obstetric ultrasound
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
you must have an accurate calculation of gestational age in order to …
schedule invasive procedures in early pregnancy
accurately interpret maternal lab values
plan delivery date
evaluate fetal growth
what is EDD?
estimated date of delivery
modern term
is EDD 100% accurate?
no, babies come when they are ready
what is the most accurate determinate of gestational age/ due date predictor?
CRL- crown rump length
Before 8 weeks, most babies kinda look the same. After 12 weeks, genetics come into play and CRL is most accurate determinate of gestational age.
which trimester has the most accurate measurements? why?
1st trimester- the farther advanced the pregnancy, the less accurate the measurements are at determining GA.
less variation in individual size.
how does CRL determine GA?
CRL + 6
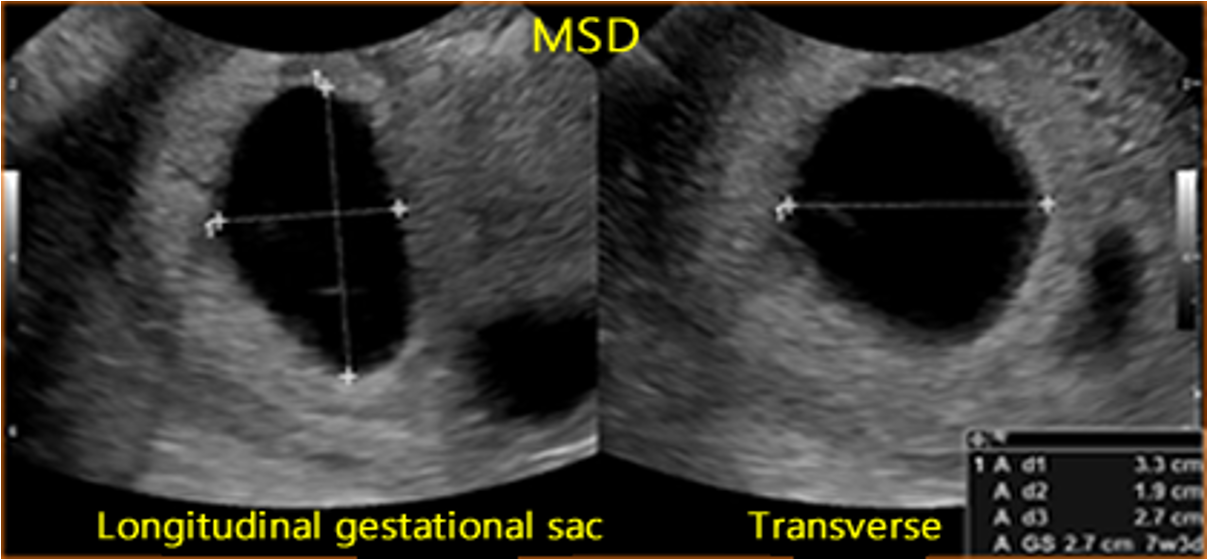
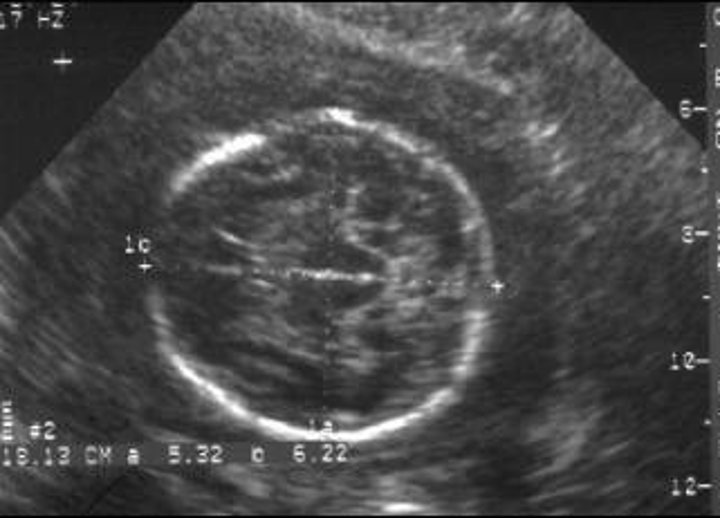
when do we measure gestational sac diameter?
5 weeks
how do we measure gestational sac diameter?
Measure all 3 planes & take average
Do NOT include echogenic ring in measurement
“inner to inner”
Measure even after CRL visible to correlate size, but do not include in gestational age calculations once CRL is visible.
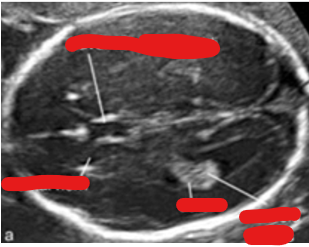
when MSD is greater than 8 mm, what should you see?
yolk sac
when MSD is greater than 16 mm, what should you see?
embryo
when MSD is greater than 25 mm with no embryo, what does this mean?
consistent with anembryonic pregnancy/ embryonic demise
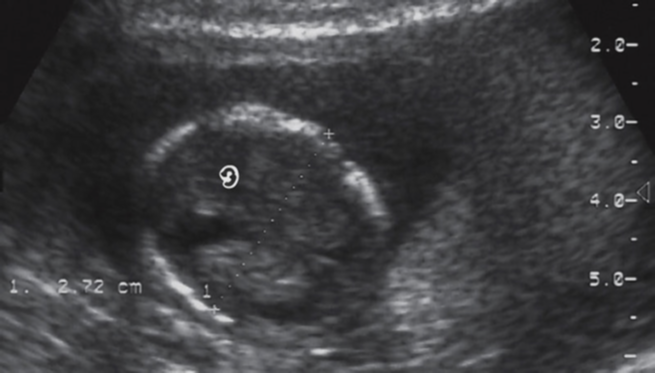
when do we measure CRL?
as early as 5.5 -6 weeks
the CRL grows how much per day?
1-2 mm/day
how do we measure CRL?
from top of head to rump
don’t include legs or yolk sac
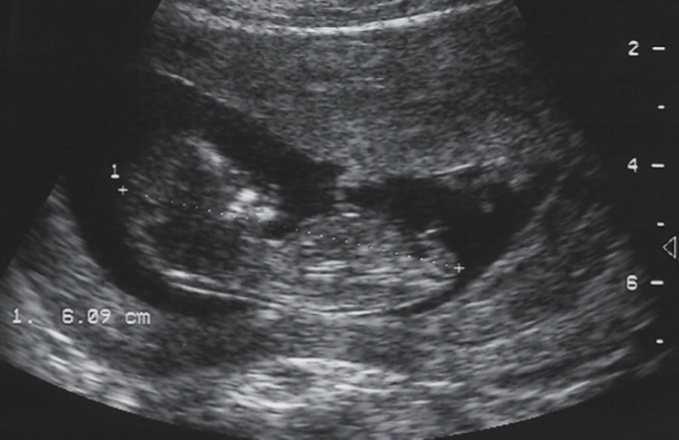
when is it impossible to get a CRL and why?
after 12-13 weeks, due to fetal flexion/ extension
when does the primitive heart begin beating?
approx 23 days after conception (5+ weeks)
FHR at 5+ weeks? 8-9 weeks? after 9-10 weeks?
5+ weeks: FHR of 110 bpm
8-9 weeks: FHR of 175 bpm
After 9-10 weeks: FHR range of 120 -180 bpm
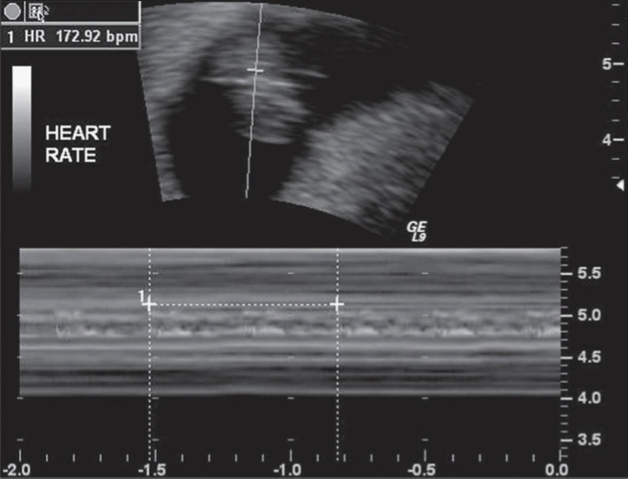
if fetal heart rate is lower than 100 bpm at 5-8 weeks, what is there high risk of?
pregnancy loss
what is BPD?
Biparietal Diameter (BPD)
Measure outer to inner edge of parietal bones
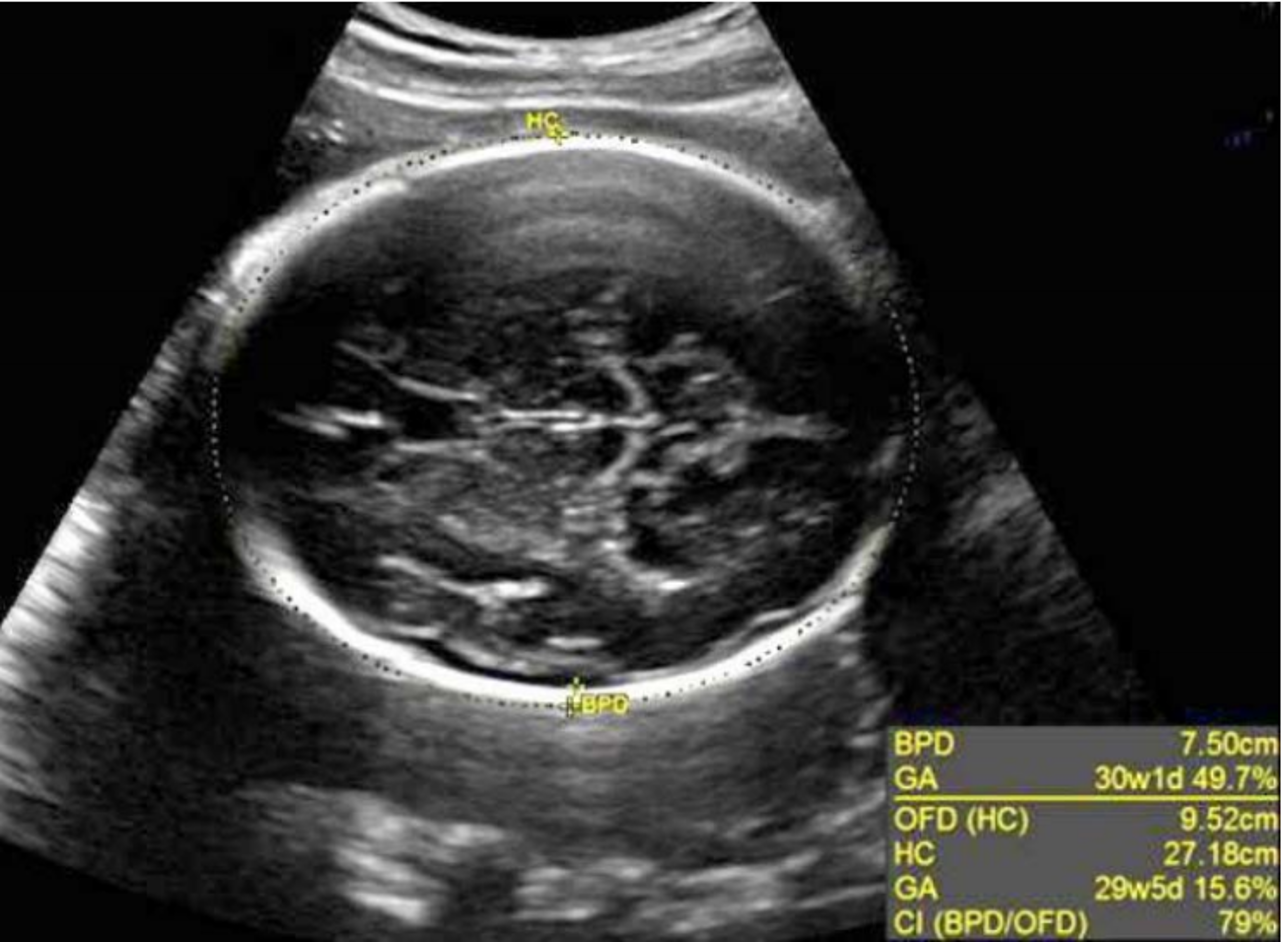
what must you see with BPD?
important landmarks:
thalami
CSP
midline falx
oval head shape
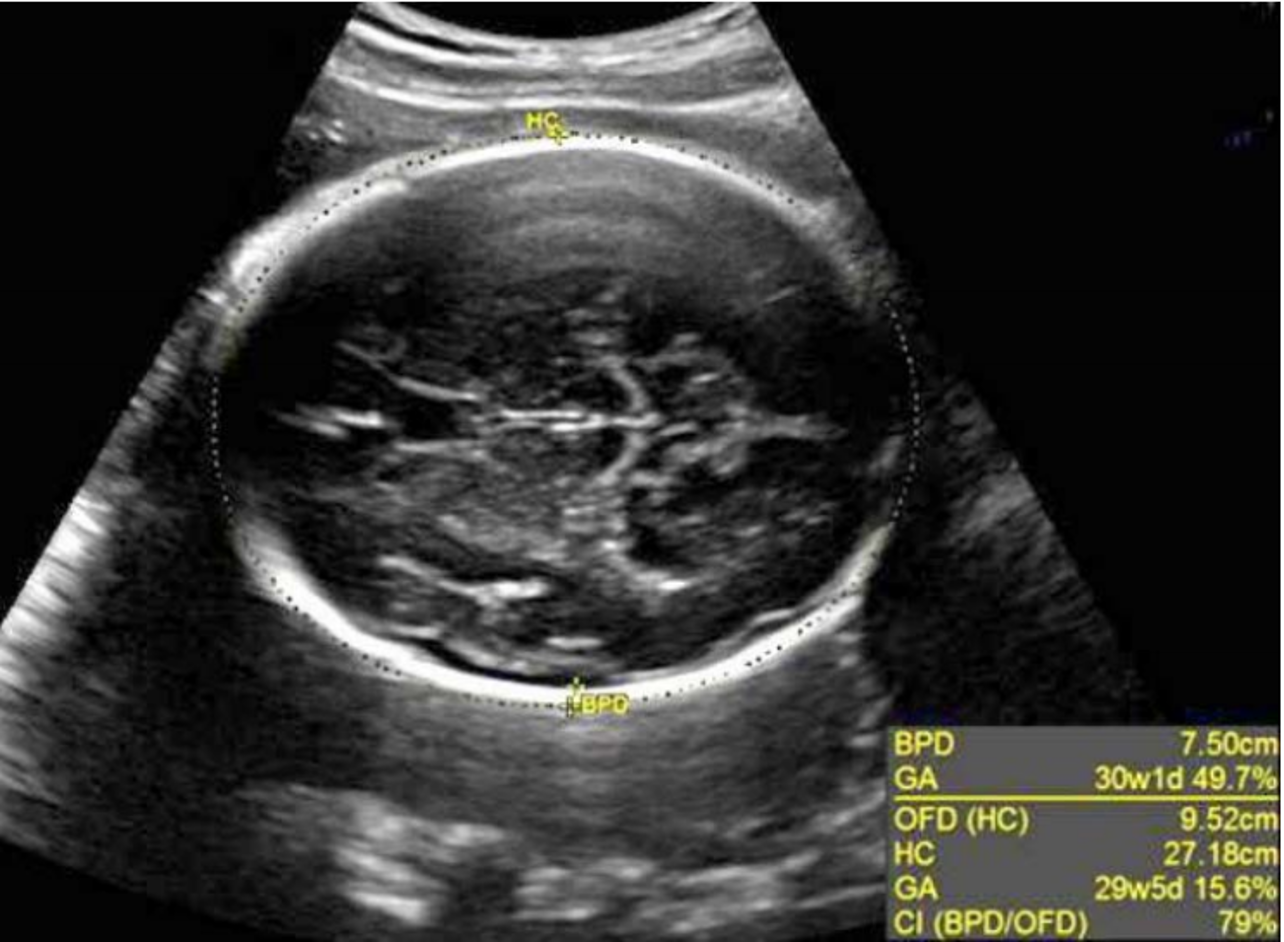
what should you do to measure BPD at 13-16 weeks?
difficult to see landmarks accurately (picture is week 14)
measure at level of choroid plexus in these cases
what is brachycephaly?
basketball shaped head
round head shape with increased BPD and decreased OFD (head circumference)
what is dolicocephaly?
egg head
elongated head shape with decreased BPD and increased OFD (HC)
what is oxycephaly/ acrocephaly?
elevated cranial vault due to craniosynostosis (early suture closure) of the coronal, sagittal, and lambdoidal sutures.
results in pointed or pyramid shaped skull.
what is head circumference?
measurement at level of BPD that measures outer perimeter of skull
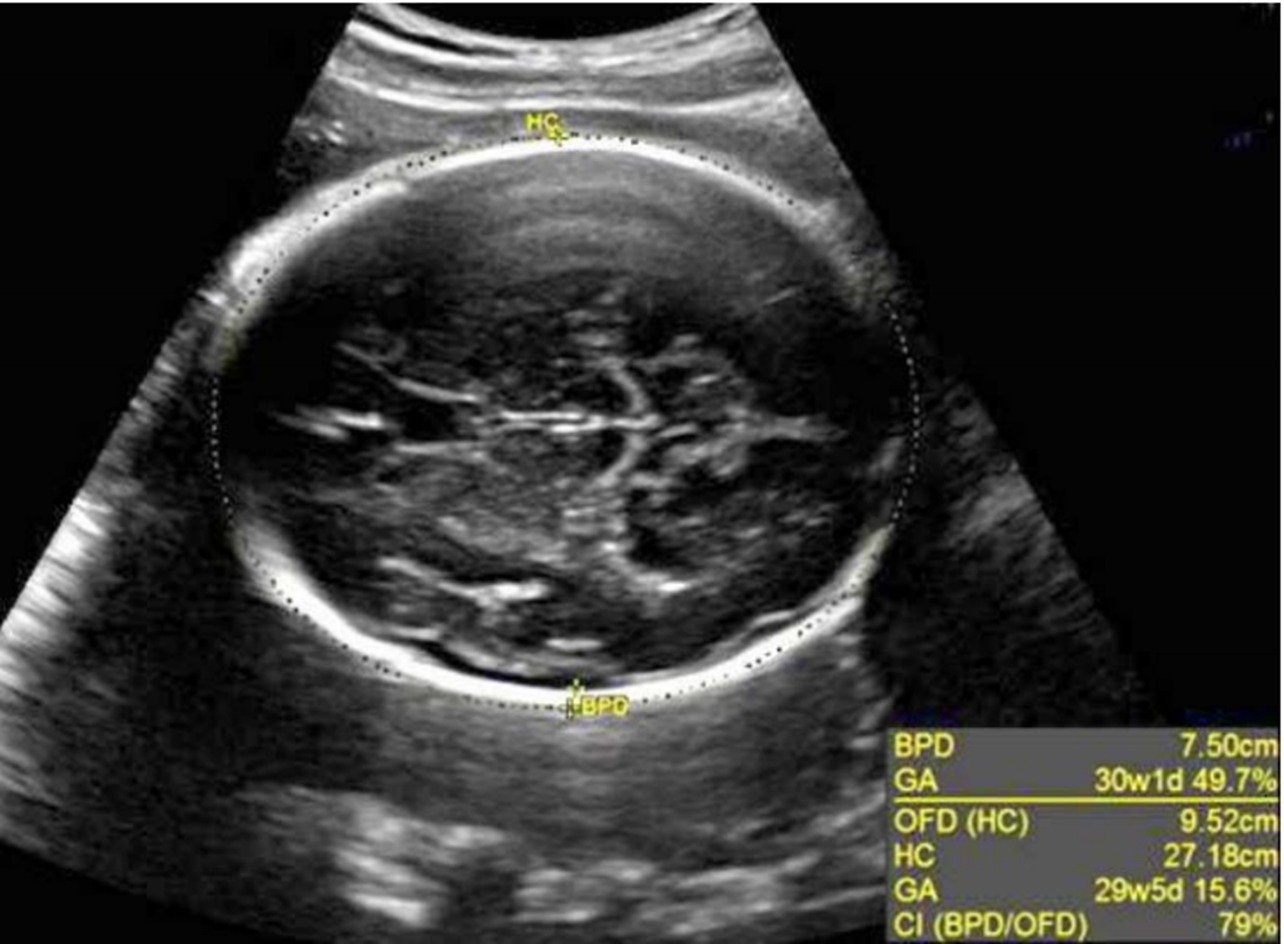
how do you measure head circumference?
Measure at level of BPD
calipers front-back or directly over BPD measurements to get accurate Occipito-Frontal Diameter (OFD is the same thing as HC!!)
what is cephalic index? formula?
ratio of BPD:OFD to evaluate for normal head shape
Formula: BPD/OFD x 100
cephalic index ranges?
Normal range is 75-85% (give or take)
CI>85% indicates brachycephaly
CI<75% indicates dolicocephaly
what is abdominal circumference?
measurement at level of liver, stomach, and umbilical vein intersection with PV
at high waist (steve urkel pants)
should be mostly round
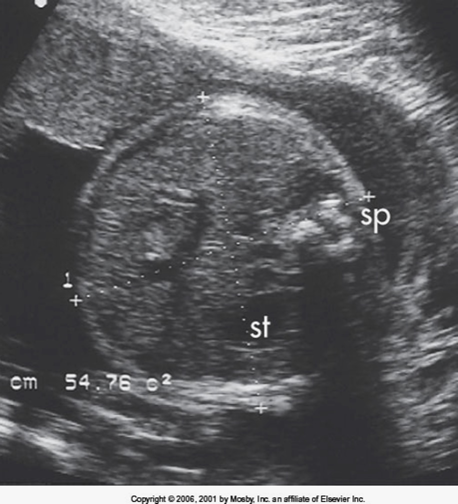
what should you not see in an abdominal circumference measurement? what should you see?
should not see kidneys— often adrenals
fetal skin
what is femur length?
what is this helpful for?
most commonly measured long bone
helpful when fetal head can’t be accurately measured
how is femur length measured?
elongate femur as much as possible
ends of bone should be blunt
measure diaphysis of femur—shaft only (do not include epiphyses)
arrow in image= distal femoral epiphysis and articular cartilage
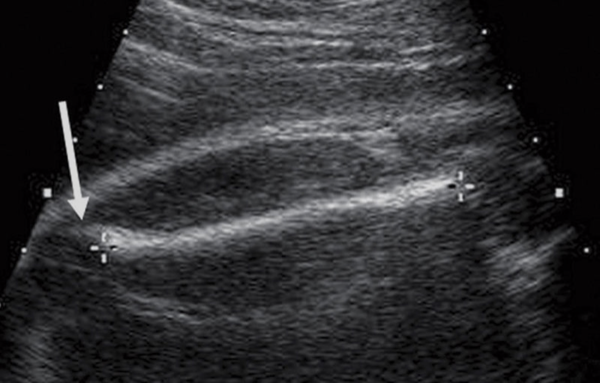
which femur should be measured in femur length?
ALWAYS MEASURE THE FEMUR THAT IS CLOSEST TO YOU (further femur is shadowed and harder to see)
why would we measure other long bones (other than femur)?
if we suspect some kind of long bone disorder
short femur is associated with…
trisomies
dwarfism
osteogenesis imperfecta
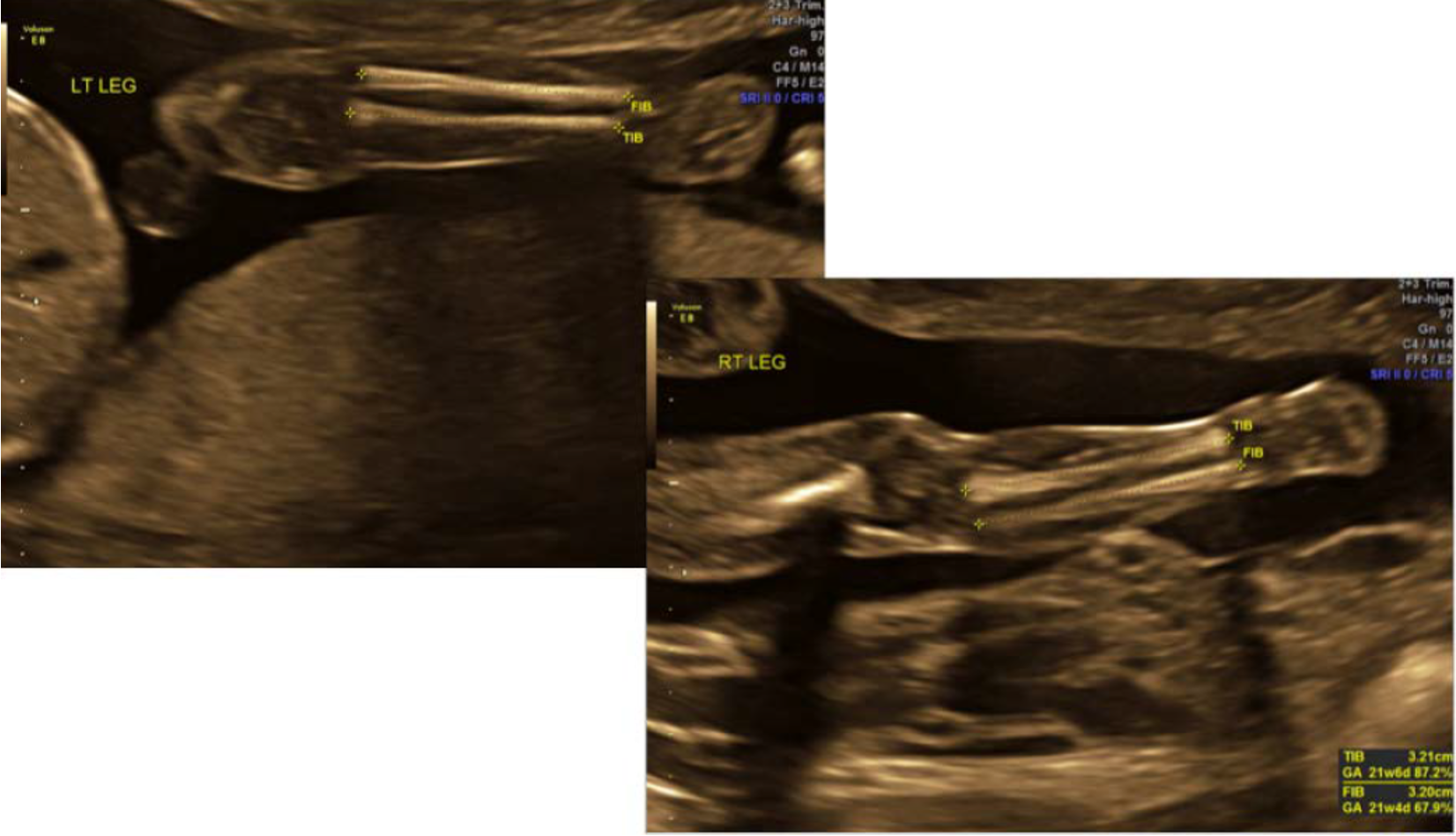
how do you differentiate tibia and fibula?
tibia thicker and in medial position
fibula is laterally located and extends more inferiorly (into ankle)
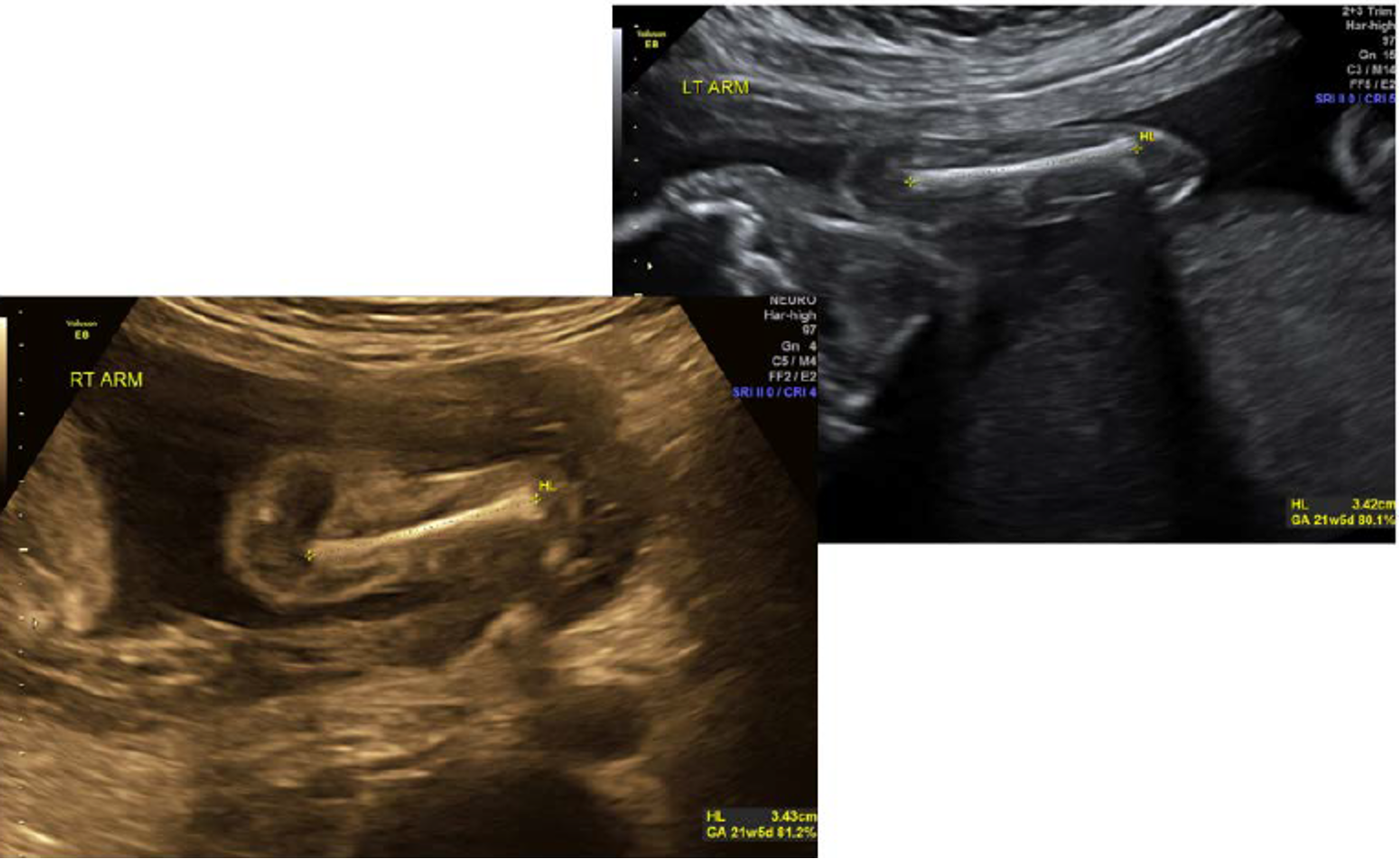
when is humerus often measured?
20 weeks
where is humerus often located?
near the fetal abdomen/thorax
how do you avoid confusing the humerus with the femur?
make connection with shoulder
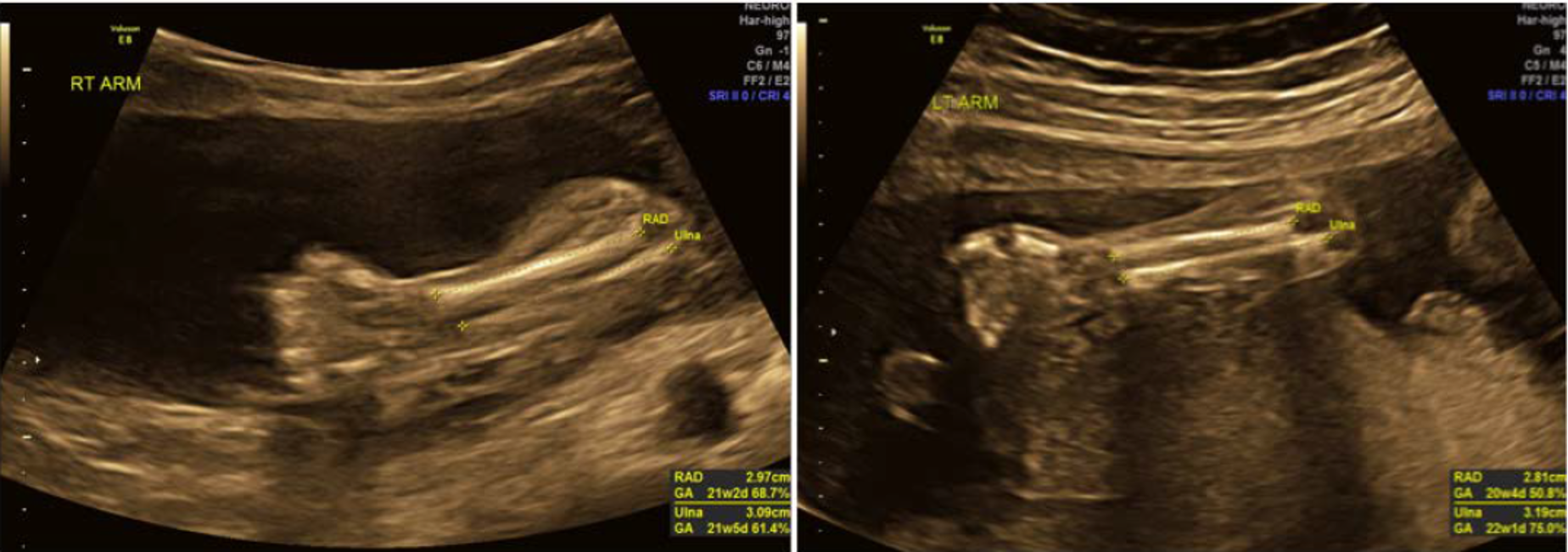
radius vs ulna?
ulna: protrudes further into elbow joint, a little thicker
radius: on side of wrist next to thumb
what is orbital diameter?
medial—> lateral diameter of ONE orbit
orbits should be the same size
what is orbital diameter used to detect?
micropthalmos
anopthalmos
what is binocular distance?
distance from lateral border of one orbit to lateral border of the other orbit
can be used to predict GA
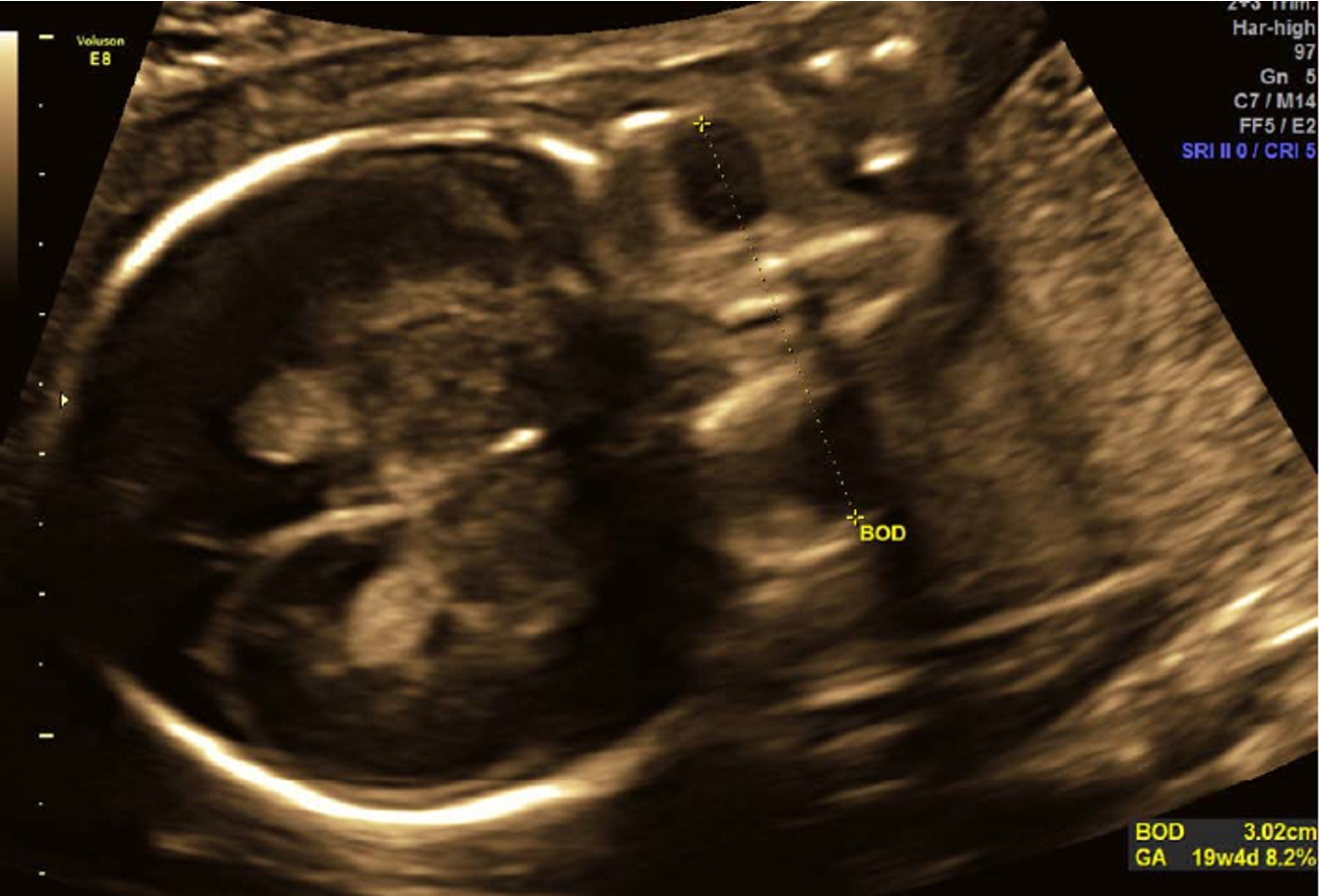
what is interocular distance?
distance from medial border of one orbit to medial border of the other
“bridge of the nose” area
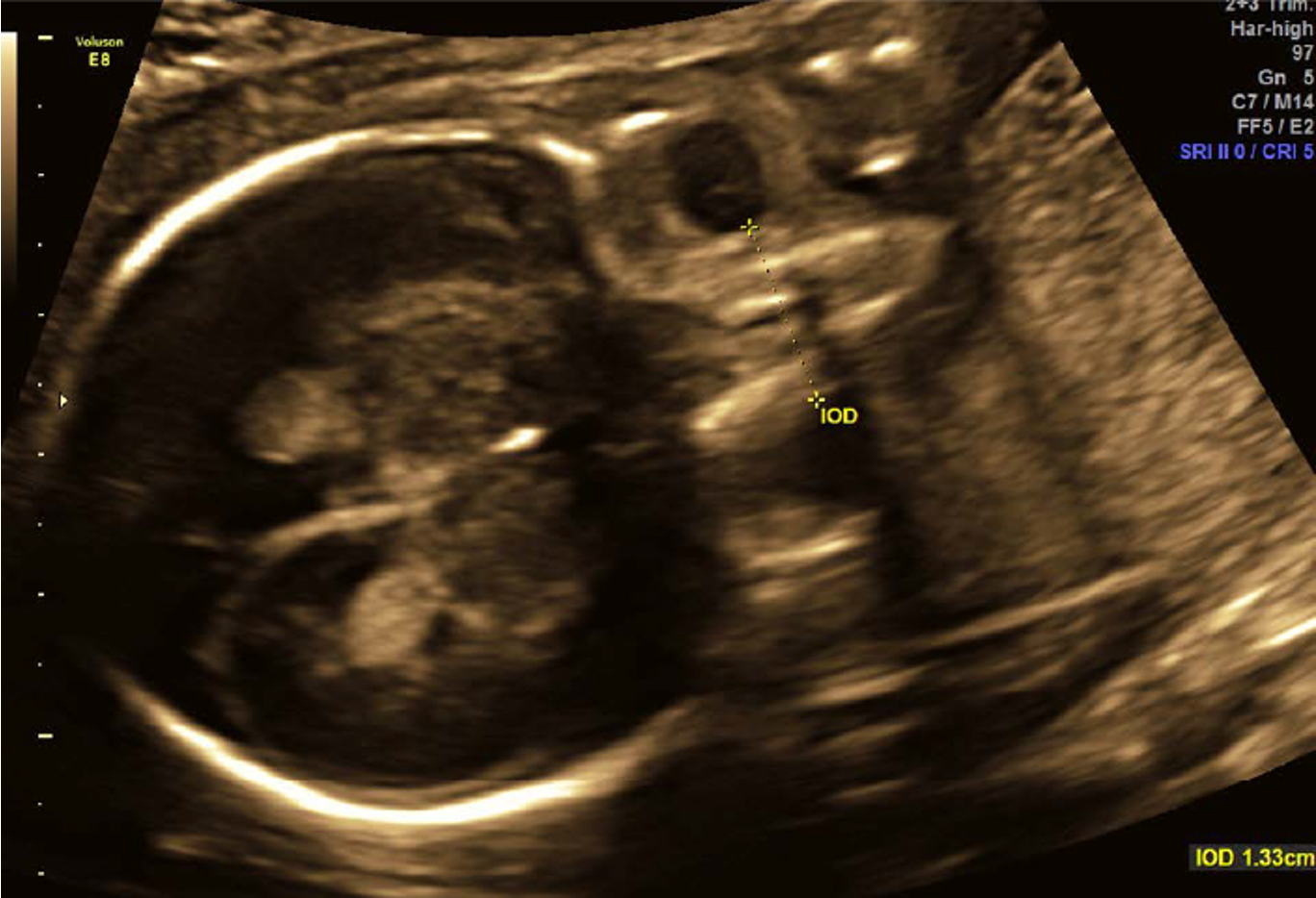
what is interocular distance used to detect?
hypotelorsim- eyes too close together
hypertelorism- eyes too far apart
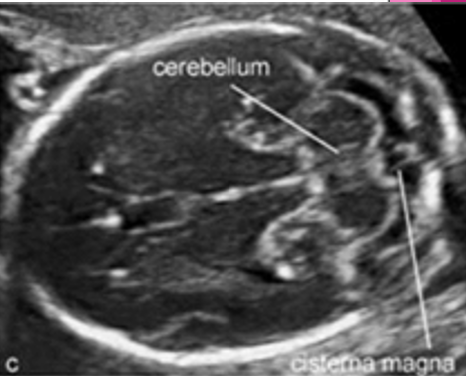
what is cerebellar diameter?
see cerebellum in transverse plane
angle inferiorly from BPD image
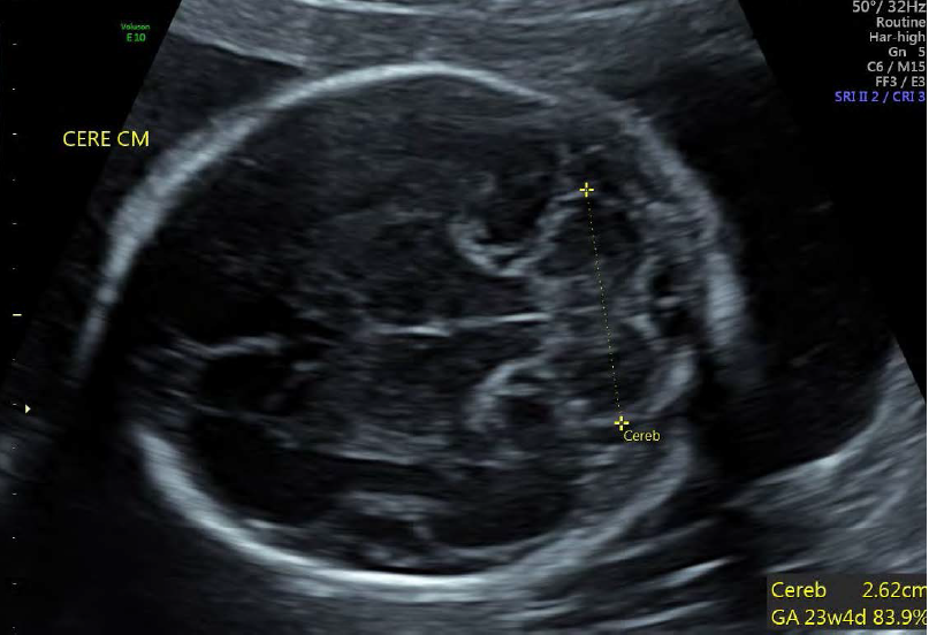
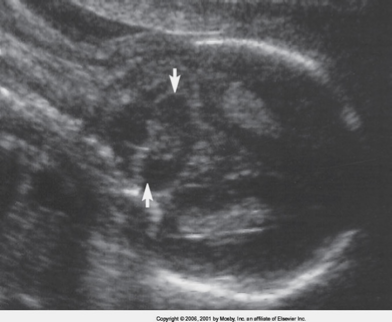
which plane can you measure cerebellar diameter from if transverse view is not available?
coronal, but not as accurate
cerebellar diameter in mm closely correlates to GA up to…
28 weeks
what is the banana sign?
flattening of cerebellum against occipital bone in cases of spina bifida/ encephalocele (banana on very right side)
what makes up the arnold chiari II malformation?
banana sign with Lemon Sign
lemon sign= inward scalloping of frontal bones
(lemon shaped at very left side of image)
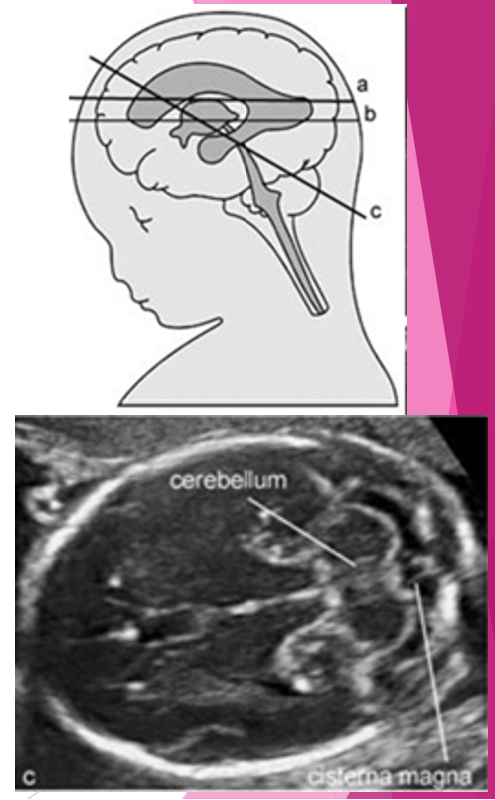
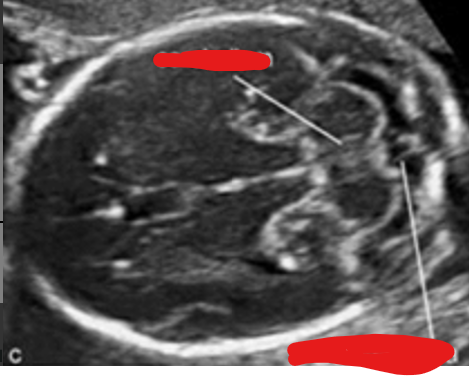
what is the cisterna magna?
fluid filled space between cerebellum and occipital bone
normal cisterna magna range?
3-11 mm
large vs small cisterna magna?
small is associated with Arnold Chiari II
large is associated with Dandy Walker Malformation
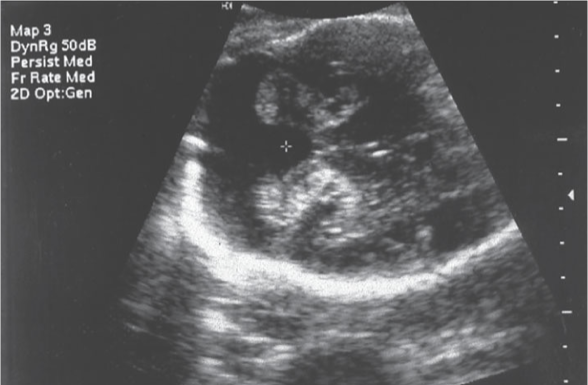
what is a nuchal fold?
thickness of skin at base of skull/ top of neck (NOT NT)
if enlarged, associated with trisomies (especially 21)
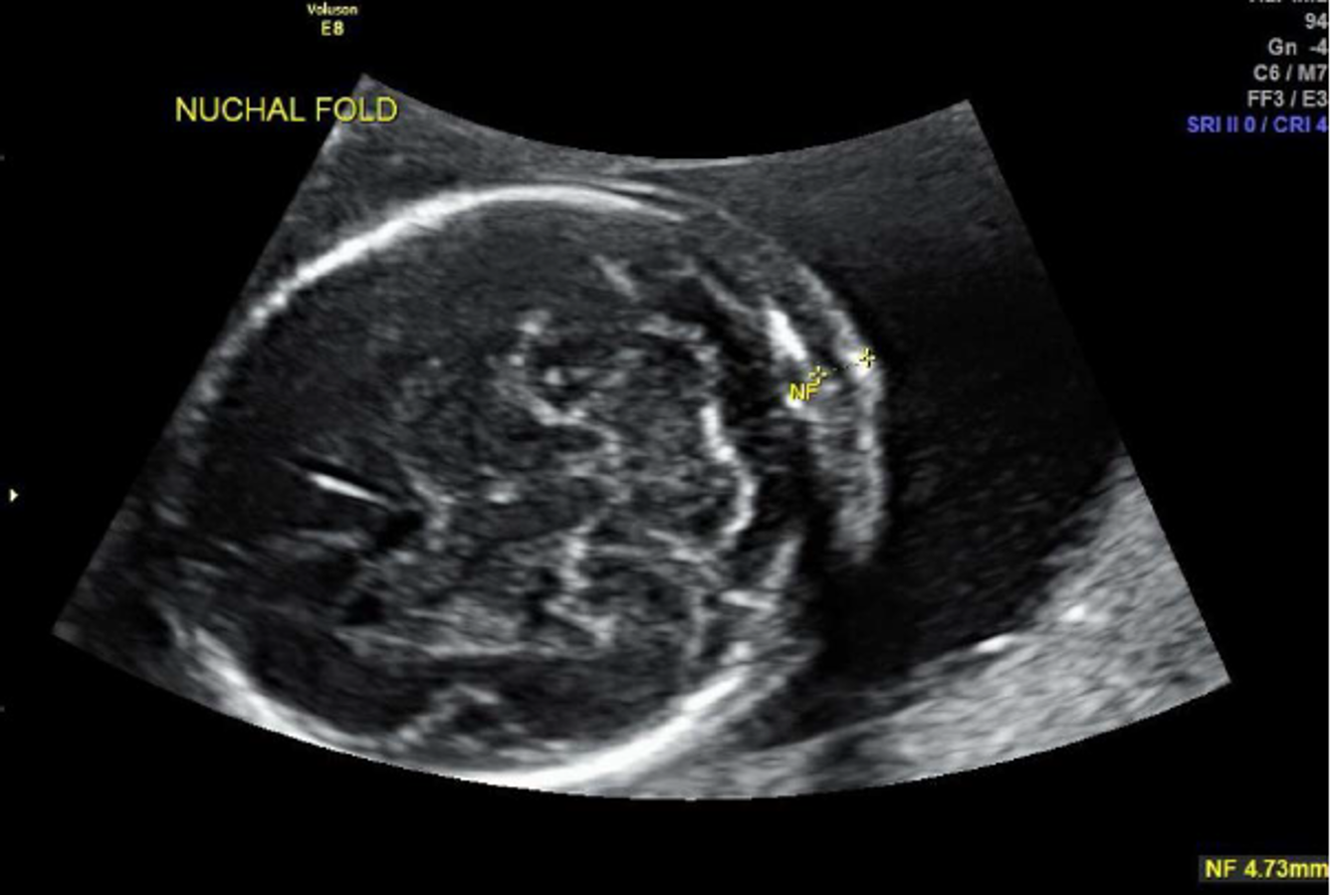
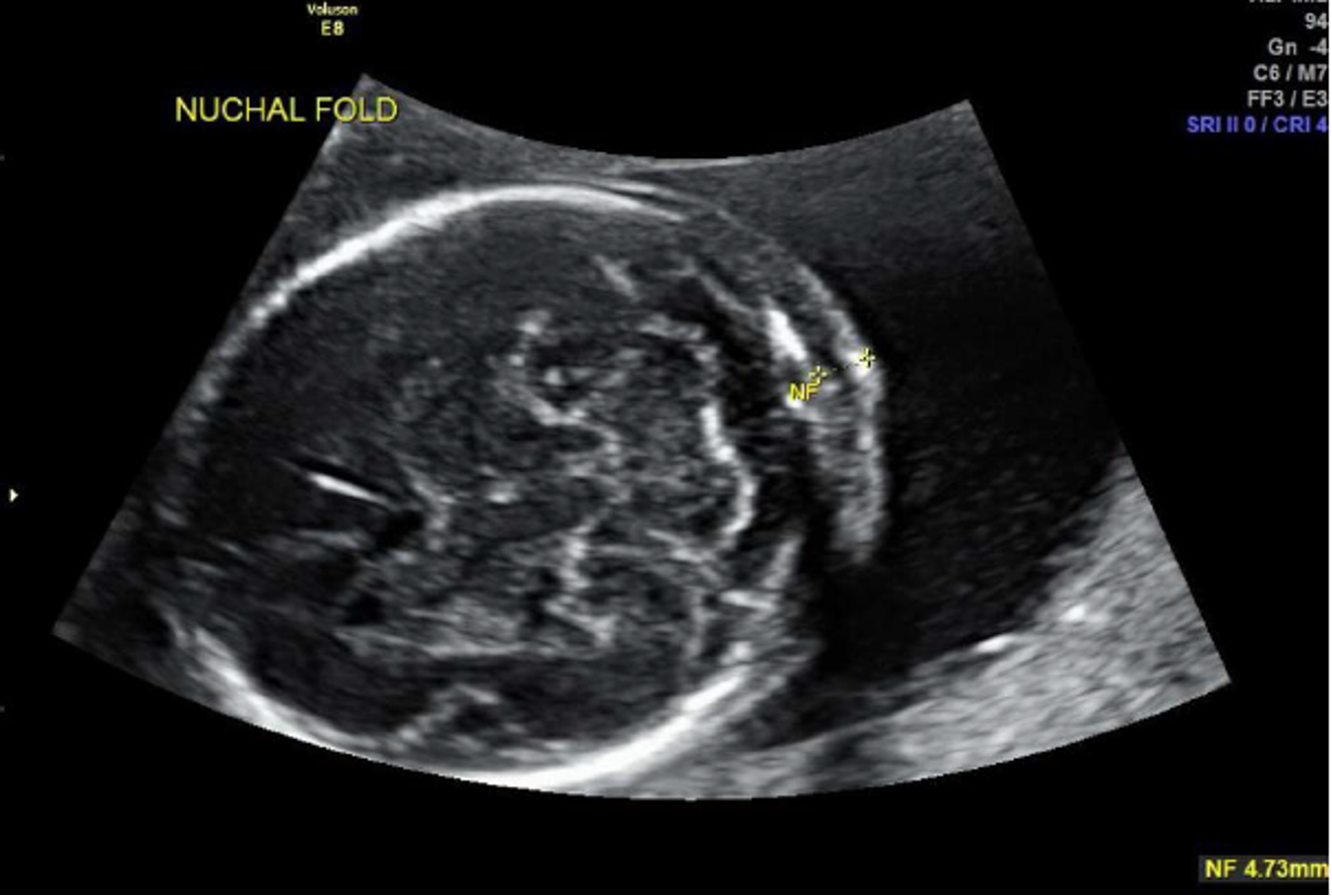
normal nuchal fold?
less than 6 mm
what is normal lateral ventricle diameter?
less than 10 mm
just above thalami in posterior cerebrum
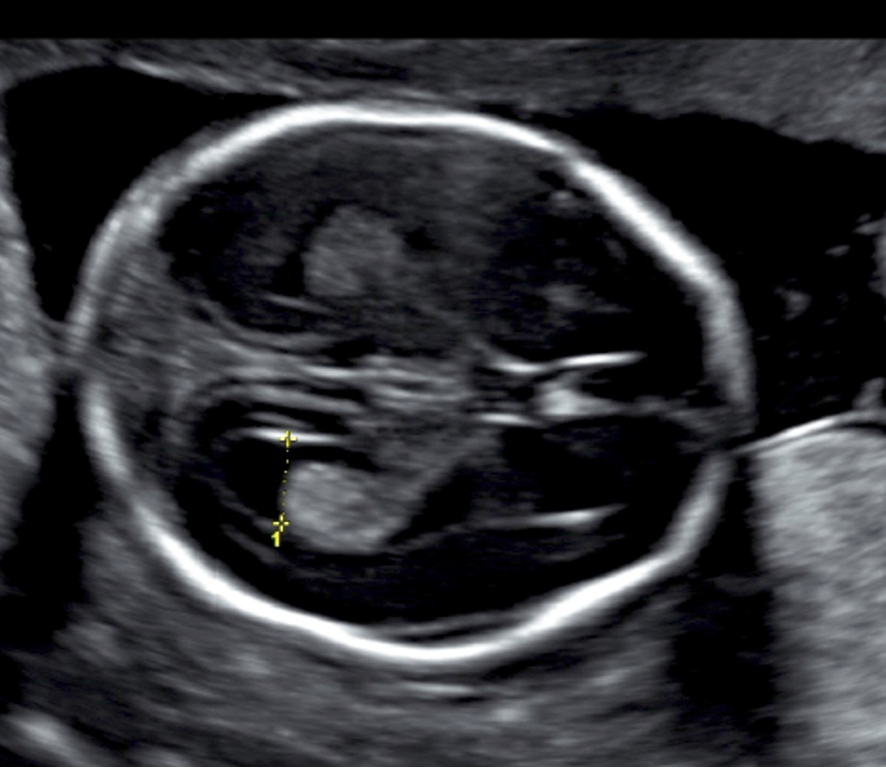
large lateral ventricle associated with?
hydrocephalus (image is dilated!)
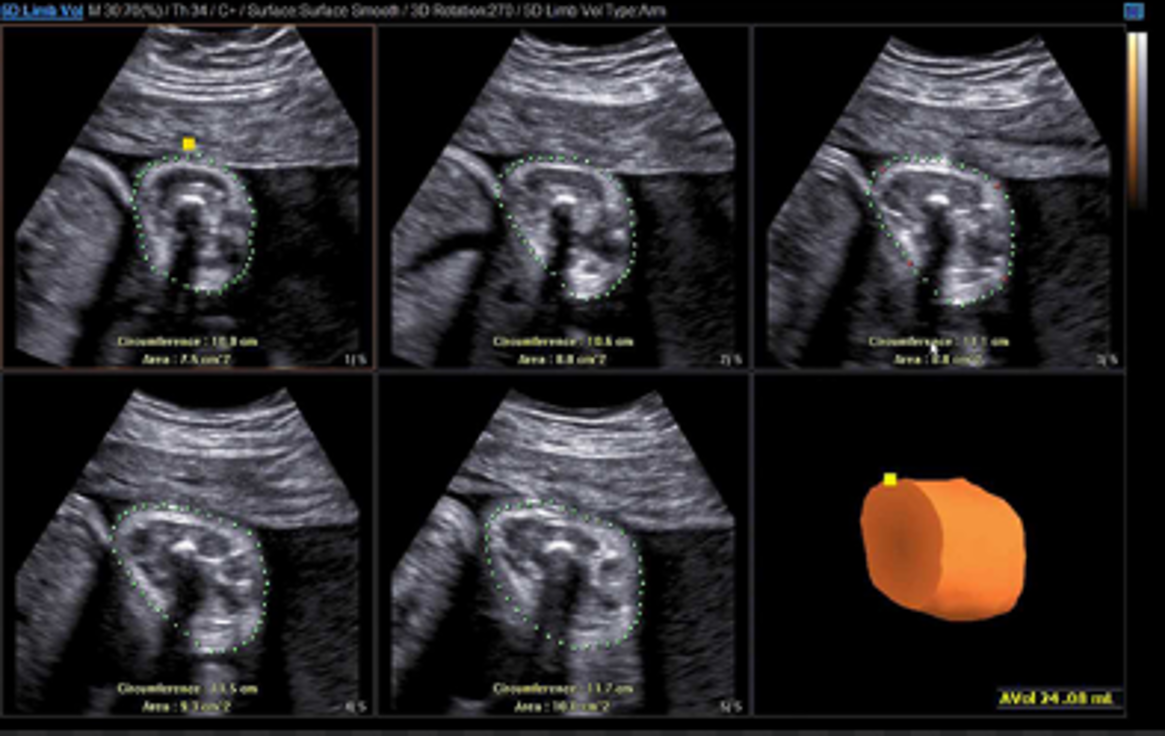
3D thigh for fetal weight?
measure thigh volume to assess soft tissue mass
may be good indicator for fetal growth
strongly correlated with 2D assessments of fetal weight
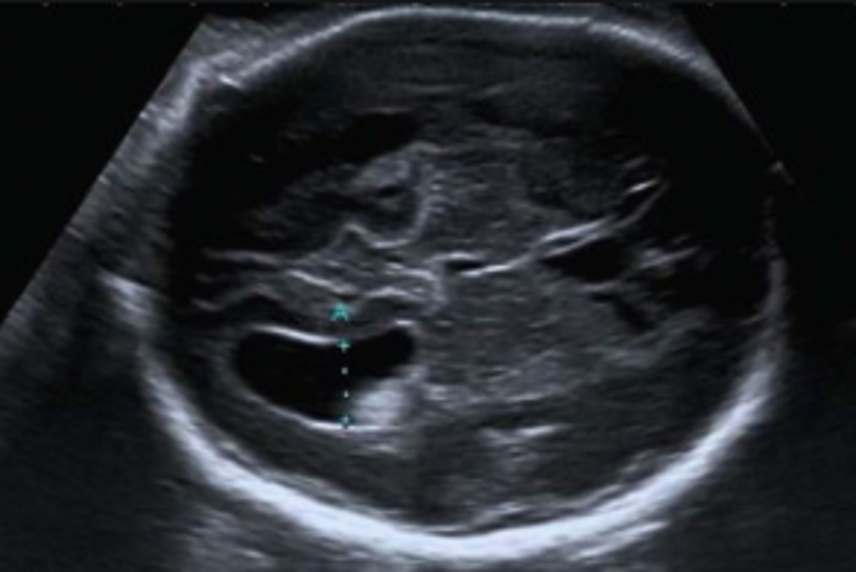
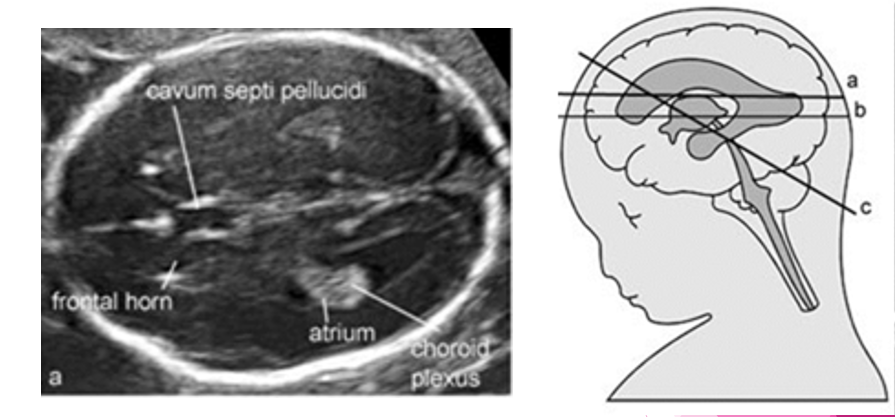
where do we measure the lateral ventricle? ( brain scan plane)
landmarks:
frontal horn
cavum septi pellucidi
atrium
choroid plexus
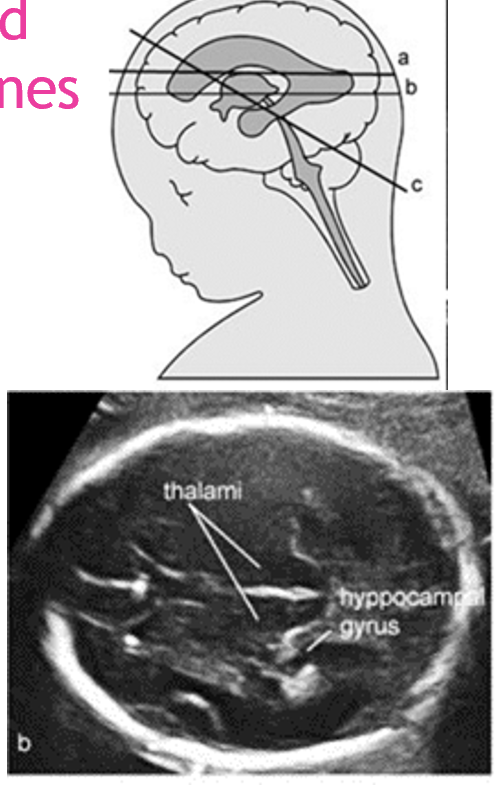
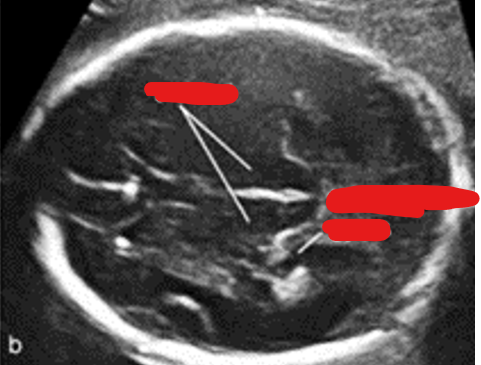
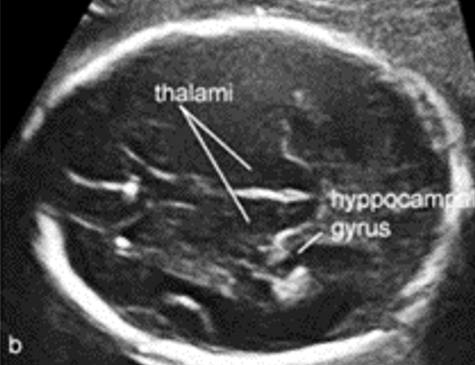
where do we measure the BPD/ HC? ( brain scan plane)
landmarks:
thalami
hippocampal gyrus
where do we measure the cisterna magna and nuchal fold? ( brain scan plane)
landmarks?
cerebellum
cisterna magna
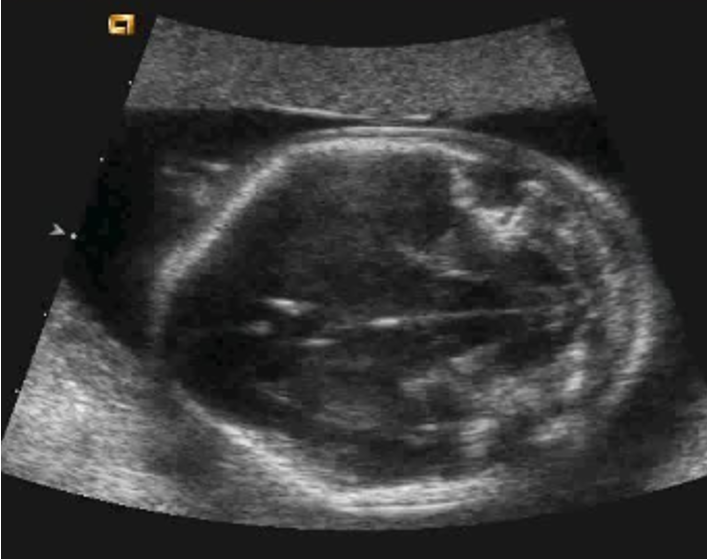
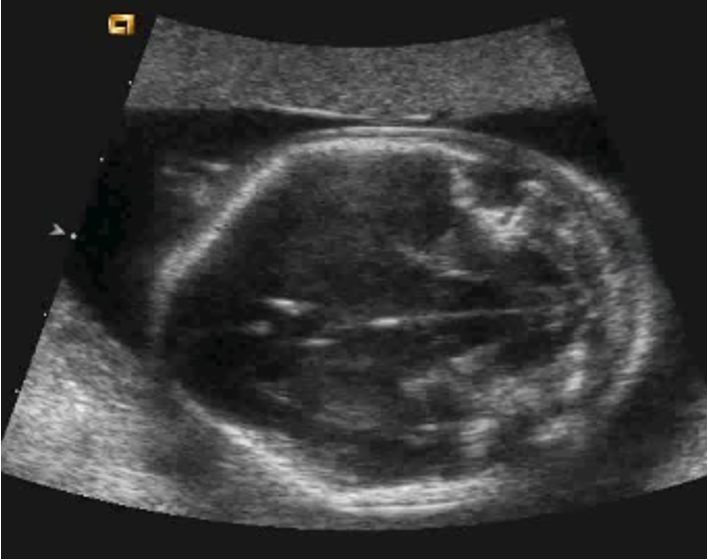
label this image and state scan plane:
BPD/ HC
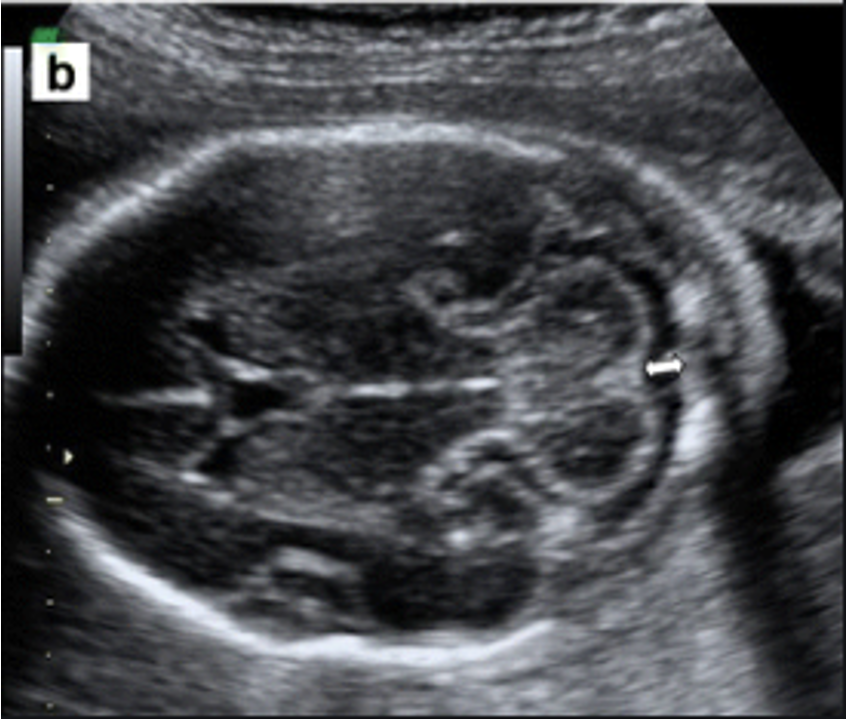
label this image and state scan plane:
cisterna magna and nuchal fold
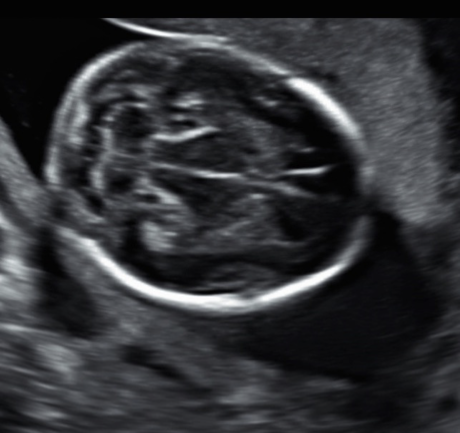
label this image and state scan plane:
lateral ventricle