chapter 8: articulation
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is articulation?
Articulation is the site where two or more bones meet up.
What is the function of the joints?
The joints have two main functions:
1. giving the skeleton mobility (being able to move)
2. holding the skeleton together in place (preventing absurd/unwanted movement)
1. Joint Classifications: Synarthroses
Immovable joints. (No movement at all under any circumstances)
2. Joint Classifications: Amphiarthroses
Slightly moveable joints. (moving, but very slightly)
3. Classification of Joints: Diarthroses
freely movable. (being able to move as wanted/needed- synovial joints)
Bone Classification (two)
Bones are classified based on:
1.material which binds (holds) the bones together
2.whether or not it has a joint cavity
Three structural classifications of the joints: Fibrous
Bones are joined together by a dense fibrous connective tissue. There are no joint cavities present and most of the joints are synarthroses (not moveable at all).
Three types:
1. Sutures- held together by interlocking CT, only found in the skull.
2. Syndesmoses- Joint held together by a ligament. (ex. Tibia and fibula)
3. Gomphoses-"peg in socket" fibrous joint. (ex. Periodontal ligament hold the tooth in socket)
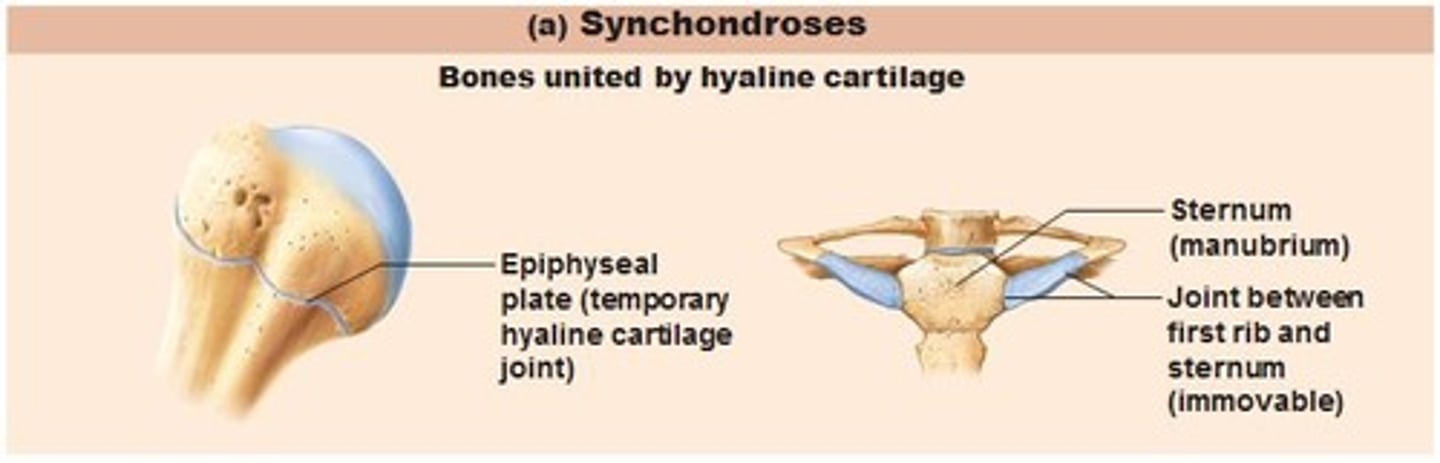
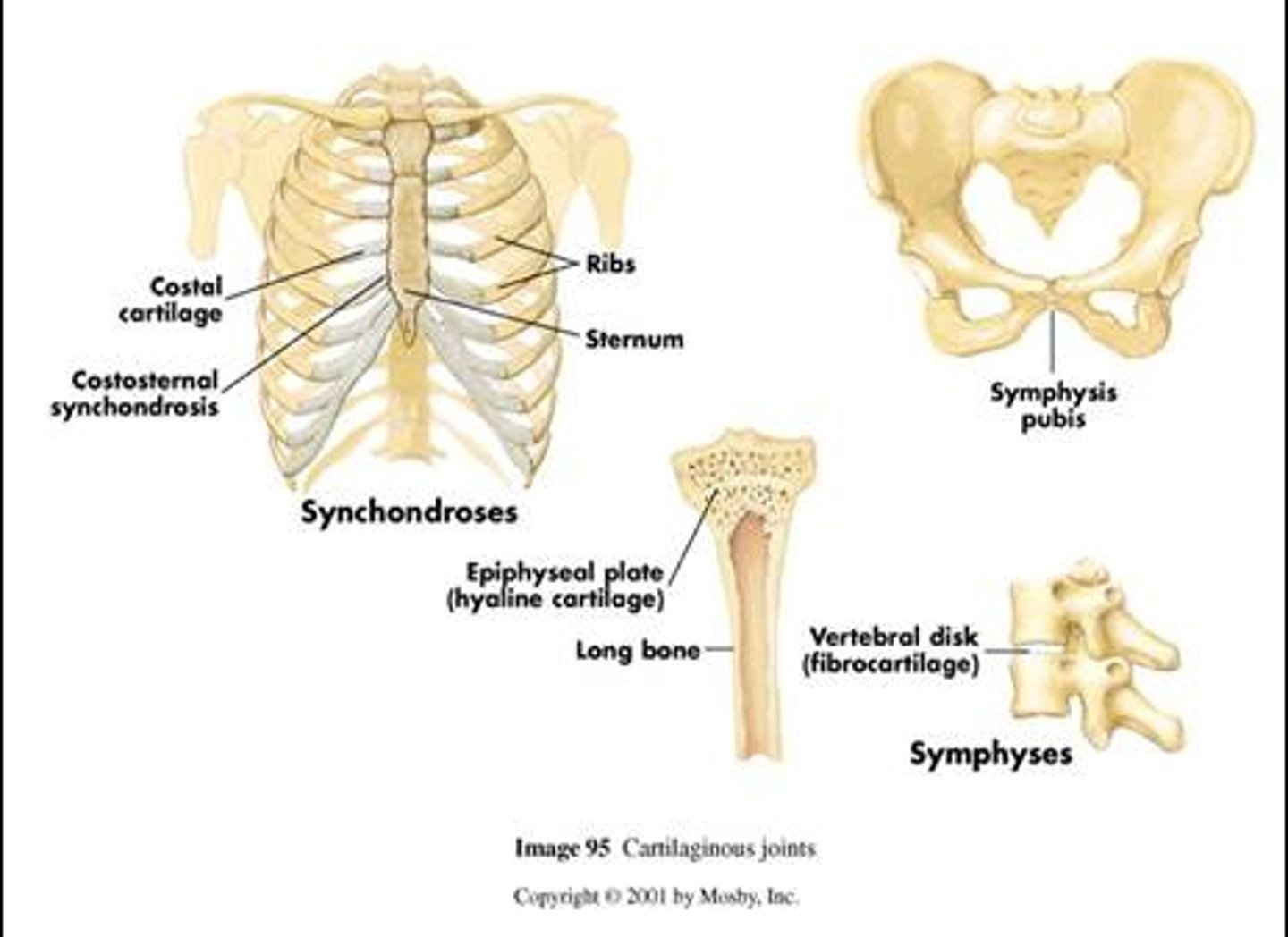
Three structural classifications of the joints: Cartilaginous
Bones are united by CARTILAGE; there is no joint cavities present here.
Two types:
1.Synchondroses- bones united by hyaline CARTILAGE. (ex. joints between the first rib and the sternum).
2.Symphyses- hyaline cartilage COVERS the articulating surfaces STRONG. The symphyses is flexible and amphiarthroses (slightly moveable).(ex. the pubic symphysis)
Three structural classifications of the joints: Synovial
All are diarthrotic (freely and completely moveable). This is the most common joint in our body and includes all the limb joints.
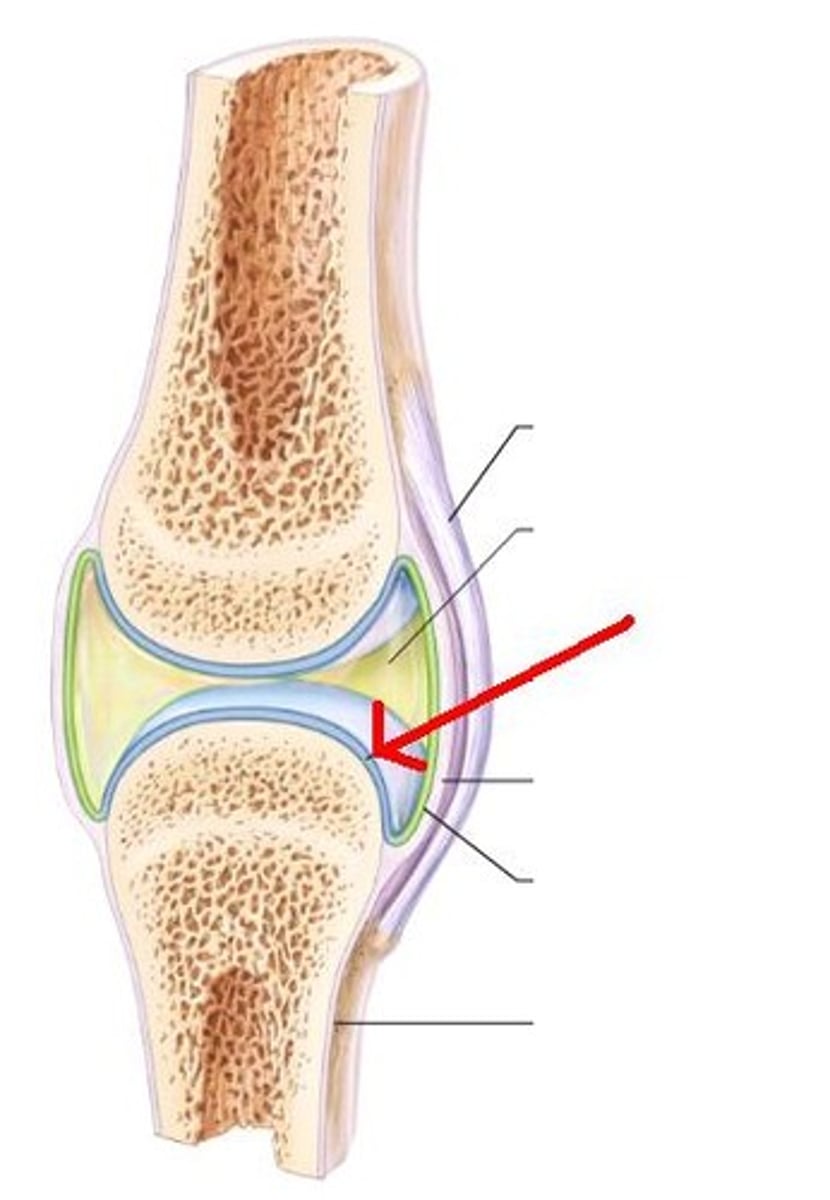
Synovial Joints: Friction reduction-SYNOVIAL FLUID
Friction reduction- a viscous slippery fluid that that filters plasma and hyaluronic acid. It helps lubricate and nourish the articular cartilage and provides rich nerve and blood vessel supple.
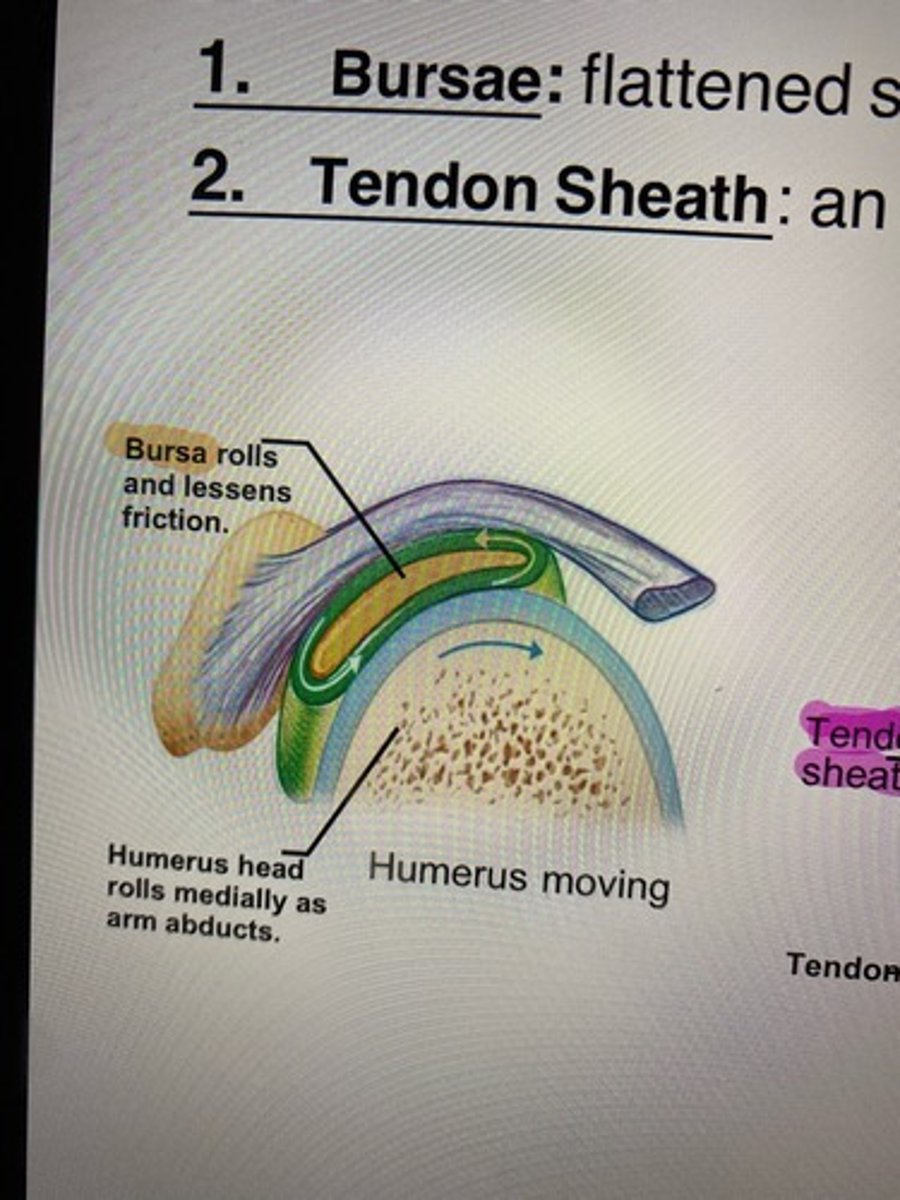
Synovial Joints: Friction reduction- Bursae
A flattened, fibrous sacs that is lines with synovial membranes, which contains synovial fluid and acts as the "ball bearings" where the ligaments, bones, muscles, and skin tendons may rub together.
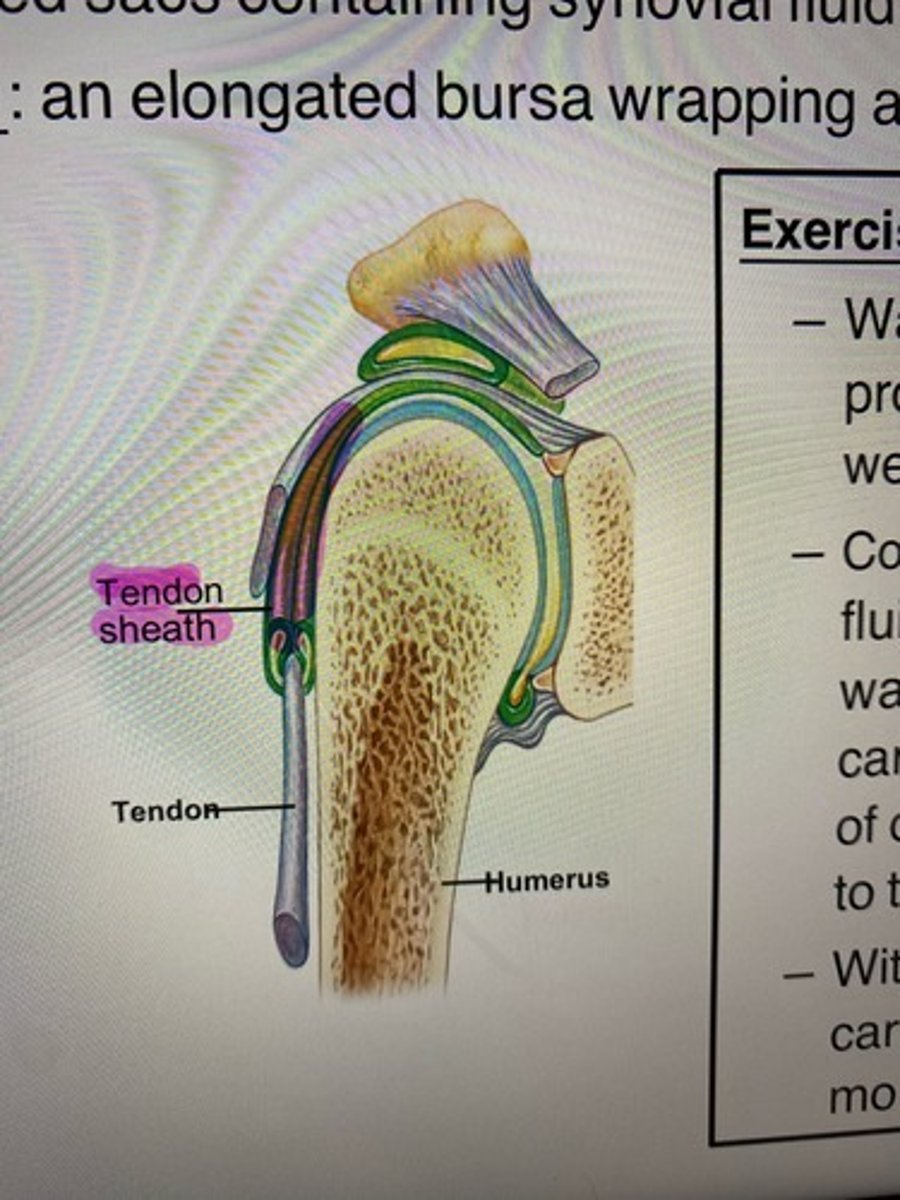
Synovial Joints: Friction Reduction-Tendon sheath
The ELONGATED bursa that wraps around the tendon completely. (ex. the frontal section that goes through the right shoulder joint)
Synovial Joints: Range of motion
1. Nonaxial- slipping movement only
2. Uniaxial- movement in one plane
3. Biaxial- movement in two planes
4. Multiaxial- movement in/around ALL three planes.
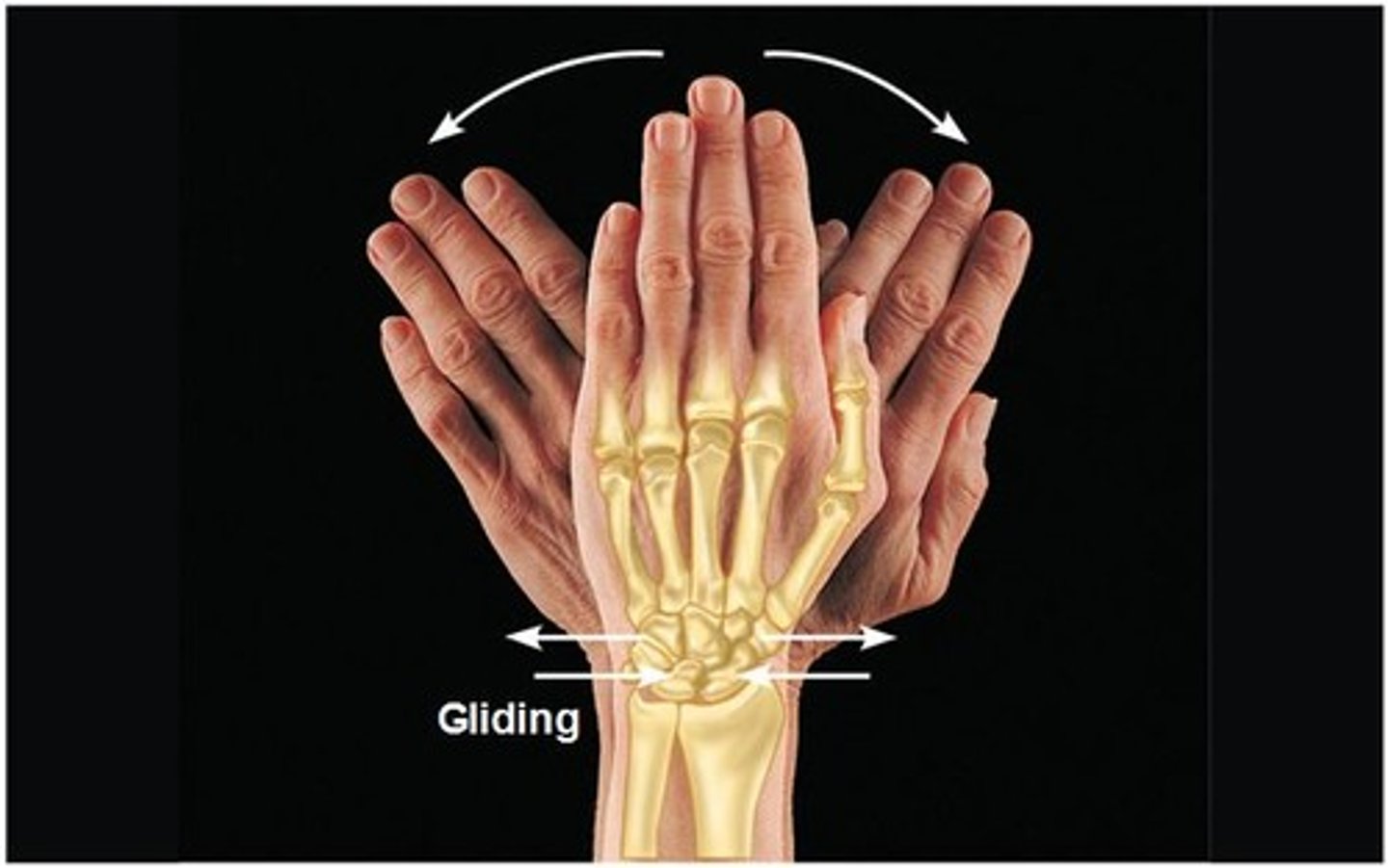
Gliding movement
one flat bone surface glides or slips over another similar surface. (ex. the gliding movement at the wrist)
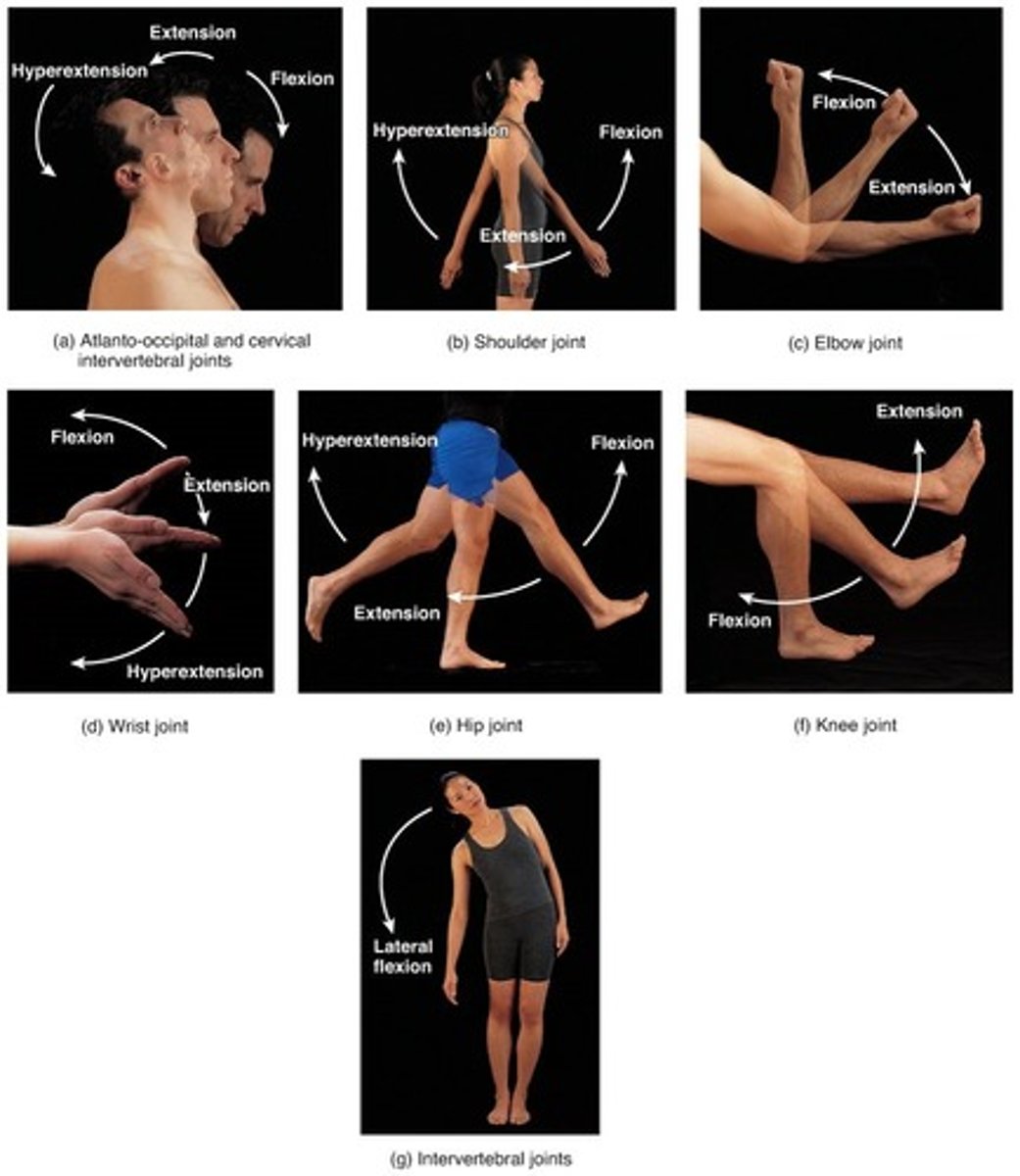
Angular movement
The angular movement of one bone to another.
the process of:
1.flexion
2.extension
3.abduction
4.adduction
5.circumduction
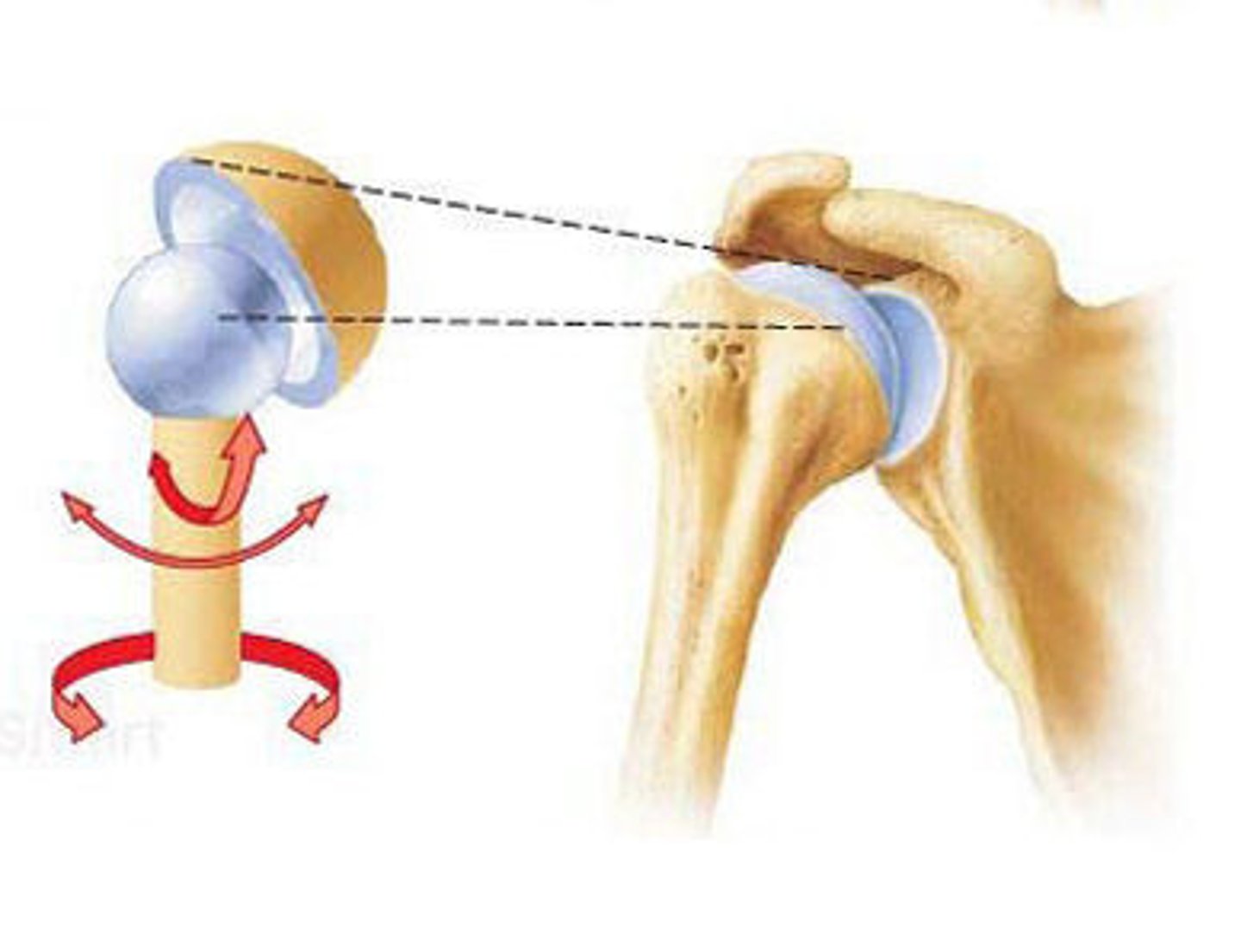
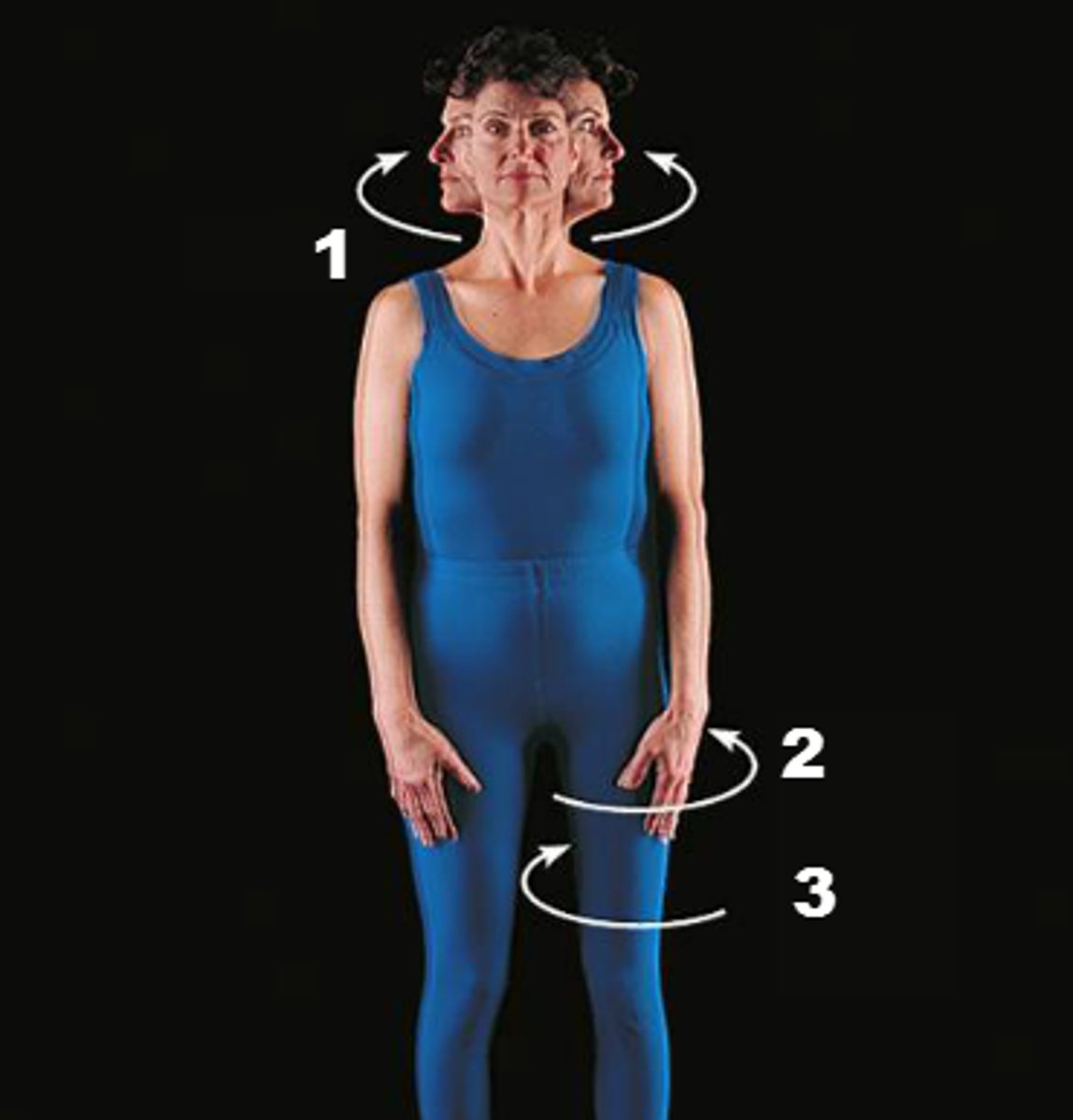
Rotation
The medial and lateral rotation of the joints and bones in relation to each other.
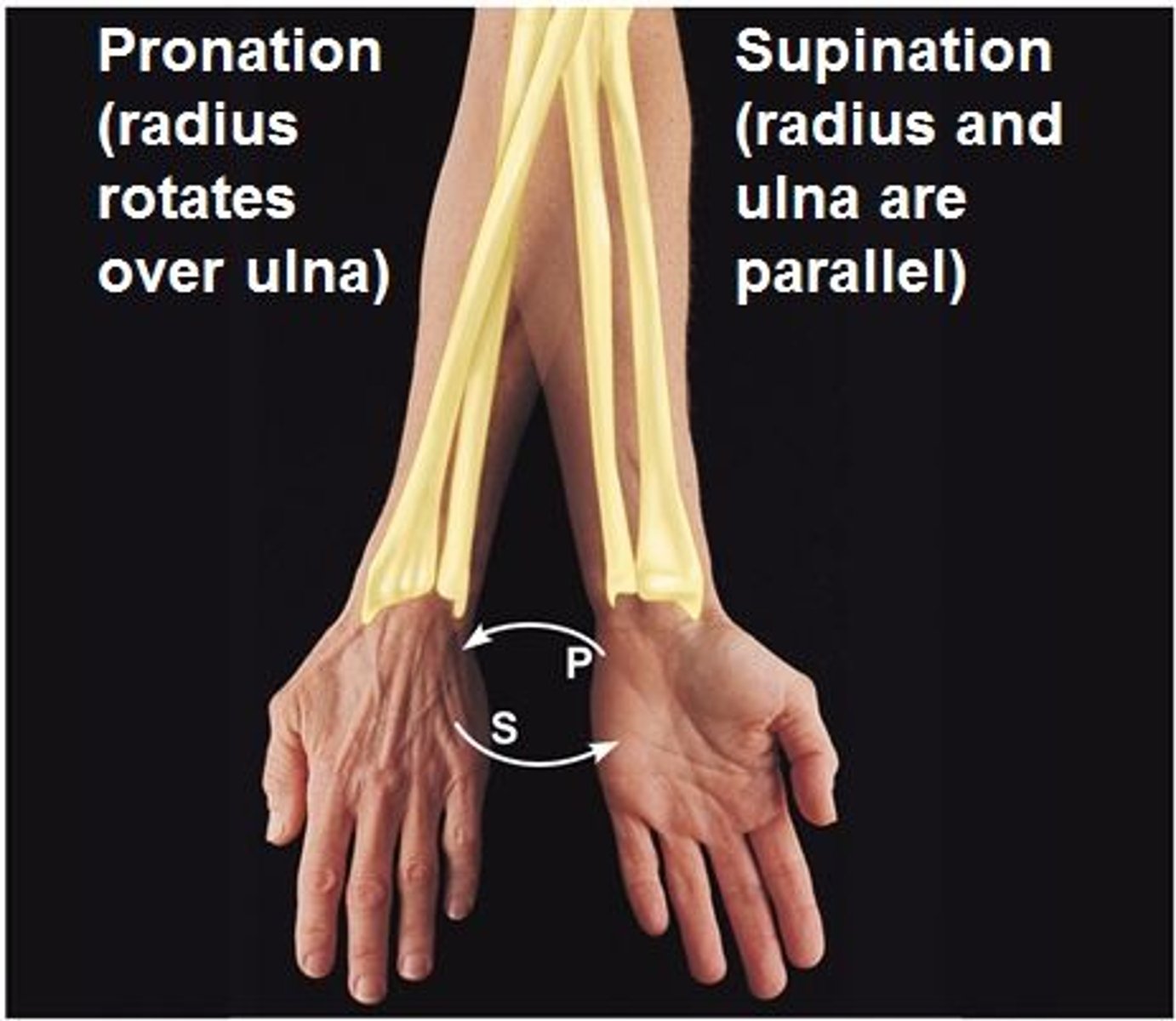
Pronation and supination
turning the hand to a palm down or palm up position
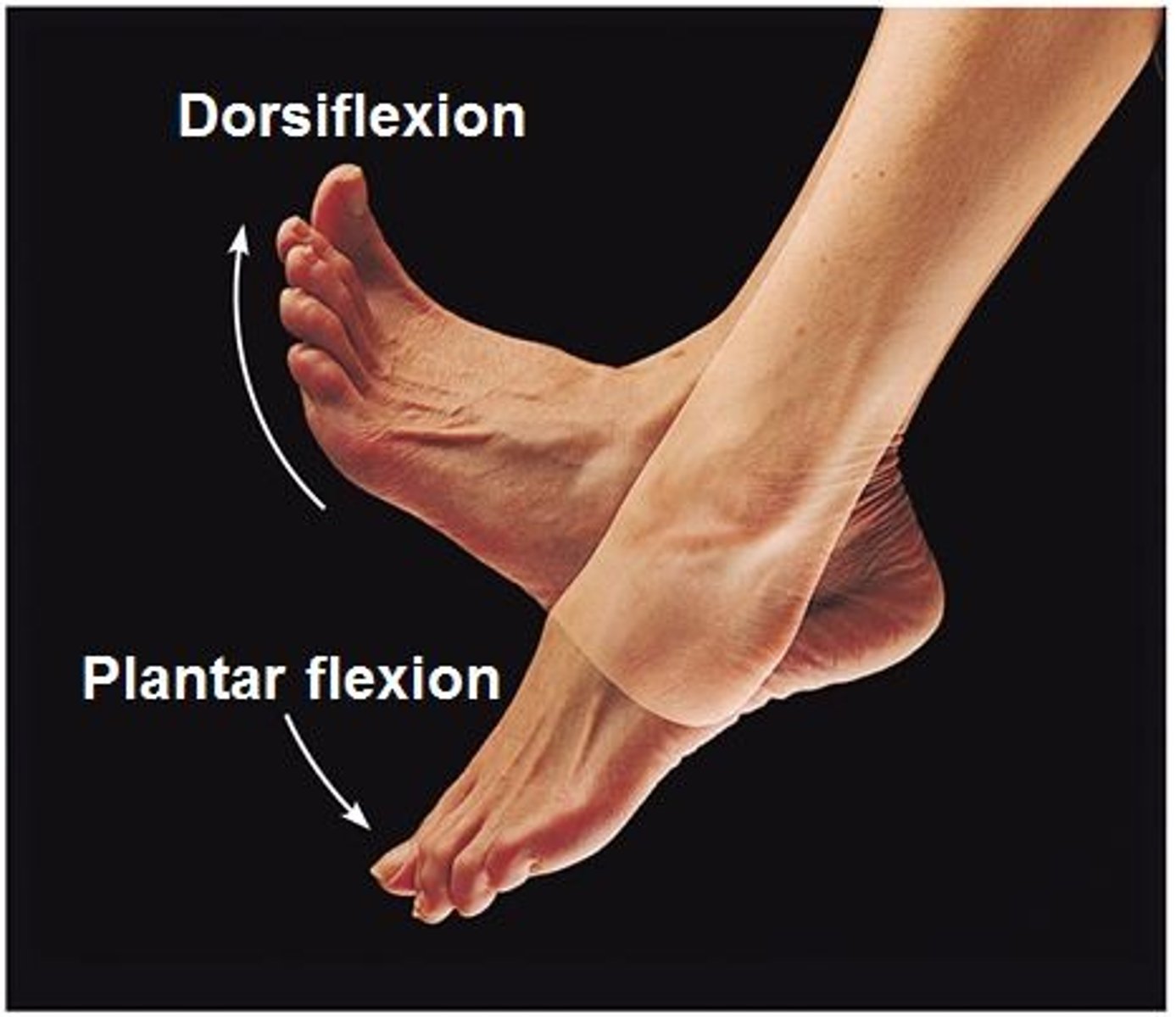
Dorsiflexion and Plantar flexion
up and down movement of the foot
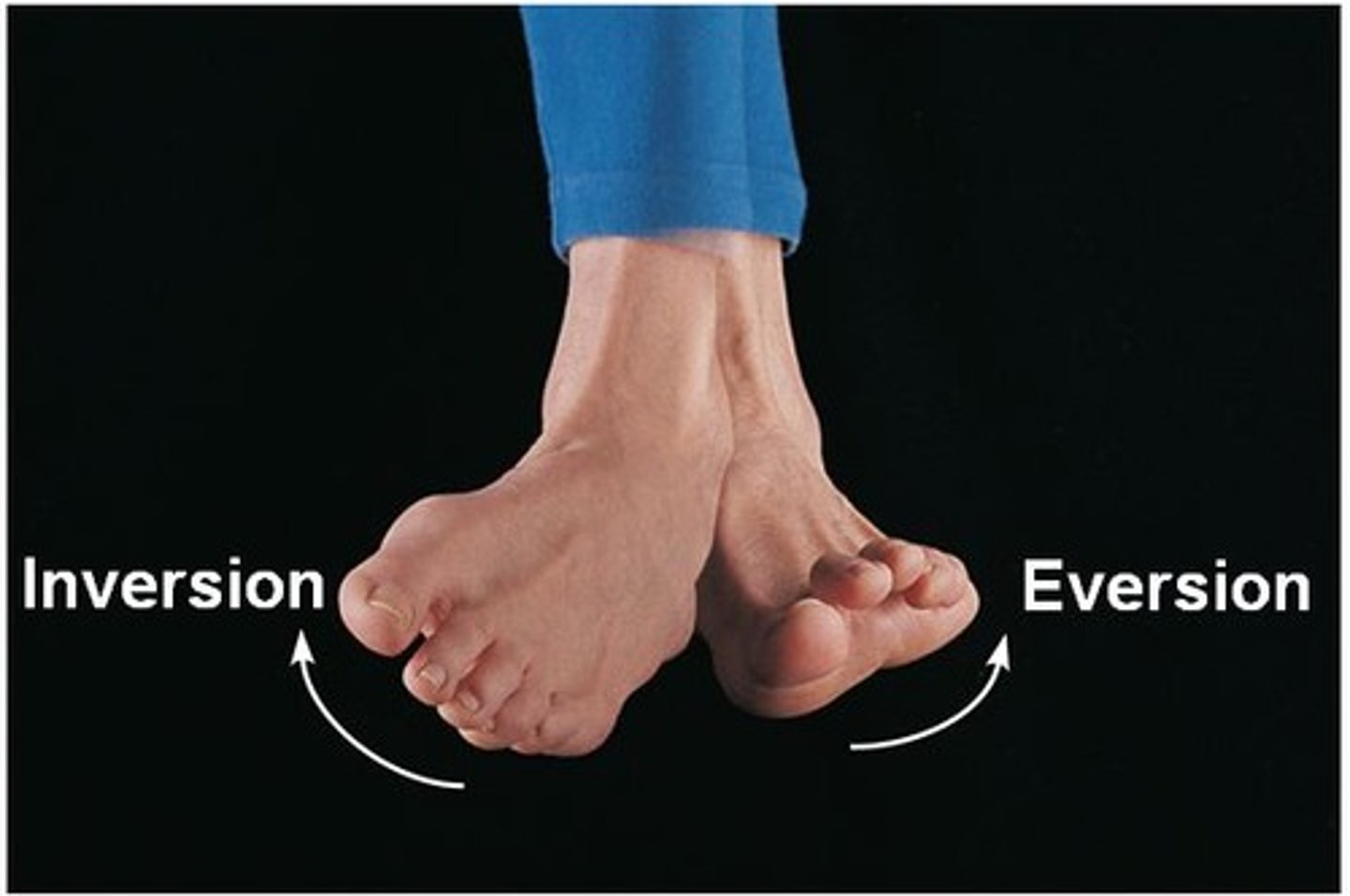
Inversion and Eversion
movements of the sole of the foot medially or laterally (side to side)
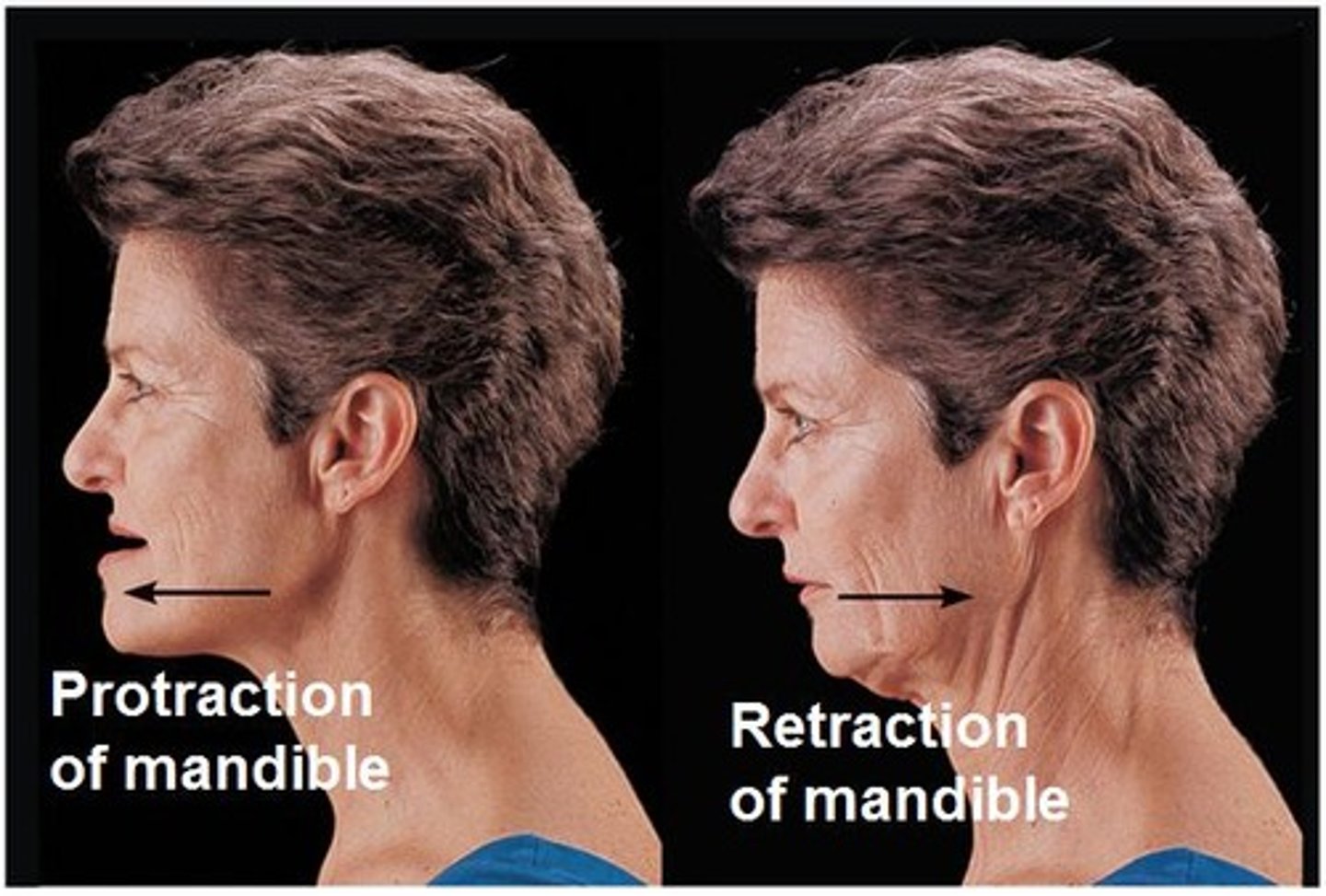
protraction/Retraction
Anterior / posterior movement along transverse plane
Ex. Mandible (stick chin out / pull chin back)
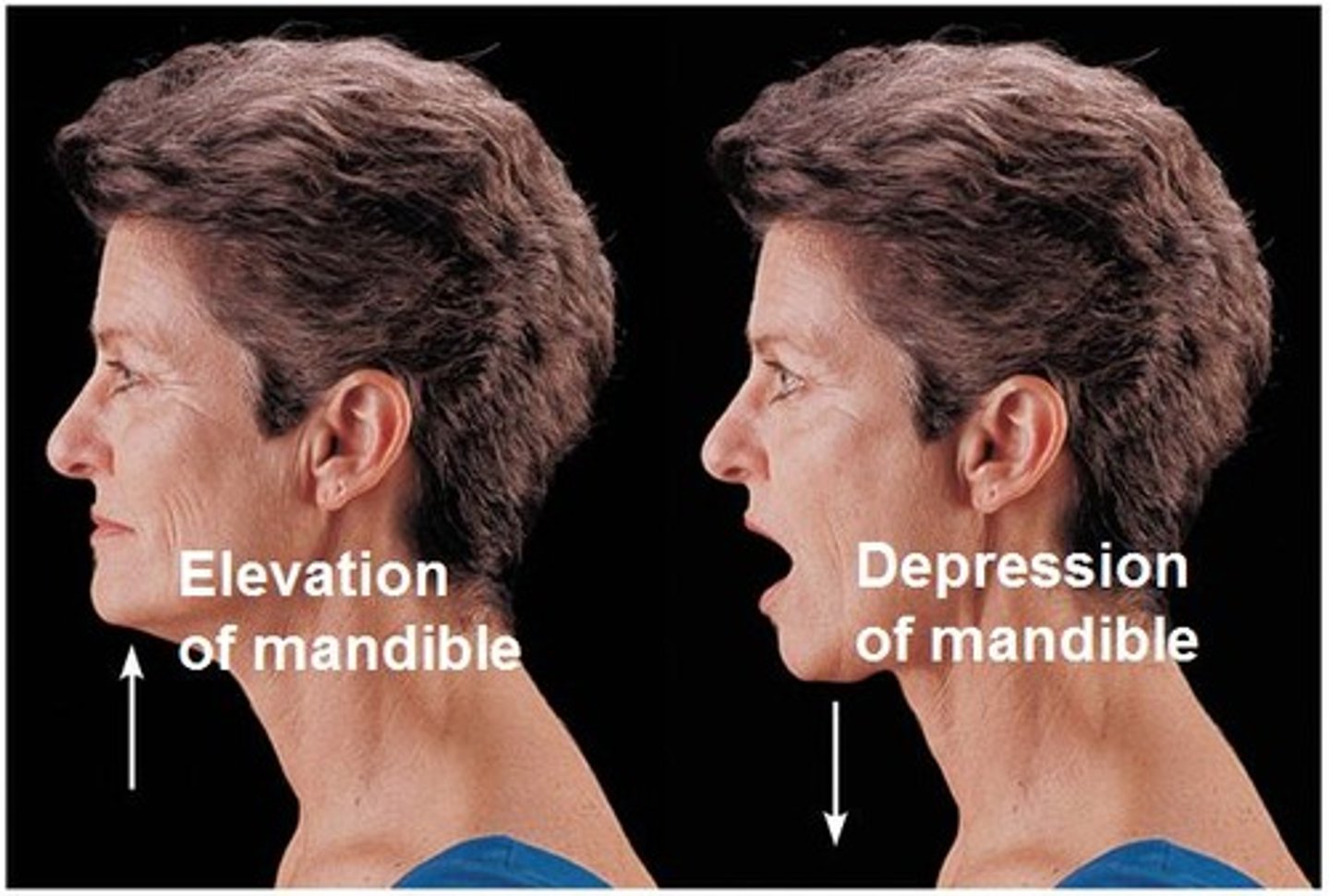
Elevation and depression
Up and Down movements such as opening and closing ones mouth, shrugging shoulders etc.
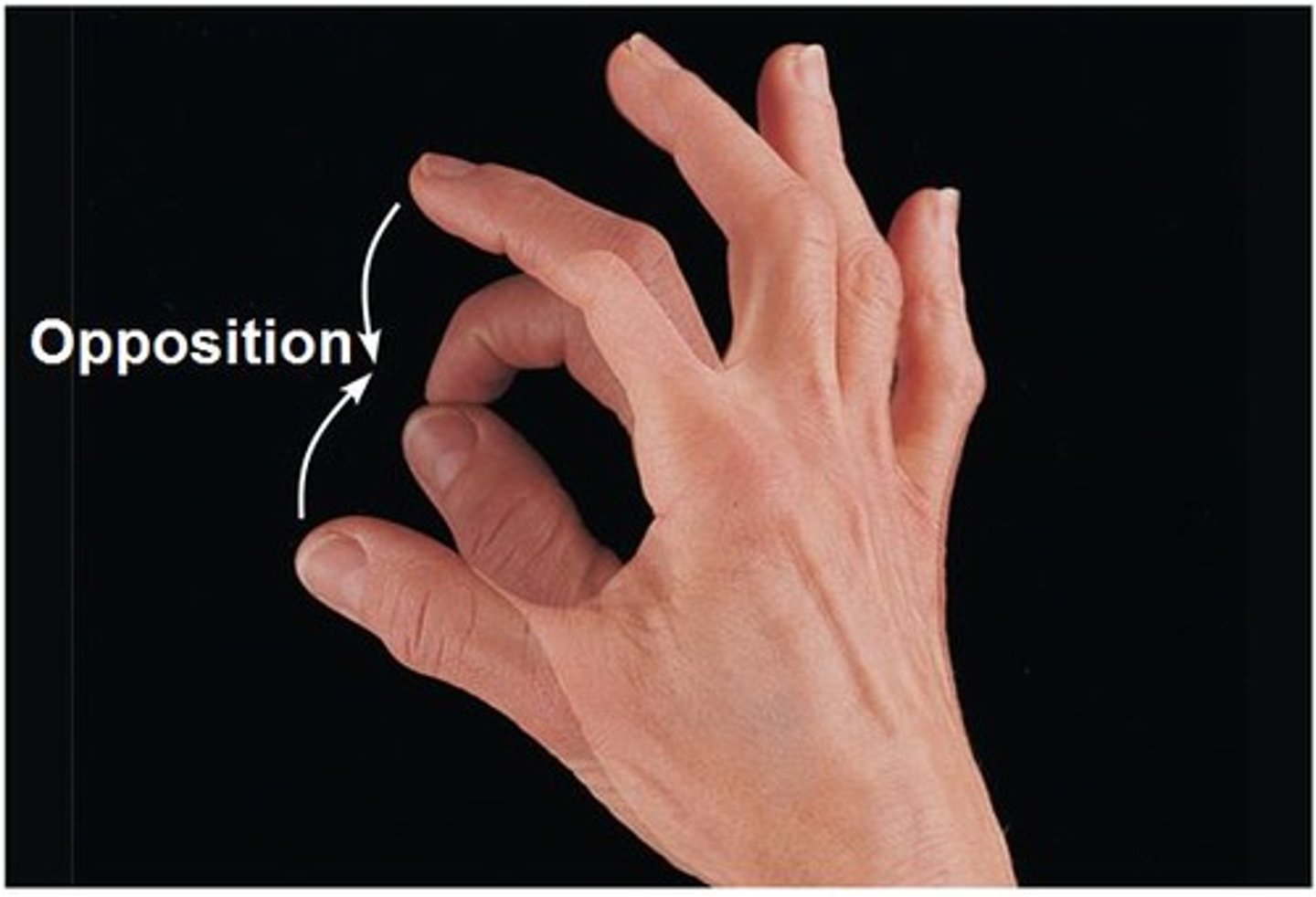
Opposition
touching an opposite finger with the thumb
Synovial Joint classification
We have six types, based on the articular surface:
1.Plane
2.Hinge
3.Pivot
4.Condyloid
5.Saddle
6.Ball and socket
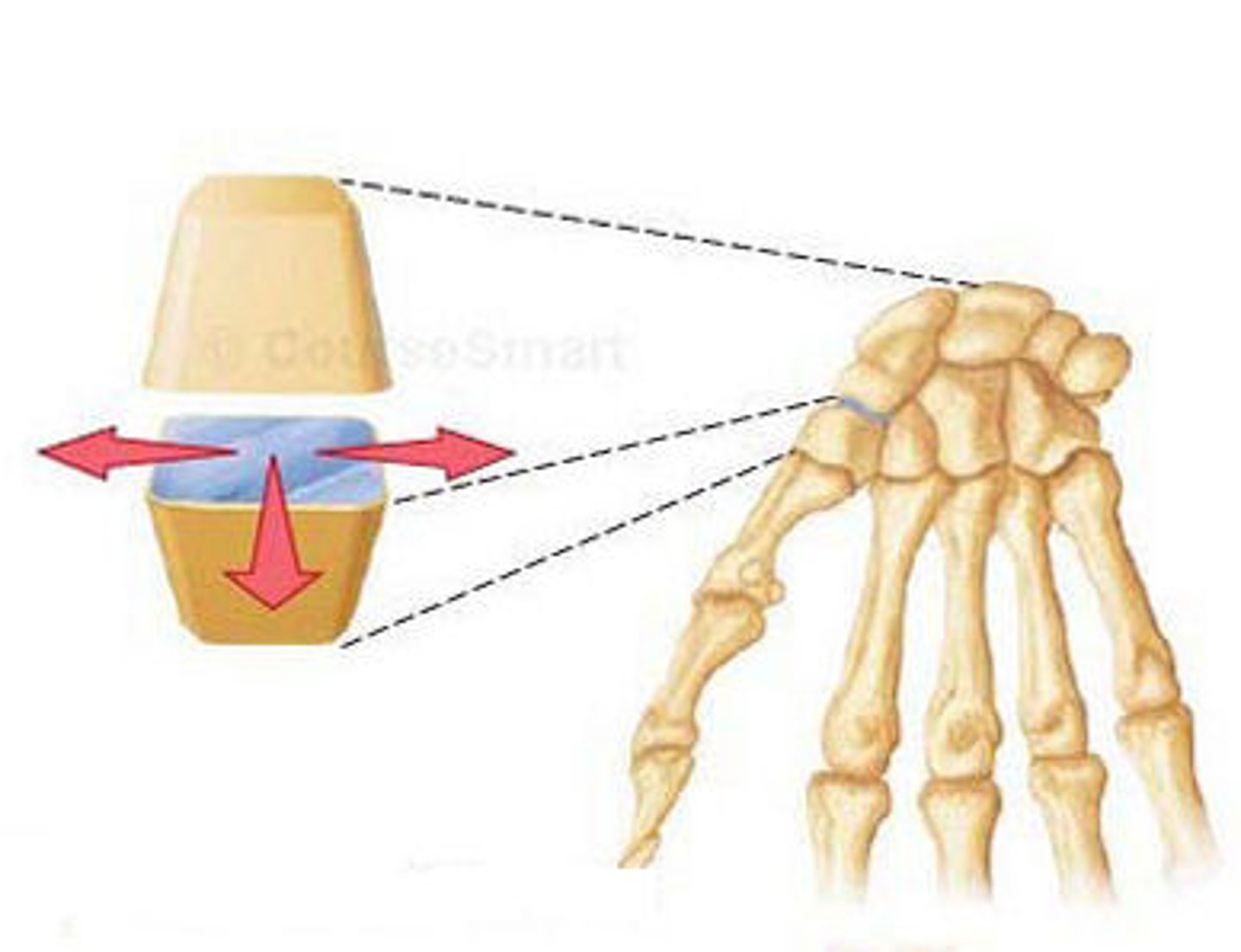
Plane Joint (intercarpal joint)
A nonaxial joint that has a flat and articular shape. Made for short gliding movements.
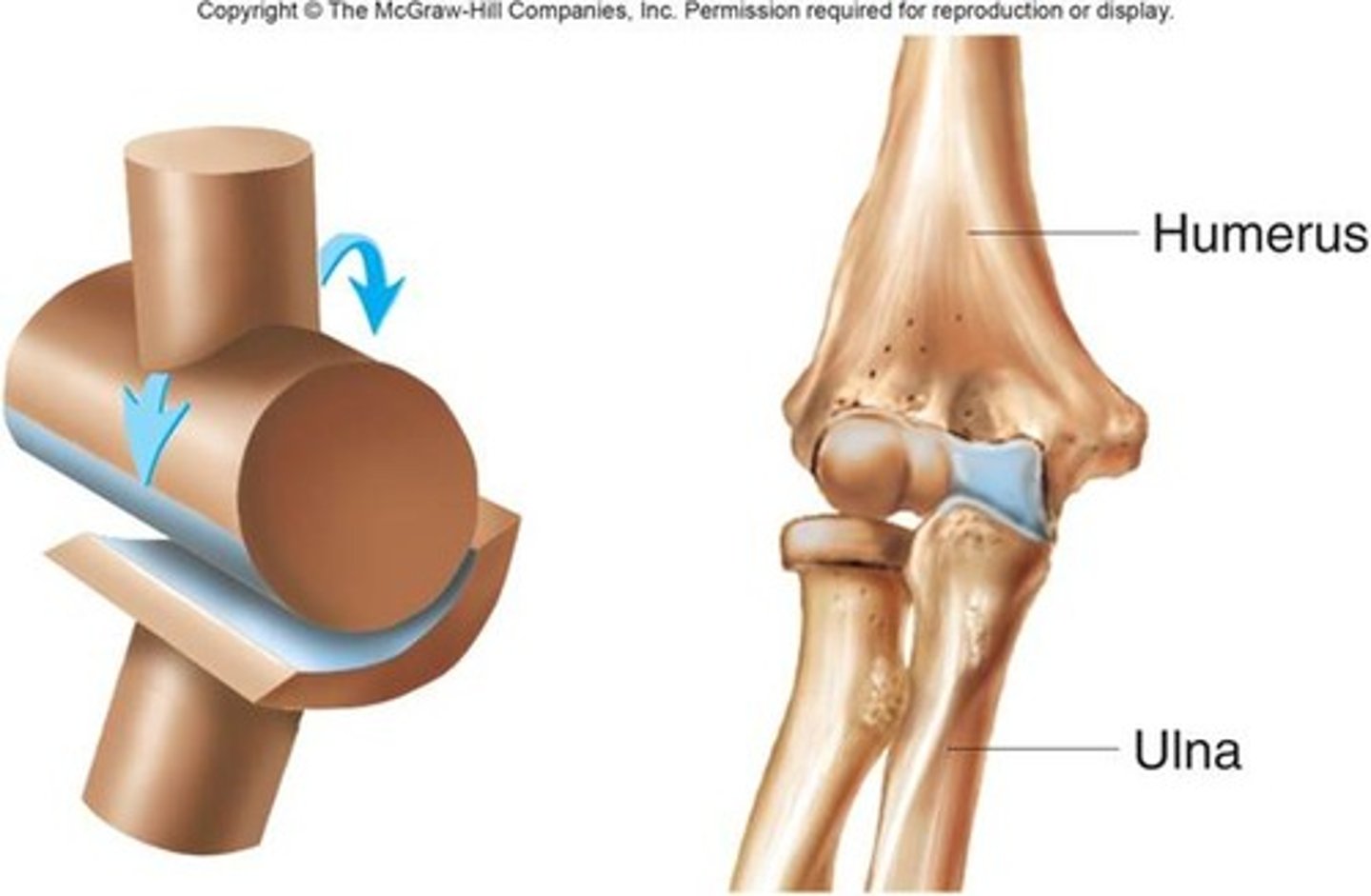
Hinge Joint (elbow)
The rounded end of one bone articulating with a ring of another bone. This joint has only uni(!)axial movements.
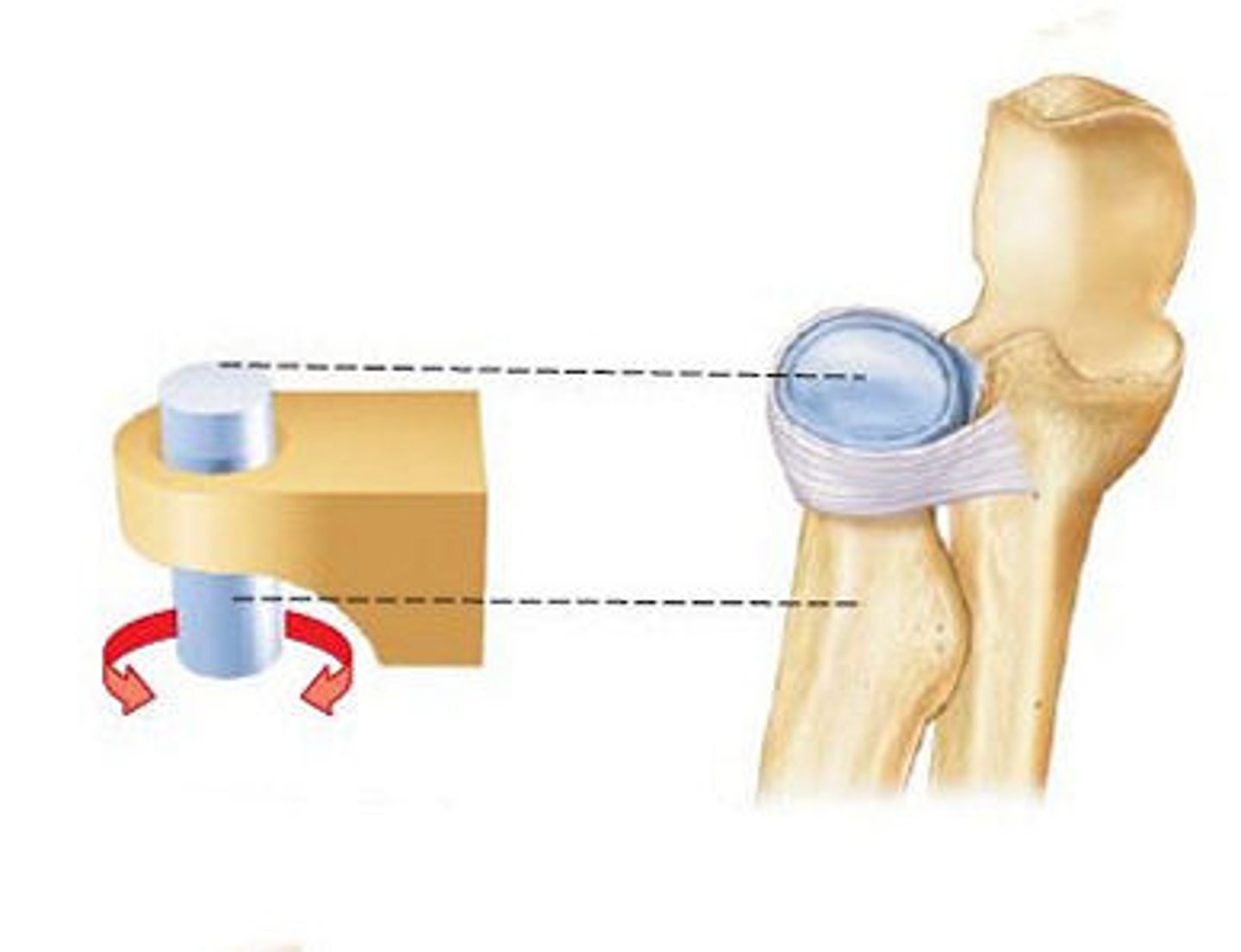
Pivot Joint (proximal radioulnar joint)
rotating bone turns around an axis: connection between radius/ulna and humerus
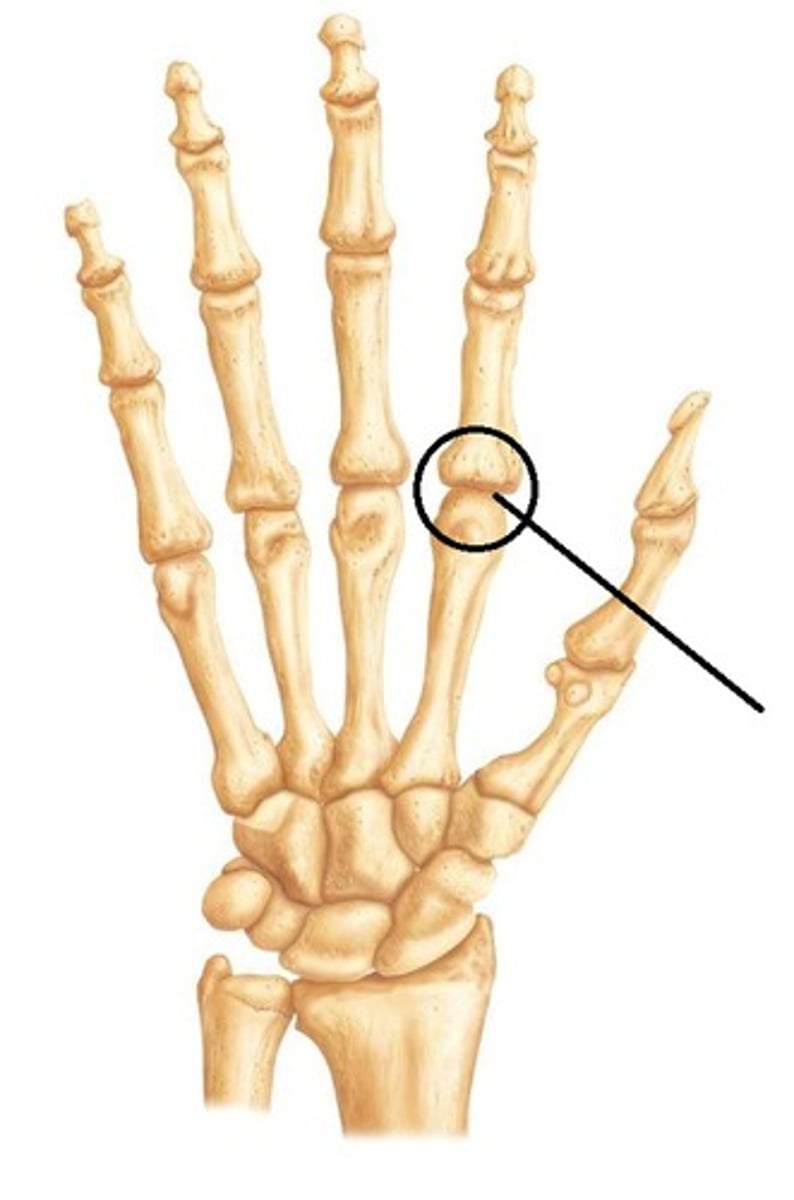
Condyloid joint (metacarpophalangeal joint)
Both articular surfaces are oval and permit all angular movements
Saddle joint (carpometacarpal joint
of thumb)
Biaxial (2 axis), allow greater freedom of movement than condyloid joints
Each articular surface has both concave and convex areas
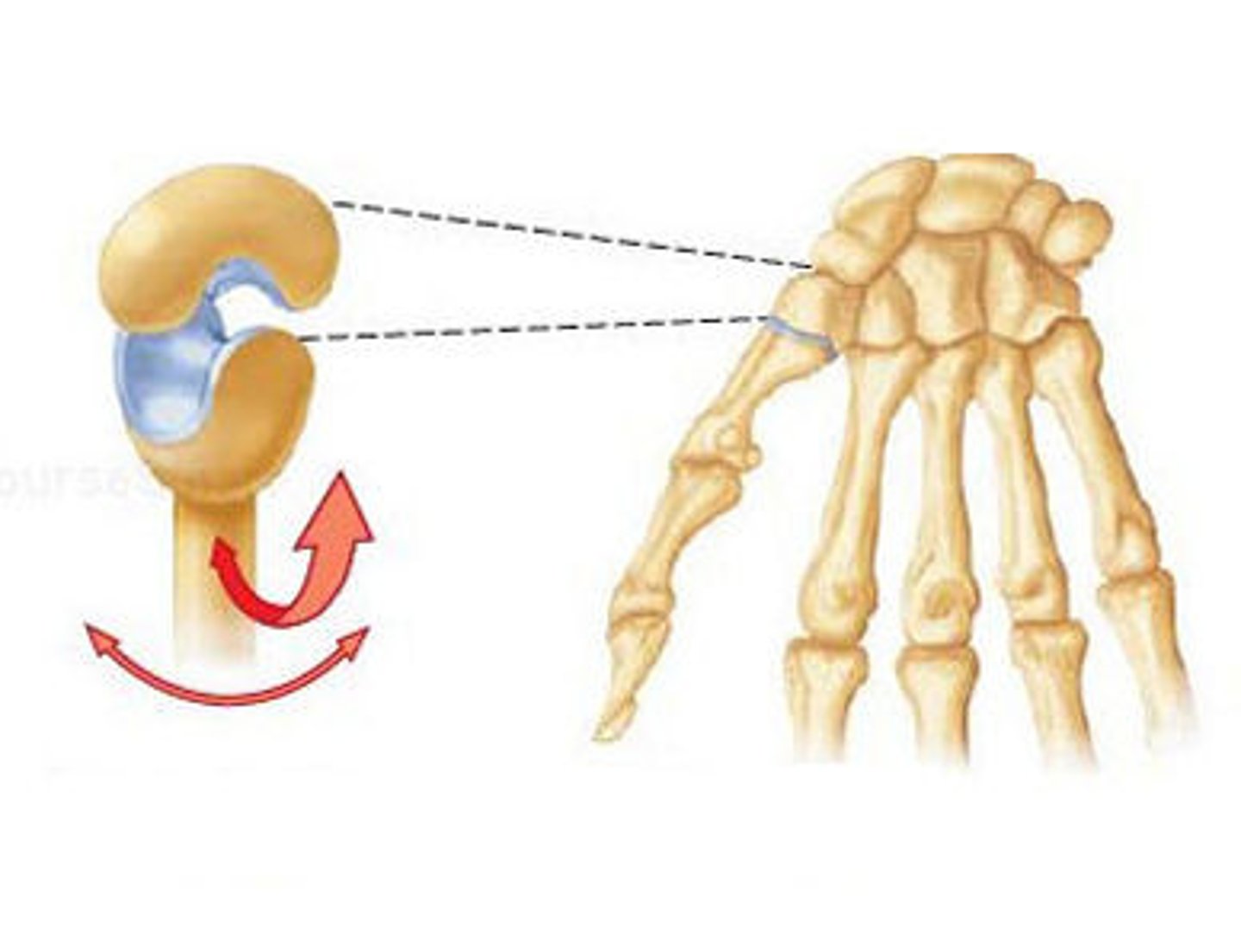
Ball and socket joint (shoulder joint)
The most freely movable synovial joint in the body.