Chapter 8 Practice Questions
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
The economy’s potential output corresponds to the level of
natural employment
Aggregate demand is defined as
the relationship between the total quantity of goods and services demanded and the price level, all other determinants of spending unchanged
the aggregate demand curve slopes downward
because as the price level falls, the net export component of aggregate demand increases
What is the interest rate effect that explains why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward
it refers to the effect of changes in the price level on interest rates which in turn affects the quantity of investment demanded
which of the following best explains the multiplier effect as a result of a $100 million increase in government spending on highways
the government spending creates a demand for domestically produced goods and services which in turn increases income and higher incomes will lead to increased consumption
suppose that government spending on defense rises by $50 billion. What happens to the aggregate demand curve if the multiplier is greater than one?
it shifts right by more than $50 billion at each price level
suppose investment rises by $50 billion at each price level. If the value of the multiplier is 1.5, what is the amount of change in real gdp demanded at each price level?
$75 billion
suppose that an increase in government purchases of $100 million caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right by $350 million at each price level. What is the value of the multiplier
3.5
the short run in macroeconomic analysis is a period:
in which wages and some other prices do not respond to changes in economic conditions
the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical at
potential output
in the long run, an increase in aggregate demand, all other things unchanged, will cause the price level to
increase and potential output to remain stable
the rise and fall of real gdp over the course of the business cycle suggests that
the economy may not always be in long-run equilibrium
True/False: the short-run aggregate supply curve is drawn holding price level constant
false
True/False: the short-run aggregate supply curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between production and the price level
true
True/False: the short-run aggregate supply curve is a result of the stickiness or inflexibility of some prices and wages
true
True/False: the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping
true
a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve in response to a change in the price level is called a
change in the aggregate quantity of goods and services supplied
the short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward because of
wage and price stickiness
what are two explanations for price stickiness
1) there are adjustment costs associated with changing prices such as the cost of printing new price lists
2) firms may have explicit long-term contracts to sell their products to other firms at specified prices
using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, predict what happens in the short run when the federal government enacts a cut in the personal income tax rates
the aggregate demand curve shifts right; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real gdp increase
suppose the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium. Which of the following events leads to a decrease in the price level and an increase in real gdp in the short run?
a decrease in health insurance premiums paid by firms raises the cost of employing labor
True/False: Potential output is the level of output an economy can achieve when labor is employed at its natural level
true
True/False: Potential output is the long run output level that guarantees price stability
false
True/False: Potential output is also called the natural level of real gdp
true
True/False: If a country is producing its potential output, then it is producing at a point on its production possibilities curve
true
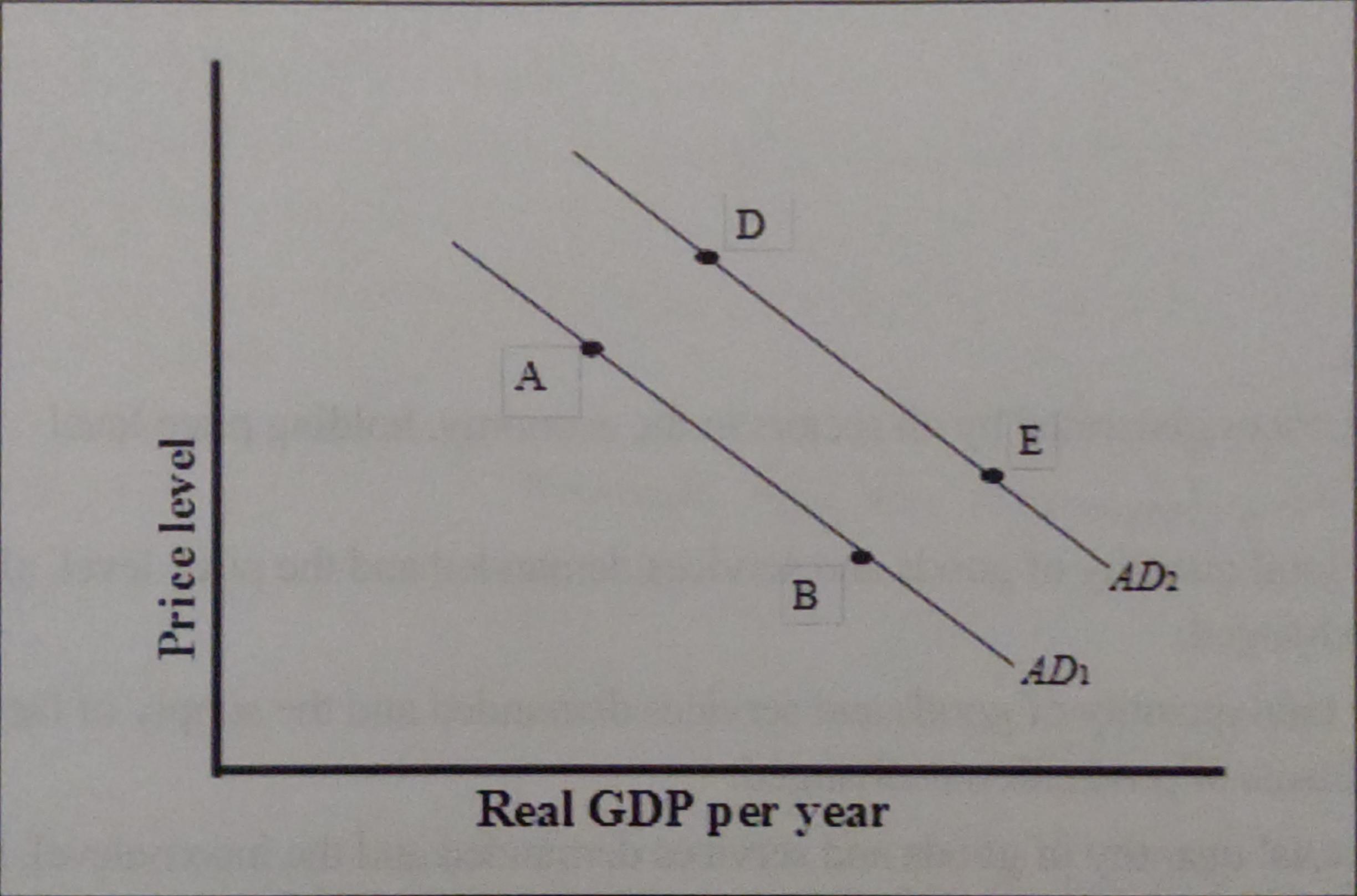
a movement from point A to point B
is a change in aggregate quantity demanded resulting from a lower price level
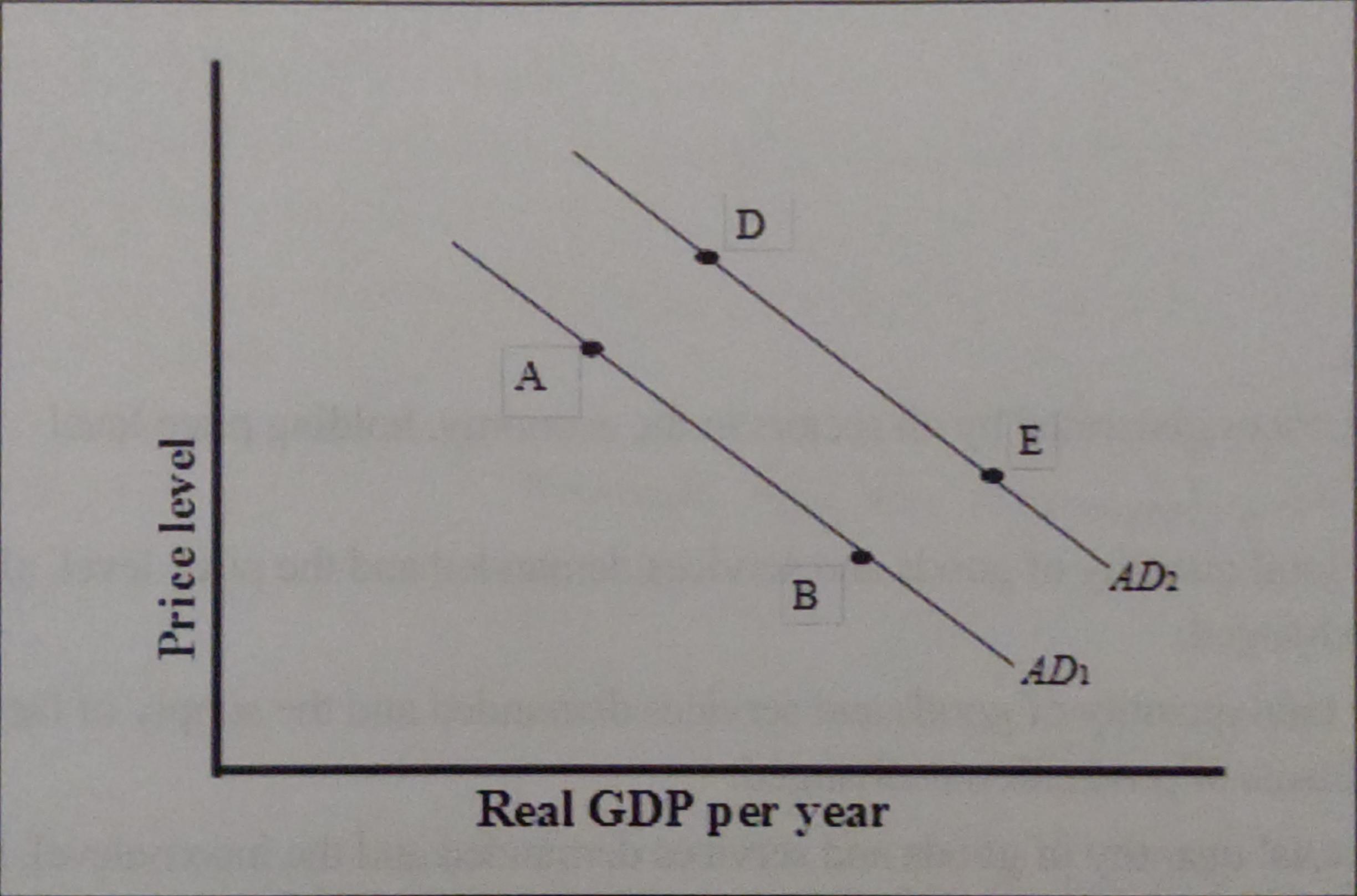
what could have caused a movement from point A to point D
an increase in household wealth
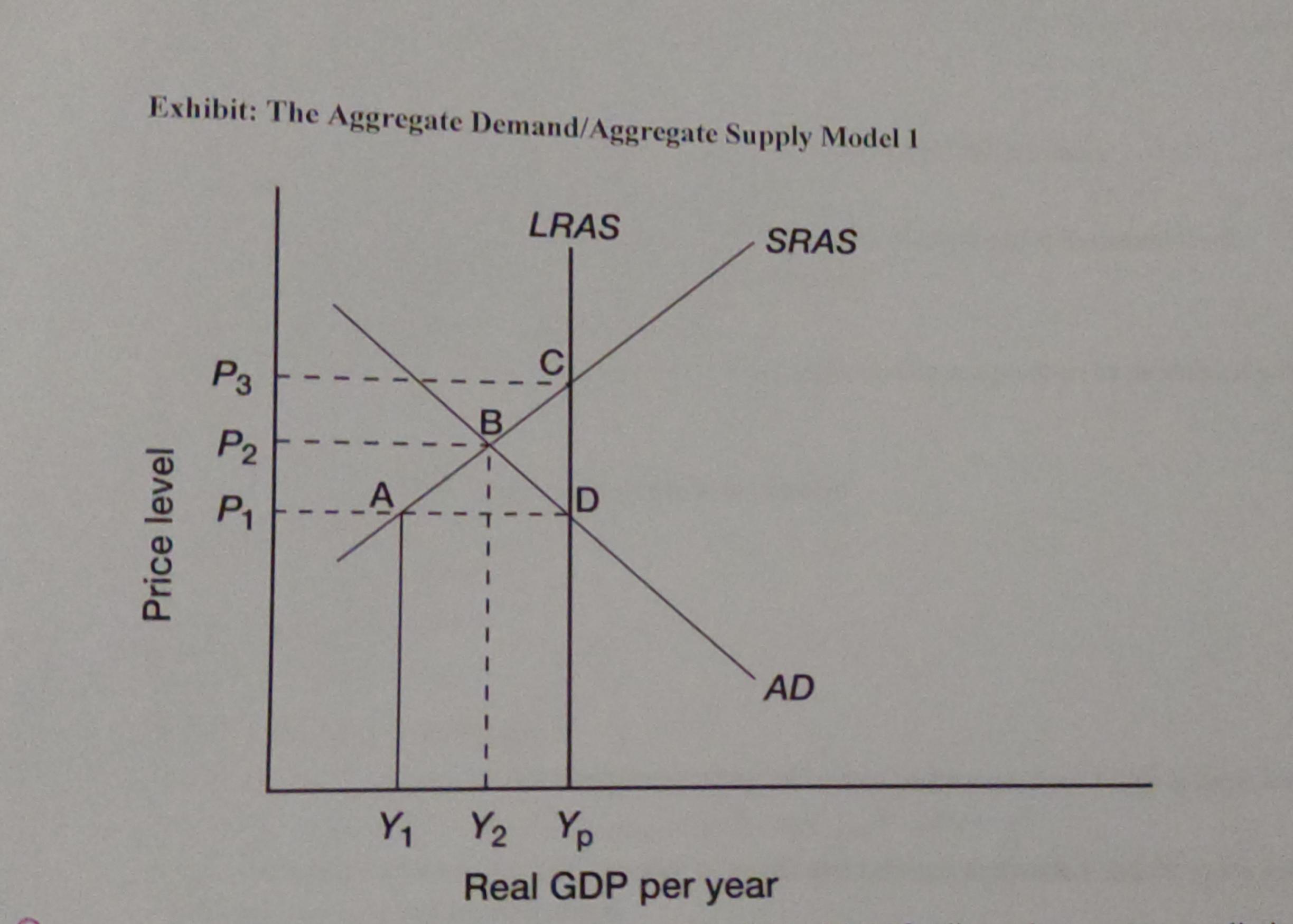
if policymakers attempt to eliminate the gap in the economy, they will typically attempt to
increase AD
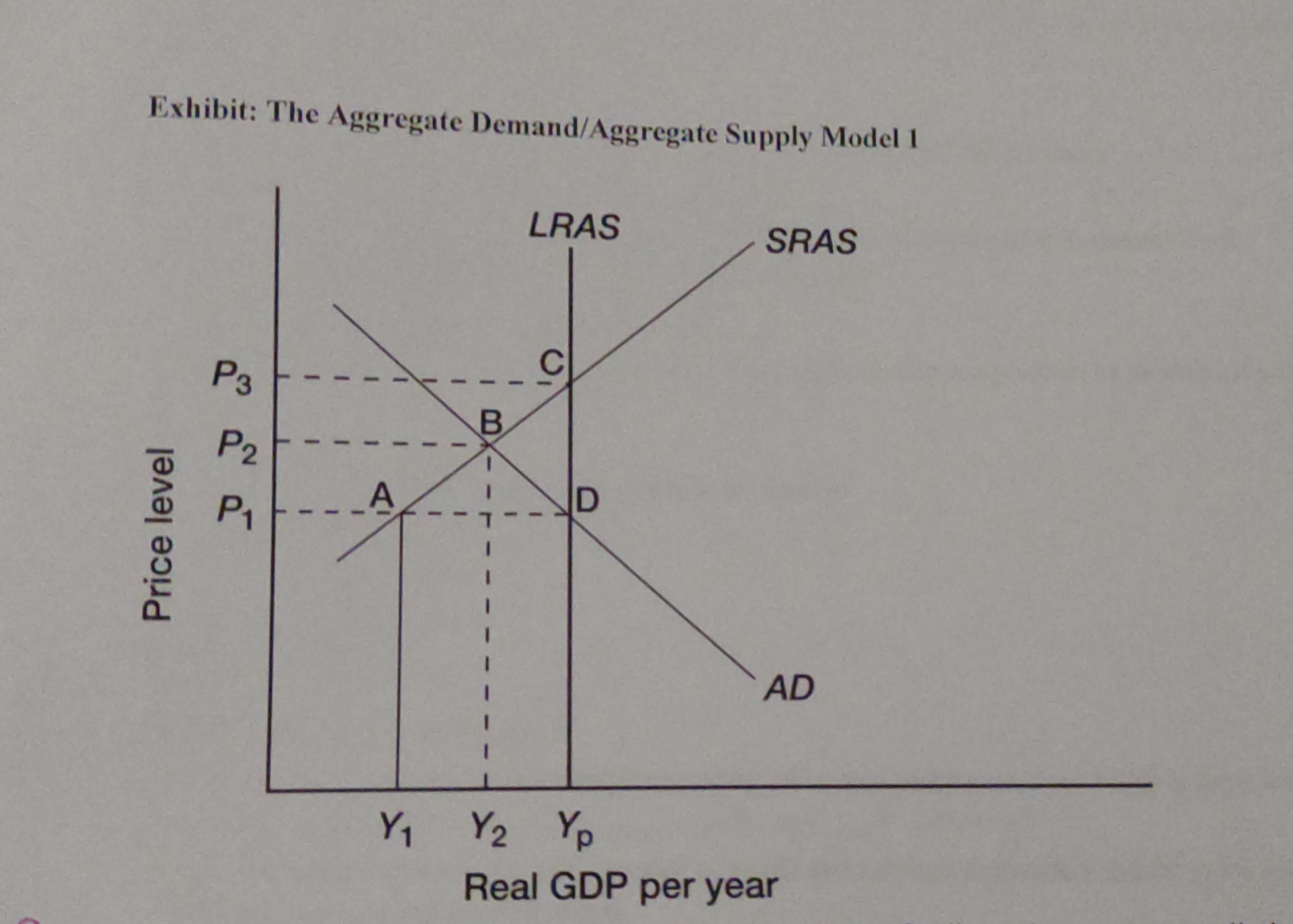
if policymakers allow the economy to self-correct back to potential output, that self-correction will occur because of a(n)
increase in SRAS
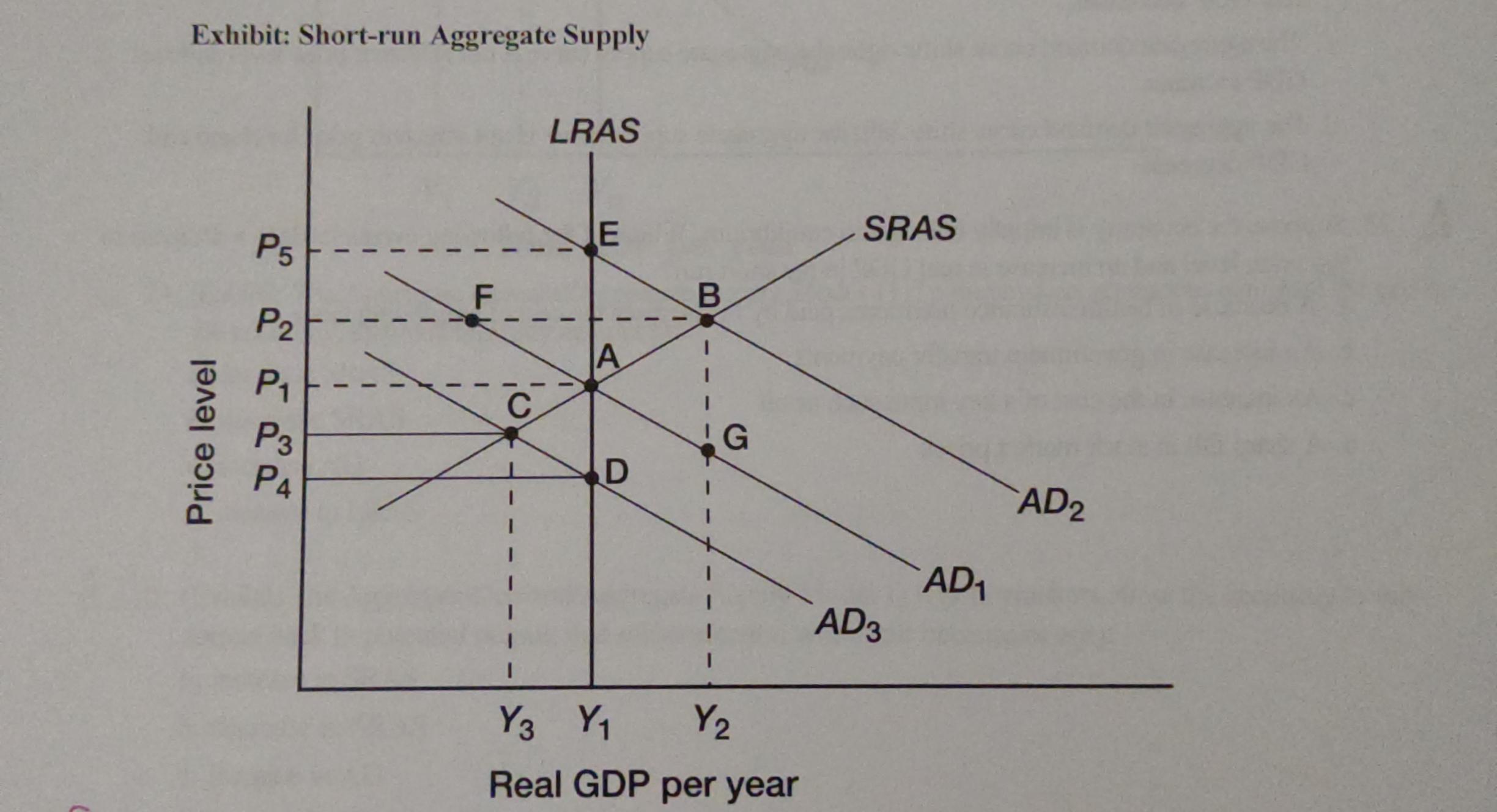
suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose net exports increase. In the short run:
those who were structurally or frictionally unemployed will now find jobs at the going nominal wage rate
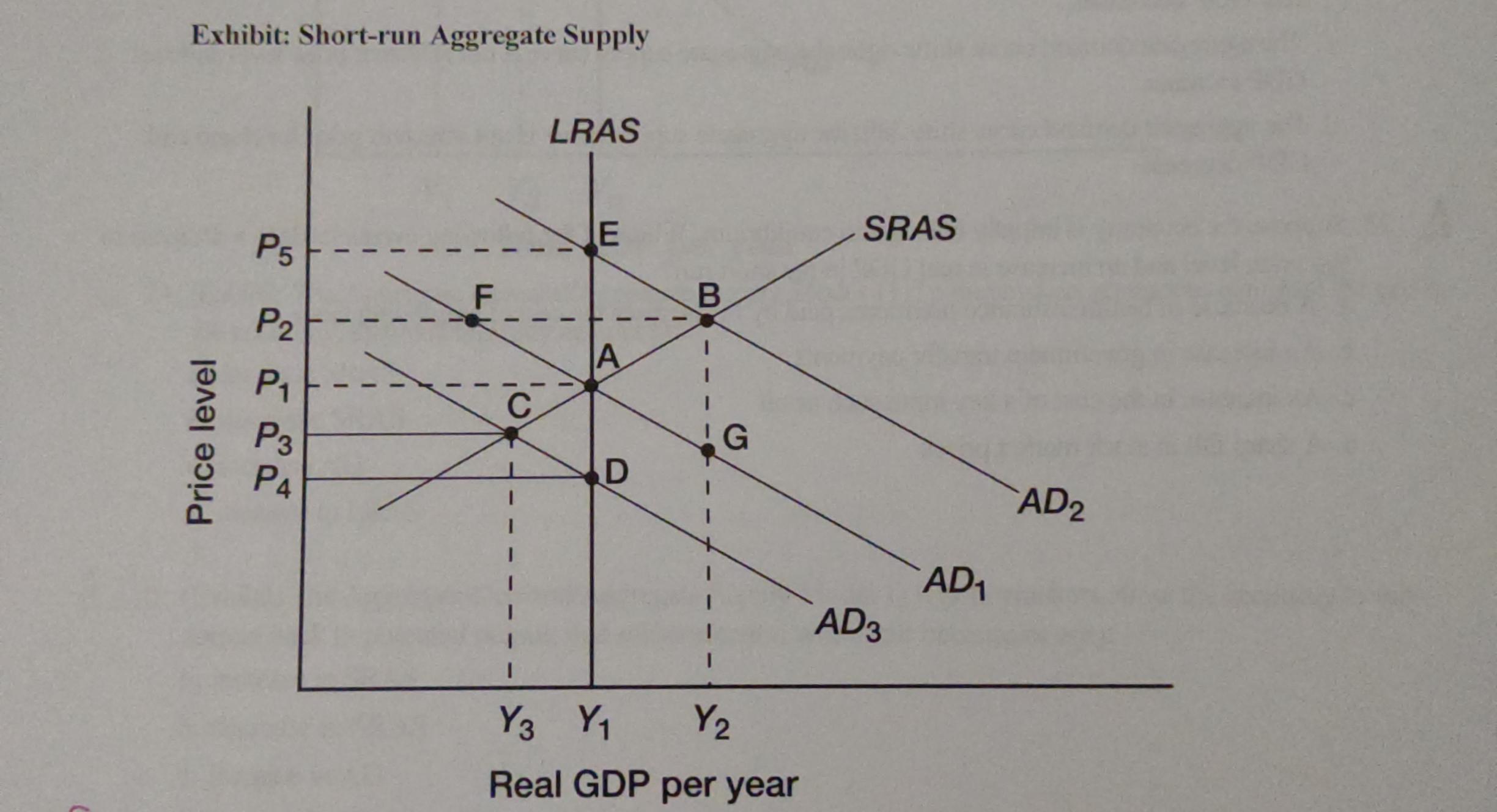
suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose the stock market crashes, significantly reducing household wealth. What happens in the short-run?
real gdp decreases to Y3 and the price level falls to P3