3.5 proteins: biological molecules & cell membranes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
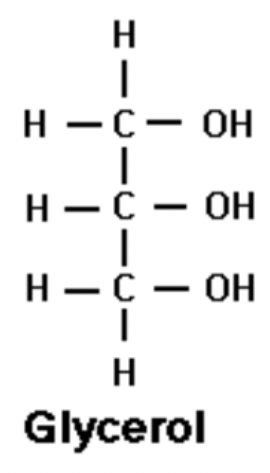
glycerol
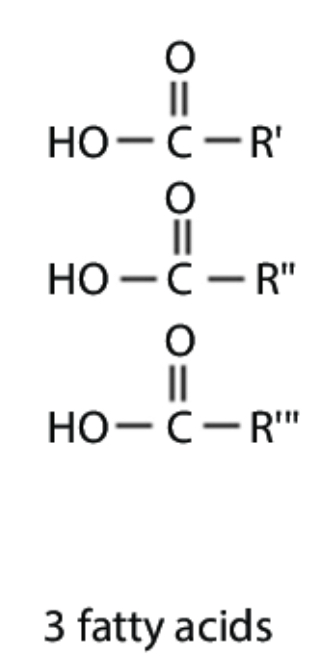
3 fatty acids
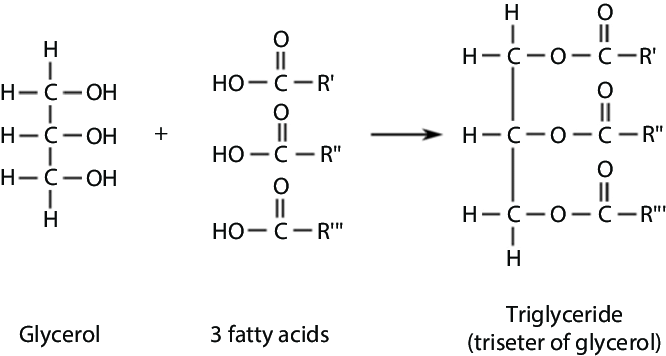
what does glycerol and 3 fatty acid form?
(H2O released due to condensation) Triglyceride and 3H2O
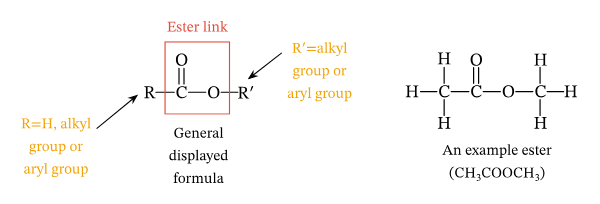
ester bond
In a triglyercide after a condensation reaction
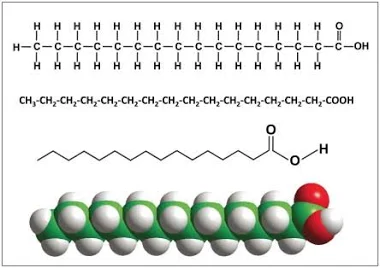
saturated fatty acid
CnH2nO2
single carbon to carbon bonds
mainly solid at room temps
straight, good storage in animals
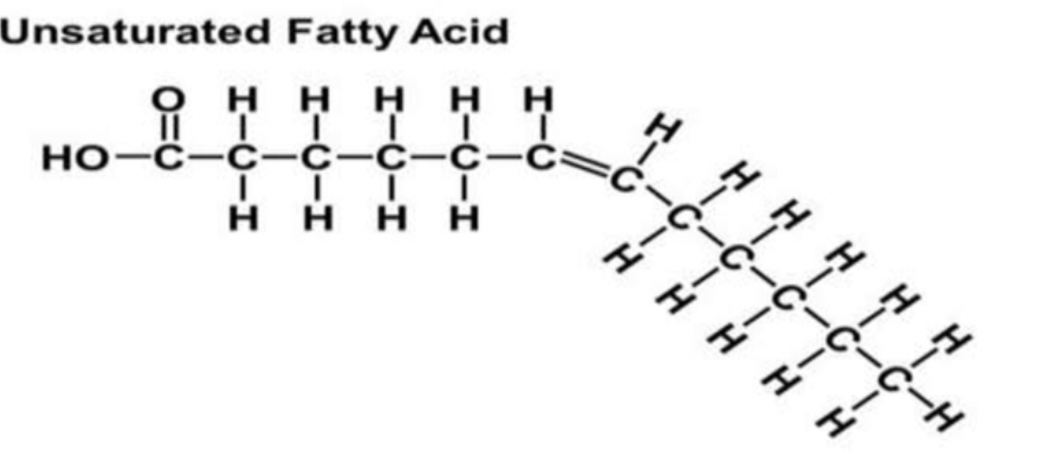
unsaturated fatty acid
one or more double bonds between carbon to carbon
mainly liquid at room temps
not straight (eg, oil)
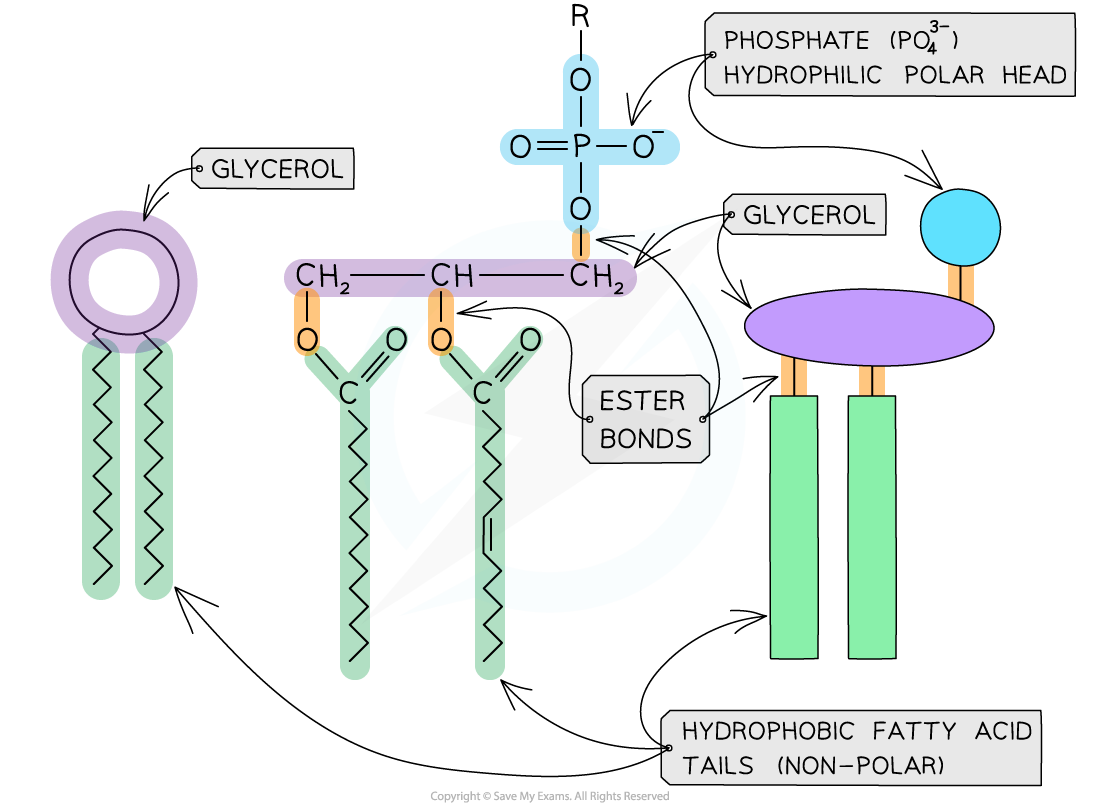
phospholid formation
roles of lipids in biological organisms
phosphorus: biological membranes, electrical impulses (myelin sheath)
Triglyceride: Energy reserves, thermal insulation, organ protection (kidneys) and metabolic water (water releases)
Wax: waterproofing reduces water loss
LDL (low density lipoproteins
a diet of LDL can affect the coronary arteries with antheroma, due to fatty deposits reducing blood flow therefore oxygen towards heart
when food is digest and absorbed in the small
intestines, lipids and proteins combine to make lipoproteins
if diet is high in saturated fats, this will form LDL, leads to heart disease/attack = antheromas in coronary arteries
BAD cholesterol
HDL (high density lipoproteins)
diet high un unsaturated fats causes the body to make more high density lipoproteins
HDL carries harmful fats to the line to be broken down and disposed of
GOOD cholesterol
testing for lipids
1) mix sample with ethanol (orange-brown with the equal amount of water ratio
2) shake so lipids will be dissolved
POS will be milky cloudy white emulsion
NEG will be clear
3 uses of lipids
energy store, thermal insulation, electrical insulation of nerves, buoyancy, waterproofing and protection of delicate organs (kidney)
what part of a phospholipid is hydrophobic and hydrophillic?
hydrophobic - fatty acid tails (non polar)
hydrophillic - phosphate heads (polar)
explain the compounds needed to form a phospholipid
Glycerol, two fatty acid tails and a phosphate group (PO4-)
explain the role of HDL
high density lipoproteins remove cholesterol from the blood
why are lipids a good biological molecule for storing energy?
they can store lots of energy in one molecule - twice as much as carbs
Acetic acid is non-polar, what other molecules will be attracted to it?
other non polar molecules such as the fatty acid tails of a phospholipid
describe the structure of a fatty acid tail
Carboxylic acid group, bonded to repeated CH groups, ends with a CH3 group.
explain how phospholipids are arranged to from a cell membrane
bilayer - phosphate heads pointing outwards towards the polar water inside and outside the the cell.
fatty acid tails facing inwards away from the polar environment
describe the structure of an unsaturated fatty acid tail
contains 1 or more C=C double bonds
maximum number of hydrogen attached to it
what part of the phospholipid is hydrophillic
the glyercol and phosphate group
explain the role of LDL
deposits cholesterol in the arteries, this narrows them and therefore reduced blood flow
examples of lipids
triglyceride, cholesterol, phospholipid and steroid hormone
formula of gylcerol
C3H8O3
describe the properties of a saturated fat
They are solids at room temperature due to the close packing of the fatty acid tails which causes strong forces of attraction, which require more energy to overcome.
describe the structure of a saturated fatty acid tail
It contains only C-C single bonds, so it has the maximum number of hydrogen atoms bound to it.
function of the cholesterol in the cell membrane
makes the CM stable and fluid
name the bond between a glycerol and fatty acid tails
ester bond
describe the properties of unsaturated fats
They are liquids at room
temperature due to the kink in the fatty acid tail which means the tails cannot pack as close together, weakening the forces of attraction.