1102 bullshyt
1/208
Earn XP
Description and Tags
kine 1102
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
209 Terms
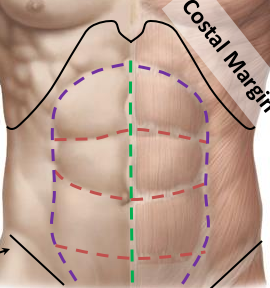
what are the four quadrants of the abdomen
RUQ
RLQ
LUQ
LLQ
What are the 3 regions of the right part of the abdomen (superior to inferior)
Right hypochondriac
Right lumbar
Right inguinal
What are the 3 middle regions of the abdomen
Epigastric
Umbilical
Suprapubic
what are the 3 left regions of the abdomen
L hypochondriac region
L lumbar region
L inguinal region
What are the two planes of the abdomen and their levels
Subcostal - L1
Transtubercular - L5
function for layers of abdominal wall
assists in expiration
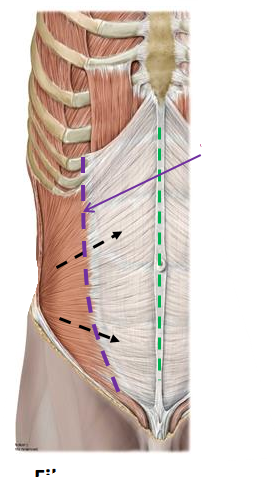
external oblique muscle fiber orientation
anterior/inferior
internal oblique muscle fiber orientation
anterior/superior
transversus abdominis muscle
horizontal/transversefiber orientation of muscle
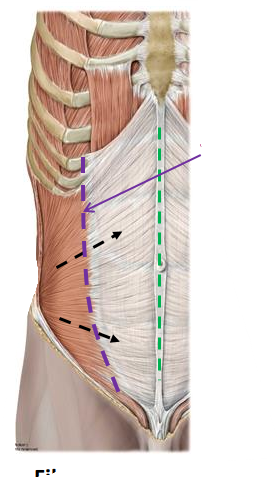
what is the purple line
linea semi-lunaris
what is the green line
linea alba
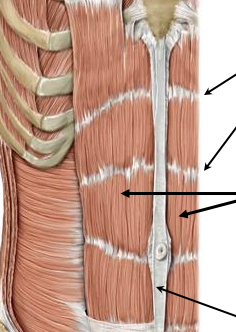
what muscle is the thick black line pointing to
rectus abdominis muscle
rectus abdominis muscle functions (2)
compression of abd contents + flexion
what is the red line
transverse intersections
layers posterior to rectus abdominis (4)
Parietal Peritoneum
Transveralis Fascia
Apon of Transverse Adbominis
½ Apon of Int Oblique

layers anterior to rectus abdominis (posterior to anterior)
½ Apon of Int Olique
Apon of Ext Oblique
Scarpa’s Fascia
Camper’s Fascia
Skin

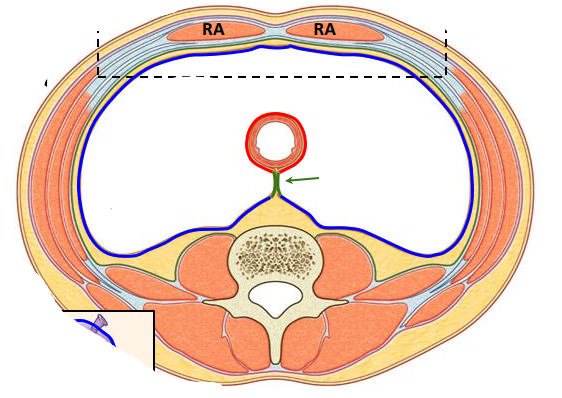
what do the colours represent
red: visceral peritoneum
blue: parietal peritoneum
green: mesentery
what are intraperitoneal organs
surrounded by visceral peritoneum
what are retroperitoneal organs
behind parietal peritoneum
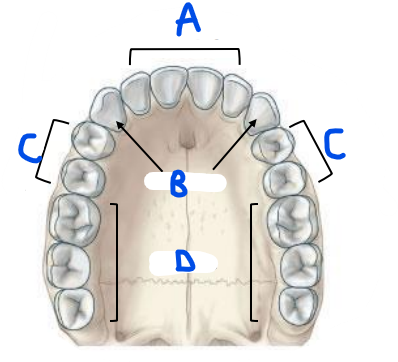
label (maxillary teeth, inferior)
a) incissors
b) premolars
c) canines
d) molars
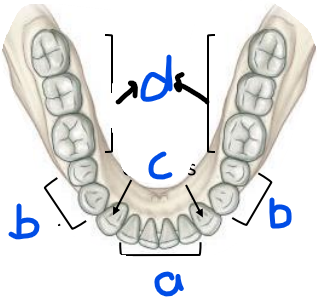
label (mandibular teeth, superior view)
a) incissors
b) premolar
c) canines
d) molars
intrinsic muscles of the tongue do..
shape/form tongue (longitudinal, transverse, and horizontal)
extrinsic muscles of the tongue do…
gross motor movement of the tongue
pharynx
directs food from oral into esophagus
phases of swallowing (3)
oral: tongue moves ant/posteriorly (voluntary)
pharyngeal: closure of nasal and laryngeal (invol)
esophageal: peristalsis (invol)
epiglottis purpose
prevent food/drinks from entering airways
foregut componets
esophagus (abdominal) to the D3/D4 segment (includes liver, gallbladder, pancreas & spleen)
hindgut components
distal 1/3 transverse colon to the rectum
MIDGUT
D4, jejunum to the proximal 2/3 transverse colon
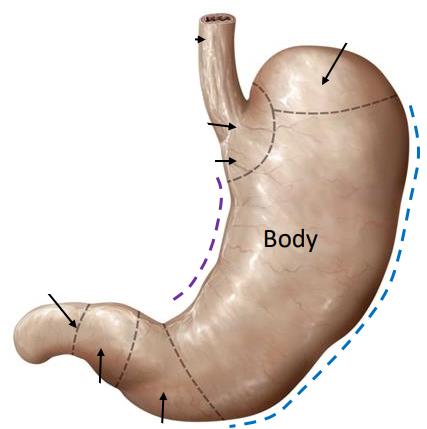
label the blue and purple lines
lesser curvature
greater curvature
what is the pathway of food through the digestive system (8)
mouth
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum)
large intestine
rectum
anus
is there digestion occuring at the esophagus?
no its just propulsion to the stomach
where does chemical digestion occur (3)
Mouth
Stomach
Small intestine
where does mechanical digestion occur? (3)
Mouth
stomach
small intestine
who supplies blood for the foregut (esophagus, stomach, D1-D3/4, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, spleen)
celiac trunk
who supplies blood for the midgut (D3/4, jejunum, ileum, cecum, ascending colon, proximial 2/3 transverse)
superior mesenteric artery
who supplies blood for the hindgut (distal 1/3 transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum)
inferior mesenteric artery
where is the opening in the diaphragm for the inferior vena cava?
TVIII (T8)
where is the opening in the diaphragm for the esophagus
TX (T10)
where is the opening in the diaphragm for the aorta
TXII (T12)
5 processes of digestion (IPDAE)
ingestion
propulsion
digestion (chem and mechanical)
absorption
elimination
where is bile produced
liver and gallbladder
pancreas function
pancreatic juice prod and blood sugar maintainance
where can the liver be found
ribs 5-9 anteriorly or ribs 8-12 posteriorly
ductus venosus (fetal reminant)
get O2 rich blood to baby FAST
ligamentenum teres (fetal remnant)
remnant of umbilical vein
minor duodenal papilla gets bile from what duct
accessory pancreatic duct
major duodenal papilla receives bile from where (2)
pancreatic duct and common bile duct
4 concentric layers of the GI tract (deepest to superficial)
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa (intraperitoneal)/Adventitia (retroperitoneal)
Purpose of each:
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa (intraperitoneal)/Adventitia (retroperitoneal)
secretion, digestion, absorption, protection
structural support
peristalsis
covered with layers
enzymes secreted in the oral cavity
salivary amylase — sugars
lingual lipase — lipids
chem digestion substances in the stomach (5)
HCl
intrinsic factor
pepsinogen
gastric lipase
hormone gastrin
Purpose of these substances in the stomach for chem digestion
HCl
intrinsic factor
pepsinogen
gastric lipase
hormone gastrin
denature proteins
b12 absorption
digestion of proteins
lipid breakdown
secretion of gastric juices
purpose of small intestine
absorption of water (through osmosis) and nutrients, mostly occurring in the jejunum
mechanical digestion in the small intestine
segmental contraction for churning/mixing enzymes
chemical digestion in small intestine (duodenum mostly)
complete breakdown of everything
fats — emulsion fr bile and digestion from lipase
proteins — proteases
(digestive sys) lacteal is a
lymphatic vessel that absorbs fats/lipids and fat sol vitamins
goblet cell does what
secrete mucus
enteroendocrine cell does what
hormone secretion
paneth cell does what
secretes lysozyme and can do phagocytosis
4 types of transports
active
secondary active transport
facilitative diffusion
simple diffusion
active transport vs secondary active transport
active — use of atp
secondary — use of stored atp
facilitated vs simple diffusion
facilitated — protein channel
simple — substance just enters
sucrose crafting formula
glucose + fructose
maltose crafting formula
glu + glu
lactose craftin formula
glu + galac
absorption of proteins by
active transport (Na/K pump) and secondary active transport
method of absorption of lipids
simple diffusion of micelles

large intestine purpose
absorption of a lil bit of water and left over nutrients
three phases of digestion (NOT TYPES)
cephalic phase
gastric
intestinal
(digestive syst) cephalic phase
sensory input causes secretion of saliva and gastric juices
gastric phase
food entering stomach causes churning
intestinal phase
chyme entering small intestine causes inhabitation of gastric secretion
diaphragm ligaments (lateral to medial) (_____ arcuates)
lateral arcuate
medial arcuate
median acruate
left and right kidneys do what
filter blood to produce urine
left and right ureters do what
transport urine to bladder
bladder does what
stores organs for urine until it is eliminated
urethra does what
expels urine to exterior
does the right kidney sit higher than the left kidney
right sits lower
are degenerating kidneys taken out when a new one is transplanted
no
nut cracker syndrome
compression of left renal vein
segmental artery supplies what
arteries that go to the 5 segments of the kidney
interlobar artery supplies what
extend along renal columns, supplying lobes of kidney
arcuate artery supplies what (medulla)
arch along base of medulla
three layers of ureters (inner to outer)
transitional epithelial mucosa
smooth muscle
fibrous connective tissue
constriction sites of the ureters
hilum of kidney
pelvic brim
during passage through the wall of the bladder
urachus to median umbilical ligament (fetal reminant)
before birth the urachus is open but after birth its closed
internal urethral sphincter is for
autonomic control (involuntary)
external urethral sphincter is for what control
somatic control (voluntary)
male urethra vs female urethra
male is longer
male also transports urine and semen
functions of renal system/kidneys (4)
excretion of waste and toxins
ion conc regulation
maintain blood osmolarity
regulating blood vol
nephron
functional unit of kidney that filters blood and produces waste products to be excreted
components of the nephron
renal corpuscle
renal tubule
components of renal corpuscle (2)
glomerulus (capillaries)
bowman’s capsule
components of renal tubule (4)
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
loop of henle (LoH) — ascending and descending
distal convoluted (DCT)
collecting ducts (CT)
pathway of filtrate through nephron (11)
bowman’s capsule
PCT
descending LoH
ascending LoH
DCT
Collecting duct
papillary duct
minor calyx
major calyx
renal pelvis
ureter
functions of nephron (3)
glomerular filtration
tubular reabsorption
tubular secretion
what are in the functions of the nephrons:
glomerular filtration
tubular reabsorption
tubular secretion
glomerular filtration — filtration of blood plasma
tubular reabsorption — movement of substances into capillaries
tubular secretion — movement of waste into tubule
glomerular filtration rate depends on (2)
capillary blood pressure
osmotic pressure btwn glomerulus and bowman’s capsule
where does majority of filtrate reabsorption occur in the renal system occur
PCT