Urine Microscopy
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Different findings in urine and what they clinically can mean.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
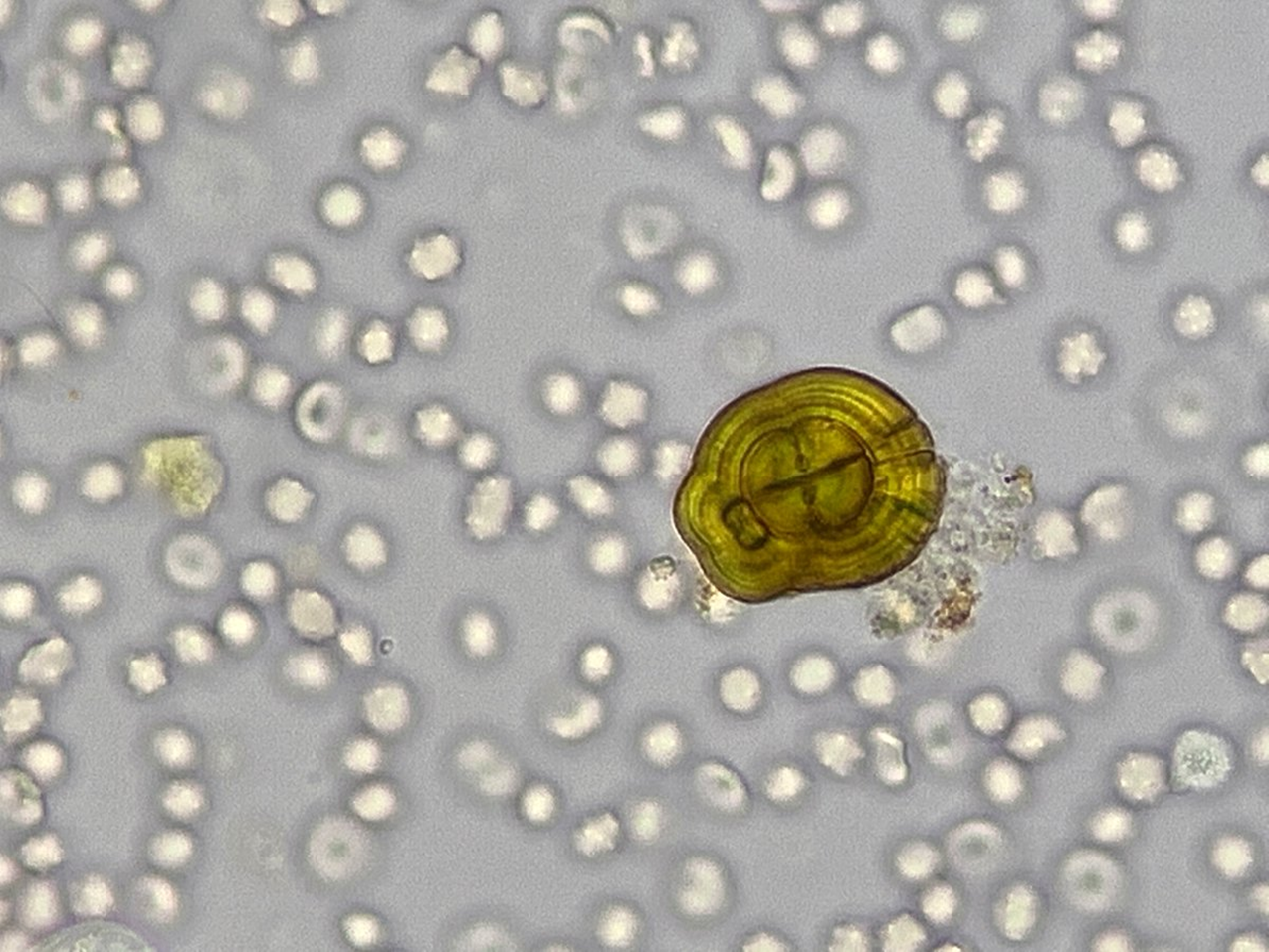
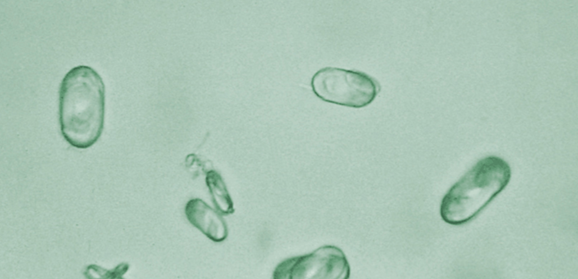
RBC
Reported as average/10 HPF
RBC
Reported as average/10 HPF
RBC
Associated with glomerular membrane damage or vascular injury within the genitourinary tract
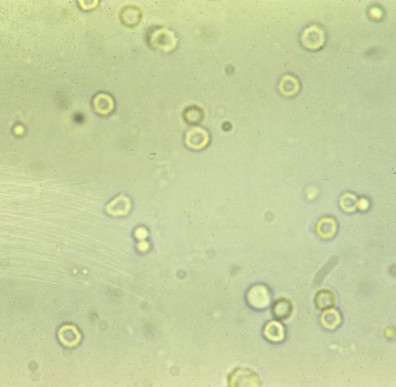
WBC
Reported as average/10 HPF
WBC
Reported as average/10 HPF
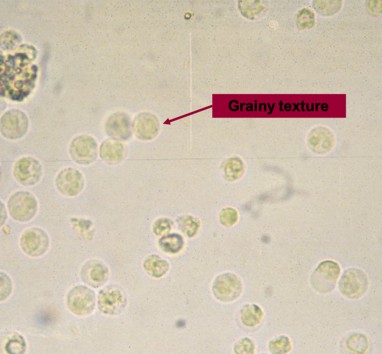
Pyuria
Increase in urinary WBC
Neutrophil
Predominant WBC found in urine sediment
Neutrophil
May produce a sparkling appearance “Glitter Cell”
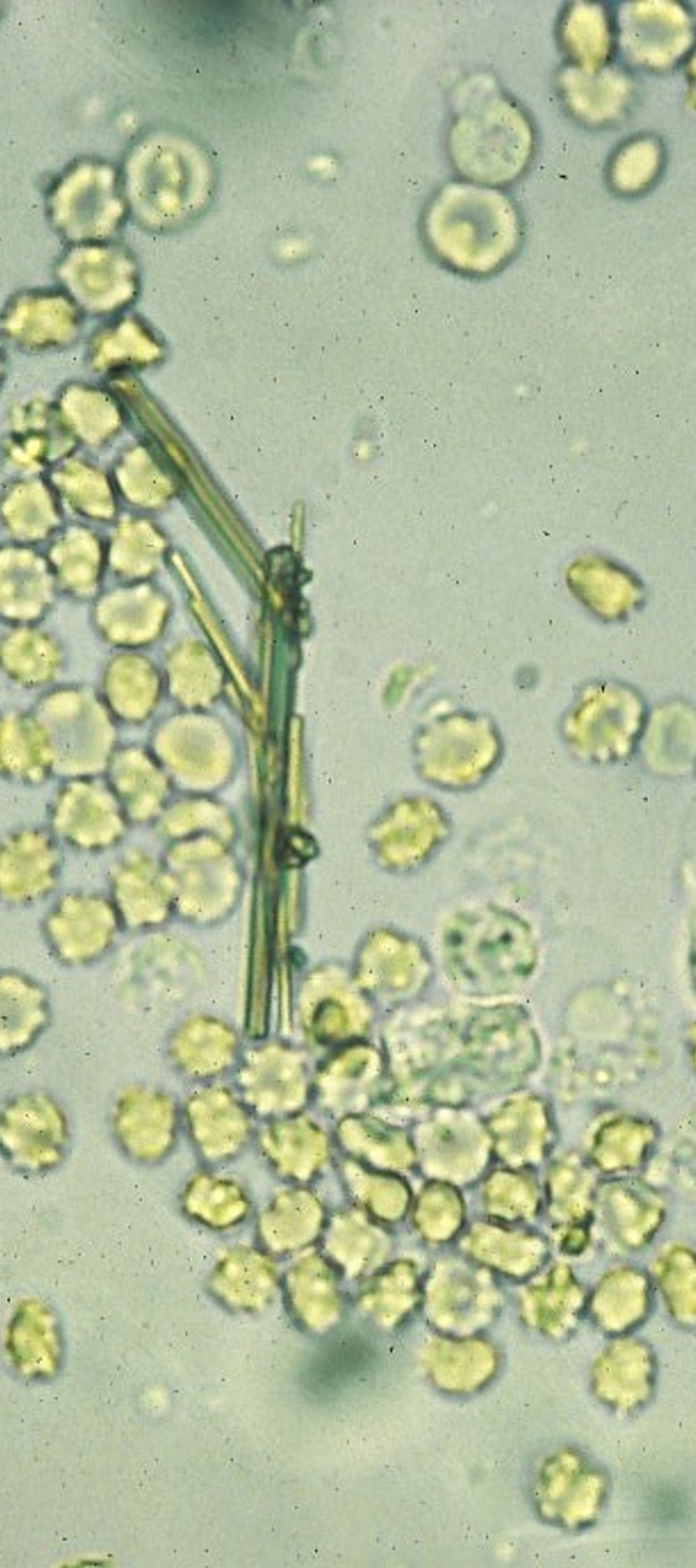
Squamous Epithelial Cells
Reported on LPF or HPF
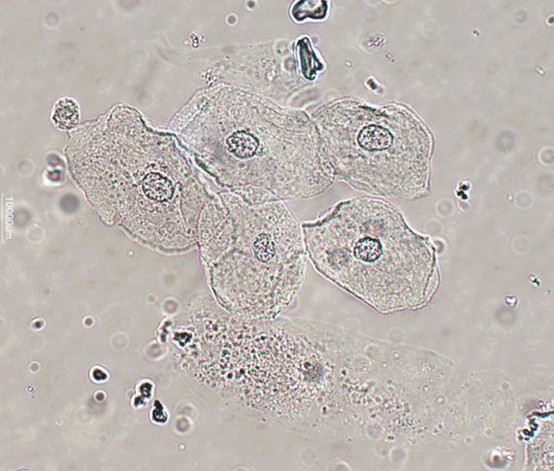
Transitional Epithelial Cells
Reported on HPF
Transitional Epithelial Cells
Clinical insignificant in small numbers but could increase viral infection (refer to pathologist)
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
Report HPF
RTE
Could Indicate Renal Tubule Necrosis (Not good)
Oval Fat Bodies
HPF
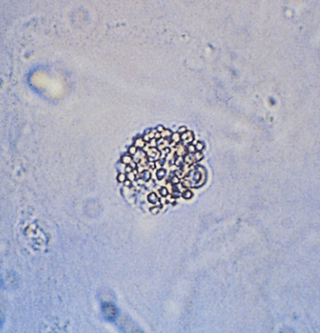
Oval Fat Bodies
RTE cells that have absorbed lipids present in the glomerular filtrate
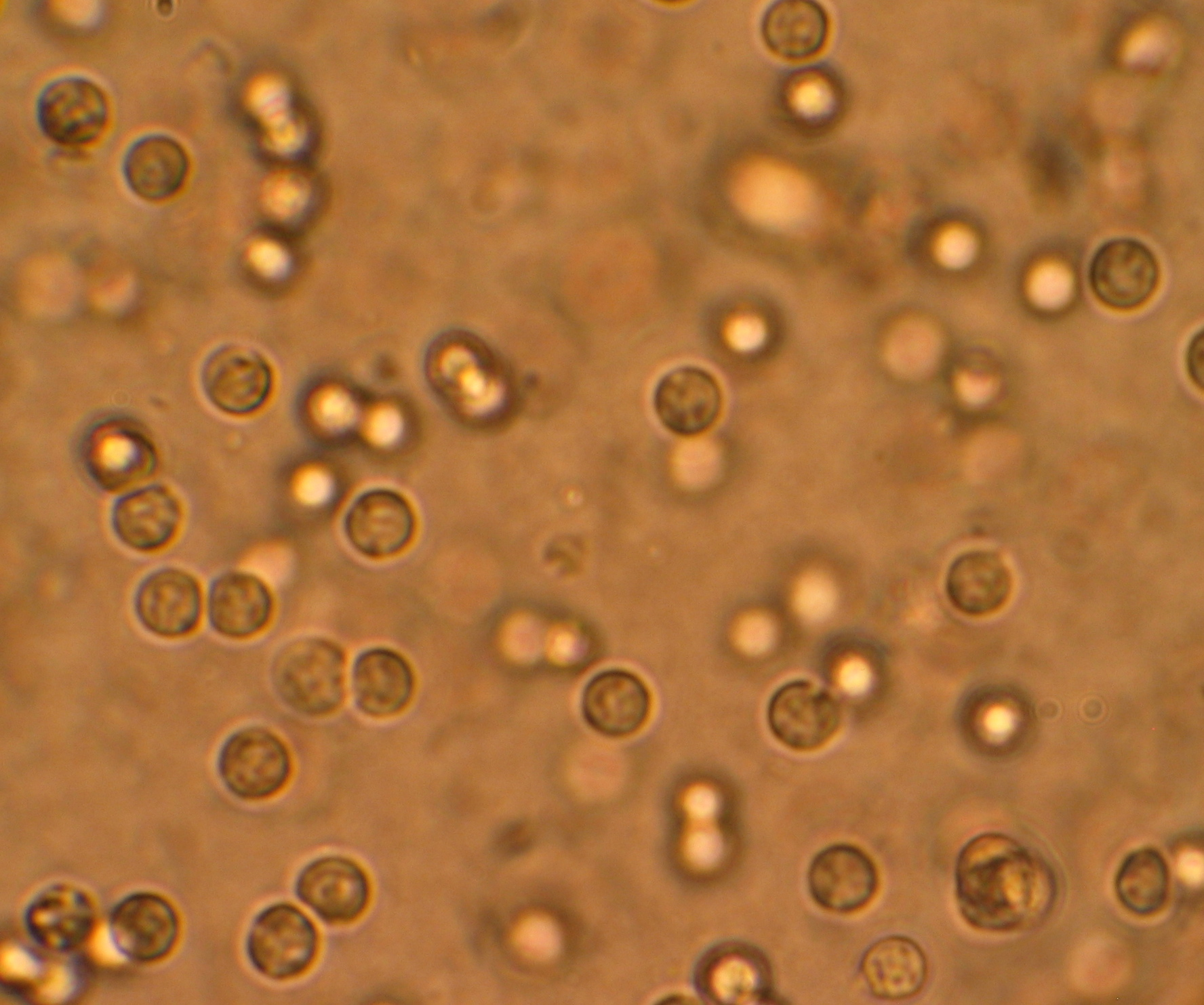
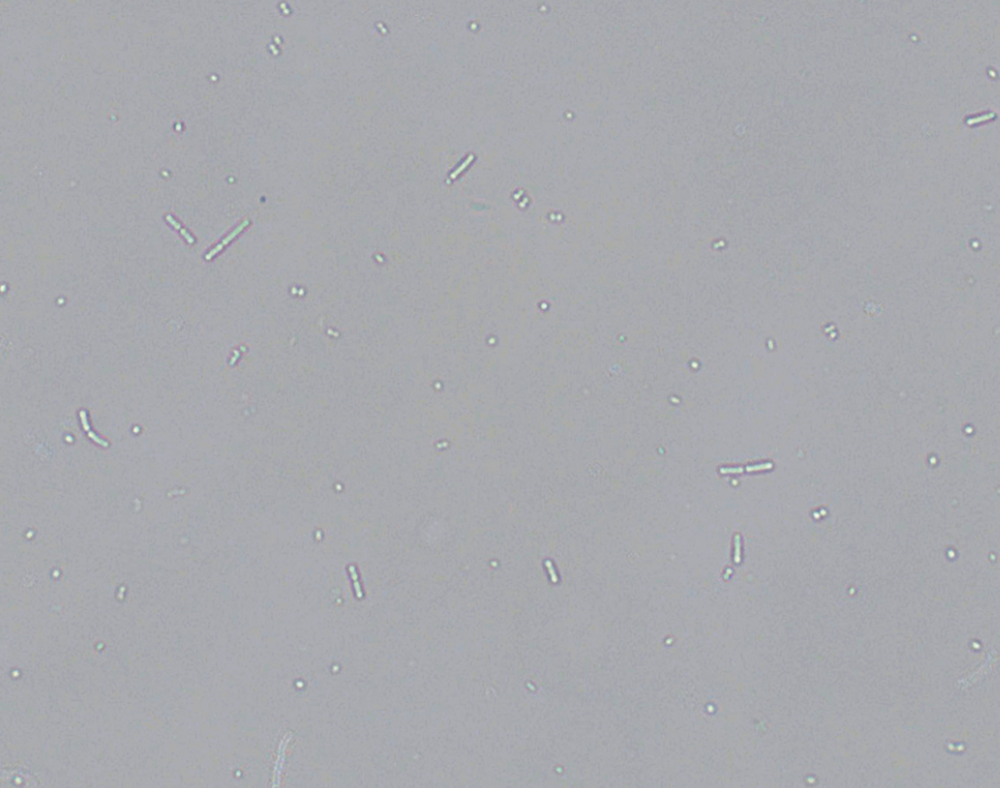
Bacteria
HPF
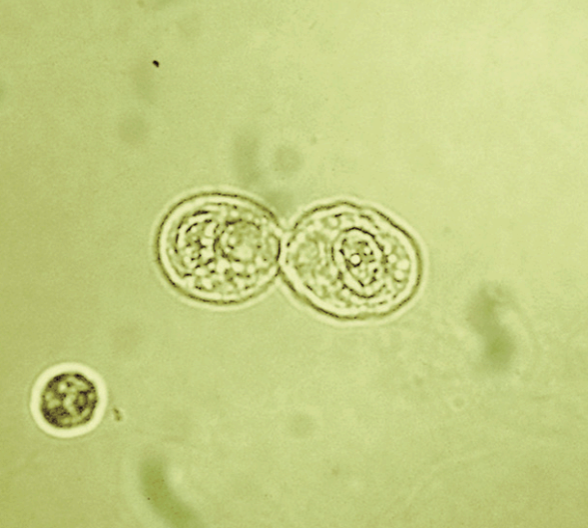
Yeast
HPF
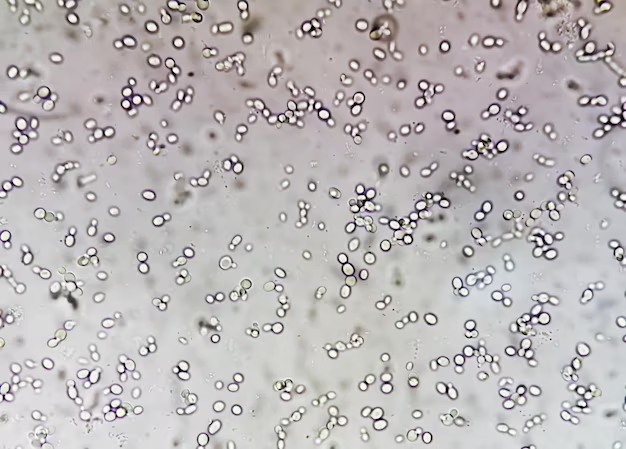
Candida albicans
Most common yeast in urine that is seen in diabetic or immunocompromised patients
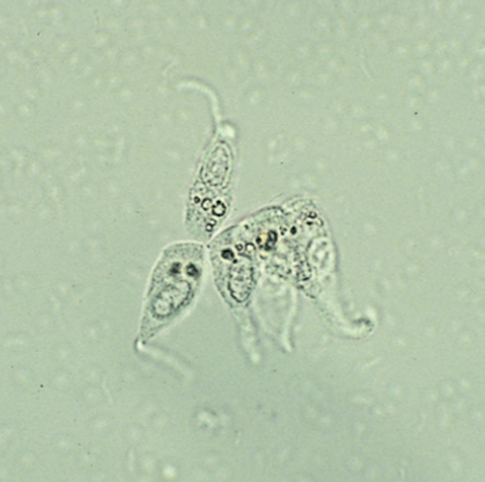
Parasite
HPF
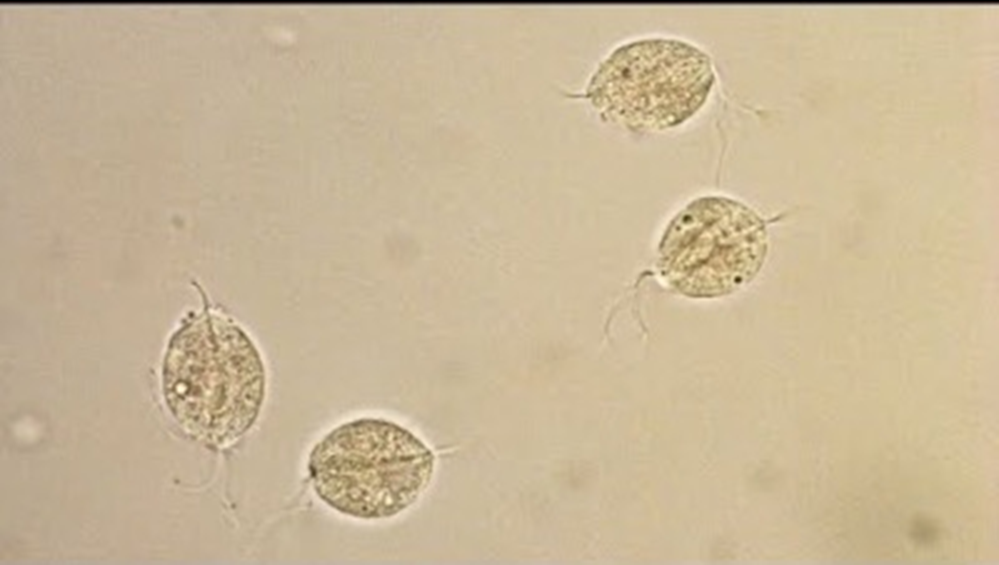
T. vaginalis
Most commonly encountered parasite in urine
Sperm
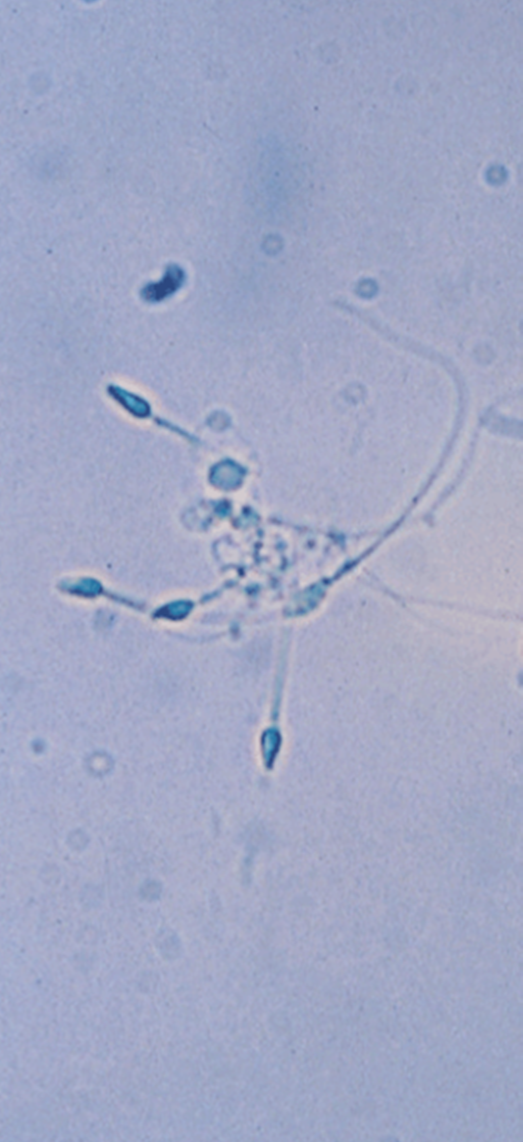
Sperm
Typically insignificant unless found in a patient who is a minor
Mucus
LPF
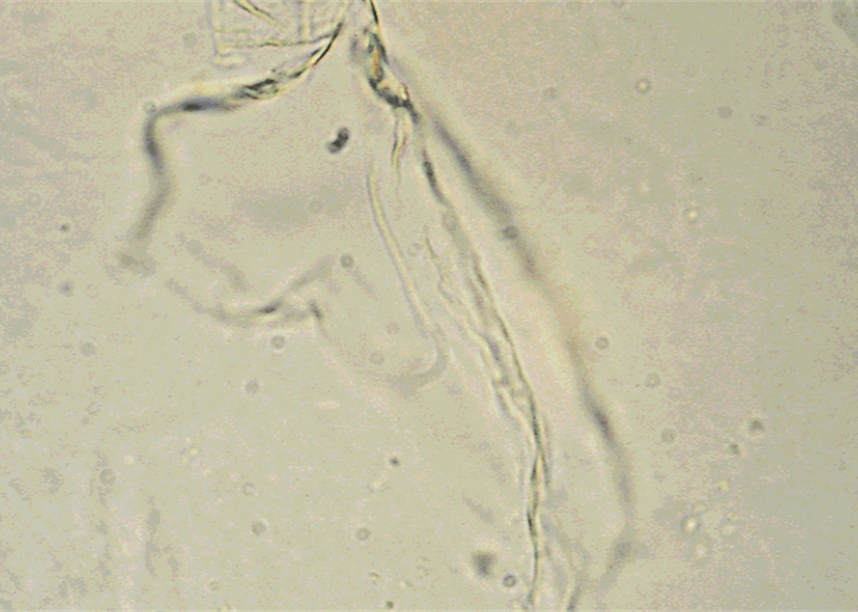
Mucus
Protein material made by the glands and epithelial cells
Hyaline Casts
LPF
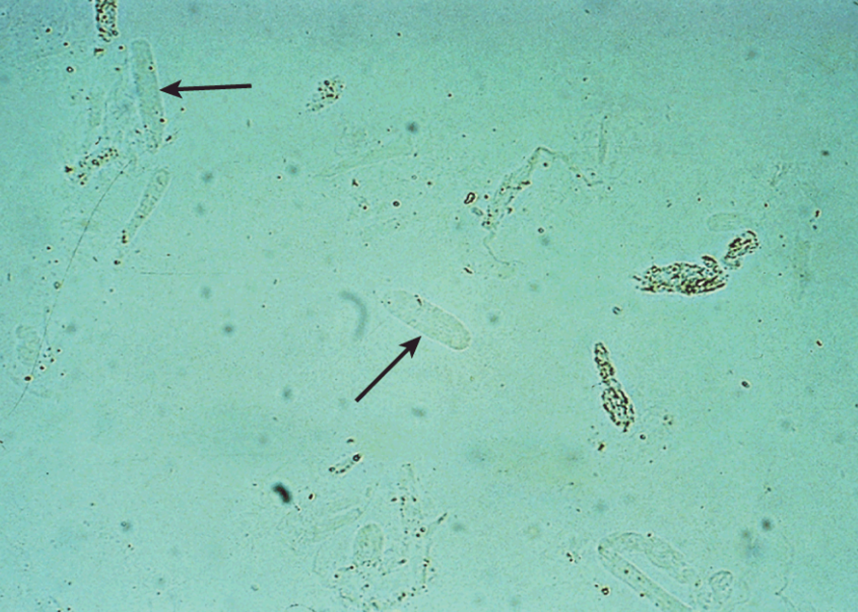
Hyaline Casts
Almost completely made of uromodulin. Increased numbers after strenuous exercise, dehydration, or pathological causes (acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease and CHF)
Hyaline Casts
Common in these pathological issues: acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease and CHF
RBC Cast
LPF
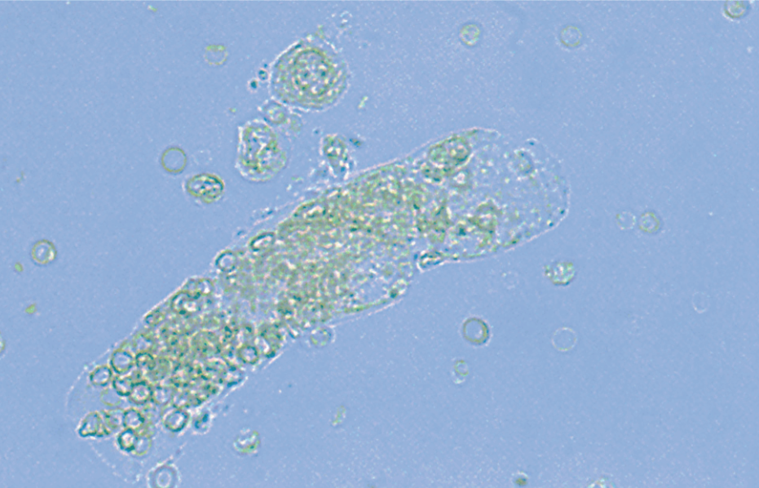
RBC Casts
This can indicate bleeding within the nephron or glomerular damage
WBC Casts
Confirm on HPF
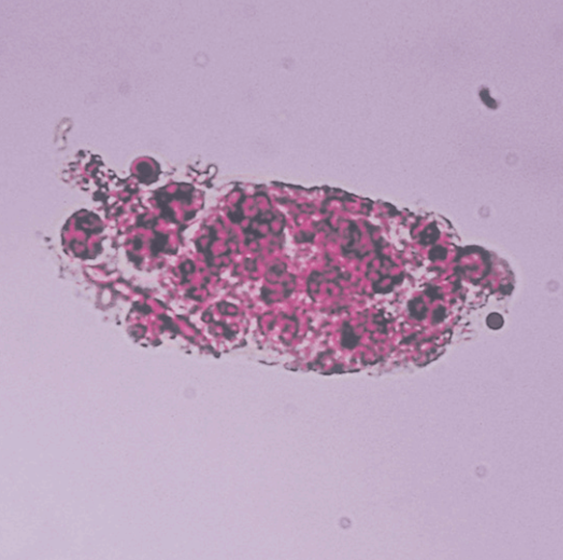
WBC Casts
Indicates nephron infection/inflammation and a marker for pyelonephritis (upper UTI) vs. cystitis (lower UTI)
Epithelial Cell Casts
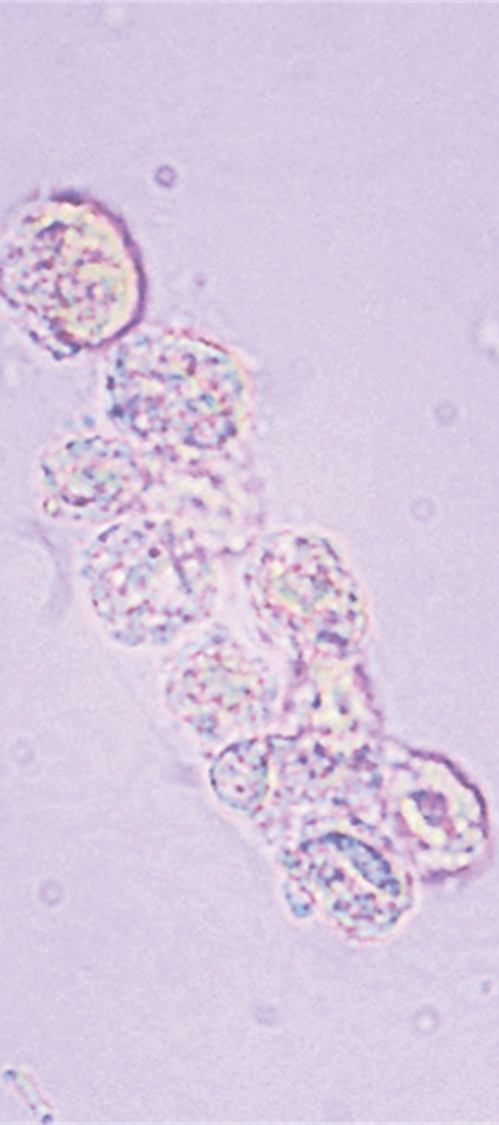
Epithelial Cell Casts
May be present due to heavy metal toxicity, chemicals, drugs, viral infections, allograft rejection
Fatty Casts
Highly refractile
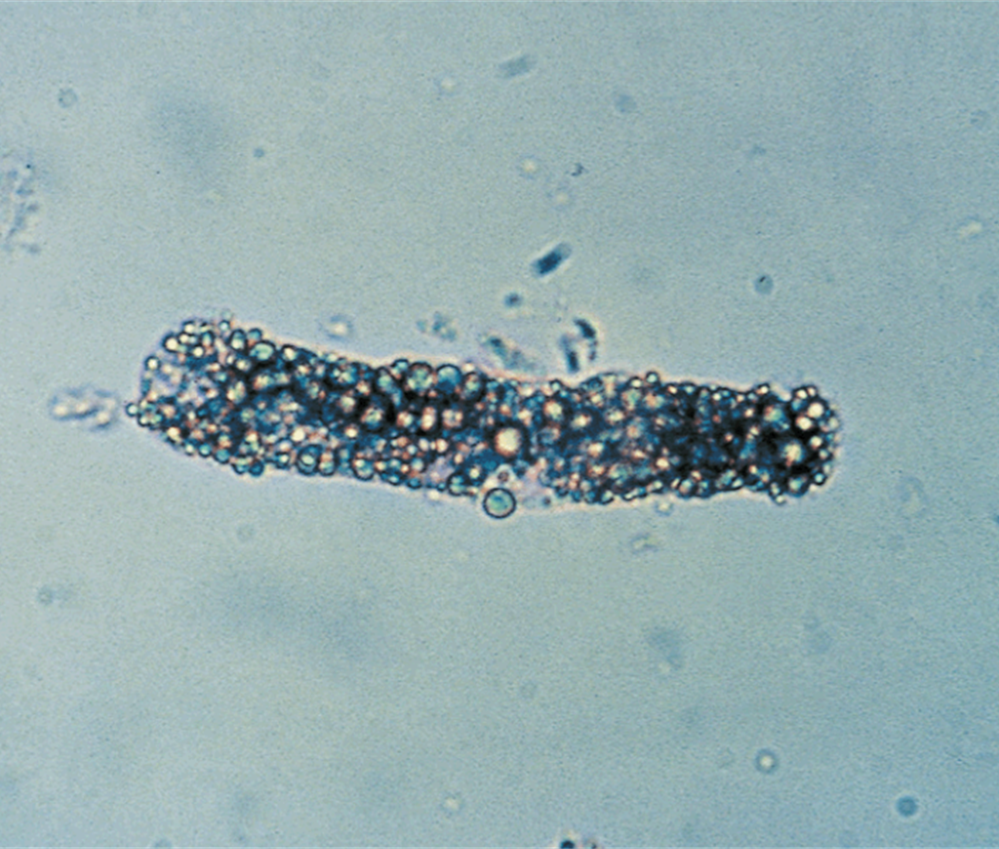
Fatty Casts
Seen with oval fat bodies in disorders causing lipiduria
Fatty Casts
Associated with Nephrotic syndrome, Sometimes toxic tubular necrosis, diabetes mellitus, and crush injuries
Granular Casts
HPF
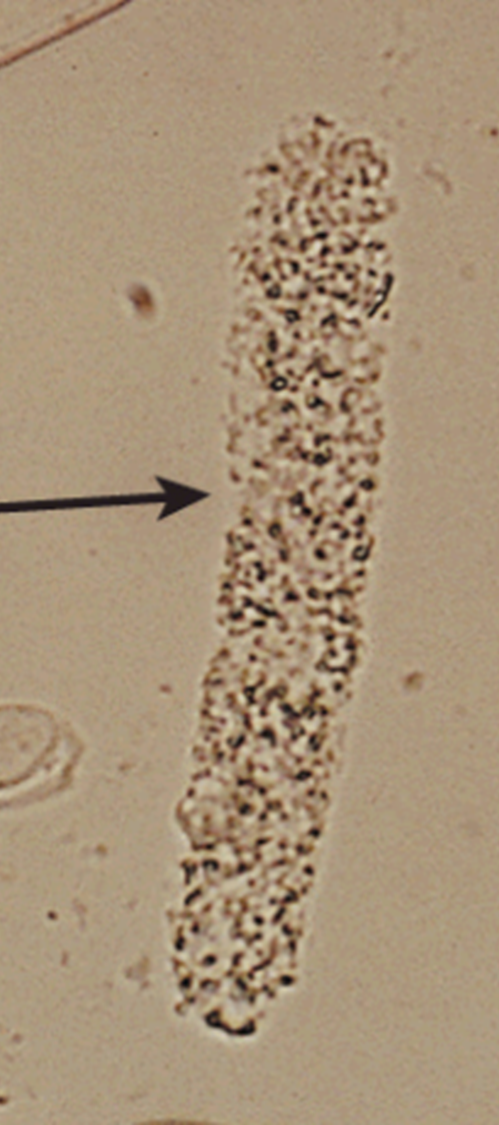
Granular Casts
Could indicate disintegration of cellular casts, tubule cells, or protein aggregates filtered by the glomerulus
Waxy Casts
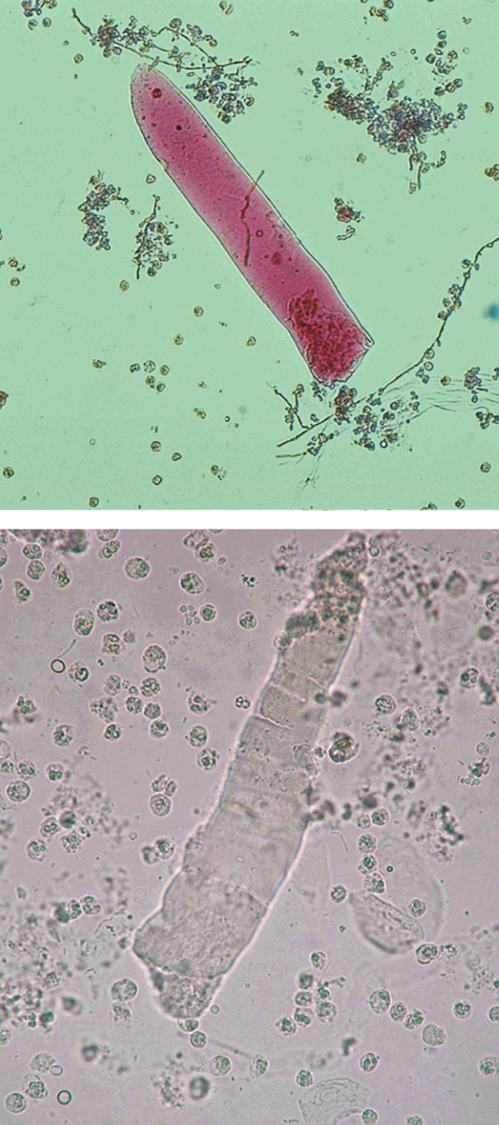
Waxy Casts
Indicates extreme urine stasis - chronic renal failure
Broad Casts
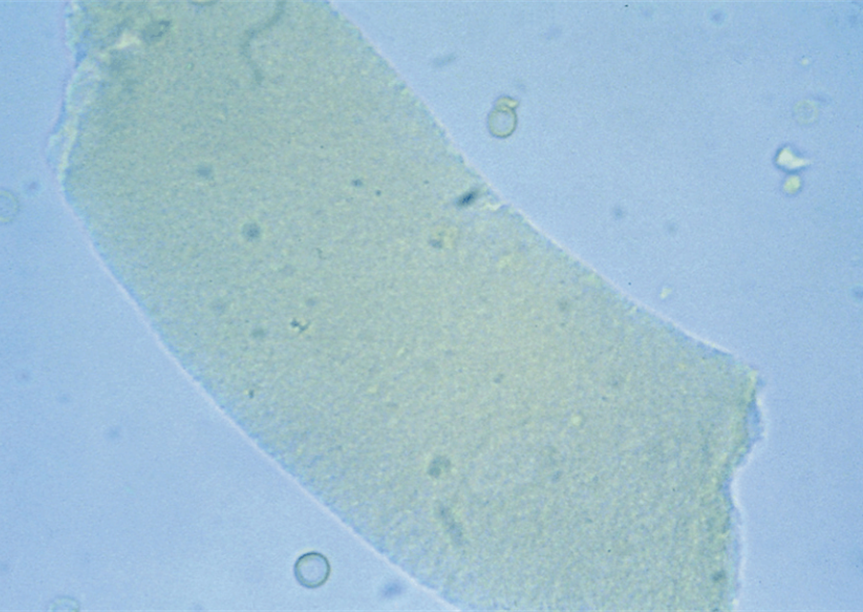
Broad Casts
“Renal Failure Casts” mold of the distal convoluted tubules
Amorphous Urates
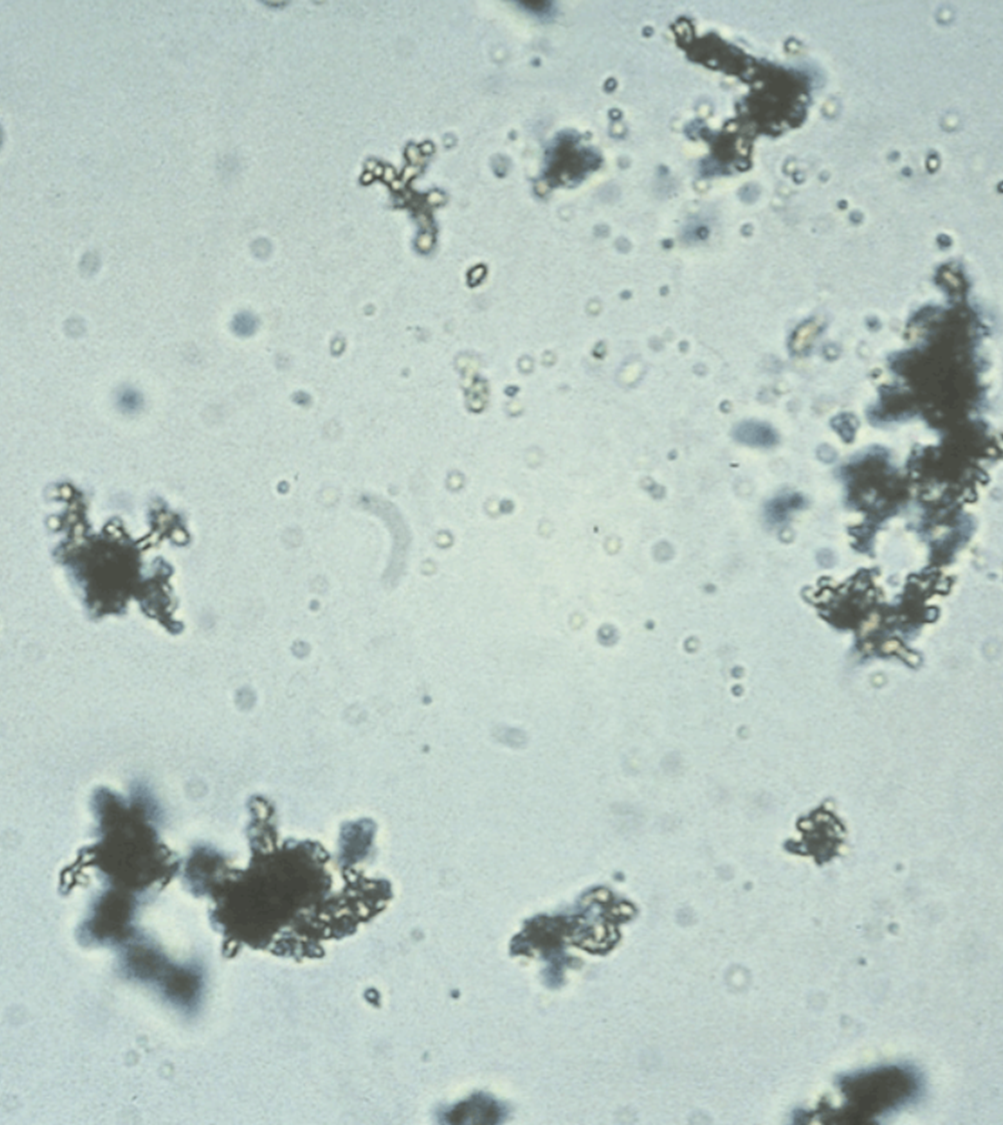
Amorphous Urates
Normally seen in acidic urine with a pH of >5.5
Uric Acid Crystals
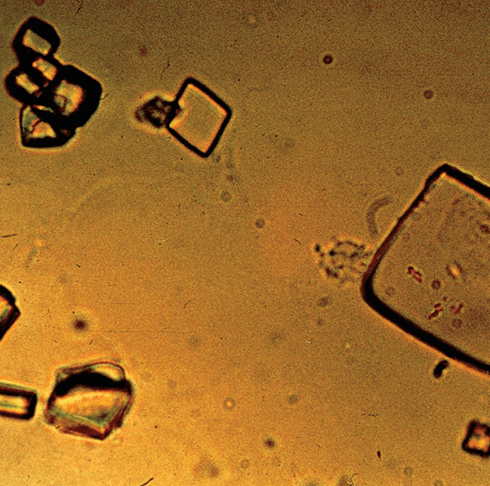
Uric Acid Crystals
Normally in urine, but increased amounts can be seen in gout, leukemic patients receiving chemo, or patients with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Hippuric Acid Crystals
No clinicial significance
Sodium Urate
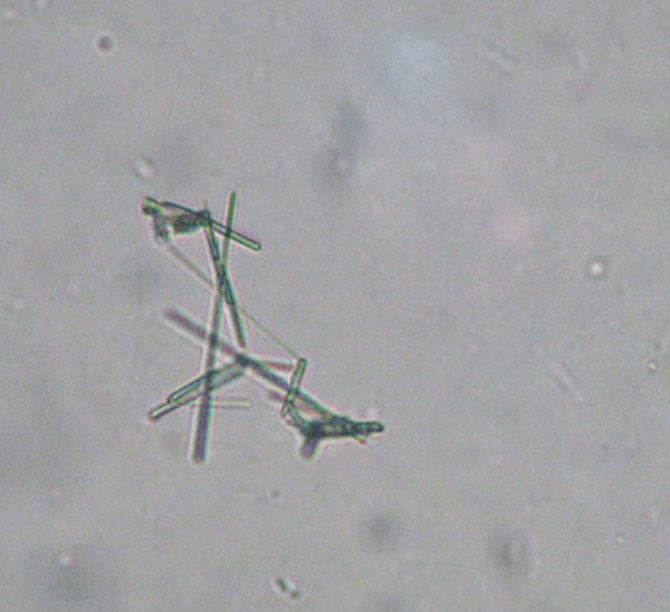
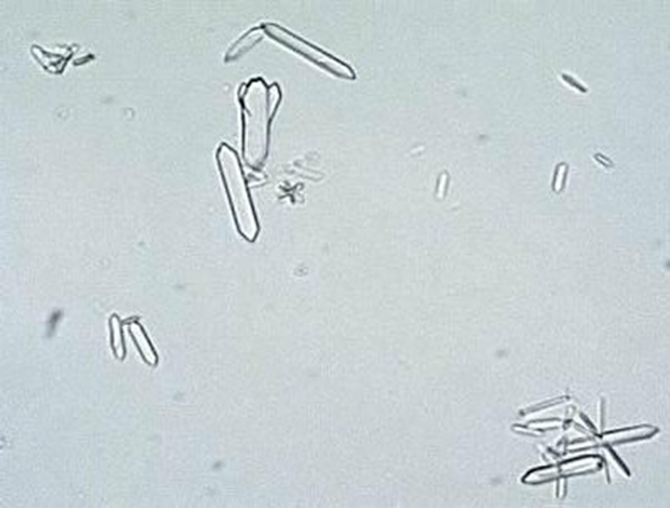
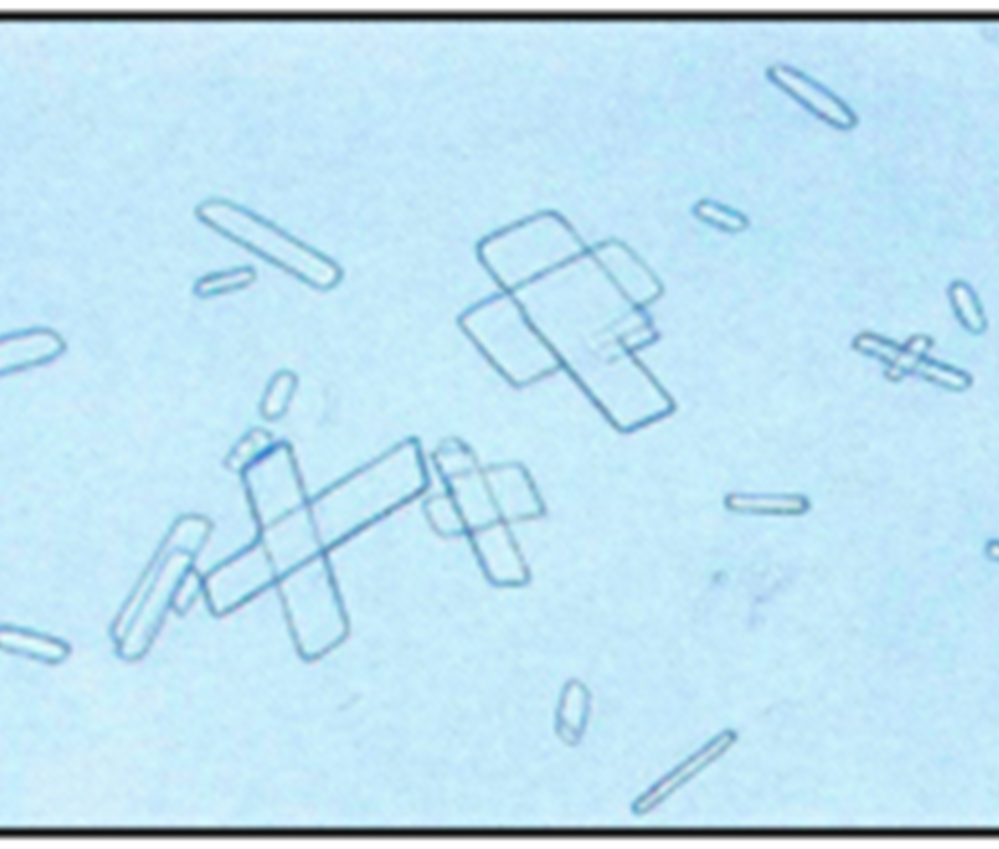
Calcium Oxalate
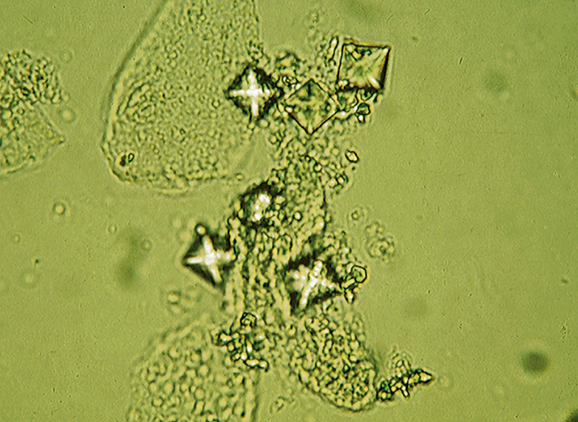
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium Oxalate
In increased numbers it could indicate formation of renal calculi
Amorphous Phosphates
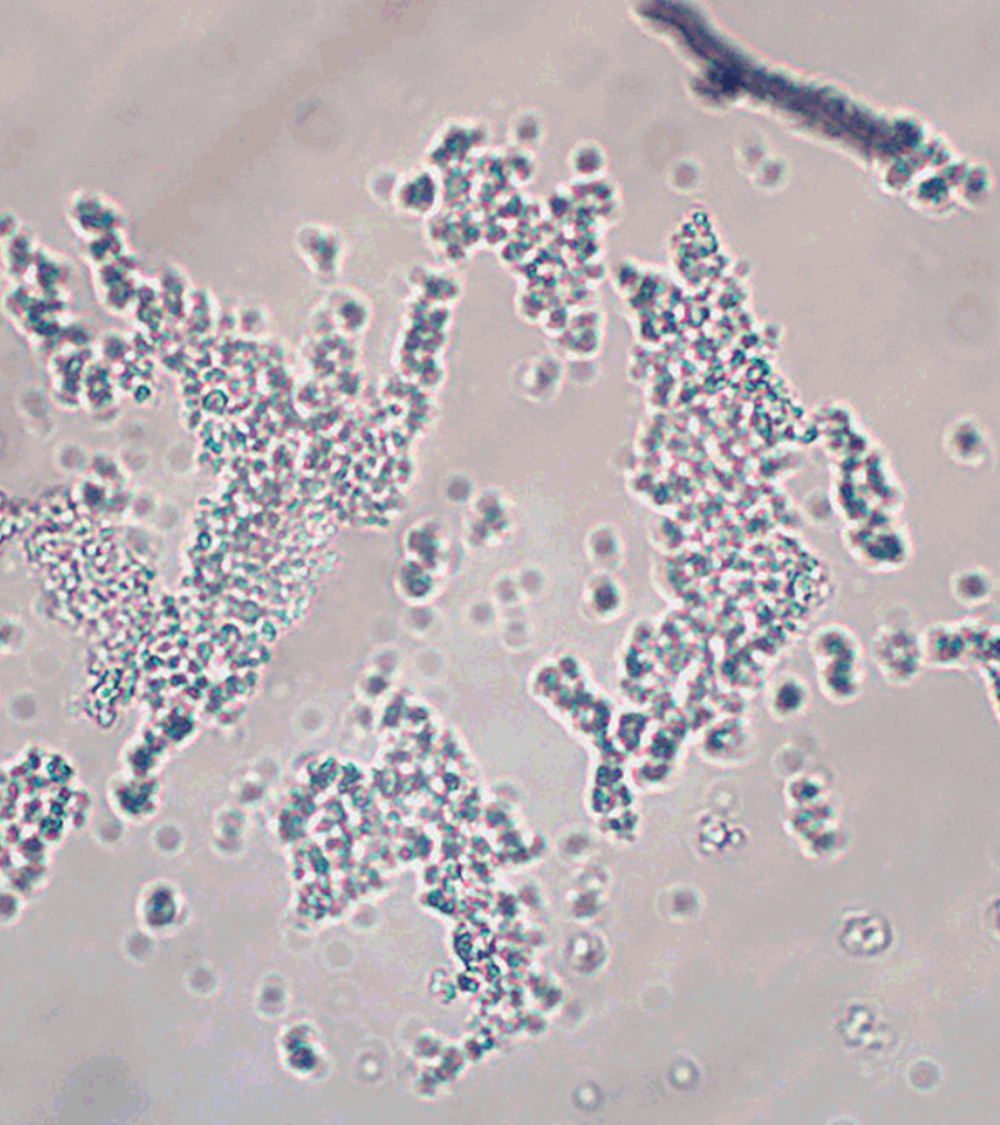
Triple Phosphate
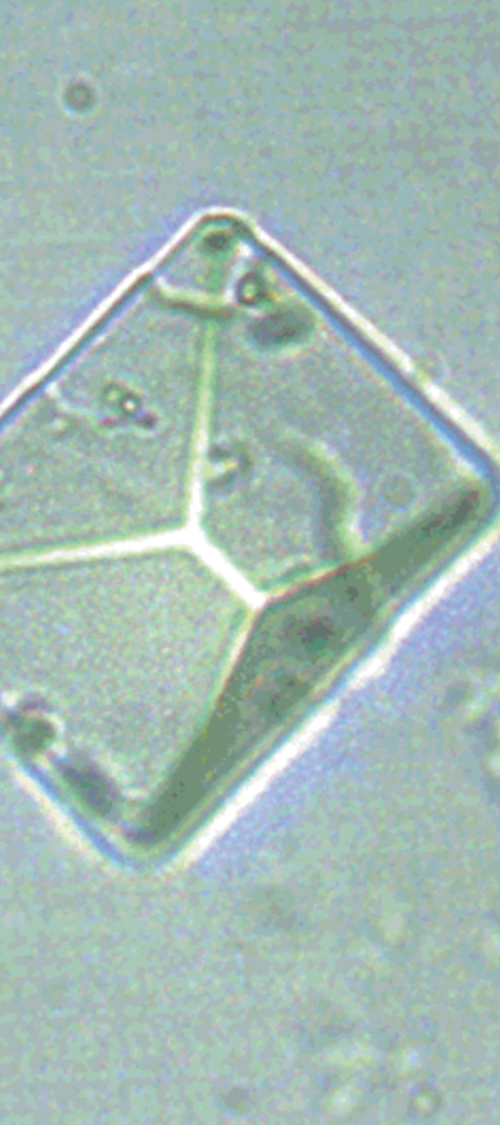

Calcium Carbonate
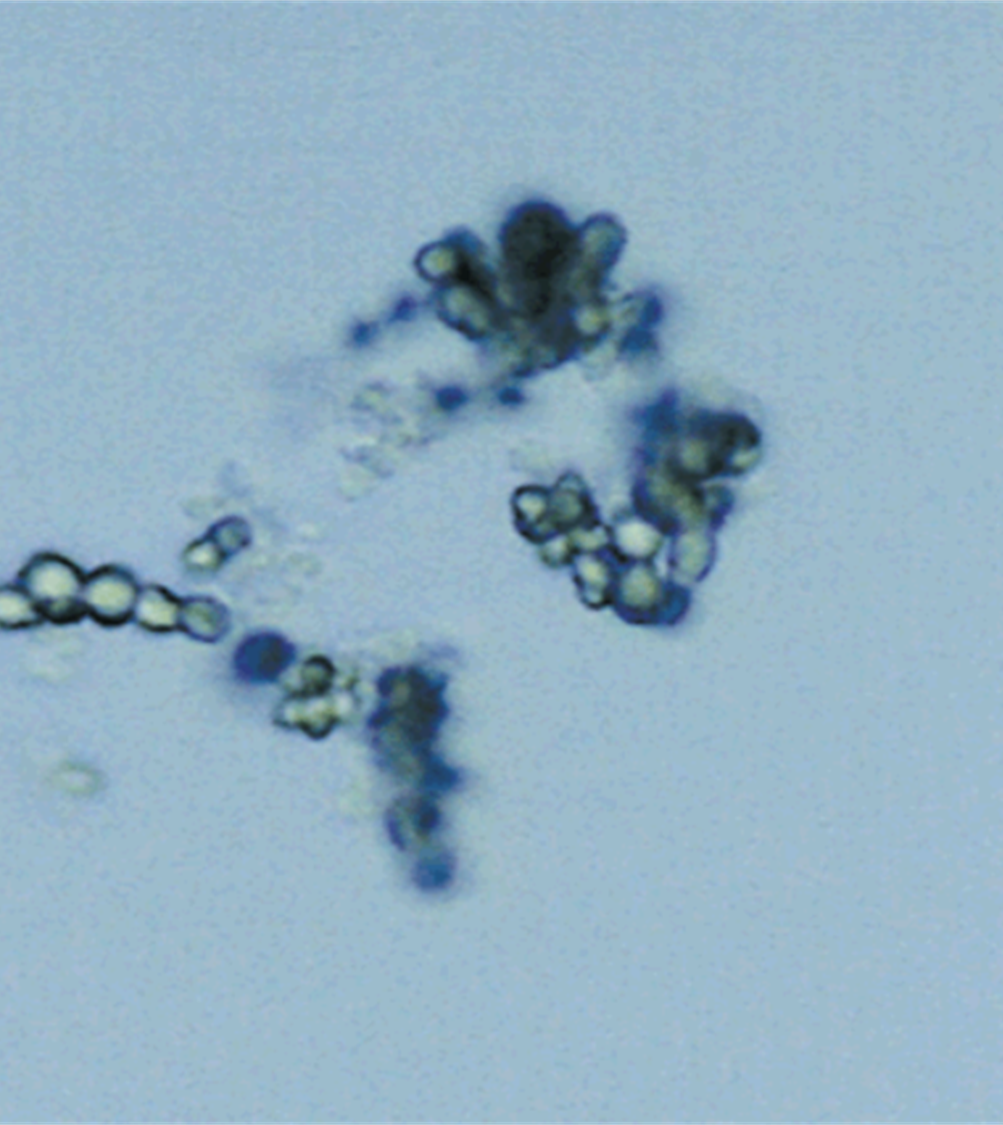
Ammonium Biurate
“Thorny Apple”
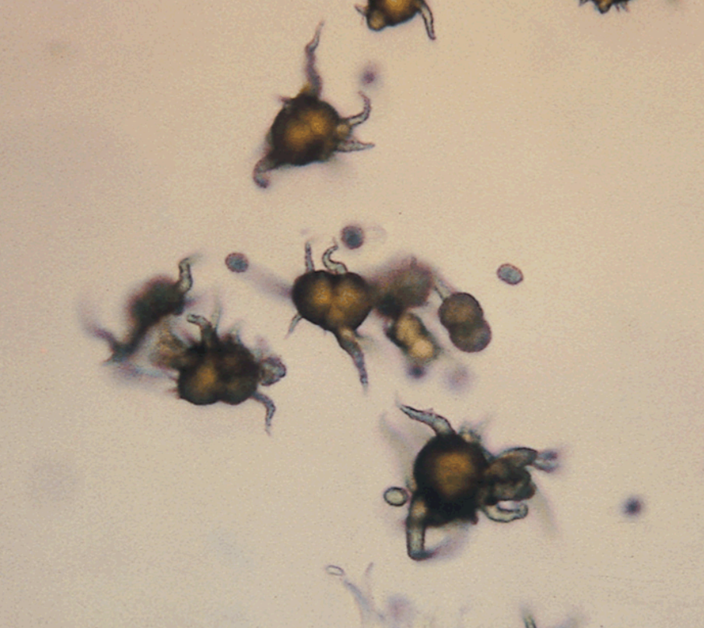
Cystine Crystals
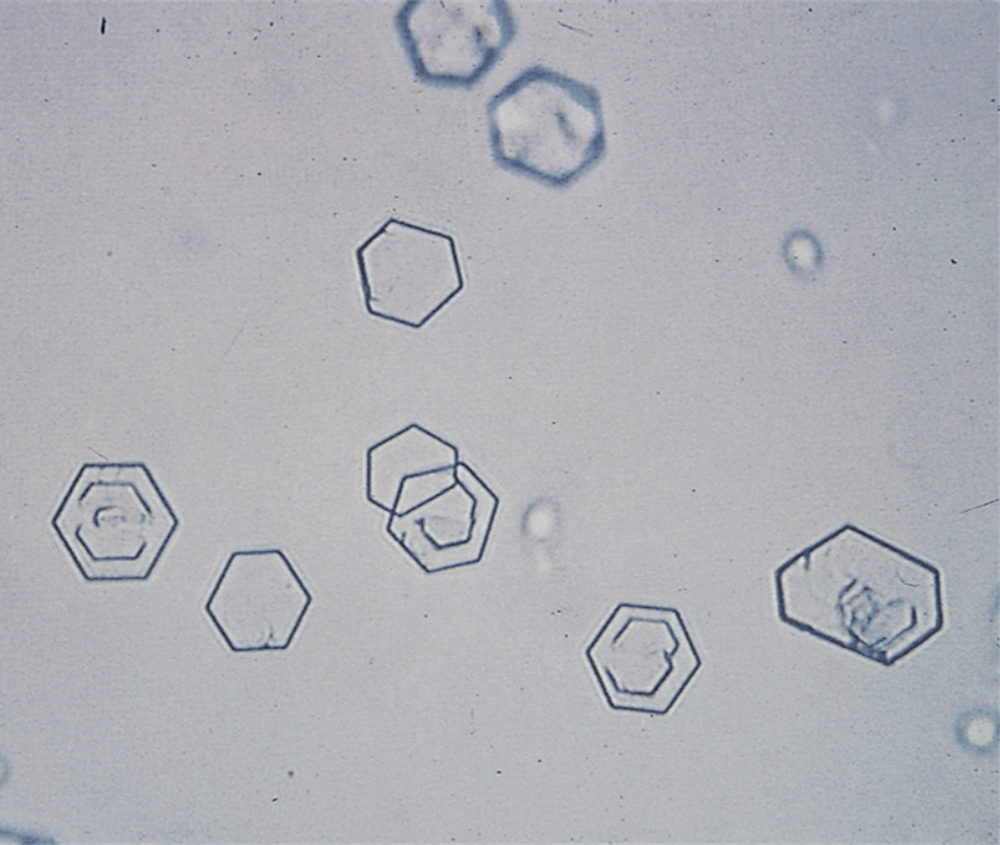
Cystine Crystals
Found in patients with cystinuria
Cholesterol Crystals
Highly birefringent
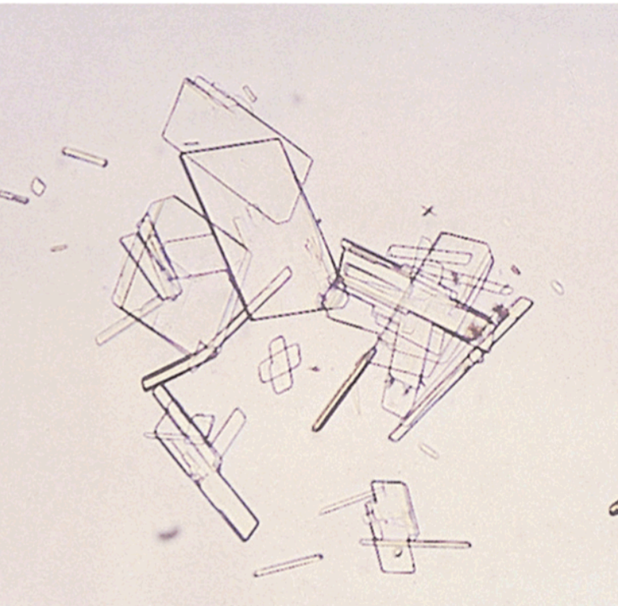
Cholesterol Crystals
Associated with disorders producing lipiduria (Nephrotic Syndrome)
Radiographic Dye Crystals
Bilirubin Crystals
Seen in patients with liver disorders
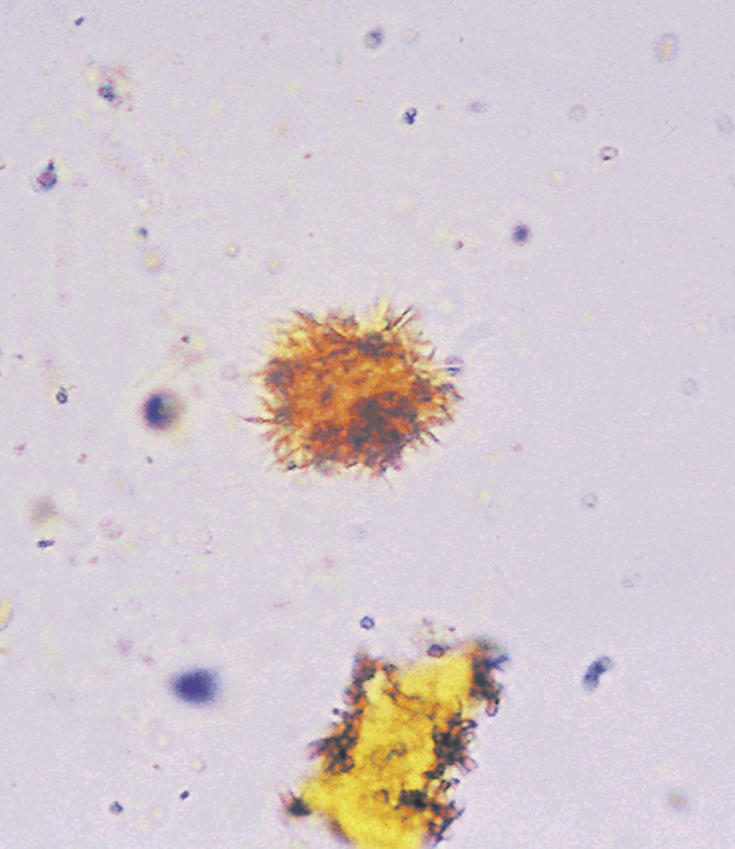
Leucine Crystals
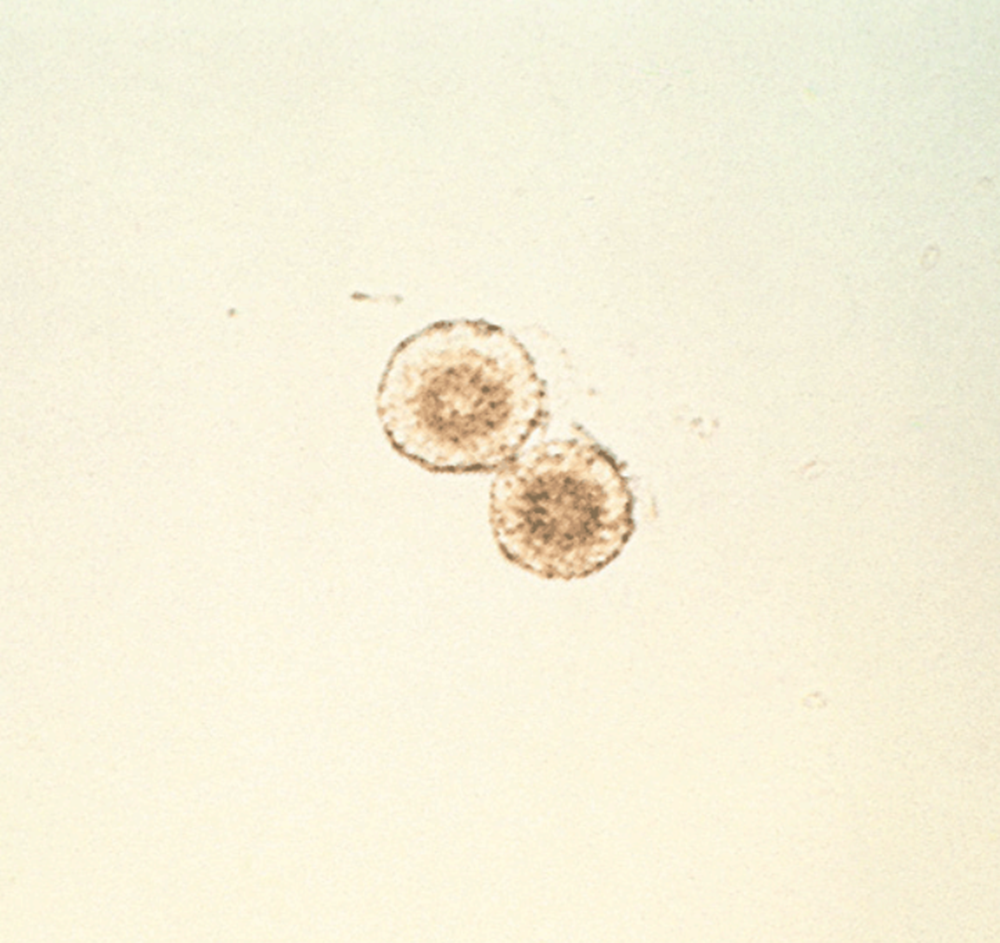
Tyrosine Crystals
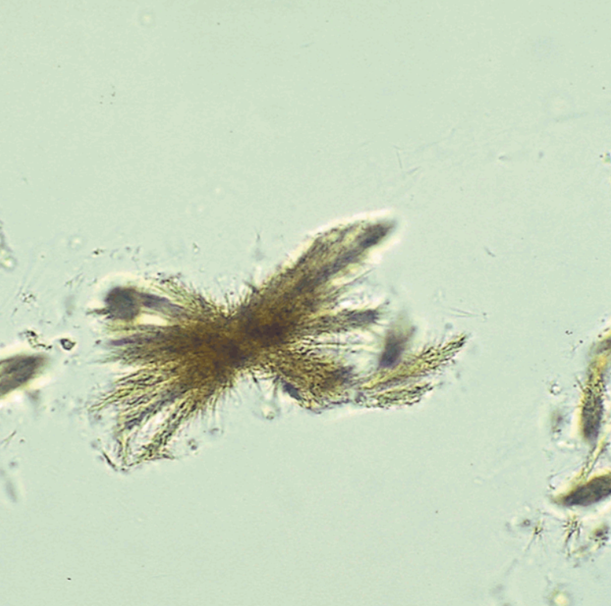
Bilirubin, Leucine, and Tyrosine Crystals
Three main crystals found in liver diseases
Sulfonamide Crystals
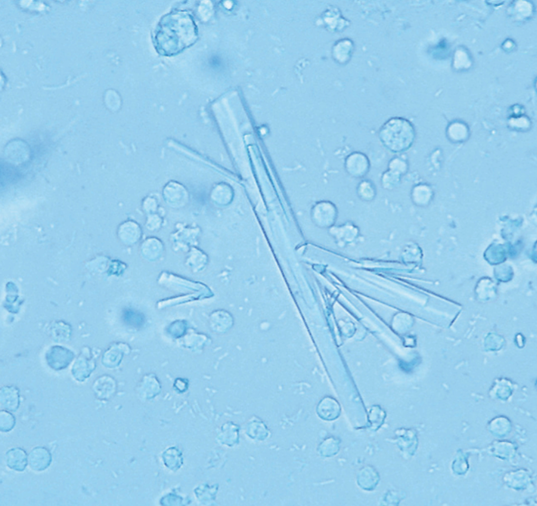
Ampicillin Crystals
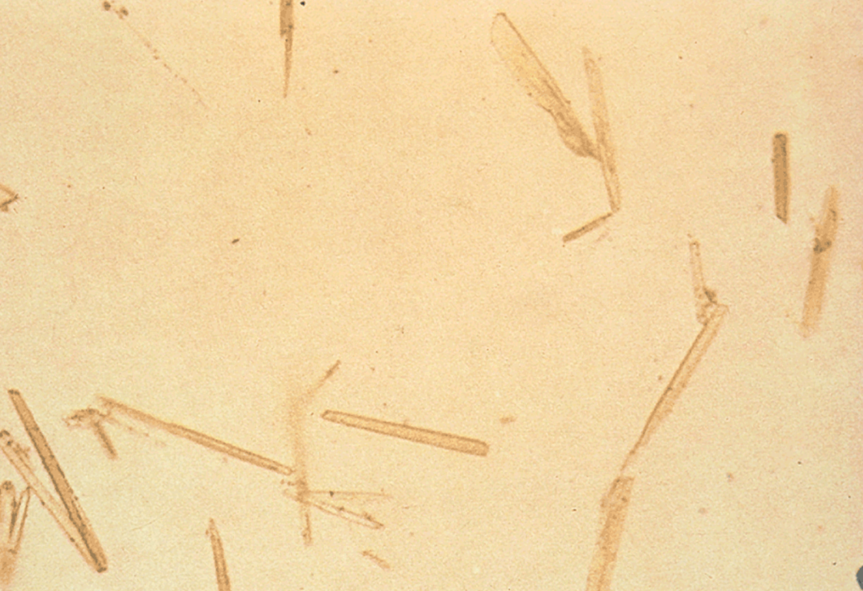

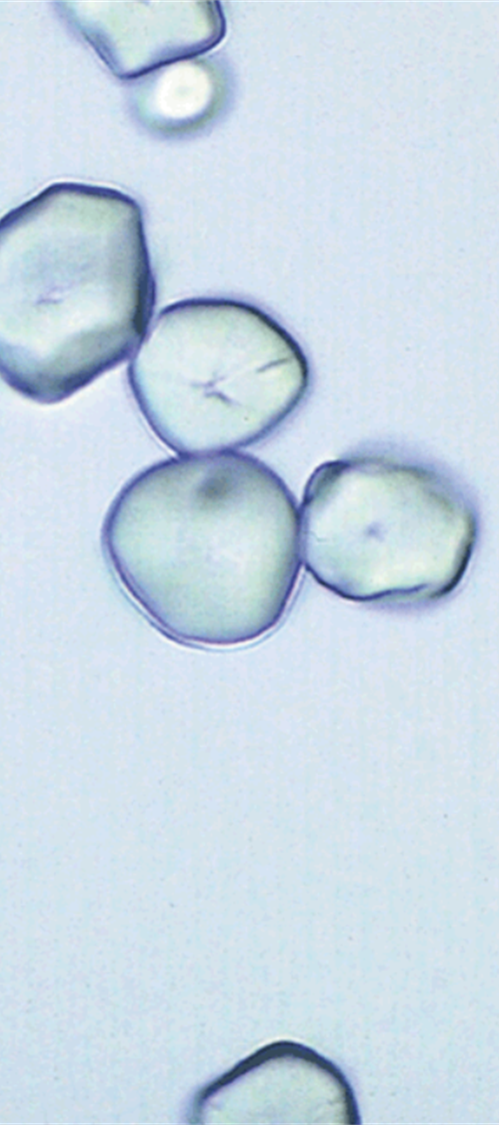
Starch Crystals
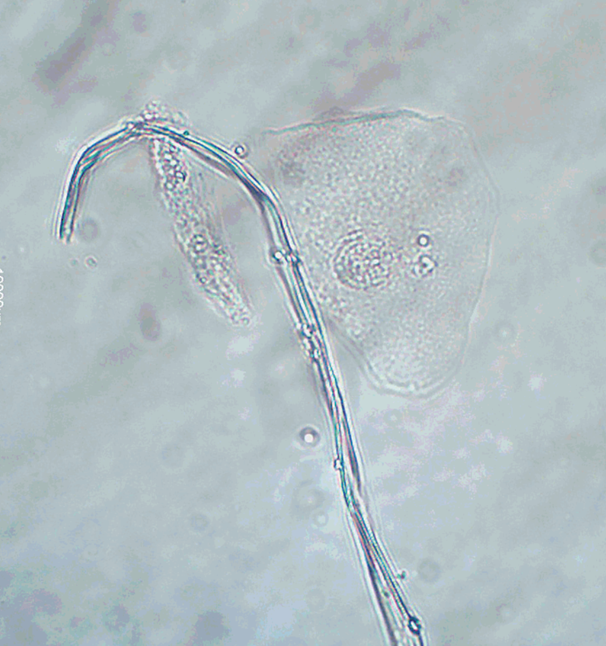
Fibers
Starch Granules
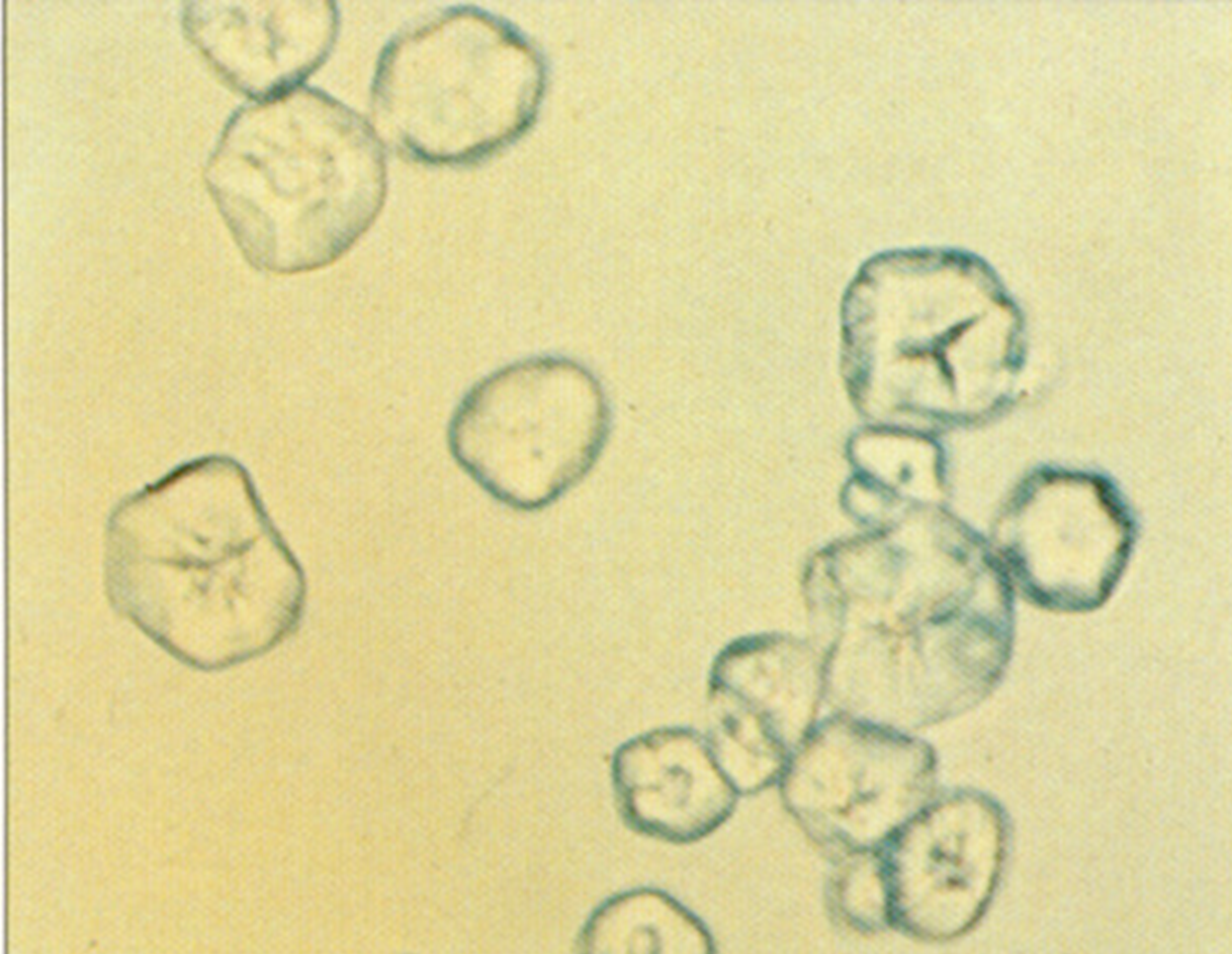
Calcium Oxalate
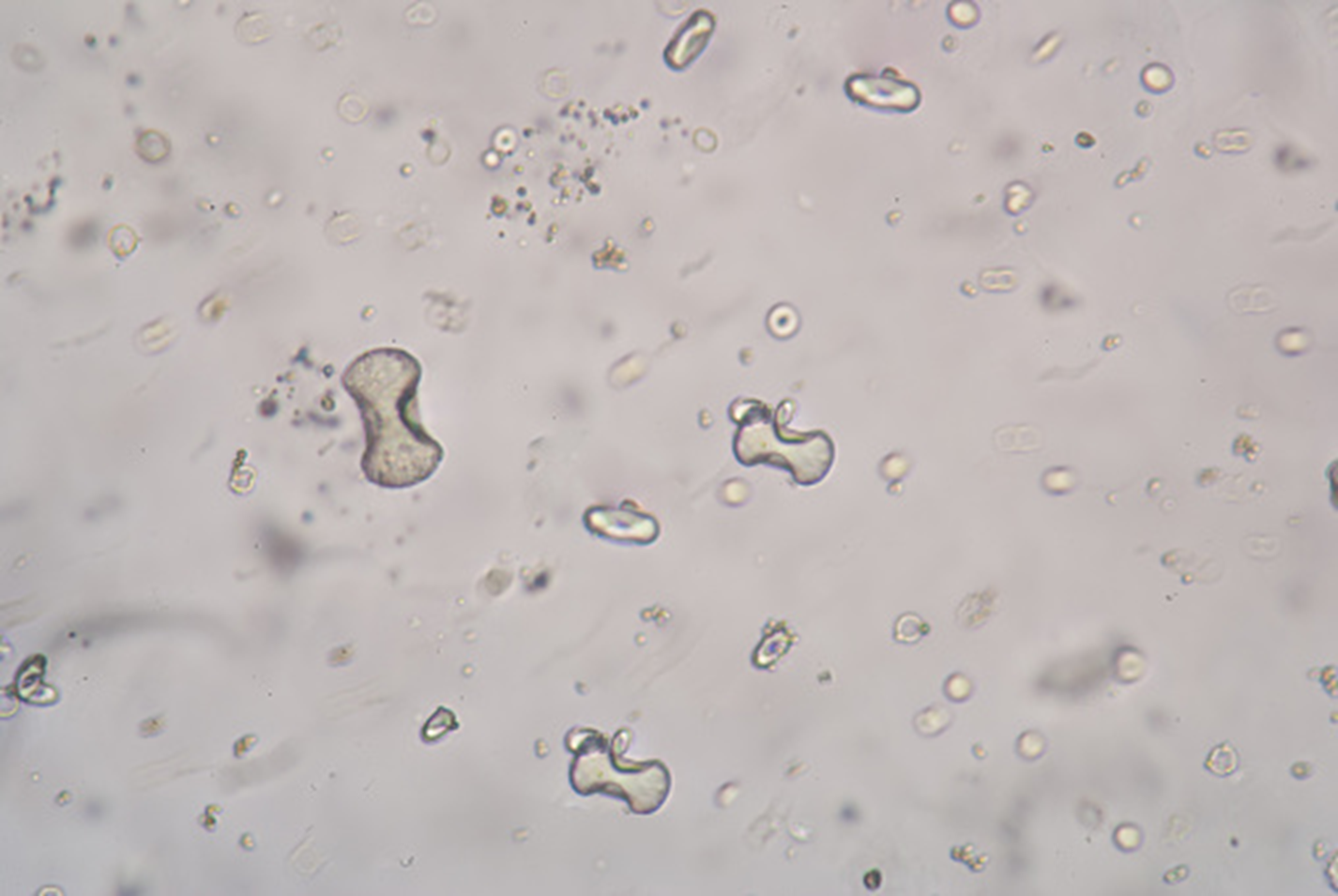
Leucine Crystal