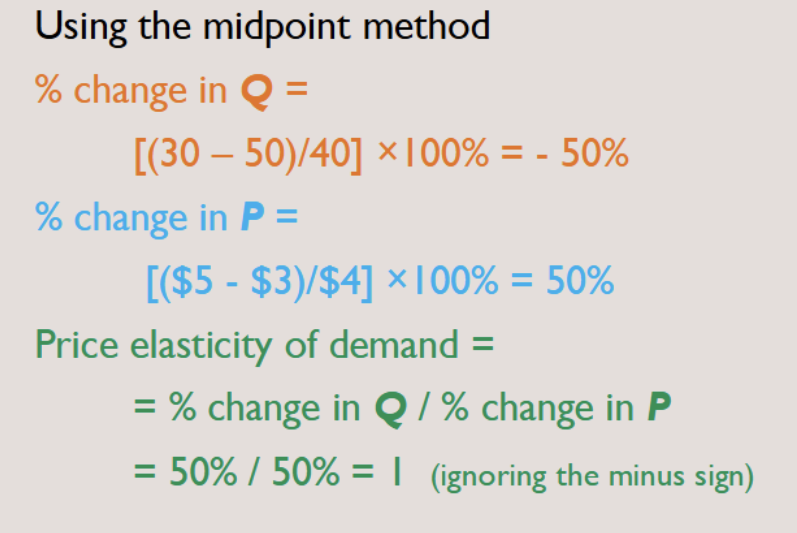
Midpoint Formula:
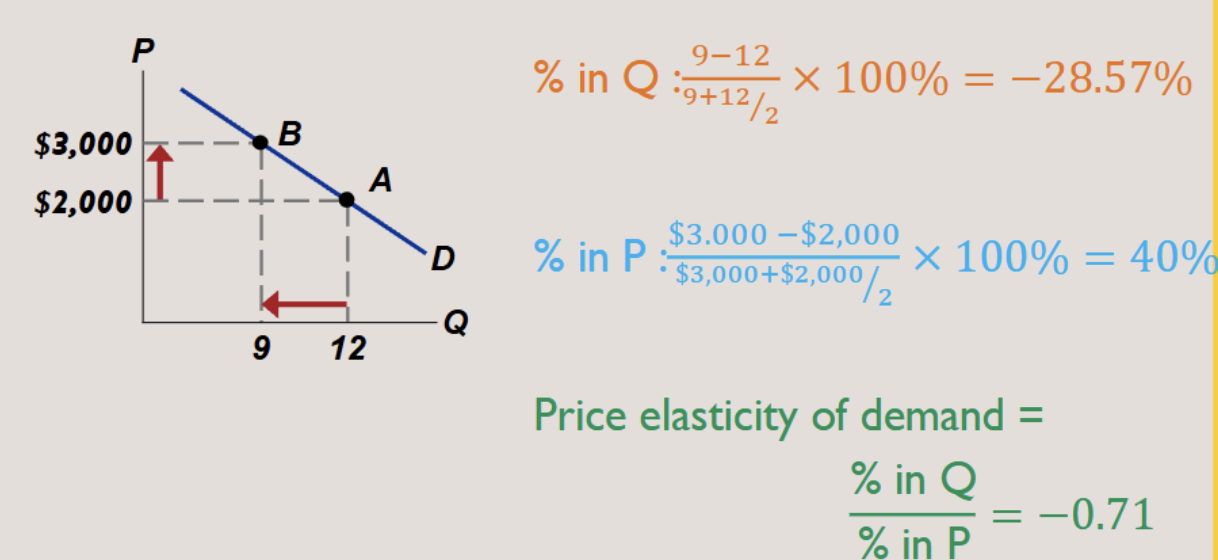

More midpoint formula example
Demand Determinants for Elasticity
Price elasticity is higher when close substitutes are available (items that can replace them)
Price elasticity is higher for narrowly defined goods than for
broadly defined ones
Price elasticity is higher for luxuries than for necessities.
Price elasticity is higher in the long run.

PRICE ELASTICITY AND TOTAL REVENUE
For a price increase, if demand is elastic
▪TR decreases: the fall in Q is proportionately greater
than the rise in P.
▪ The extra revenue from selling units at a higher price is smaller than the decline in revenue from selling fewer units.
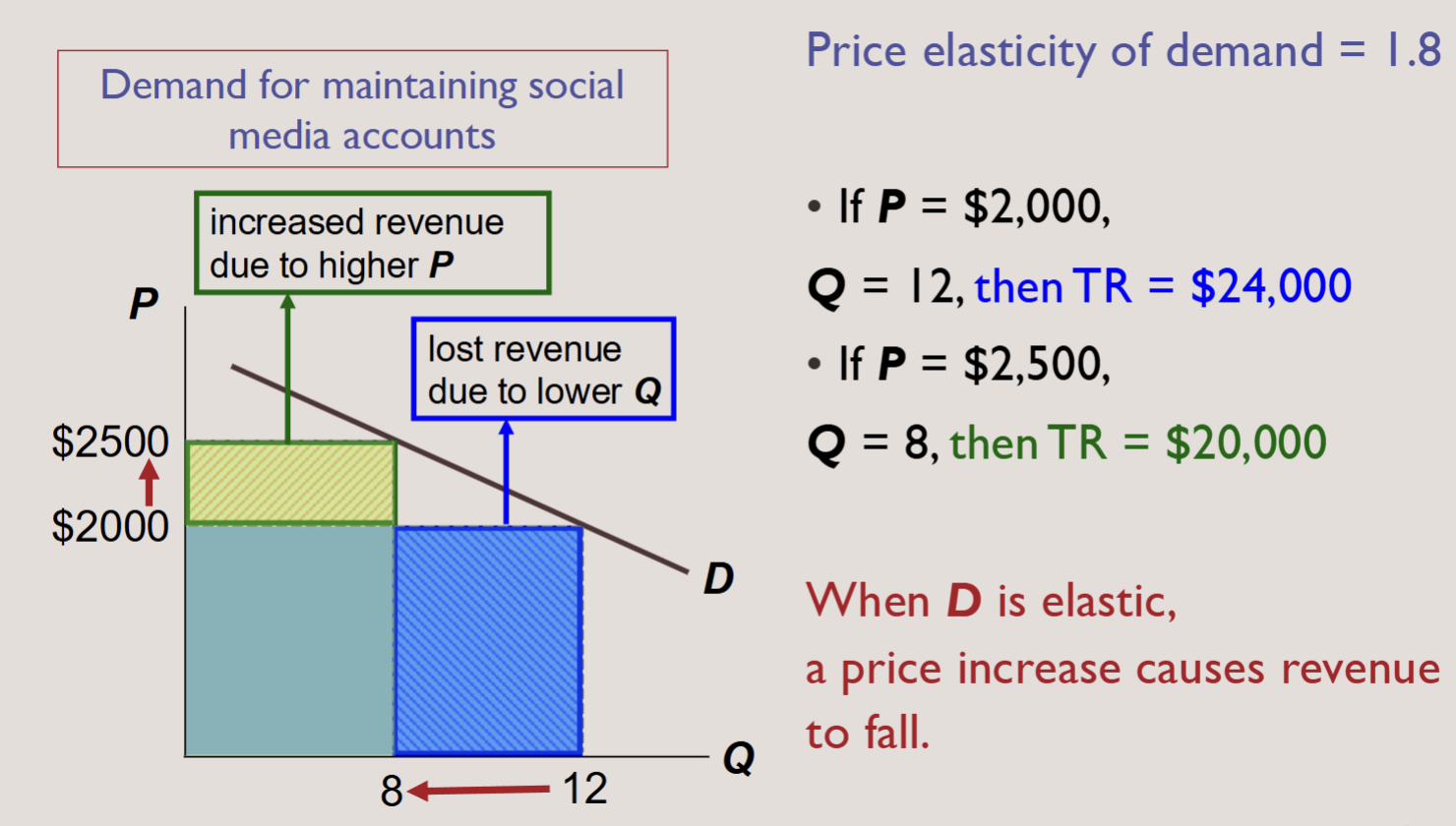

PRICE INELASTICITY AND TOTAL REVENUE
For a price increase, if demand is inelastic
▪TR increases: the fall in Q is proportionately smaller than the rise in P.
▪ The extra revenue from selling units at a higher price more than offsets the decline in revenue from selling fewer unit
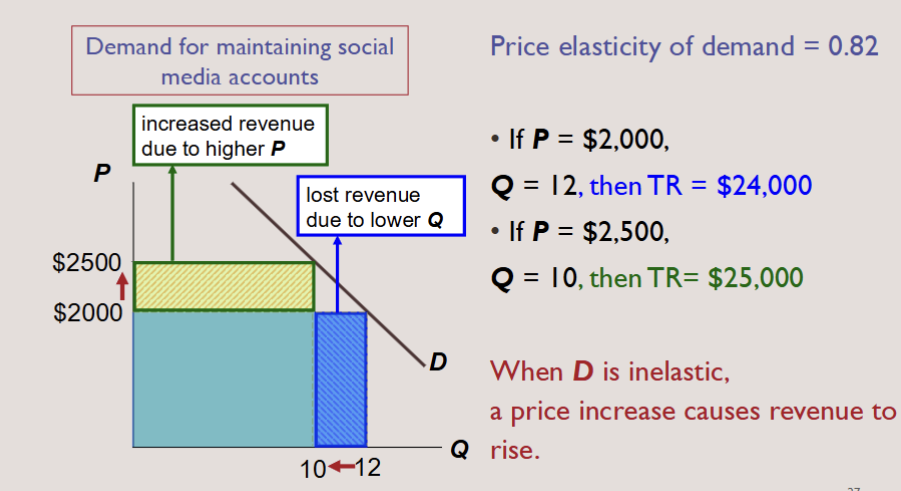
PRICE UNIT ELASTIC AND TOTAL REVENUE
When demand is unit-elastic, the quantity effect equals the price effect.
– So an increase in price exactly balances the reduction in the quantity demanded.
• In this instance, total revenue doesn’t change.
Income Elasticity of Demand Formula
-Normal goods: income elasticity > 0
-Inferior goods: income elasticity < 0
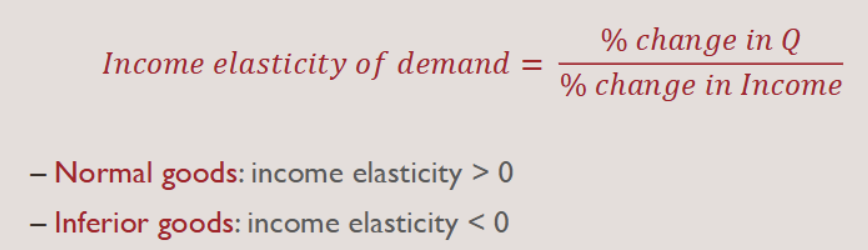
Cross price elasticity of demand
How much the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good
1) substitutes:
cross-price elasticity of demand is positive .
An increase in the price of one brand of cookies will increase the demand for other brands.
2) complements:
cross-price elasticity of demand is negative.
An increase in the price of milk causes a decrease in demand for Oreos.

PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY
Elasticity of supply captures the sensitivity of quantity supplied to changes in price.
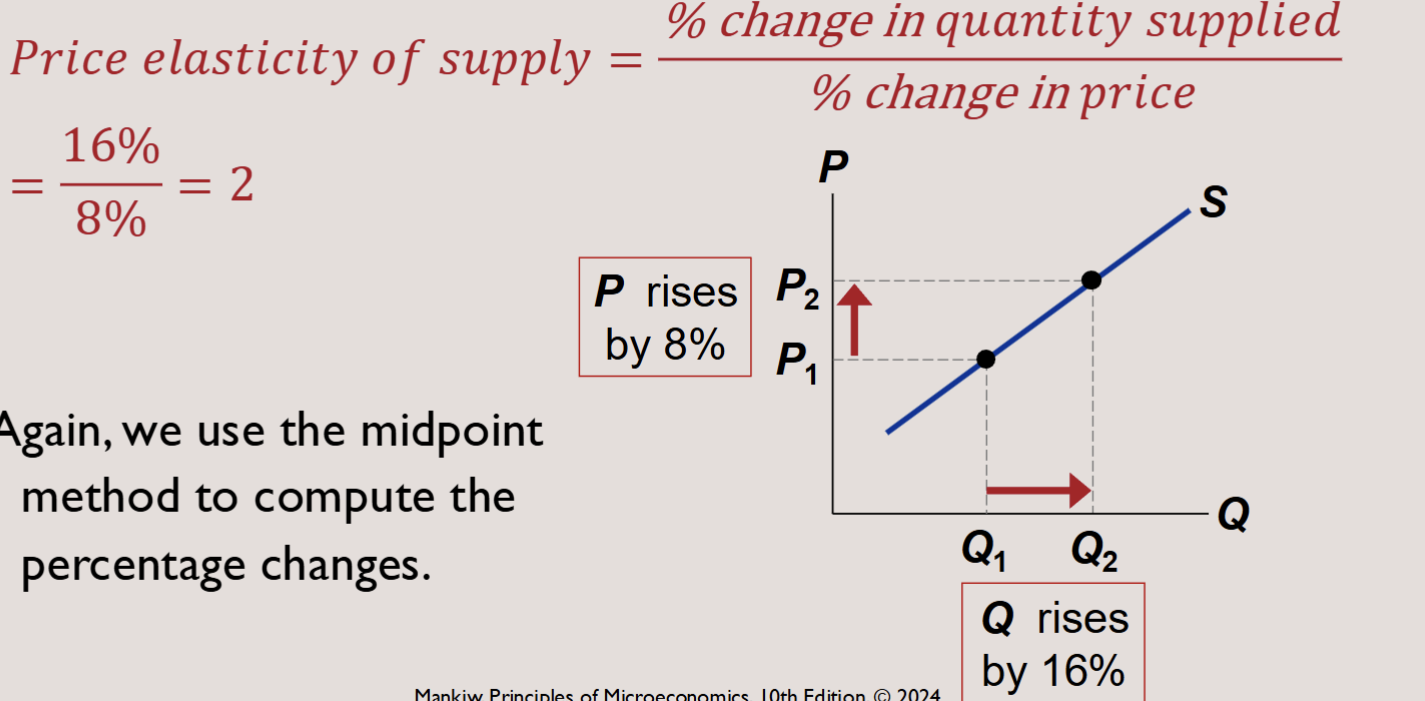
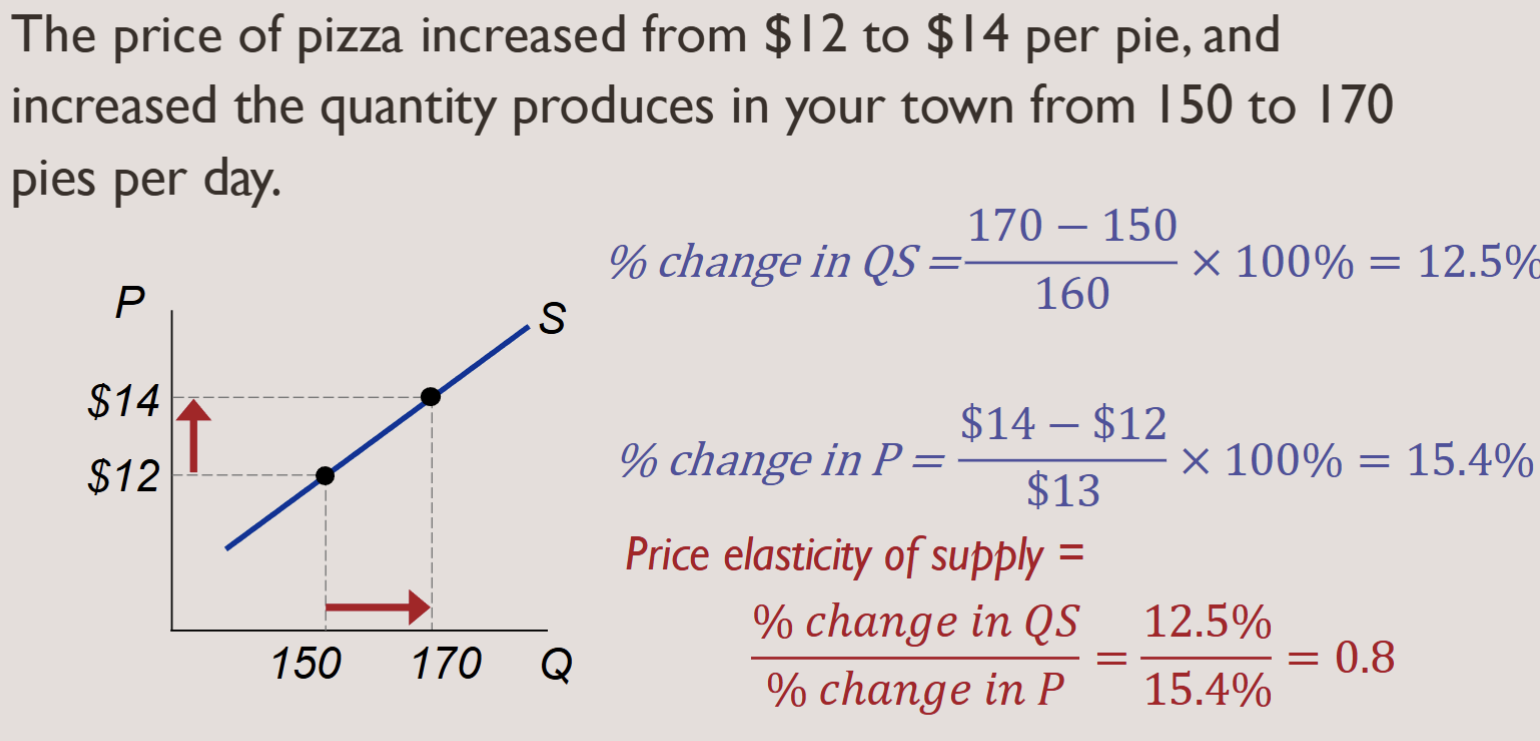
PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY Example
Supply unit elastic/elastic/inelastic
Supply is unit elastic
– Price elasticity of supply = 1
Supply is elastic
– Price elasticity of supply > 1
Supply is inelastic
– Price elasticity of supply <1
Supply unit elastic/elastic/inelastic determinants
Greater price elasticity of supply
– The more easily sellers can change the quantity they produce
Price elasticity of supply is greater in the long run than in the short
run
– In the long run: firms can build new factories, or new firms may
be able to enter the market