Exam 1
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
biomechanics
the study of the mechanics of living things
- combines biology and physics
three ways to prevent injuries
1) identify risk factors
2) analyze movement to calculate risk
3) understand how forces interact
ways to minimize biomechanical stressors
identify and mitigate stressors associated with
- manual handling
- lifting
- pushing
- pulling
- any physical movement
ways to prevent musculoskeletal disorders
identify risk factors
- repetitive motions
- forceful exertions
- awkward postures
- prolonged static loading
Newton's first law of motion
an object will remain at rest of in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force
- "law of inertia"
ex) starting a sprint or balance while standing
Newton's second law of motion
the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass
- "law of acceleration"
- F = ma
ex) jumping or throwing a ball
Newton's third law of motion
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. when one object exerts a force on another, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first
- "action, reaction"
ex) walking, running, or swimming
force
a push or pull, exerted by one object on another
- interactions between objects that cause change in motion or shape
- characterized by magnitude/strength, direction, and point of application
- external (gravity, moving cars) or internal (pull of a muscle, ligamentous resistance)
- F = ma
contact force
where two objects physically touch each other
non-contact forces
where two objects do not physically touch each other
ex) gravitational or electromagnetic forces
types of forces
- gravity
- muscle force
- ground reaction force
- joint contact force
- frictional force
- tension and compression
- shear force
- fluid force
ground reaction force (GRF)
the forces that act on the body as the result of its interaction within the ground
- equal and opposite in direction and magnitude to the force the body applies to the ground
ground reaction force vector
the vector representing ground reaction force
- where it passes in relation to the body indications what "moment" will occur at that joint
tension force
collinear forces acting in opposite directions to stretch or pull apart
compression force
loading, collinear forces acting in opposite directions
- the act of pressing together
shear force
a force acting parallel to the surface of an object
torsion force
a force that twists a body
effects of force on the body
- motion
- stability
- injury risk
- performance
- structural adaptation
acceleration of gravity
9.8 m/s^2
kinematics
descriptors of motion
ex) joint angle, velocity, planes of motion, direction
kinetics
forces causing motion
ex) ground reaction force, force of bat on ball
moment
the measure of the tendency of a force to produce rotation about an axis (an instant of torque)
- the rotational effect of a force around an axis or pivot point
- moment = force x distance
- unit is Newton-meters (Nm)
moment arm
shortest distance from an action point (end of the lever) to the joint center
torque
measure of the degree to which a force causes an object to rotate about an axis
- T = Fd
- rotational force that produces torsion or rotation around an axis
- interchangeably with moment
- used mostly with joints and muscles
first class lever
two forces on either side of the axis with the fulcrum in the middle
- see-saw
second class lever
resistance force is in the middle with effort force and fulcrum on either side
- wheelbarrow
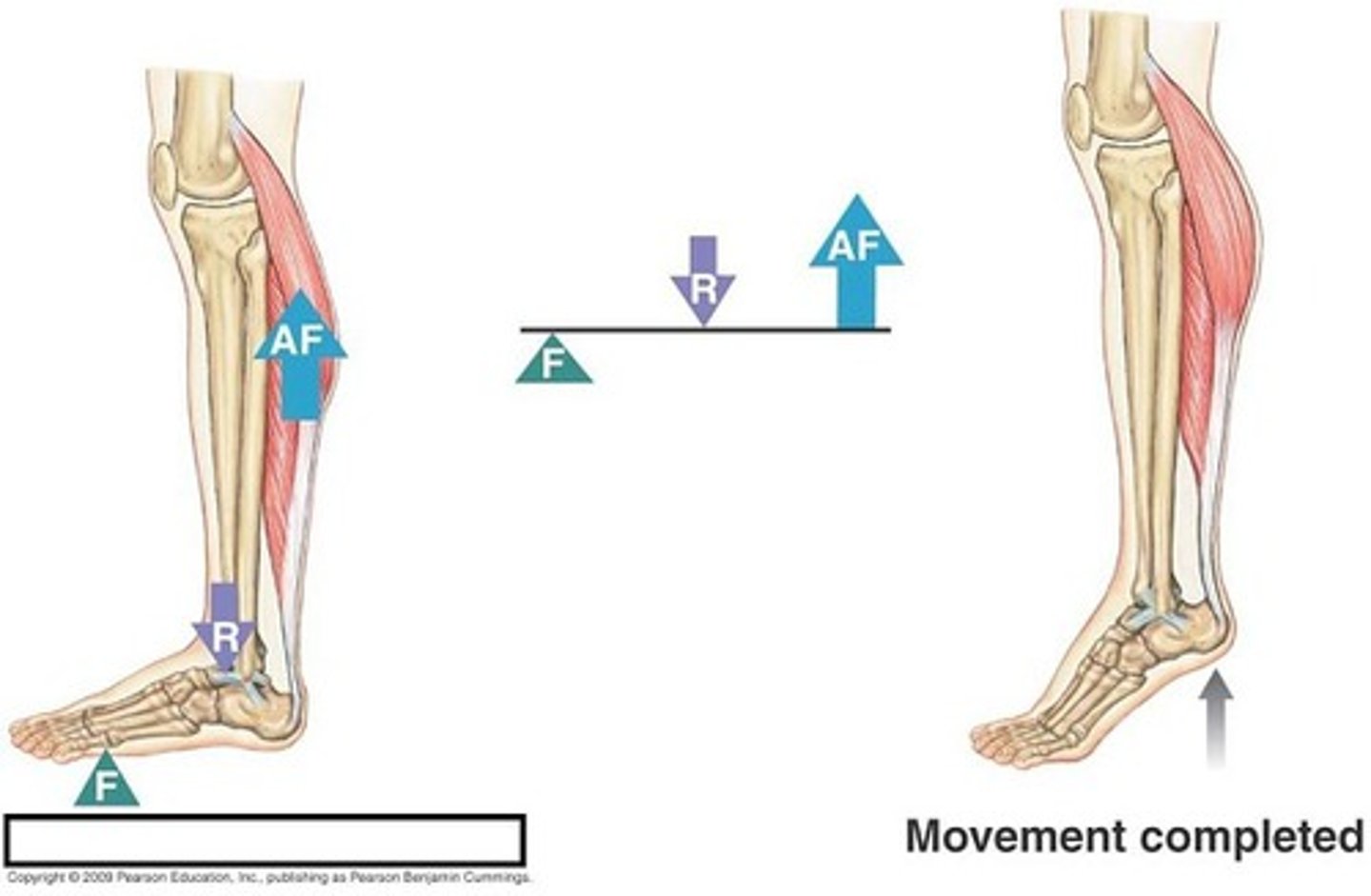
third class lever
both effort force and resistance force are on the same side of the fulcrum
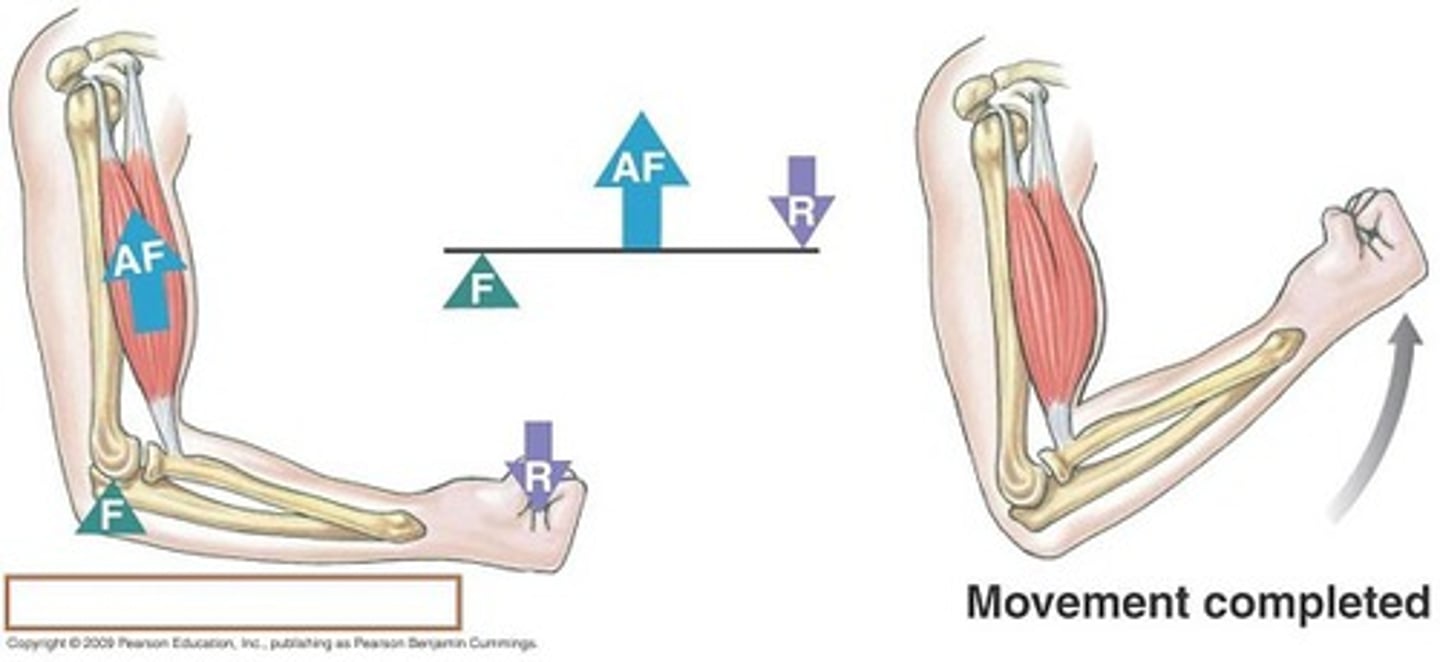
kinetic chain
a series of rigid links or segments (bones or body parts) interconnected by a series of joints
open kinetic chain
a kinetic chain in which one end of the chain is "free" to move in space so that one segment may occur independently of the other segments
closed kinetic chain
a kinetic chain in which the end of the chain is fixed (on the ground, on a door handle, etc). motion of one link in the chain will cause motion at all other joints
center of mass
single point of a body about which every particle of its mass is equally distributed
- the point at which the force of gravity may be considered to act
- approximately 1/2" anterior to S2
line of gravity
action line of the force of gravity, vertically acting on the center of mass
base of support
the area formed under the body by connecting with one continuous line all points in contact with the ground
balance
maintaining the line of gravity within the base of support
stress
the intermolecular resistance within a body to the deforming actions of an outside force
- stress = force / area (N/m^2)
strain
deformation, or change in dimensions of a body as a result of the application of a force
stress strain curve
E = Young's modulus (modulus of elasticity) = slope of the curve (stress over strain)
- material's stiffness
- the higher the modulus of elasticity, the less deformation under load
elastic phase
material has undergone force, but still returns to its original shape after removing the force
plastic phase
material has undergone force, and can no longer return to original shape after removing the force
- material has "yielded"
yield strength (point)
the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically
Wolff's law
bone strength increases and decreases as the functional forces on the bone increase and decrease
remodeling
mechanical strain (deformation) causes the bone to change in shape and strength
avulsion fracture
tendon or ligament pulls a small chip of bone away from the rest of the bone
- tensile loading
- tendons are stronger in tension than bones
ex) explosive throwing or jumping
five functional units of the upper extremity
1) shoulder girdle
2) shoulder joint
3) elbow
4) wrist
5) hand
shoulder girdle
clavicle and scapula
- articulates with the torso, humerus, and sternum
- sternoclavicular joint
- acromioclavicular joint
- coracoclavicular joint
motions at the shoulder girdle
- elevation
- depression
- upward rotation
- downward rotation
- protraction
- retraction
shoulder girdle elevation
levator scapulae and upper trapezius
shoulder girdle depression
pectoralis minor
shoulder girdle upward rotation
lower trapezius
shoulder girdle downward rotation
rhomboids
shoulder girdle protraction
serratus anterior
shoulder girdle retraction
rhomboids and middle trapezius
stabilizers
large muscles to protect unstable joint
- very small areas of articulation
- lots of mobility
- creates a stable base for the other muscles to pull from
movers
muscles that move the body
- shoulder girdle initiates most upper extremity activities
ex) over arm throwing - after torso motion, shoulder protraction initiates and contributes to speed of the throw
shoulder joint
articulation of the glenoid fossa with the head of the humerus
- glenohumeral joint
- very unstable due to shallow socket --> depends on rotator cuff muscles for stability
- most compromised joint in the body
motions at the shoulder joint
- flexion
- extension (deltoid)
- abduction (supraspinatus)
- adduction (infraspinatus)
- horizontal abduction
- horizontal adduction
- internal rotation
- external rotation (deltoid)
rotator cuff muscles
S - supraspinatus
I - infraspinatus
T - teres minor
S - subscapularis
- all originate on scapula and attach on head of humerus
- stabilizer for shoulder joint
shoulder joint movers
- deltoid
- coracobrachialis
- pectoralis major
- latissimus dorsi
- teres major
- biceps
- triceps
shoulder joint abduction
occurs at the glenohumeral joint, acromioclavicular joint, sternoclavicular joint, and scapulothoracic joint
- the first 120° is glenohumeral abduction (last 60° is all scapular upward rotation)
- at a certain point, the clavicle stops elevating and posteriorly rotates
supraspinatus
first move of shoulder abduction
- gets the humerus rolling in the glenoid fossa before the deltoid takes over
rotator cuff injuries
rotator cuff impingement syndrome or subacromial impingement syndrome
- almost always supraspinatus (location under the acromion)
- more about the tendons than the muscles --> tendons become stretched and can no longer hold the humeral head in the glenoid fossa, deltoid muscle pulls the head up too high in abduction --> impingement
- people with narrowed space between acromion and humerus are predisposed
- friction = irritation, inflammation, and wear
shoulder dislocation
glenohumeral joint is most commonly dislocated joint in the body
- shallow fossa and loose structure
- extreme mobility, but little surface area
- usually due to an outside force (accident)
motions at the elbow
- flexion
- extension
- pronation
- supination
elbow flexion/extension
occurs at humeroulnar joint
- most stable in close packed position of full extension
- door hinge (very simple)
what class lever is the biceps?
third class lever
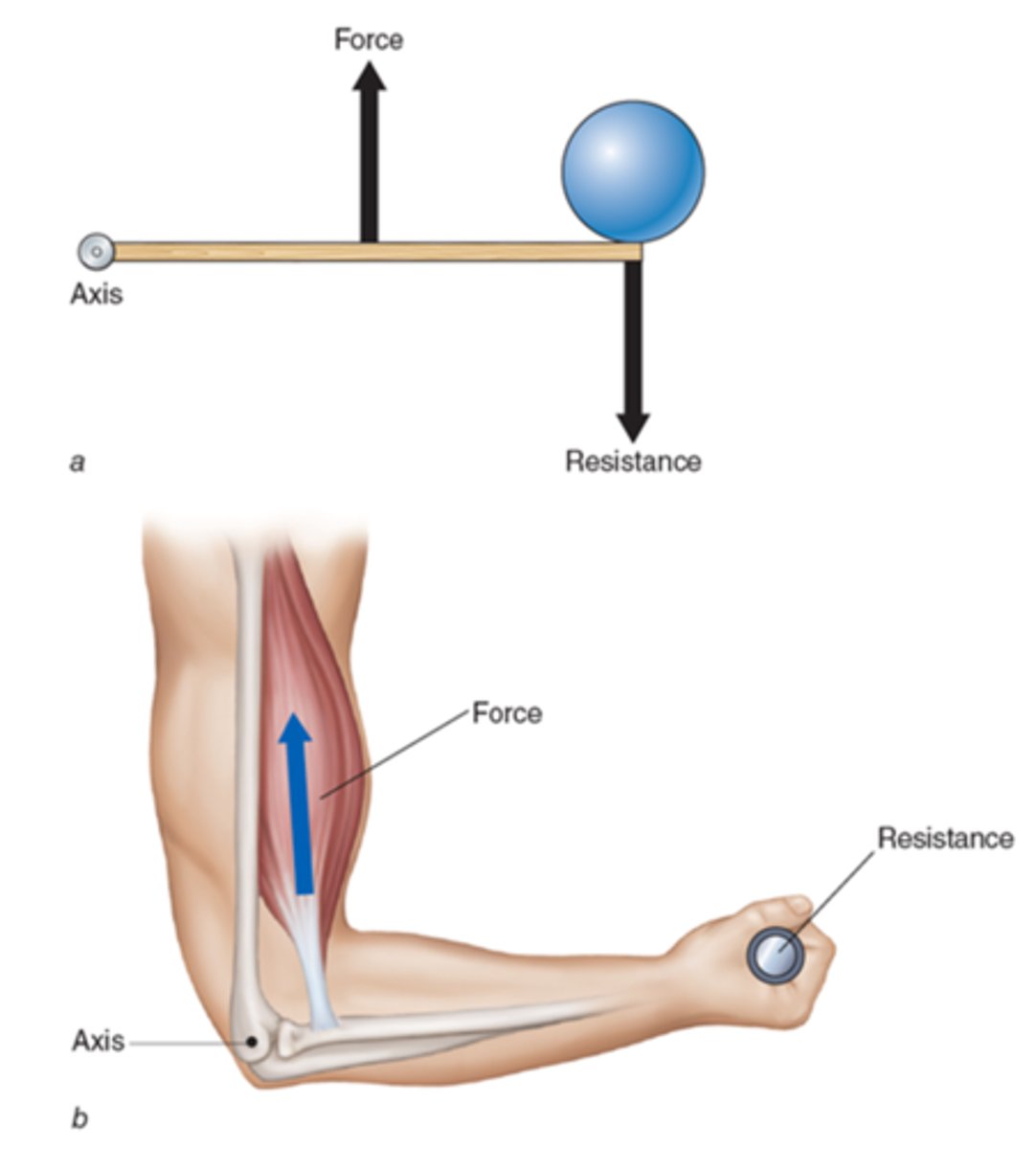
what class lever is the triceps?
first class lever
elbow pronation/supination
occurs at radioulnar joint
- radius rolls medially and laterally over ulna
- annular ligament binds the head of the radius to the radial notch of the ulna
ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) sprain
UCL resists valgus stress at the elbow
- caused by overuse and microtearing
ex) high velocity/force throwing motions
tommy john surgery
- palmaris longus or hamstring tendon harvested
- holes drilled through humerus and ulna
- tendon is threaded through