Outer Ear
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are the parts of the peripheral auditory system?
Outer Ear
Middle Ear
Inner Ear
What does the Outer Ear consist of?
Pinna
External auditory canal
Pinna
Comprised of skin + cartilage
Tympanic Membrane
Located at the end of the external auditory canal
What are the major landmarks of the Pinna?
Helix
Antihelix
Lobe
Triangular fossa
Cymba concha
Crus of helix
Cavum concha
Antitragus
Tragus
Intertragal notch
Characteristics of the external auditory canal
Curved ‘S’ shaped
Stretches from pinna to tympanic membrane
1/3 is cartilaginous
2/3 comprised of bone
Function of the Pinna
Sound enhancement
Localizations
What is the resonant frequency an adult can hear?
2700-3400 Hz
Function of the external auditory canal
Channel acoustic energy to the eardrum
Produce cerumen
Protect the eardrum
Serves as a resonator with one closed end
Function of the Outer Ear
Enhance certain frequencies
Protect
Aid in localization
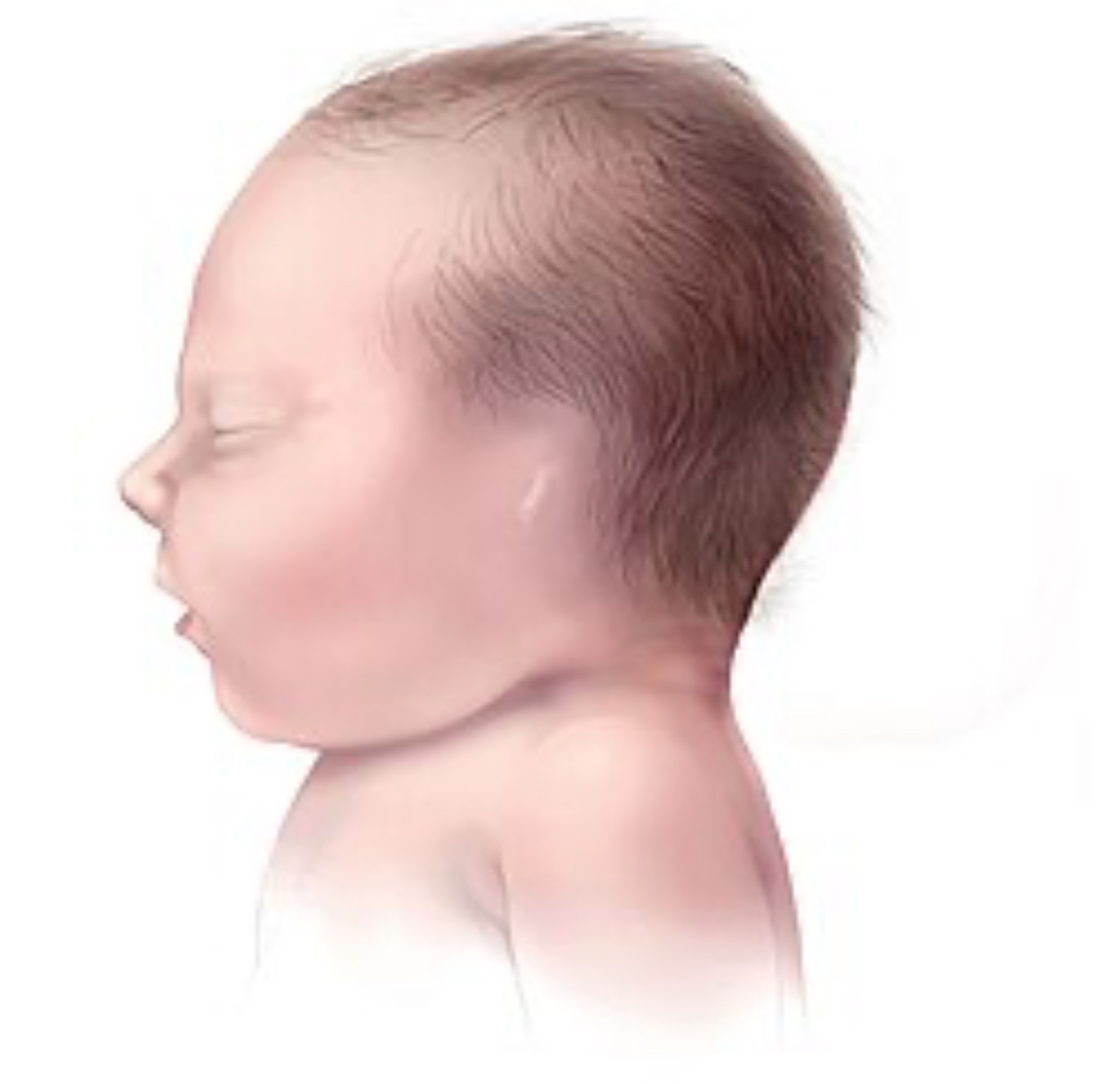
Anotia
Location: Pinna
Absent pinna
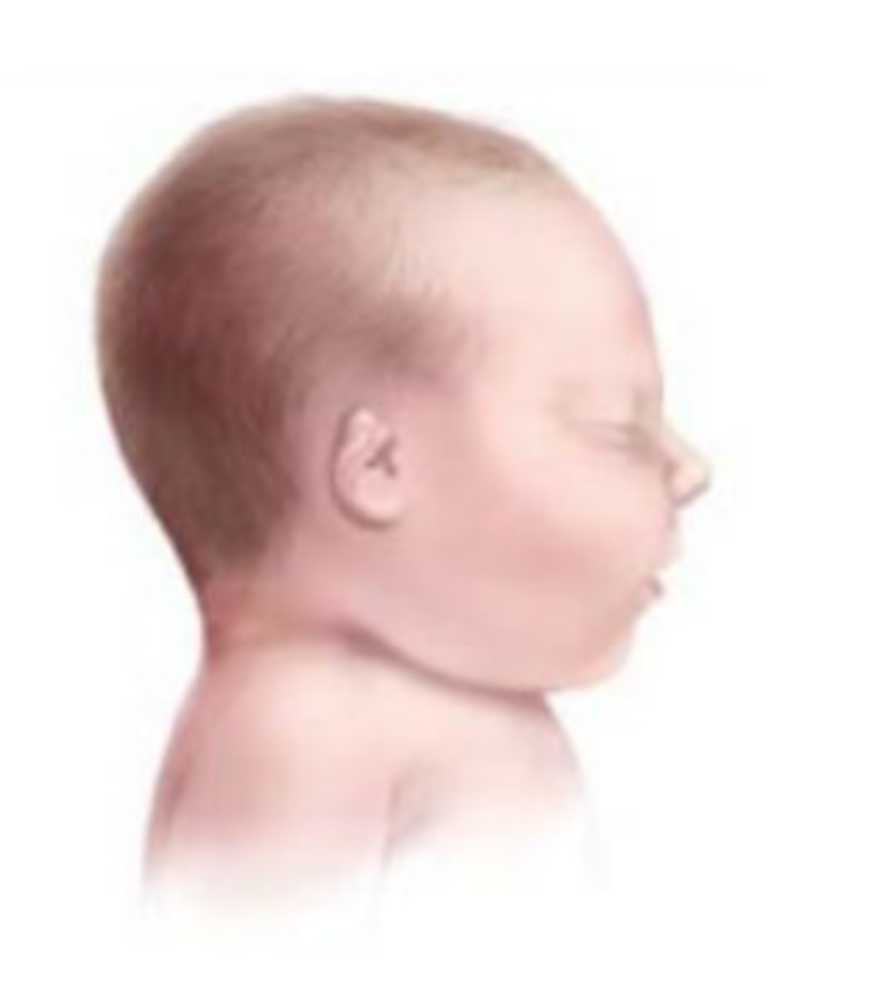
Microtia
Location: Pinna
Small pinna with or without landmarks
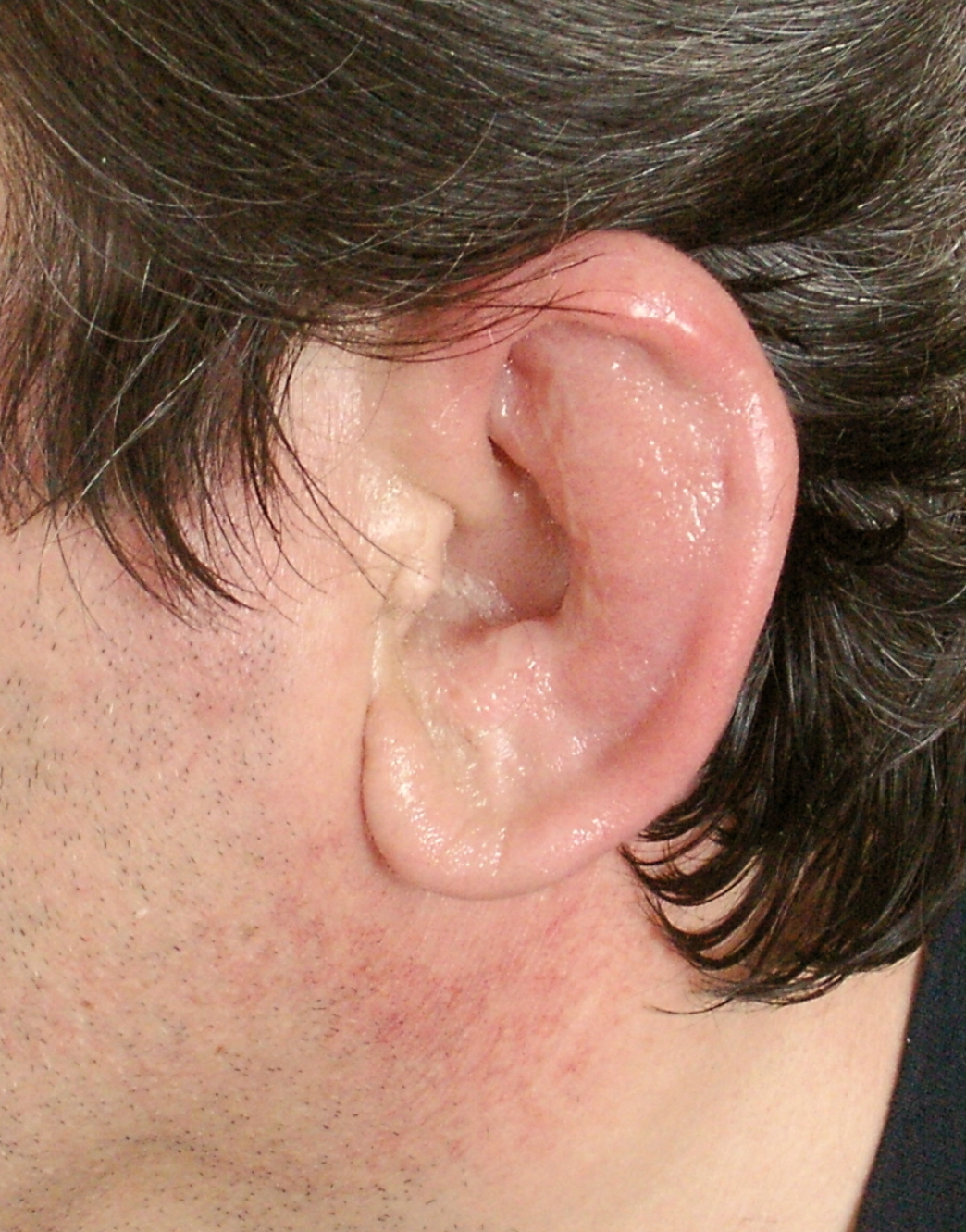
Perichondritis
Location: Pinna
Infection of tissue surrounding cartilage
Bacterial infection with swelling
Redness
Pain
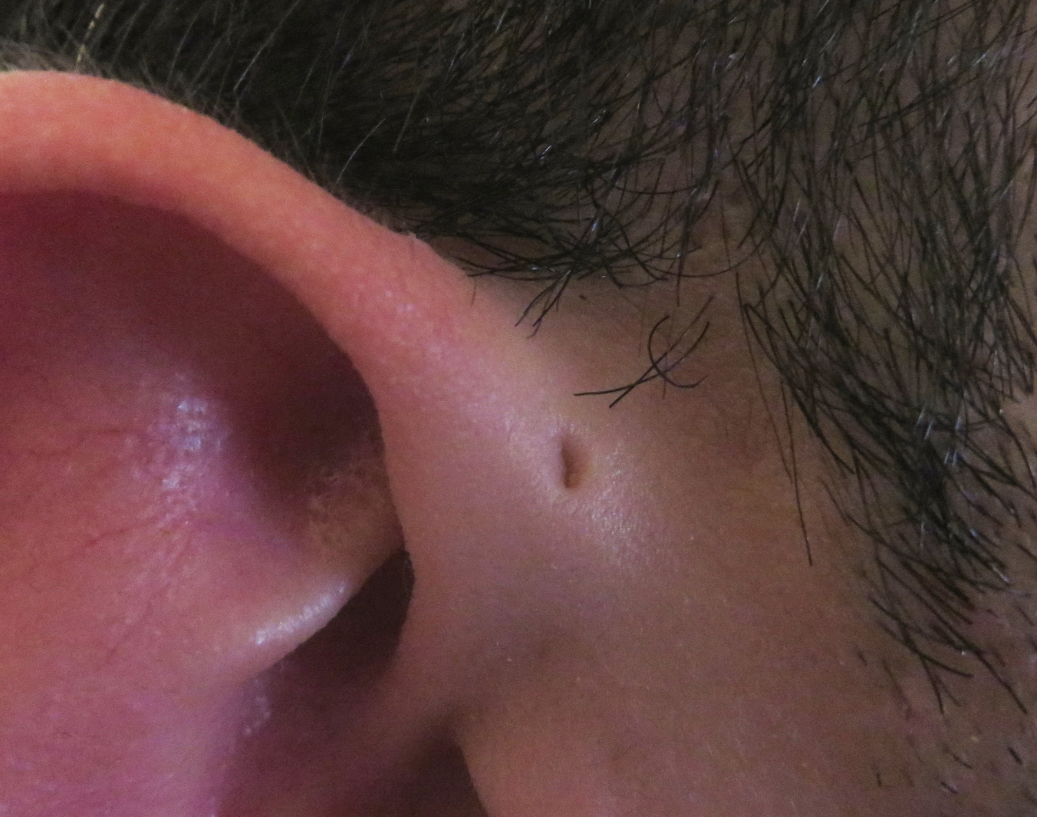
Preauricular fistula
Location: Pinna
Depression in skin
Anterior to helix + superior to tragus
Stenosis
Location: External Auditory Canal
Narrowing of the external auditory canal
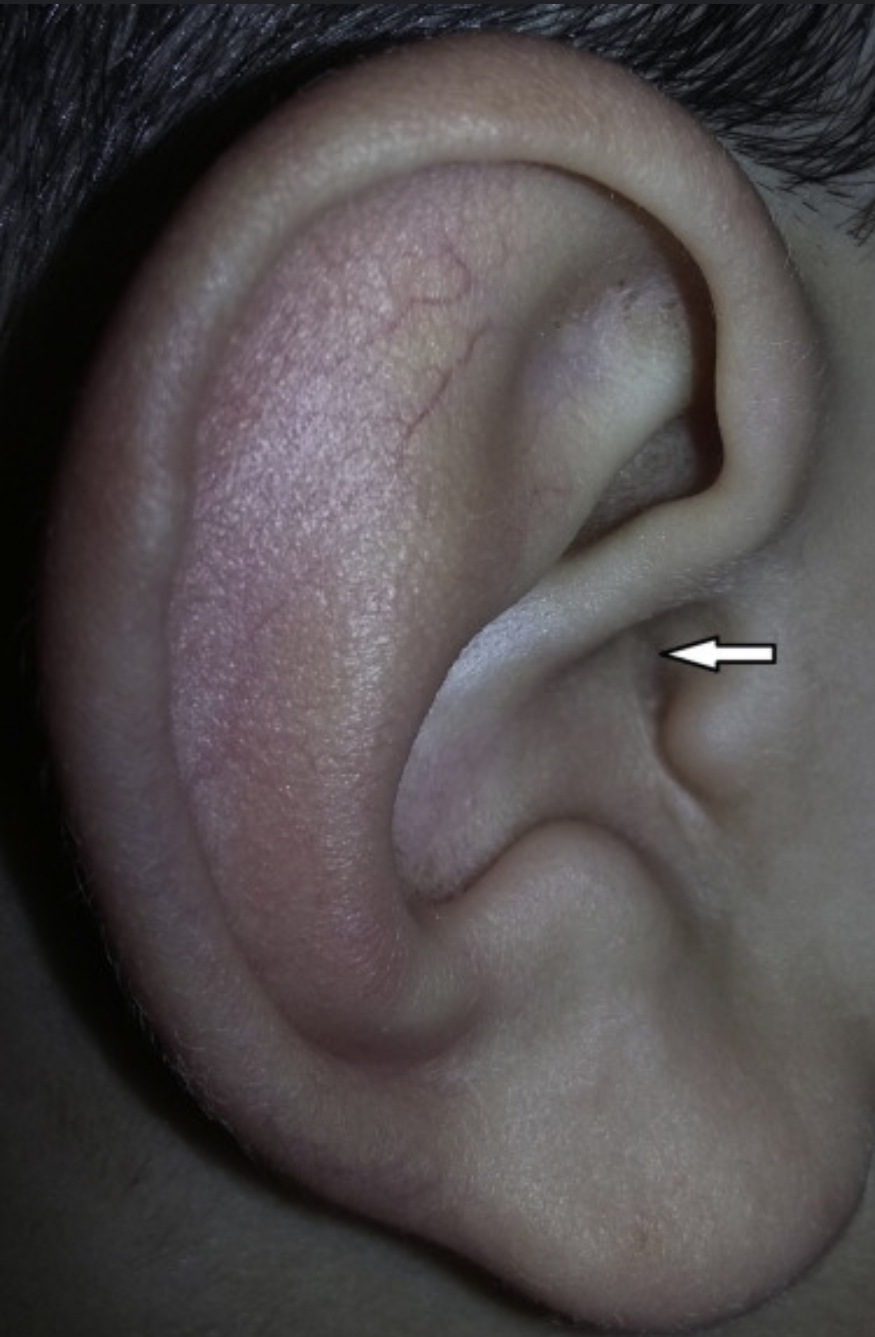
External otitis
Location: External Auditory Canal
AKA ‘swimmer’s ear’
Possible fever +/or drainage from external auditory canal
Likely pain
Swelling of pinna
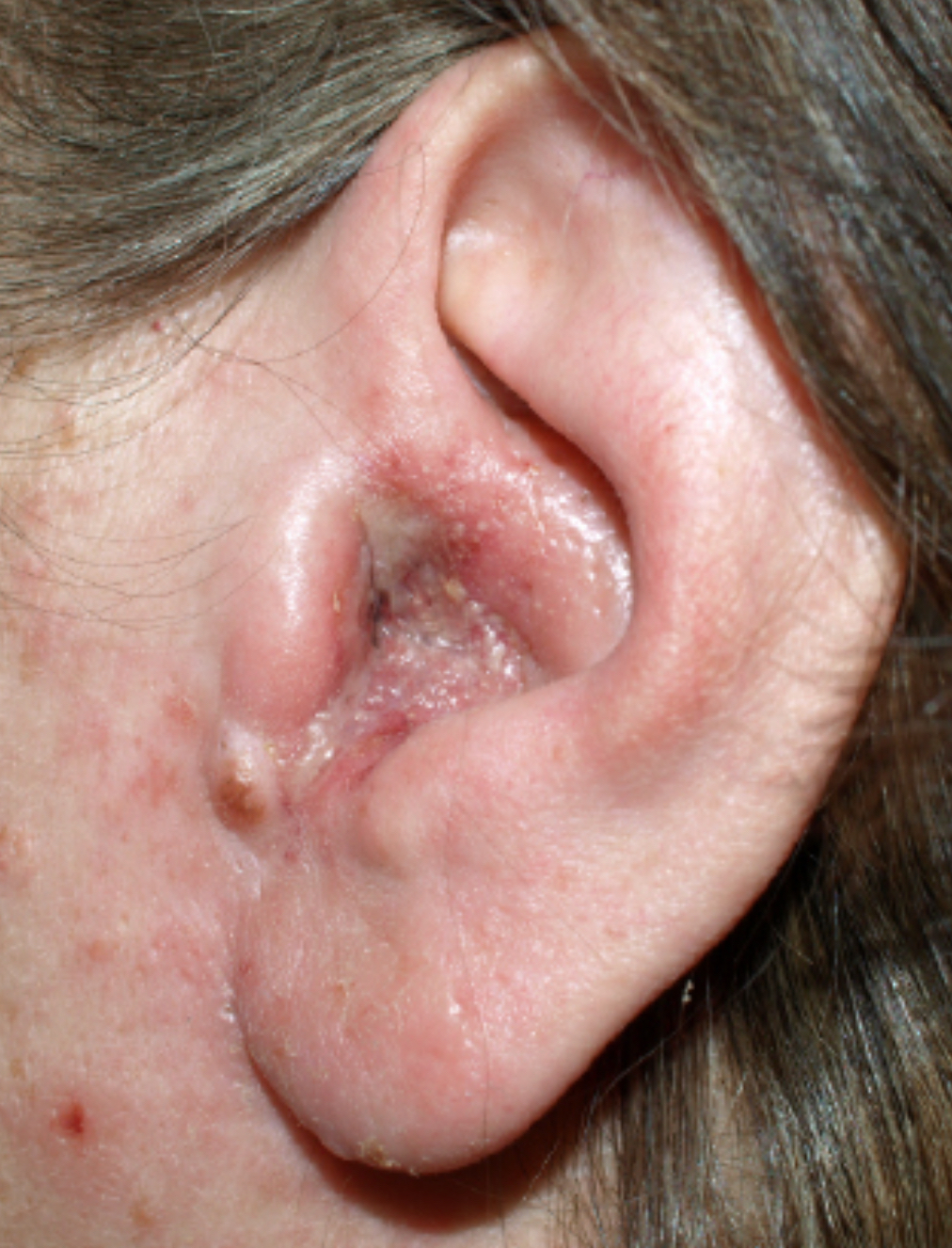
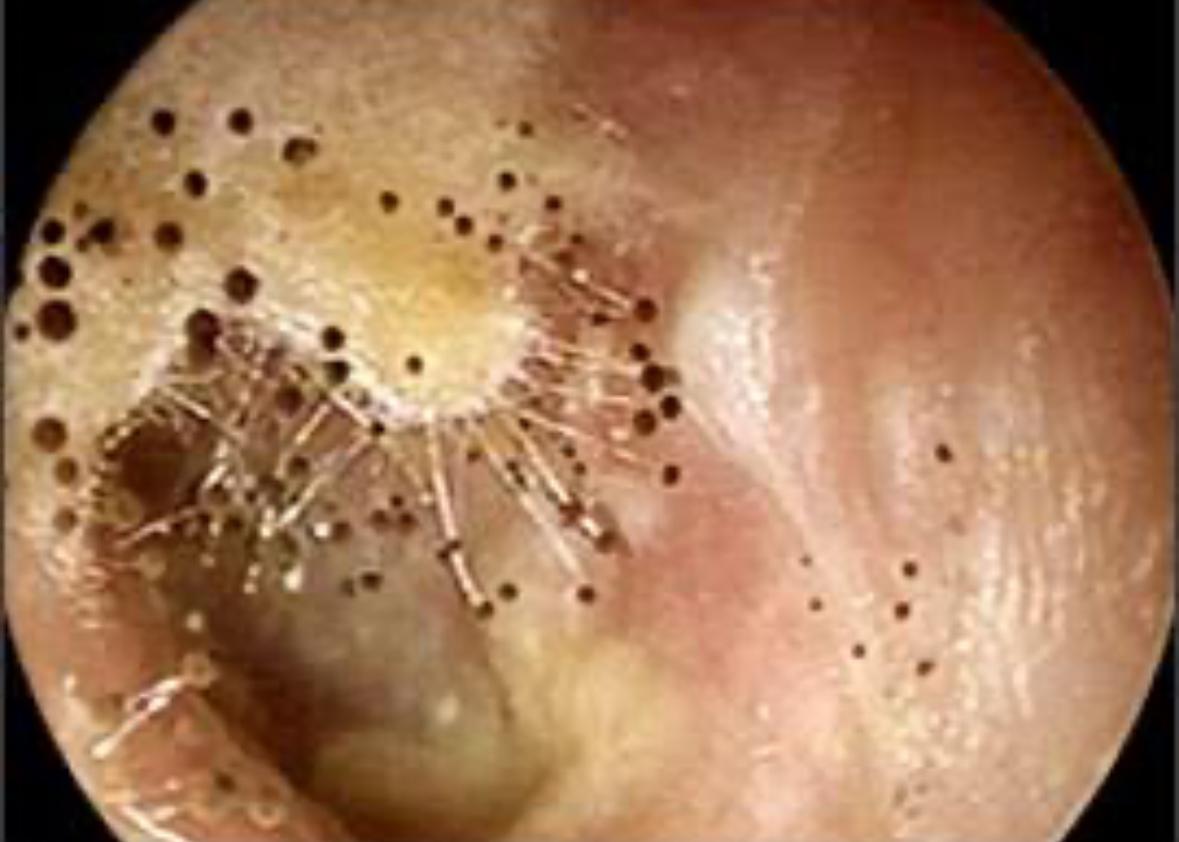
Otomycosis
Location: External Auditory Canal
Fungal infection
Itching
Possible pain
Burning
Discharge
Hearing loss
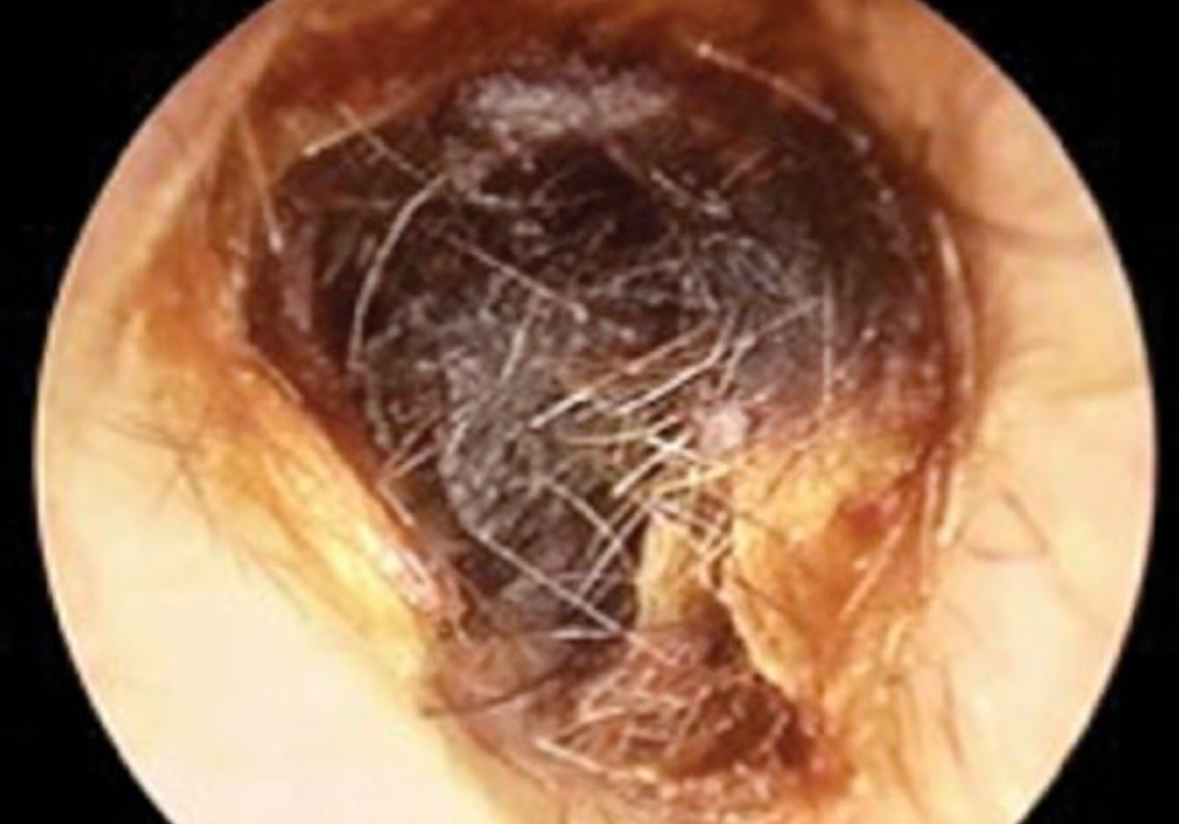
Cerumen impaction
Location: External Auditory Canal
Ear wax
Decrease in hearing
Localization
Knowing the direction of a sound source in the horizontal plane
High frequency differences between ears also help us locate sound sources in different planes (front, above, back)
Sound enhancement resonant frequency
1500 Hz or 1.5 kHz
What is the cause of Anotia?
Congenital (present at birth)
May be associated with a syndrome
What is the cause of Microtia?
Congenital
May be associated with a syndrome
What is the cause of Perichondritis?
Skin Conditions
What is the cause of Preauricular fistula?
Congenital
Disruption during development
What is the cause of Stenosis?
Age
Or may be congenital
What is the cause of External Otitis?
Bacterial or fungal infection
Humid Environment
Skin Condition
Trauma/abrasion
What is the cause of Otomycosis?
Skin conditions
Humid Environments
What is the cause of Cerumen?
Hearing aid use
Narrow ear canals
Cotton swab use
What is the treatment for Anotia?
Possible surgical reconstruction
Amplification if indicated
What is the treatment for Microtia?
Possible surgical reconstruction
Or amplification if indicated
What is the treatment for Perichondritis?
Antibiotics
What is the treatment for Preauricular?
Antibiotics if infection/discharge
What is the treatment of Stenosis?
Possibly surgery if linked to hearing loss
What is the treatment of External Otitis?
Prescribed ear drops
What is the treatment of Otomycosis?
Prescribed ear drops
What is the treatment of Cerumen?
Cerumen removal with suction or curette