4 - Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
To understand the individual
To predict behavior
To plan treatment
To evaluate treatment outcome
Purposes of psychological assessment:
Clinical diagnosis
the process of determining whether the individual meets the criteria for a psychological disorder
Identification of presenting problem
Classification of presenting problem
Social history noting
The Basic Elements in Assessment:
Identification of presenting problem
Situational or pervasive?
Duration?
Prior attempts to help or treat?
Self-defeating or resourceful
How does problem impact social roles?
Does problem match any DSM-5 disorder criteria?
Classification of presenting problem
Treatment planning
Knowledge of range of diagnostic problem
Insurance payment
Personality factors
Social context
Good assessment includes social history noting:
Detailed information
____________ helps clinicians identify potential health risks, protective factors, and cultural factors that may influence health beliefs and practices, enabling more personalized and effective care.
Awareness of increasing population diversity
APA ethical code related to cultural competence
Cultural variables inclusion
Ensuring Culturally Sensitive Assessment Procedures: (3)
Professional Orientation
May determine assessment techniques
Does not limit clinician to one type of assessment
Reliable
Valid
Standardized
Psychological Assessments are:
Standardization
Ensures consistency in the use of a technique
Standardization
Provides population benchmarks for comparison
Structured administration
Scoring
Evaluation procedures
Examples of Standardization:
Importance of trust & rapport > Impact on assessment process
Trust & Rapport between Clinician & Client:
General physical examination
Neurological examination
Neuropsychological examination
Assessment of physical organism incorporates:
Causal factors
Symptom patterns
Many psychological problems have physical components either as:
site of organic brain disorder
extent of organic brain disorder
Neurological tests aid in determination of:
Neuropsychological examination
Involves use of expanding array of testing devices
Neuropsychological examination
Measures cognitive, perceptual, and motor performance
Neuropsychological examination
Provides clues to extent and location of brain damage
Halstead-Reitan Battery
is one of the most widely used sets of tests for assessing brain and nervous system functioning.
Halstead Category Test
Tactual Performance Test
Rhythm Test
Speech Sounds Perception Test
Finger Oscillation Task
Halstead-Reitan Battery TESTS: (5)
Assessment interviews
Clinical observation of behavior
Psychological tests
3 procedures commonly used in Psychosocial assessments include:
Face-to-face interaction
Structured interviews
Unstructured interviews
Assessment Interviews:
Mental status exam
Semistructured clinical interviews
Physical exam
The Clinical Interview and Physical Exam:
Appearance and behavior
Thought processes
Mood and affect
Intellectual functioning
Sensorium
Mental status exams: (5)
DICA (Diagnostic Interview for Children and Adolescents)
ADIS-IV (Anxiety Disorders Interview Schedule – 4th Edition)
Semistructured clinical interviews:
Appearance and behavior
•Overt behavior • Attire •Appearance, posture, expressions
Thought processes
•Rate of speech •Continuity of speech •Content of speech
Mood & affect
•Predominant feeling state of the individual •Feeling state accompanying what individual says
Intellectual functioning
•Type of vocabulary •Use of abstractions and metaphors
Sensorium
• Awareness of surroundings in terms of person (self and clinician), time, and place-”oriented times three”
Subsequent focus
Possible existence of disorder characterized by intrusive, unwanted thoughts and resistance to them
Clinical observation in natural environments
Clinical observations in therapeutic or medical settings
Use and purpose of rating scales
Clinical Observation of Behavior:
ABC Chart
a tool used to understand and track behavior, especially in behavioral psychology
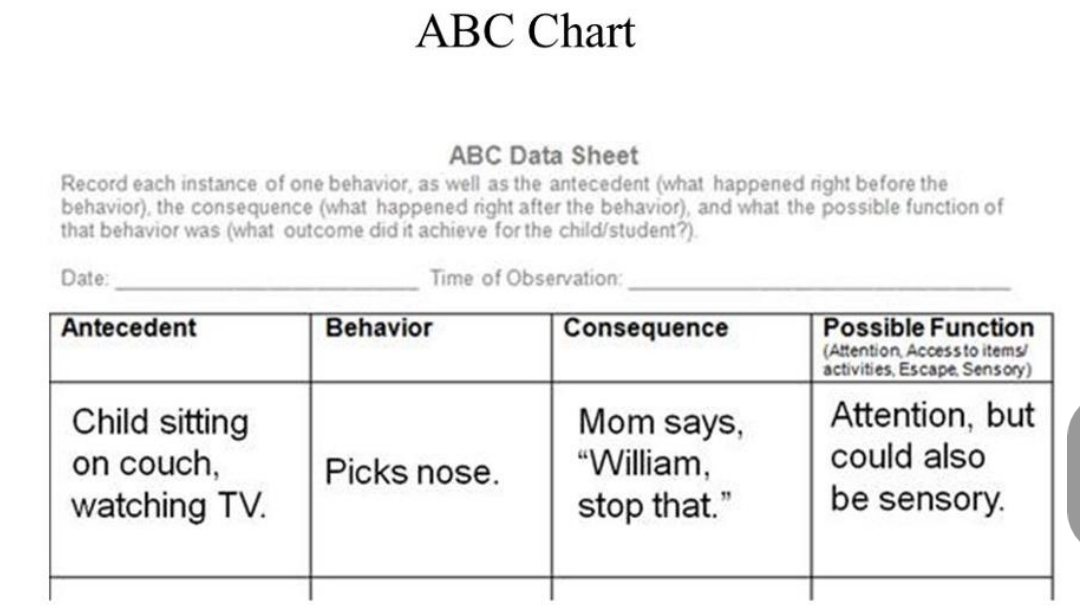
Antecedent
Behavior
Consequence
Possible Function
ABC Chart:
Expanded Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS)
Behavior Rating Scales:
Can be either formal or informal
Self-monitoring vs. being observed by others
Problem of reactivity using direct observation
Behavioral observation and behavioral assessment:
Intelligence tests
Personality tests
2 General categories of psychological tests for use in clinical practice are:
Projective personality tests
Unstructured stimuli are presented
Meaning or structure projected onto stimuli
Projections
________ reveal hidden motives
Rorschach Inkblot Test
Thematic Apperception Test
Projective personality tests include:
Herman Rorschach
10 Inkblots designed by?
Henry Murray
Thematic Approach Test (TAT) developed by?
Objective tests
Roots in empirical tradition
Objective tests
Test stimuli are less ambiguous
Require minimal clinical inference in scoring and interpretation
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
Extensive reliability, validity, and normative database
Personality tests:
Integration of Assessment Data
Developing integrated, coherent working model
Utilizing individual or team approach
Identifying definitive picture vs. discrepancies
Potential cultural bias
Theoretical orientation of clinician
Under-emphasis on external situation
Insufficient validation
Inaccurate data or premature evaluation
Ethical issues in assessment include:
Introduction of order
Communication establishment
Prevalence rates
Clarification of insurance issues
Benefits of classification (abnormal behavior) include:
Categorical
Dimensional
Prototypal
Differing Models of Classification
3 basic approaches include:
DSM-5
DSM-5 TR
Formal Diagnostic Classification of Mental Disorders:
DSM-5
More comprehensive and more subtypes of disorders
DSM-5
Allows for gender related differences in diagnosis
DSM-5
Provides structured interview regarding cultural influences
Prolonged Grief Disorder
A new disorder added to the DSM-5-TR
Stimulant-induced Mild Neurocognitive Disorder
New disorder added to address lingering cognitive effects from stimulant use
Codes for Suicidal Behavior and Self-Injury
The DSM-5-TR includes codes for reporting suicidal and non-suicidal self-injurious behaviors without requiring a formal diagnosis.