Biology test 1: Subject 1, Animal phylogeny
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
monophyletic
derived from a single common ancestor
polyphyletic
derived from more than one common ancestor
Nervous Tissue
present in animals. neurons and supporting cells function to conduct signals.
muscle tissue
functions in movement via contraction. contraction results from the interaction of actin & myosin
3 muscle tissues
smooth, cardiac, skeleton.
neuron
cells that transmit signals to and from muscles.
metazoa
multicellular animals
Parazoa
group within metazoan that lack true tissues
Eumetazoa
true tissues are present
Radiata
animals with radial symmetry
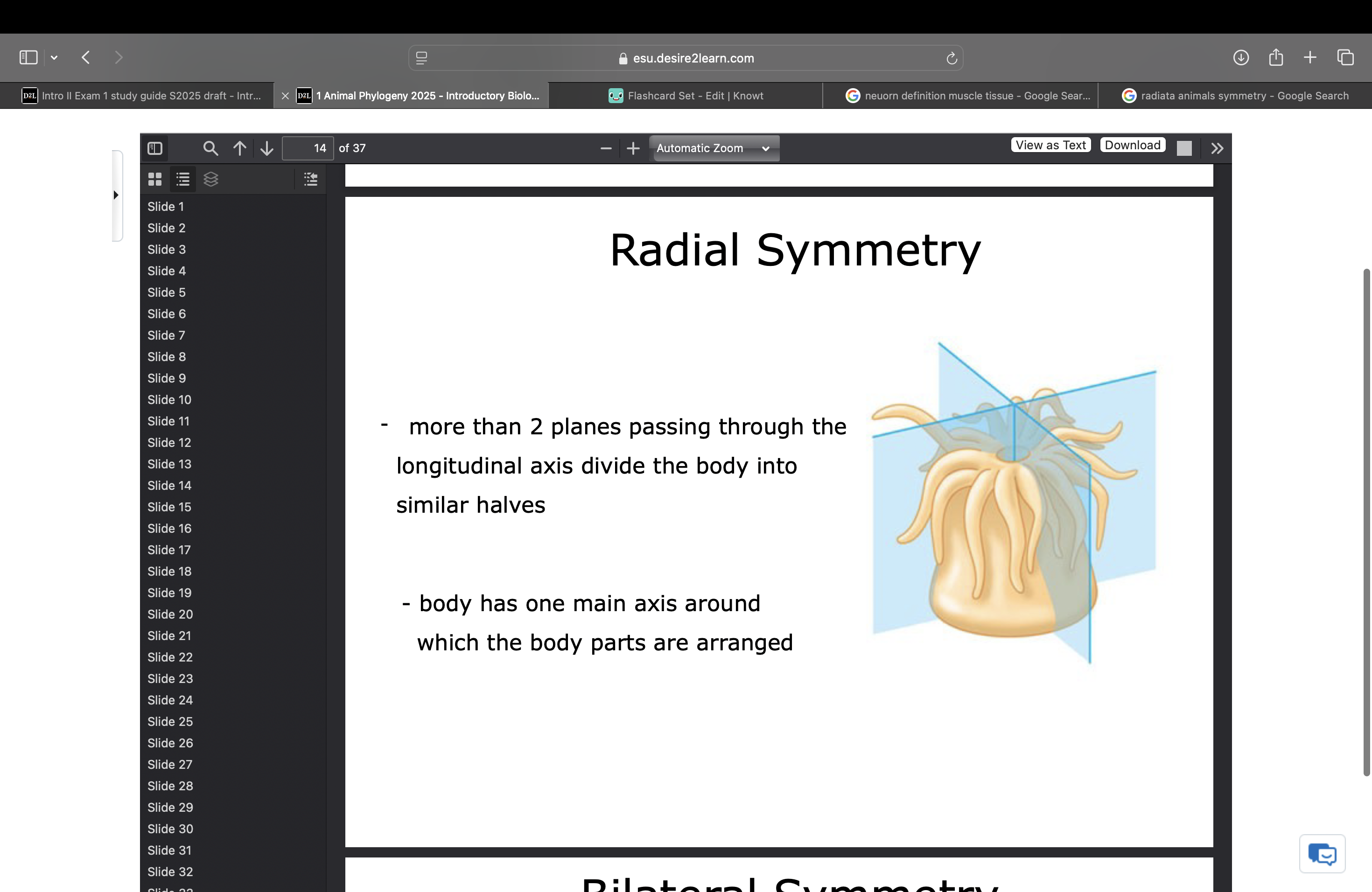
radial symmetry
more than 2 planes passing through the longitudinal axis divide the body into similar halves. body has one main axis around which the body parts are arranged.
radiata animal examples
Ctenophora, cnidaria
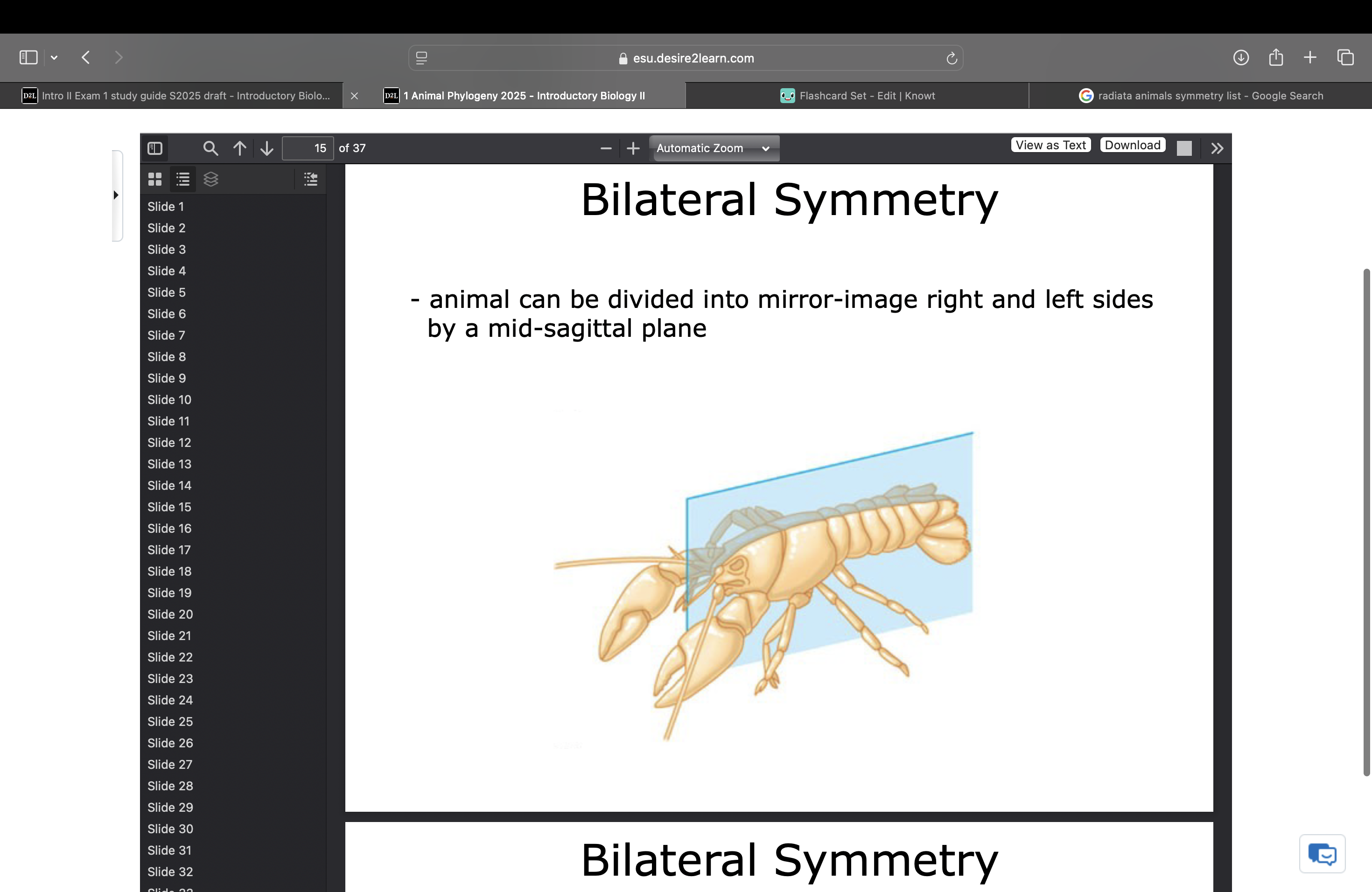
Bilateral symmetry
animal can be divided into mirror-image right and left sides by a mid-saggital plane (plane going through middle)
Anterior
The front or head end of an orgasm or body part.
Posterior
The back or tail end of an organism or body part.
Dorsal
The upper or back side of an organism or body part.
Ventral
The lower or belly side of an organism or body part
Lateral
The sides of an organism, away from midline
Medial
towards the midline or center of an organisms body.
germ layers
tissues that come from embryonic layers.
Endoderm
The innermost germ layer of an embryo. Develops into the digestive system, liver, pancreas, and respiratory system.
Ectoderm
The outtermost germ layer of an embryo, gives rise to the skin, nervous system, and sensory organs.
Mesoderm
the middle germ layer of embryo which develops into muscles, bones, the circulatory system, and other internal structures
diploblastic
animals that develop from embryos with 2 germ layers.
triploblastic
animals that develop from embryos with 3 germ layers.
Germ layers in a triploblastic animal
ectoderm is outer covering and nervous system, endoderm is gut liver and lungs, mesoderm is muscles.
diploblastic animals
cndiarians and ctenophores develoop from 2 germ layers
triploblastic animals
platyhelminths, echinoderms, chordates, mollusks, arthropods, annelids
cephalization
evolutionary trend towards concentrating nervous and sensory structures at the anterior end.
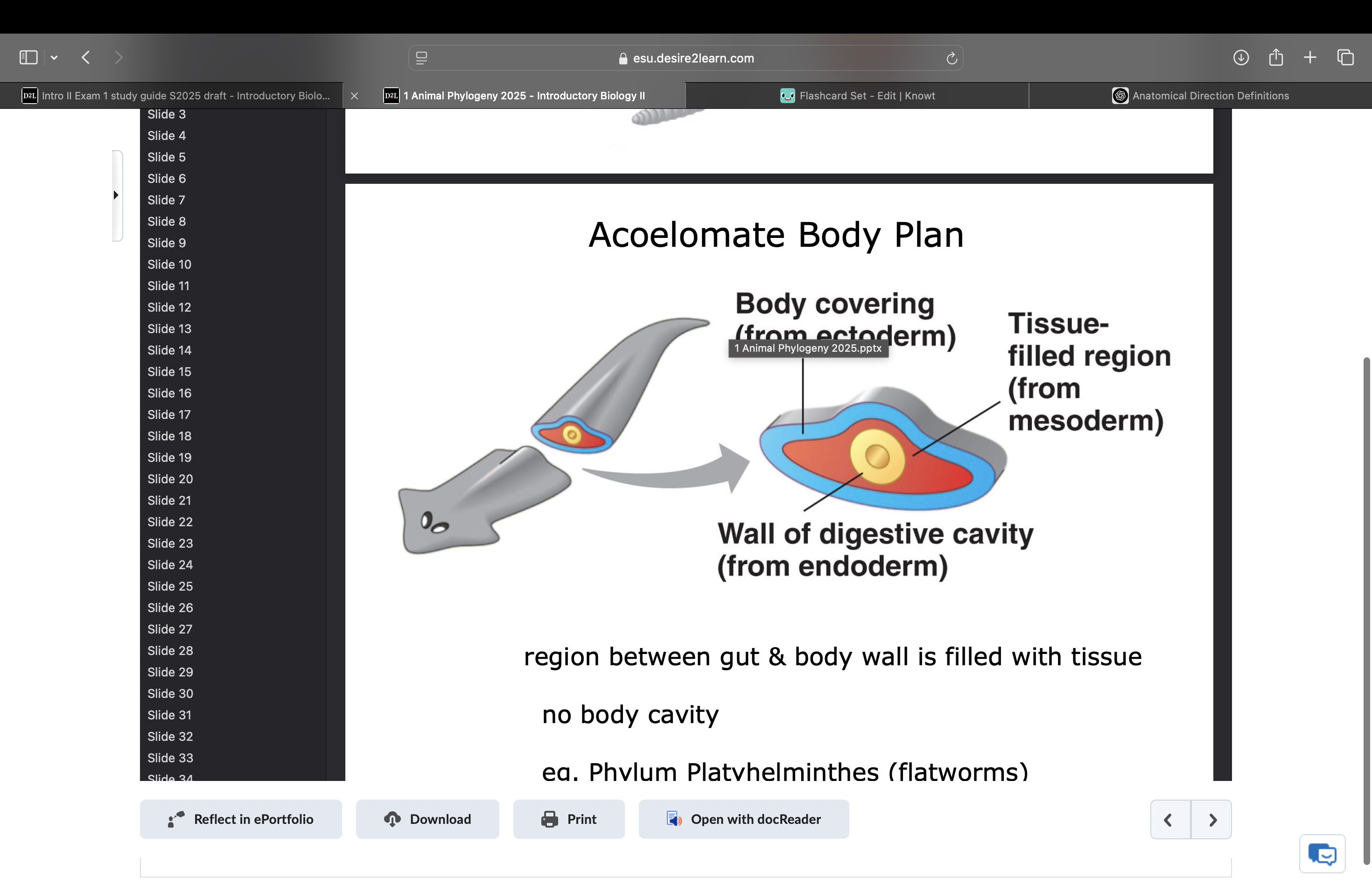
acoelomate
no body cavity, region between gut and body wall is filled with tissues. ex phylum platyelminthes
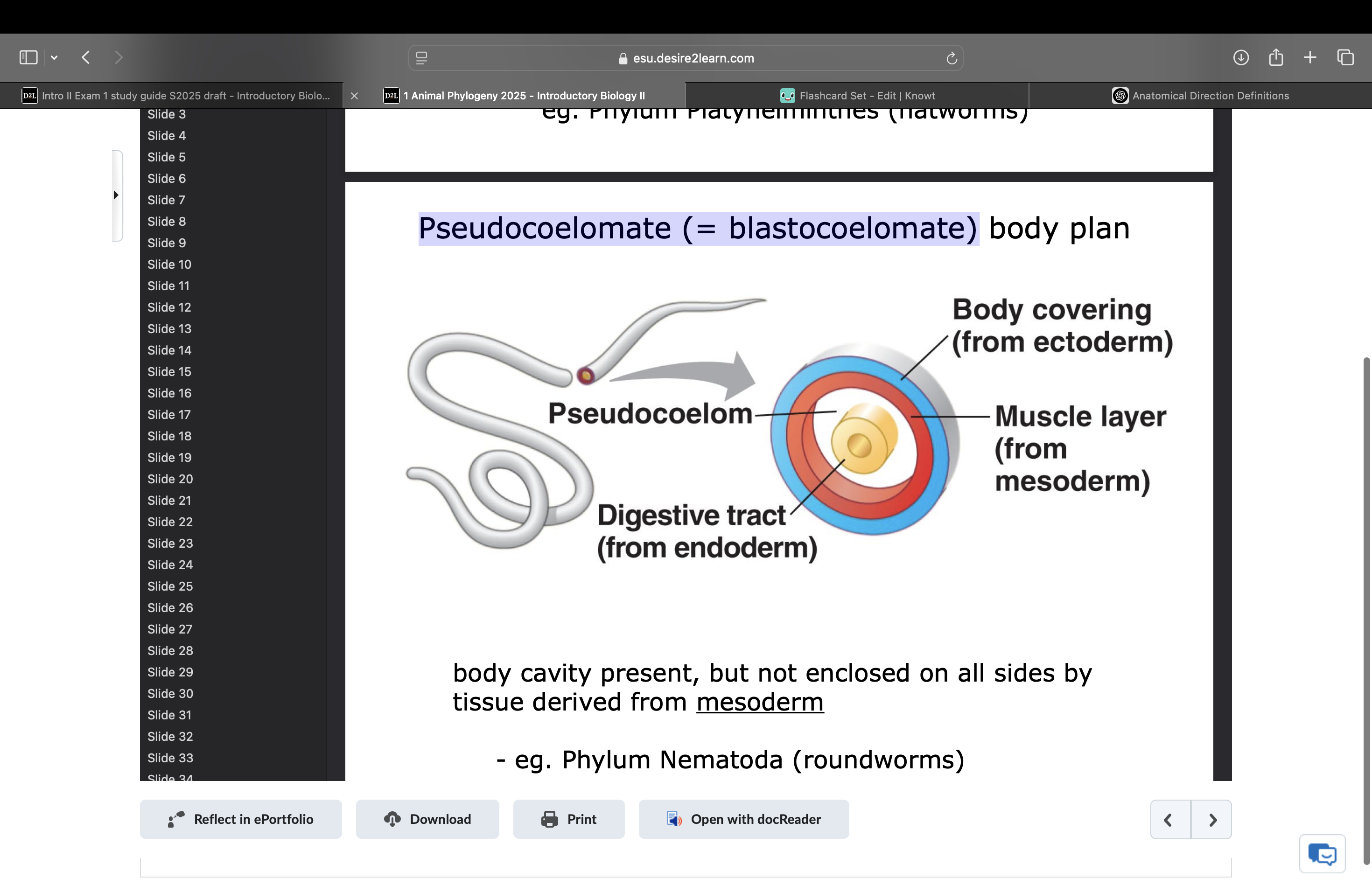
Pseudocoelomate (= blastocoelomate)
body cavity present but not enclosed on all sides by tissue derived from mesoderm. ex phylum nematoda
Coelomate
body cavity is present and is enclosed on all sides by tissue derived from mesoderm. ex phylum annelida
Protosome
development characteristic where the blastophere becomes mouth and cleavage is spiral.
Deuterostome
development characteristic where blastophere becomes anus and cleavage is radial.
lophotrochozoan
protostome group. possesses a lophophore and/or a torchopore larva. includes ectropocts, molluscs , and annelids.
Ecdysozoa
protosome group. Needs to shed their exoskeleton to grow this is known as molting or ecdysis. includes arthropods and nematodes (round worms).
zygote
fertilized egg
cleavages
numerous cell divisions that the zygote undergoes.
blastula
stage at which the embryo is a hollow ball of cels.
gastrulation
formation of a layered embryo (gastrula). may occur in invagination
blastocoel
The fluid-filled cavity inside a blastula that provides space for cell movement during early embryonic development.
blastopore
The opening that forms during gastrulation, which can develop into the mouth in protostomes or the anus in deuterostomes.
archenteron
The primitive gut formed during gastrulation that eventually develops into the digestive tract of the organism.