Lab 9 - thyroid hormone, cortisol, growth hormone
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what is the functional unit of the thyroid gland?
follicles
what hormones are thyroid hormones like?
steroid-like amine hormones
but they can be stored
how can thyroid hormones be stored if they are hydrophobic?
use thyroglobulin, a protein that cannot pass across membranes and is stored in colloid
thyroid hormone binds to receptors __ of the target cell
inside —> hydrophobic
follicles trap __ for the synthesis of thyroid hormone
Iodide
steps of synthesis, storage, and secretion of thyroid hormone
1) TSH binding and iodine transport into colloid
2) TG synthesis and exocytosis into colloid
3) T3 & T4 synthesis
4) TG + T3 + T4 synthesis
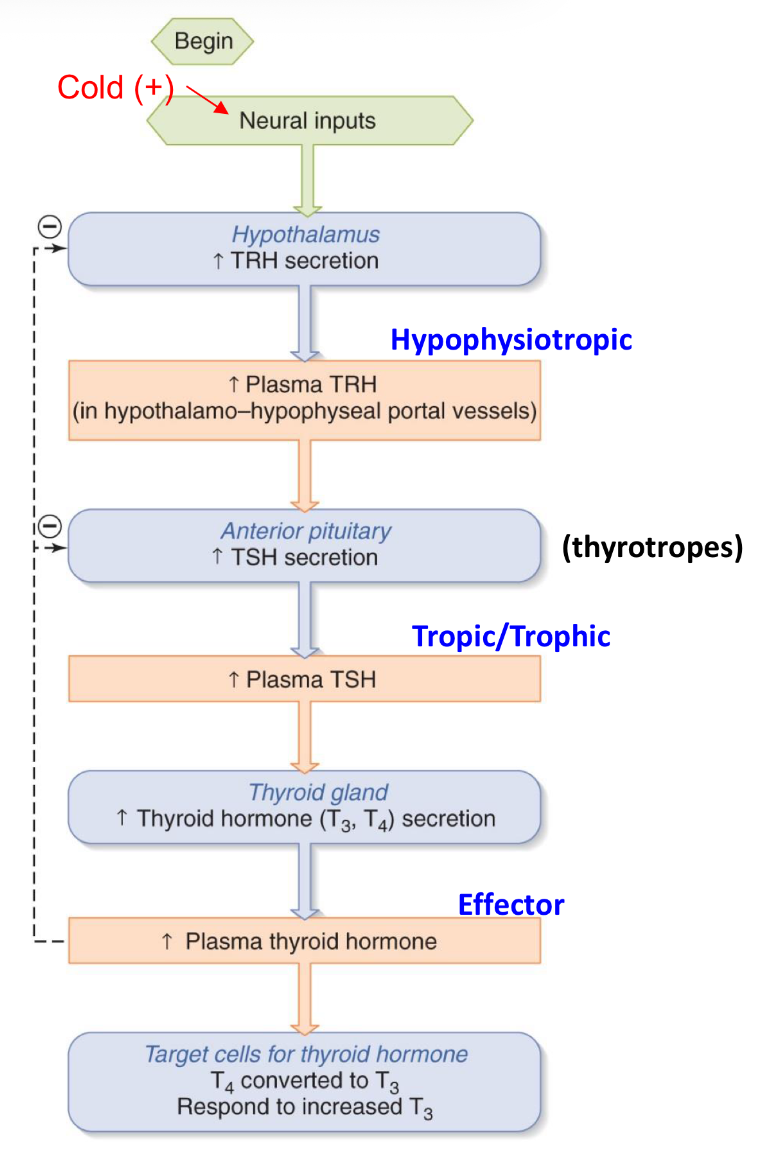
thyroid hormone cascade
3 hormones:
TRH
TSH
thyroid hormone (T3 & T4)
actions of thyroid hormone (4)
metabolic actions - basal metabolic rate (body temp)
permissive actions - increases beta-adrenergic receptor (catecholamine expression)
growth and development - TH is needed for production of growth hormone
growth and development - essential for fetal and adult NS function/development
hypothyroidism
conditions characterized by plasma concentration of thyroid hormone that are chronically below normal
hyperthyroidism
conditions characterized by plasma concentration of thyroid hormone that are chronically above normal
causes & symptoms of hypothyroidism
causes: iodine deficiency, thyroid damage, or autoimmune destruction
symptoms: low metabolism, weight gain, cold intolerance, low BP, low HR, fatigue, stunted growth, decreased cognitive function
development of goiter from hypothyroidism
groiter develops bc of lack of negative feedback and low plasma thyroid levels that causes increase in TSH and TRH
causes & symptoms of hyperthyroidism
causes: tumors or autoimmune disease (Graves’ disease)
symptoms: high metabolism, weight loss, increased appetite, heat intolerance, increased HR, anxiety, constant fight-or-flight state, goiter
zona gomerulosa
aldosterone (salt)
aldosterone regulates Na+ and K+ and blood volume (bc water follows salt)
cortex and steroid hormone
zona fasciculata
cortisol and small amount of androgens (sugar)
cortex and steroid hormone
zona reticularis
secretes mostly sex steroids - androgens (sex)
the androgen, DHEA, contributes to the pubertal growth spurt in both sexes and is important in inducing secondary sex characteristics in females
cortex and steroid hormone
medulla
epinephrine and norepinephrine
catecholamines
2 parts of adrenal glands
cortex (3 parts) and medulla
the production of specific adrenal steroid hormones in each zone is determined by which ___ are present in each zone
enzymes
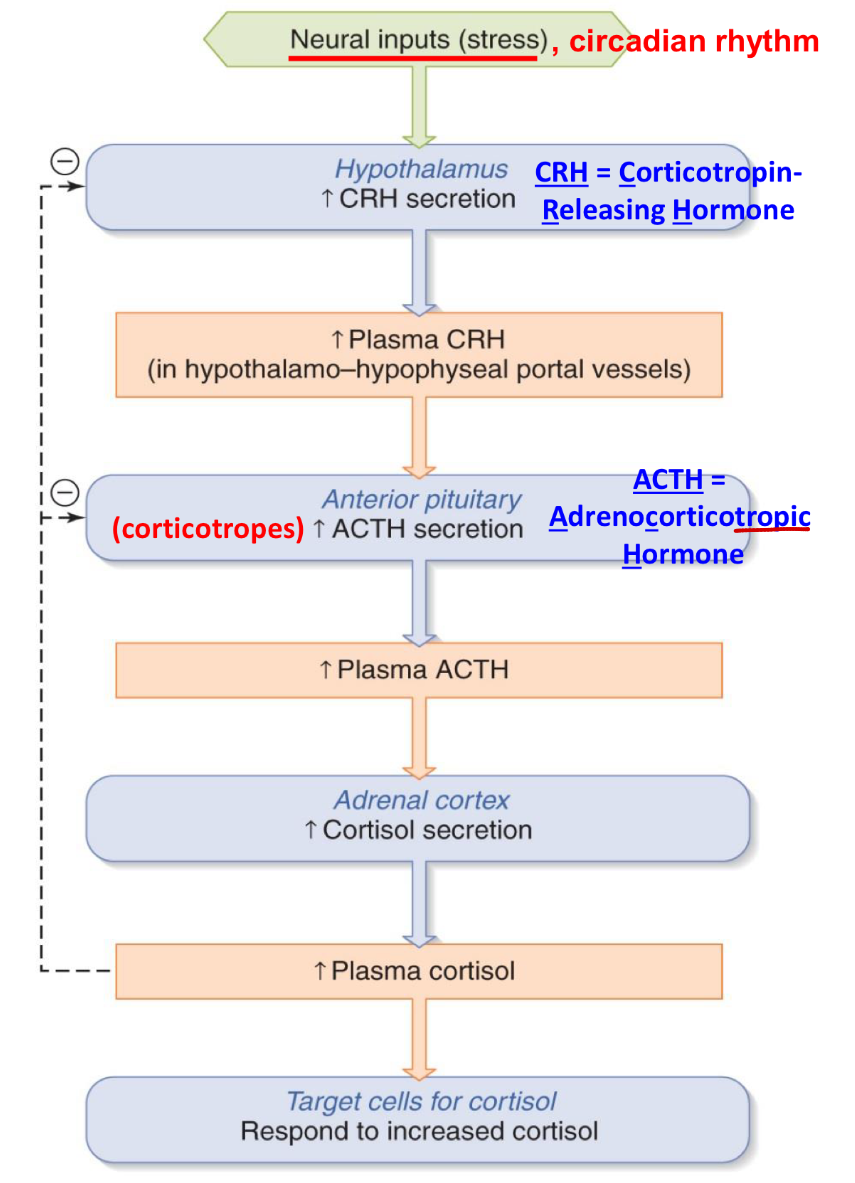
cortisol cascade
3 hormones - CRH, ACTH, cortisol
physiological functions of cortisol (nonstress) (4)
metabolic effects - glucose production btw meals
permissive of adrenergic receptors in the cardiovascular system
anti-inflammatory/anti-immune - prevent hyper-response
fetal/neonatal development of brain, intestines, lungs, glands
functions of cortisol in stress (6)
metabolic effects - catabolizes body stores of nutrients thereby mobilizing glucose, fatty acids, amino acids for energy and tissue repair
bone resorption
support sympathetic responses related to vasoconstriction
stimulates erythropoietin - replaces RBC’s if bleeding out
anti-inflammatory/immunosuppression - prevent rejection of transplanted organ
inhibition of non-essential function
andrenal insufficiency
cortisol hyposecretion (lack of cortisol)
primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s Disease)
caused by: destruction of adrenal cortex
primary effector organ
results in: hypotension, low blood glucose, high plasma ACTH and high CRH
secondary adrenal insufficiency
caused by: anterior pituitary dysfunction
loss of ACTH
results in: similar symptoms as in primary adrenal insufficiency, but with low plasma ACTH
cushing’s syndrome vs disease
Cushing’s syndrome: hypercortisolism and all of its effects, regardless of the original cause
Cushing’s disease: a case of Cushing’s syndrome when the cause is identified as an ACTH-secreting tumor
stress increases the levels of (6)
aldosterone - increases Na+ retention and BP
vasopressin - increases water retention and BP
growth hormone
glucagon
beta-endorphin - pain reliever/mood elevation
epinephrine
stress decreases the levels of (1)
insulin
less insulin —> the levels of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids in the plasma increase
hyperplasia
chondrocytes undergoing cell division (mitosis)
hypertrophy
older chondrocytes enlarging
epiphyseal growth plate
open —> cartilage is still growing
closes at the end of puberty
environmental factors influencing growth (4)
adequate nutrition (esp protein)
freedom from chronic illness/disease
freedom from chronic psychosocial stress
sleep
hormonal influences on growth (8)
growth hormone
insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)
insulin
thyroid hormone
testosterone
estrogens/DHEA
other peptide growth factors in organs
cortisol (anti-growth effects)
growth hormone cascade
hormones - GHRH (+), SST (-), GH, IGF-1

functions of growth hormone (GH)
promotes postnatal growth
metabolic effects
mobilize glucose for energy (prevents storage)
mobilize fatty acids for energy (lipolysis)
functions of IGF-1
promotes postnatal growth in organs, body-wide, and locally in bone by stimulating hyperplasia and hypertrophy
end result of growth hormone cascade
enhances amount body protein, burns fat, prevents glucose storage, promotes bone and organ growth
dwarfism
bones escify way too early
growth plates close too early
gigantism
too much GH before epiphyseal plates close
acromegaly
too much GH after epiphyseal plates close
thickening of bones and heart