REBP SBA
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:02 PM on 11/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Randomised control trial
study where no. of similar people are randomly assigned to 2/more groups to test specific drug/treatment/intervention. 1 group (experimental group) has the intervention being tested, the other (comparison/control group) has alternative intervention/placebo/ no intervention at all.
2
New cards
Single-blinded study
treatment assignment (to either experimental or control group) is unknown to patients
3
New cards
double-blinded study
neither the subjects nor the investigators know who is receiving the active treatment
4
New cards
Triple Blinded Study
The study subjects, investigators, and statistician analysing the data are kept in the dark.
5
New cards
practice creep
gradual change in practice without founded evidence base
6
New cards
practice drift
Deviating from standard practice/loss of knowledge despite it existing
7
New cards
Duty of Care
The duty of all persons to exercise a reasonable amount of care in their dealings with others. Failure to exercise due care is negligence.
8
New cards
Power relationships & coercion
consent in appropriate setting, issue information in advance of treatment date
9
New cards
anonymity/confidentiality
Participants privacy must be protected/keep data secure + confidential
10
New cards
Risk of harm
researchers not put participants in a situation where they might be at risk of harm as a result of their participation/ pt should fully understand + can pull out whenever
11
New cards
Equity in treatment
participants should be fully aware of risk/benefit of study + option of not participating
12
New cards
Fully informed consent
Entails giving participants comprehensive info concerning nature + purpose of study + their role in it.
13
New cards
Access to medical records
pts should be able to see/obtain copies of their medical records + request corrections if they identify errors.
14
New cards
research
The systematic enquiry of materials + sources to extend knowledge + reach new conclusions.
15
New cards
service evaluation
evaluation of how well a service is achieving its aims.
designed + conducted to define/judge a current service. results can be used to inform local decision making
designed + conducted to define/judge a current service. results can be used to inform local decision making
16
New cards
Clinical audit
The use of research methods to determine whether existing clinical knowledge, skills and resources are effective and are being properly used/investigating effect care has on outcome + quality of life for pts
17
New cards
What is methodology?
The process utilised for data collection process
18
New cards
What is a method?
What was carried out/ Research Design Choices
19
New cards
paradigm
model e.g., Qualitative Data, Quantitative Data, Mixed Data
20
New cards
Qualitative Approach
Understand subjective experiences, beliefs, and concepts, emphasizes people's experiences in their own words, and researcher's interpretation of those experiences
21
New cards
Quantitative Approach
Measure variables, describe frequencies, averages, and correlations, Test hypotheses + effectiveness of new treatment/ program/product
22
New cards
mixed methods
research approach combining quantitative + qualitative elements; involves measurable data + the individual's subjective response to it.
Multiple methods used to increase the validity of the findings - 'data triangulation'
Multiple methods used to increase the validity of the findings - 'data triangulation'
23
New cards
Questionnaire
a written set of questions to be answered by a research participant to collect (hopefully) consistent data from many people
24
New cards
interview
A face-to-face or telephone questioning of a respondent to obtain desired information/Ideas can be explored in-depth with a smaller group
25
New cards
Survey
a detailed study for gathering information and analysing it.
26
New cards
Characteristics of good questionnaire
Validity
Reliability
Interesting
Succinct
avoid jargon
ethically approved
Reliability
Interesting
Succinct
avoid jargon
ethically approved
27
New cards
literature review
entails identifying and studying all existing studies on a topic to create a basis for new research
28
New cards
Types of questions
open ended
closed ended
Scaled questions
closed ended
Scaled questions
29
New cards
interview types
Structured
Semi structured
Focus Group/Group Interview
Unstructured
Semi structured
Focus Group/Group Interview
Unstructured
30
New cards
Hawthorne effect
A change in a subject's behavior caused by the awareness of being studied
31
New cards
Data Collection Methodologies
Experimental
Quasi Experimental
Surveys
Longitudinal Studies
Audits
Quasi Experimental
Surveys
Longitudinal Studies
Audits
32
New cards
experimental design
manipulation of independent variable + measure a dependent variable to determine a cause-and-effect relationship
33
New cards
quasi-experimental design
compares two groups that already exist in the population/ compare preselected variables to assess impact of variable changes
34
New cards
longitudinal studies
studies the same variables multiple times over time
35
New cards
Audits
Measures against Standards/Assesses current practice against guidelines
36
New cards
independent variable
experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
37
New cards
dependent variable
measured variable whose value depends on independent variable.
38
New cards
confounding variable
a factor other than the independent variable that might impact experiment
39
New cards
aims and objectives
Aim- expresses intention/aspiration of study
Objectives- explains how aims are to be accomplished/SMART
Objectives- explains how aims are to be accomplished/SMART
40
New cards
Cochrane reviews
systematic reviews of primary research in human health care and health policy; currently the highest standard in evidence-based health care. They investigate the effects of interventions for prevention, treatment and rehabilitation.
41
New cards
meta-analysis
Statistical analysis of trial data from multiple studies; Combining these brings high confidence to the results obtained so practice may change.
42
New cards
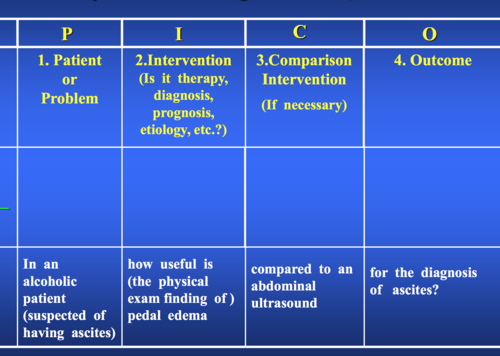
PICO analysis
43
New cards
Critical analysis
The process of critically evaluating research
44
New cards
limitations
Limitations are present in every study. in well-designed study these are not "failings" but limits of what the investigation can achieve. understanding these limitations, develops an understanding of potential impact and future research before collecting any data.
45
New cards
research outcomes and implications
How the finding may be important for policy, practice, theory and future research, supported by the evidence/ study's parameters explained by the limitations/ How will your research affect the targeted participants
46
New cards
Types of Implications (2)
practical
theoretical
theoretical
47
New cards
Practical implications
direct impact of the finding on related practices/participants
48
New cards
theoretical implications
how does it inform or shape theory?
49
New cards
Research Integrity
is conducting research so that others trust and have confidence in the methods used +the findings that result
Creates trust and confidence in the institution, research output and wider research community
Creates trust and confidence in the institution, research output and wider research community
50
New cards
Ethics
Moral standards of behaviour; principles of right and wrong
51
New cards
Research Ethics
Set of principles governing the research to protect research participants' dignity, rights and welfare. Traditionally based on investigating human experiences, now includes future impact on humans and the environment.
52
New cards
Virtue
excellence of any kind
A virtuous person is right in the middle, able to see + do what is right in the specific situation, and knows how to avoid the extremes of showing too little or too much
A virtuous person is right in the middle, able to see + do what is right in the specific situation, and knows how to avoid the extremes of showing too little or too much
53
New cards
The Nuremberg Code (1946)
set of guidelines for ethical practice in research
54
New cards
Declaration of Helsinki (1964)
undergone several revisions. shares many basic principles of the Nuremberg Code, but some differences e.g., allowed consent by a legal guardian if the research participant can't consent.
55
New cards
misconduct
- falsification
- fabrication
- misinterpretation
- plagiarism
- manipulation/malicious accusation
- fabrication
- misinterpretation
- plagiarism
- manipulation/malicious accusation
56
New cards
SMART
specific
measurable
achievable
reliability
time-bound
measurable
achievable
reliability
time-bound