Understanding Genes, Alleles, and Phenotypes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Gene
Section of DNA coding for a specific protein.
Chromosome
Long DNA strand containing thousands of genes.
Genetic code
Sequence of bases along a gene.
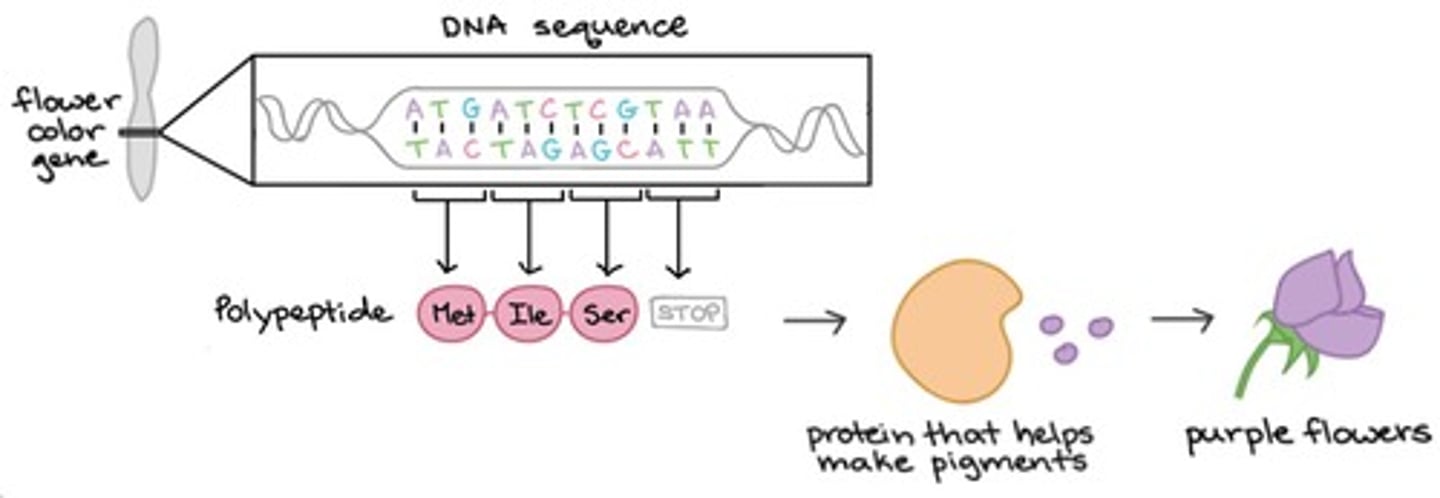
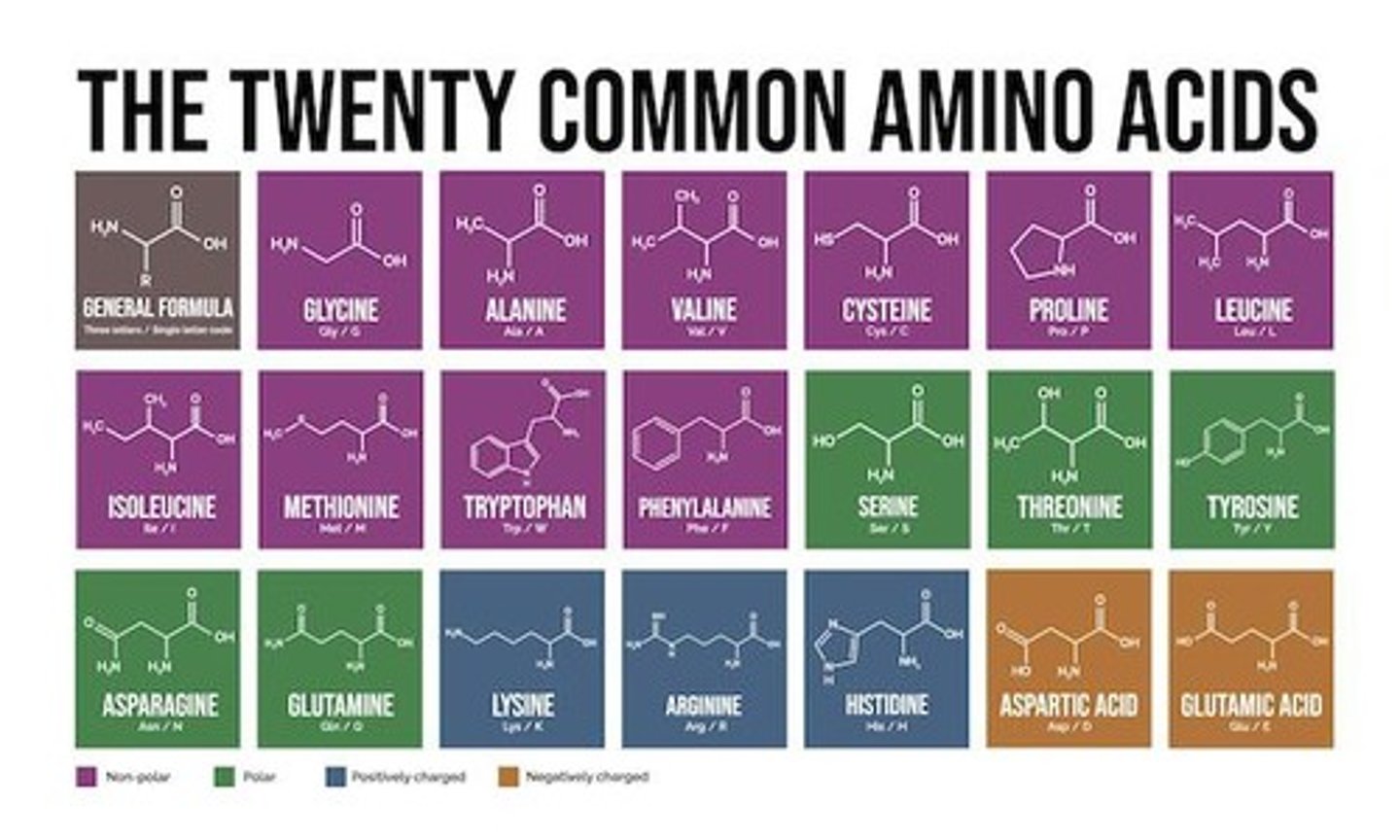
Amino acids
Building blocks of all proteins, 20 types exist.
Protein
Molecule formed by amino acids, determines function.
Trait
Characteristic of an organism influenced by proteins.
Allele
Alternative version of a single gene.
Genotype
Pair of alleles an individual possesses.
Phenotype
Physical characteristic determined by genotype.
Homozygous genotype
Two identical alleles for a gene.
Heterozygous genotype
One dominant and one recessive allele.
Dominant allele
Causes dominant phenotype in heterozygous individuals.
Recessive allele
Causes recessive phenotype only in homozygous recessive.
Dominant phenotype
Characteristic expressed in heterozygous individuals.
Recessive phenotype
Characteristic expressed only in homozygous recessive individuals.
Environmental influence
Phenotype can be affected by environmental factors.
Gene sequence
Determines amino acid order in proteins.
Protein shape
Final form of protein affects its function.
Allele position
Alleles occupy the same chromosome location.
Phenotype ratio
Proportion of different phenotypes in offspring.
Lego analogy
Genes provide instructions like Lego booklets.
Chromosome pairs
Most cells have two copies of each gene.