Air Pressure, Wind, and Cloud Types: Key Concepts for Meteorology
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the role of wind in the environment?
Wind impacts plants, moisture, human comfort, electricity, and storms.
What creates wind on Earth's surface?
Temperature variations create pressure differences that generate wind.
What instrument measures air pressure?
A barometer.
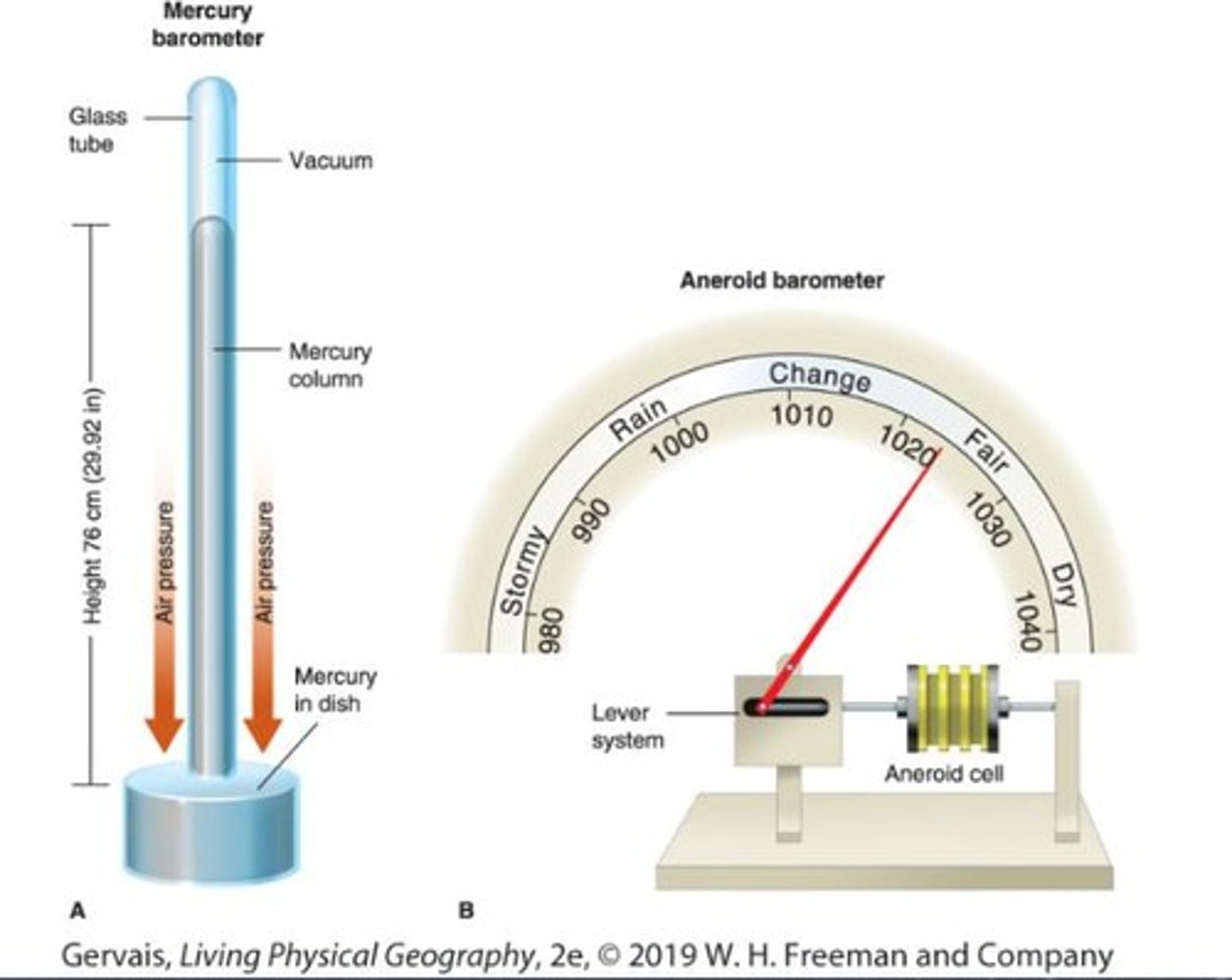
What is the highest average air pressure recorded and where?
430 m (-1412 ft) at the Dead Sea, Israel, with 1065 mb (31.44 in Hg).
What was the lowest air pressure recorded during Typhoon Haiyan?
860 mb (25.40 in Hg).
What type of air pressure is associated with warm air?
Low pressure, as warm air expands and rises.
What type of air pressure is associated with cold air?
High pressure, as cold air contracts and is more stable.
What is dynamic air pressure?
Pressure differences caused by air movement that can override thermal air pressure.
What pressure system develops over the Canadian plains in winter?
Thermal high.
What is the pressure-gradient force?
The force resulting from horizontal differences in air pressure across Earth's surface.
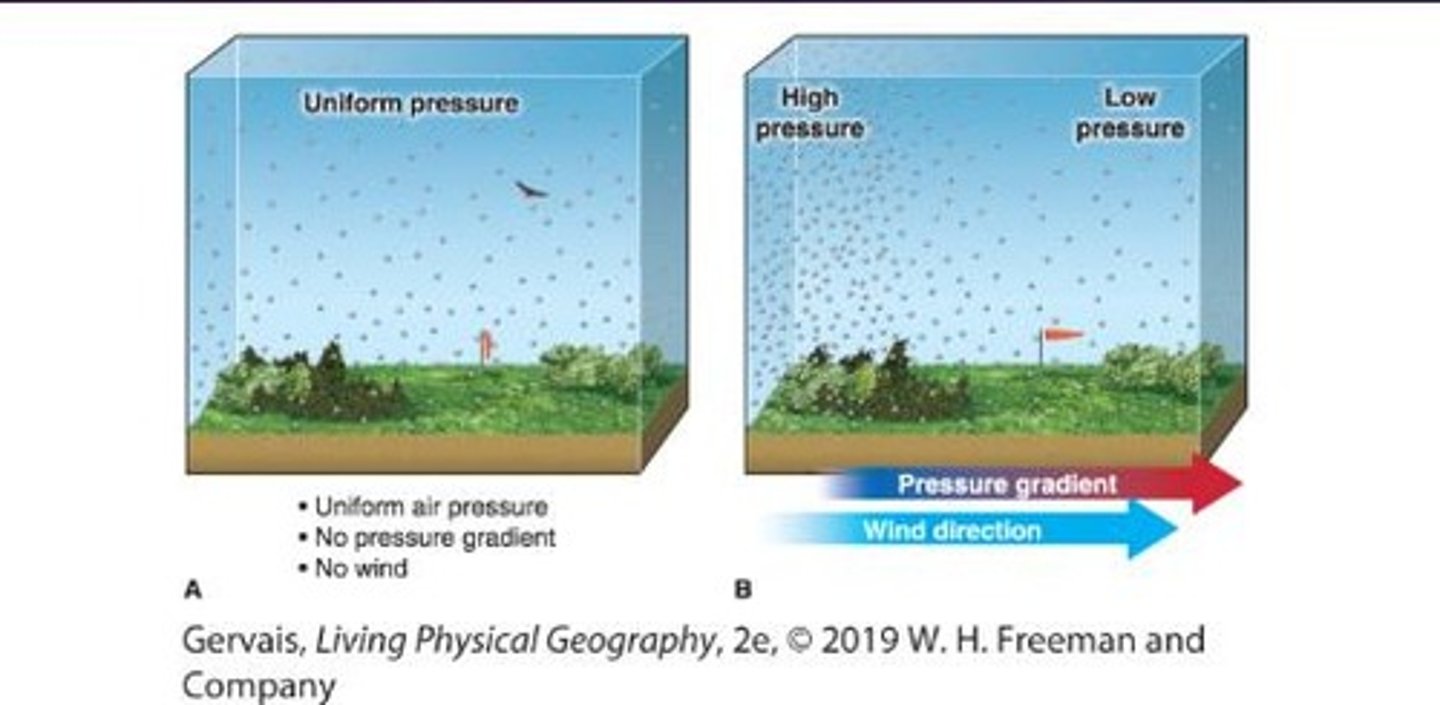
From where do air molecules move according to the pressure gradient force?
From high pressure to low pressure.
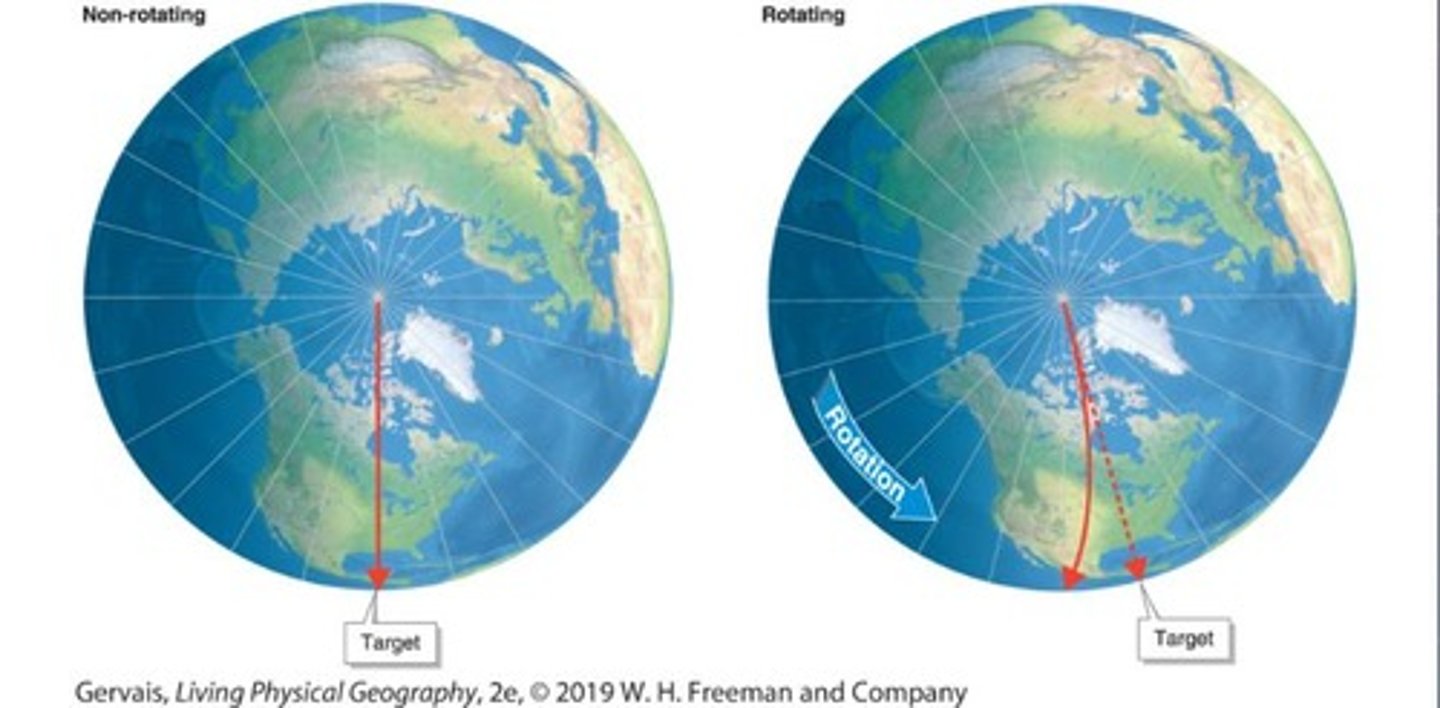
What is the Coriolis Effect?
The perceived deflection of moving objects due to Earth's rotation.
How does friction affect wind flow?
Friction slows air flow, especially near Earth's uneven surface.
What is an anemometer used for?
To measure wind speed based on a rotating propeller.
How are winds named?
Winds are named by the direction they originate from.
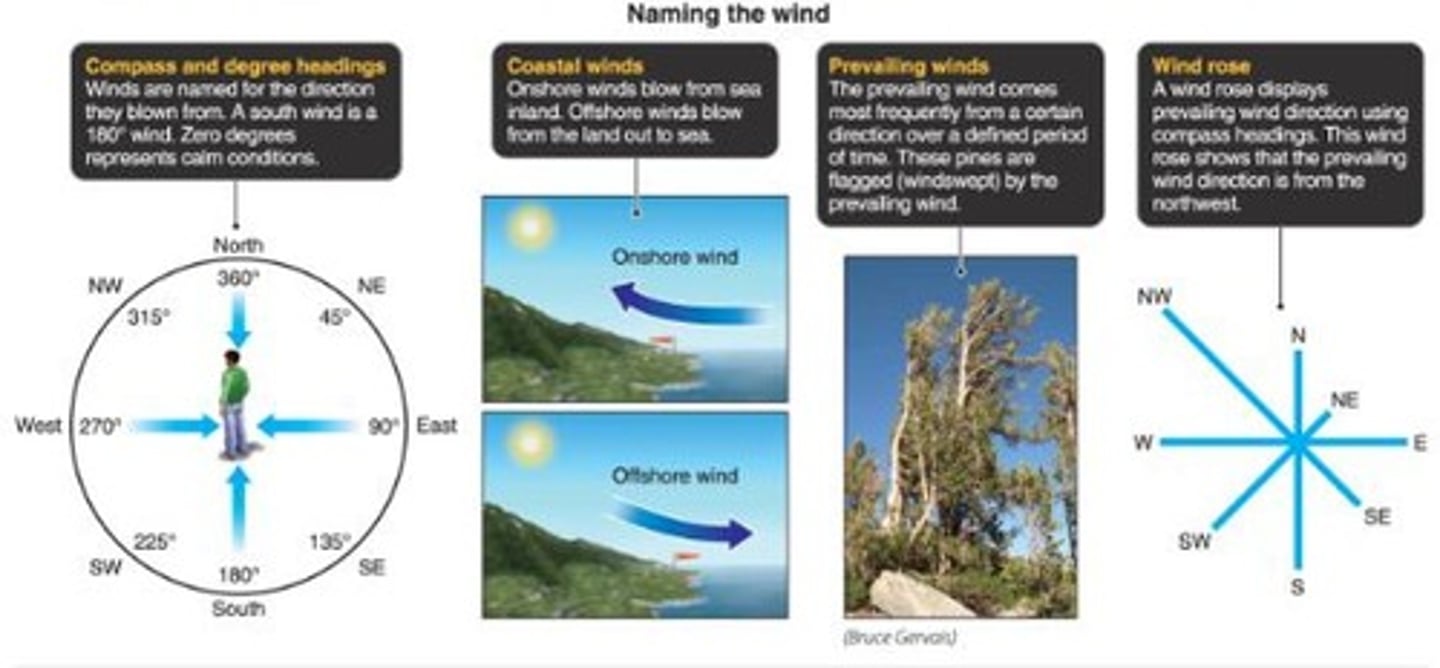
What are cyclones and anticyclones?
Cyclones are low pressure centers; anticyclones are high pressure centers.
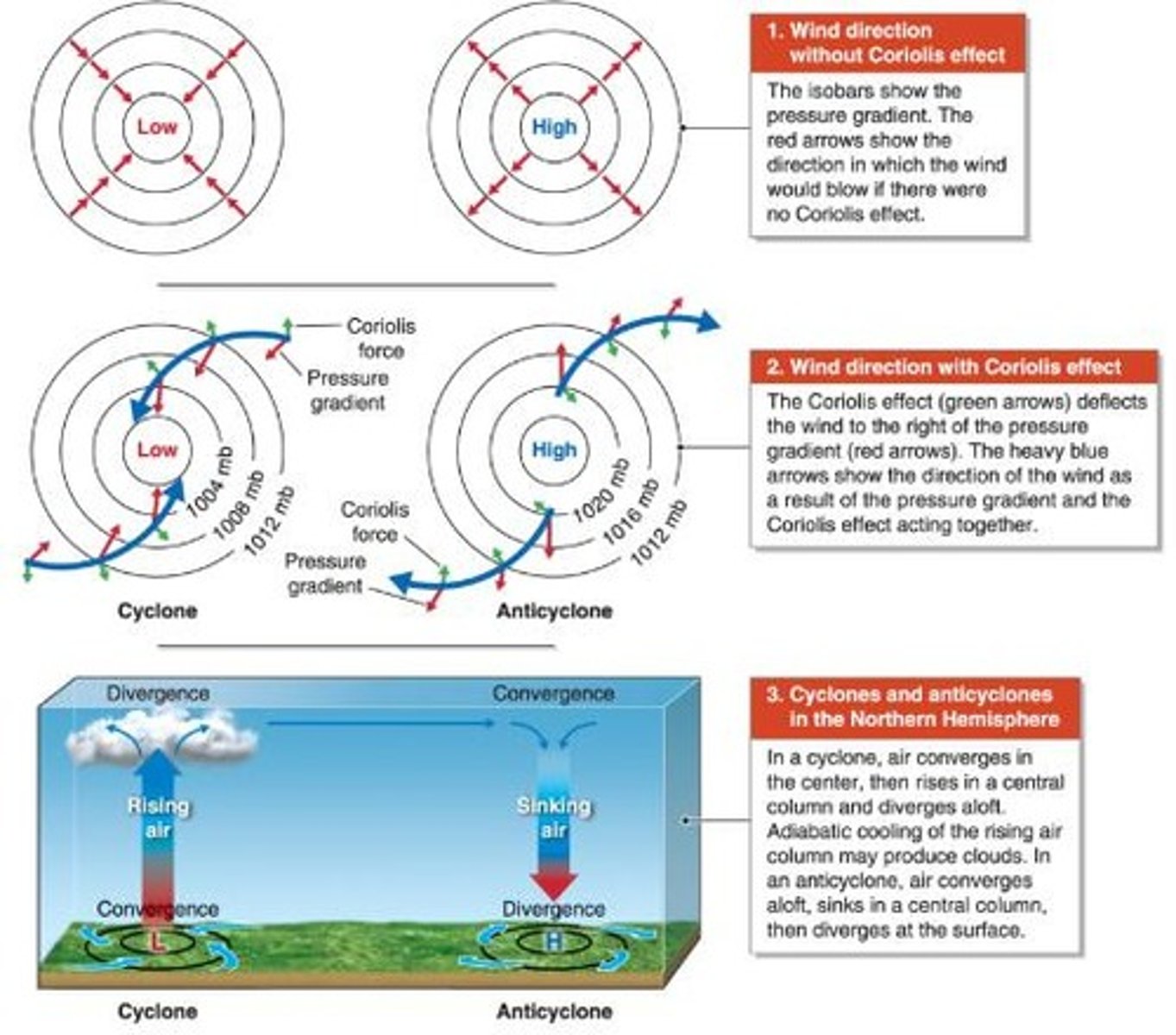
What is the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)?
A migrating area of low pressure associated with equatorial and tropical regions.
What dynamic pressure system creates most of the Earth's desert regions?
Subtropical high.
What are jet streams?
Discontinuous bands of high-velocity geostrophic winds that flow west to east at the tropopause.
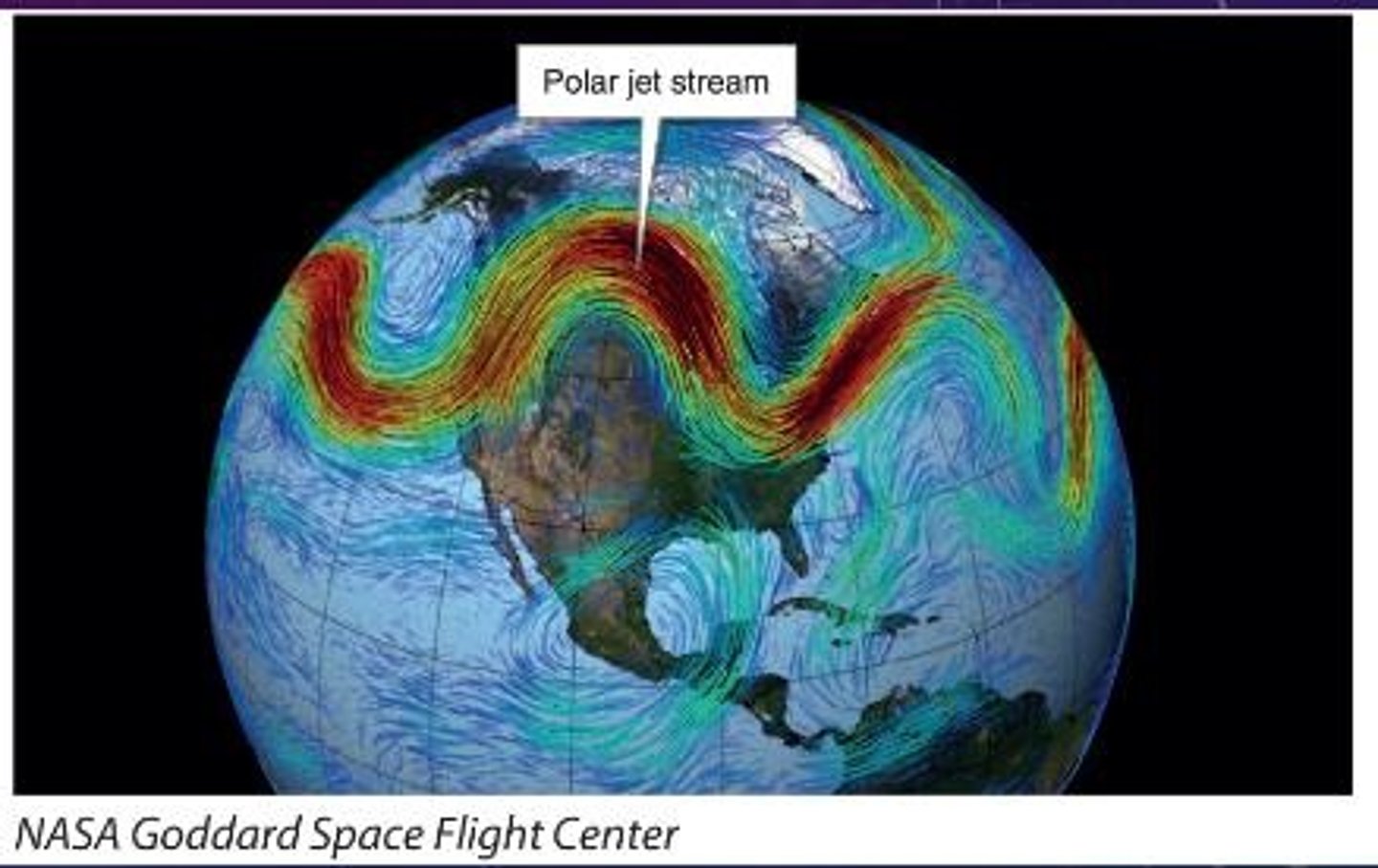
What are Rossby waves?
Undulations in the jet stream that determine weather patterns.
What pattern in Rossby waves leads to cold air outbreaks in the south?
Meridional pattern.
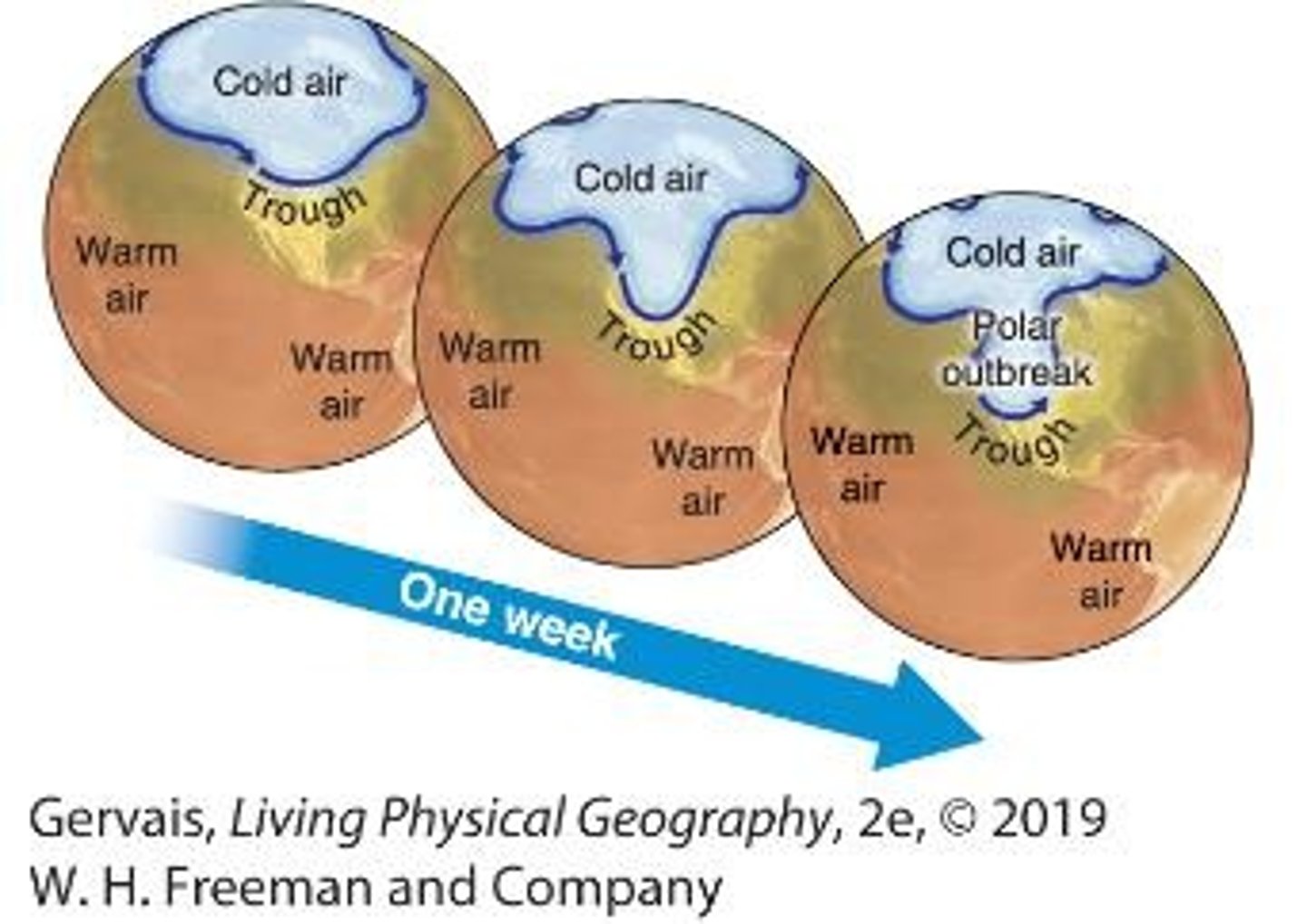
What circulation features shift with the subsolar point?
ITCZ, subtropical high, and polar front jet stream.
Which semi-permanent pressure system is a major steering current for Atlantic basin hurricanes?
The Bermuda high.
What is the Bermuda High?
A subtropical high-pressure system that influences weather patterns.
What are mountain and valley breezes?
Local winds that occur due to temperature differences between mountains and valleys.
What are Chinook and Foehn winds?
Warm, dry downslope winds that can cause rapid temperature increases.
What are Santa Ana and Diablo winds?
Hot, dry winds from the Great Basin Plateau that result from adiabatic compression.
What are katabatic (gravity) winds?
Very cold winds that flow downhill at high speeds.
What is a monsoon?
A seasonal reversal of winds that brings moisture in summer and dryness in winter.
How does the monsoon affect South Asia?
It dictates rain or drought, impacting agriculture and water supply.
What are the two seasons of a monsoon?
Summer (rainy) and winter (dry).
What is the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)?
A climate pattern with three phases: Normal, El Niño (warmer), and La Niña (cooler).
What are the impacts of El Niño?
Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns, affecting global weather.
What are the impacts of La Niña?
Cooler temperatures and typically wetter conditions in some regions.
What is wind farming?
The use of wind turbines to convert wind energy into electricity.
What is the cut-in speed for wind turbines?
The minimum wind speed (8.1 mph) at which turbines begin generating electricity.
What is the cut-out speed for wind turbines?
The maximum wind speed (62.1 mph) at which turbines stop operating to prevent damage.
What is the average atmospheric pressure at sea level?
1013.25 mb.
What are prevailing winds?
Consistent winds that blow predominantly from one direction.
What are the three cells in the global circulation model?
Hadley cell (tropical), Ferrel cell (mid-latitude), and Polar cell.
What is the significance of the polar front jet stream?
It separates cold air masses and influences cyclone formation.
Who classified cloud types and developed a method for their categorization?
Luke Howard, an English naturalist.
What are the four major categories of clouds?
Cirrus, Cumulus, Stratus, and Alto.
Describe Cirrus clouds.
Ice clouds that are wispy and feathered.
What characterizes Cumulus clouds?
Heaped and puffy clouds with vertical development.
What are Stratus clouds known for?
Uniform, flat sheets that create overcast conditions.
What altitude range do Alto clouds occupy?
Between 2,000 to 7,000 meters (6,500 to 23,000 feet).
What is the significance of Nimbo/Nimbus clouds?
They are rain-producing clouds.
What are condensation nuclei?
Particulates and aerosols that help form cloud droplets.
How many condensation nuclei are typically found in 1 m3 of air?
5 to 10 billion condensation nuclei.
What is required to form a raindrop?
1 million cloud droplets combine to make a raindrop.
What temperature conditions define warm cloud precipitation?
Temperatures greater than -15° C (5° F).
What is the Bergeron process?
A cold cloud precipitation process that produces rain or snow at temperatures below 0° F.
List the types of precipitation.
Rain, snow, freezing rain/sleet, and hail.
What is the condition for freezing rain/sleet to form?
It forms only within a temperature inversion.
What defines hail?
Ice pellets larger than 5 mm (0.20 in).
What is the record size of a hailstone that hit Vivian, S.D.?
8.63 inches in diameter and weighed 1.938 pounds.
What trend has been observed in global temperature since 1880?
Global temperature has risen just over 0.13 degrees per decade.
How much more water could the atmosphere hold with an additional 1.8 degrees of warming?
About 7 percent more water, leading to increased extreme rainfall.
What types of fog are identified?
Radiation fog, advection fog, orographic fog, and evaporation fog.
What causes radiation fog?
Radiational cooling of the surface.
What is the main characteristic of advection fog?
Moist air moves over a cool surface.
What is orographic fog?
Fog formed when air is forced to rise over mountains.
What is evaporation fog?
Fog that forms when air becomes saturated over a water body.