Biology Chapter 11 - Gas exchange in humans
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
features of gas exchange surfaces
large surface area - more molecules can diffuse at once
thin surface - shoter diffuision distance
good blood supply - gas can be carried to/from cells that need/produce them
good air ventilation - keep up concentration gradients for oxygen and carbon dioxide
function of cartilage in the trachea
prevents trachea from collapsing during exhalation, keeps the airway open for uninterrupted airflow
inhalation
diaphragm contracts
external intercostal muscles contract
ribs goes upward and outward
volume increases, pressure decreases
exhalation
diaphragm relaxes
internal intercostal muscles contract
ribs goes downward and inward
volume decreases, pressure increase
breathing system
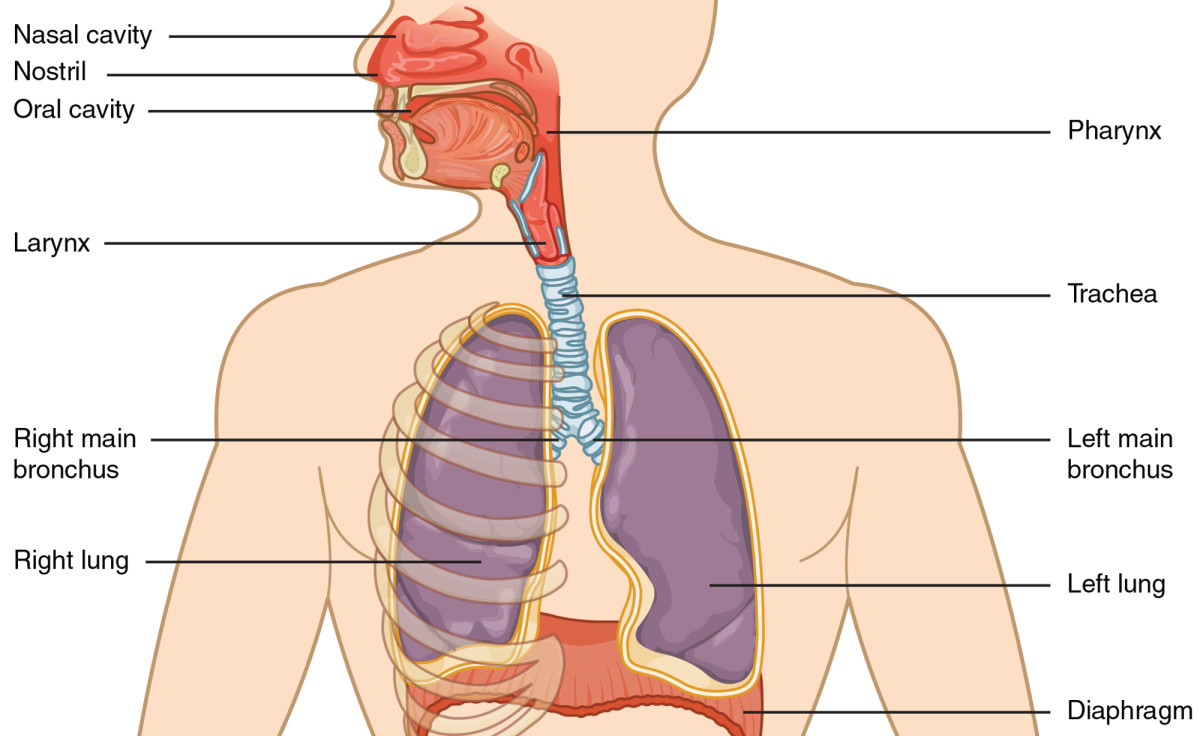
inspired air
Oxygen: 21%
Carbon dioxide: 0.04%
Nitrogen: 78%
Water vapour: lower
expired air
Oxygen: 16%
Carbon dioxide: 4%
Nitrogen: 78%
Water vapour: higher
reason for difference between inspired and expired air
oxygen: used by cells for respiration, thus reducing concentration in expired air
carbon dioxide: by product of respiration, expelled by lungs
water vapour: moisture is added from respiratory tract
nitrogen: not used or produced by body
physical activity and the rate and depth of breathing
Increased carbon dioxide concentration forms carbonic acid in the blood, lowering pH. Change is detected by the brain, which signals the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract faster and more forcefully. Leading to an increased rate and greater depth of breathing, helping to remove excess CO₂ and increase oxygen intake.
role of goblet cells, mucus and ciliated cells in protecting breathing system from pathogens and particles
goblet cells: produces mucus
mucus: forms a sticky layer lining the airways to trap harmful particles and microorganisms to prevent them from reach the lungs
ciliated cells: moves mucus up towards the throat, it is then swallowed or expelled