Plant Phys Final Exam
1/400
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
401 Terms
Respiration takes place:
a) During the day
b) During the night
c) During both day and night
d) During the day-night transitions
During both day and night
The translocation of photo-assimilates from the leaves takes place through:
a) The xylem
b) The phloem
c) Transpiration
d) Root pressure
The phloem
The physiological mechanism explaining photo-assimilate translocation is called:
a) The capillary action mechanism
b) The pressure-flow mechanism
c) The adhesion mechanism
d) The cohesion mechanism
The pressure-flow mechanism
Sink strength is a function of:
a) Phloem anatomy
b) Photosynthesis
c) Sink size and activity
d) Respiration
Sink size and activity
Photo-assimilate movement between organs depends on cell-to-cell solute movements that involve:
a) A symplastic pathway
b) An apoplastic pathway
c) Both symplastic and apoplastic pathways
Both symplastic and apoplastic pathways
A plant photosynthetic organ from which photo-assimilates are translocated
Source Organ
Plant organ receiving photo-assimilates
Sink Organ
The ratio of grain to above ground biomass
Harvest Index
Name the three main phases of photo-assimilate translocation from the leaf to the target organ
Phase #1: Phloem loading
Phase #2: Long distance transport
Phase #3: Phloem unloading
When solutes move out of the phloem into the target organ, they can follow one of two types of apoplastic pathways that are different dependent on the species (i.e., legumes vs. non-legumes). Explain the difference between these pathways.
2: sucrose goes to apoplast without a carrier. sucrose is hydrolosized by acid invertase, this is irreversable creating glucose and fructose, transported into the sink cell, combined into sucrose and tranported to the vacuole
3: sucrose is carried by an energy dependent carrier, just goes into sink cell.
The partitioning of photo-assimilates between organs receiving photo-assimilates depends on three key factors. What are they?
Vascular connection, Proximity of the sink, Sink Strength
What are names and general outcomes of the 3 key steps of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis: Sugars into pyruvate, Generation of intermediates, NADH and ATP
Citric Acid Cycle: Pyruvate metabolized, Generation of building blocks, CO2, NADH, FADH2, and ATP
Respiratory transport chain: Oxidation of electron donors and generation of ATP
Fixing N2:
a) Requires as much energy as fixing CO2
b) Requires half the energy used for fixing CO2
c) Requires much more energy than used for fixing CO2
Requires much more energy than used for fixing CO2
Positive chemotaxis involves:
a) Synthesis by roots of flavonoids followed by synthesis of lectins that bind to polysaccharides synthesized by rhizobia in response to flavonoids
b) Synthesis by roots of polysaccharides that feed the rhizobia which then release flavonoids that attract more rhizobia
c) Both
d) Neither
Synthesis by roots of flavonoids followed by synthesis of lectins that bind to polysaccharides synthesized by rhizobia in response to flavonoids
Dinitrogenase is the enzyme responsible for:
a) Reducing nitrate
b) Reducing nitrite
c) Breaking down dinitrogen triple bond
d) Synthesizing Glutamine
e) Synthesizing Glutamate
Breaking down dinitrogen triple bond
Oxygen in the bacteroid:
a) Inhibits dinitrogenase activity but benefits respiration
b) Inhibits both dinitrogenase activity and respiration
c) Promotes both dinitrogenase activity and respiration
Inhibits dinitrogenase activity but benefits respiration
The GS/GOGAT cycle operates:
a) In the roots
b) In the leaves
c) In the soil
d) a) and b)
e) b) and c)
f) a) and c)
a) and b)
Nitrate and nitrite reductase:
a) Reduce nitrate into ammonium
b) Break dinitrogen triple bond
c) Convert ammonium into glutamine
Reduce nitrate into ammonium
Only eukaryotes can achieve N2 fixation
False
The process of breaking dinitrogen triple bonds requires 3 ATP
False
Positive chemotaxis takes place during the third step of nitrogen fixation
False
Nod factors are involved in the synthesis of shorter and curled root hairs needed for infection by rhizobia
True
Rhizobia induce the development of the nodule meristem through mitogenic signals
True
The nodule meristem is generated in the root epidermis
False
The GS/GOGAT system serves a metabolic point of coordination between nitrogen assimilation, respiration and photosynthesis
True
Translocation of organic nitrogen molecules from the nodule to the target organ is more costly in carbon for tropical legumes
True
Ureides are the main form of exported nitrogen from the nodules in temperate legumes
False
Oxygen is released in the bacteroid from leghemoglobin to support N2 fixation
True
Nitrogen is exported from the nodule essentially as glutamine
True
N uptake from the soil is highest during the reproductive growth
False
N export to the seeds is highest during the reproductive growth
True
Nitrifying bacteria in the soil generate essentially ammonia
False
Nitrogen-fixing multicellular structures that develop on the roots
Nodules
The plant that makes a nitrogen fixing association
Legumes
Microbial partner of the plant during nitrogen fixation
Rhizobia
Key enzyme necessary for dinitrogen fixation
Nitrogenase
Cellular structure where the nitrogen fixation reactions take place inside the nodule
Bacteroides
Name the type of plants that are known to perform nitrogen fixation
Legumes
Name the key enzyme that is essential to nitrogen fixation
Nitrogenase
Name the immediate product of the dinitrogen-breaking enzyme
Ammonia
This product will be protonated into another form. Name this form
Ammonium
This form will be assimilated by the GS enzyme form an amino acid. Name this amino acid
Glutamine
This amino acid is not readily translocated. In the case of temperate legumes, it has to be changed into another amino acid. Name this amino acid:
Asparagine
Name the vascular tissue that is responsible for translocating this product to the target organs
Xylem
N export from the leaf to the grain decreases photosynthesis because
Reduces rubisco in the leaves, less energy for photosynthesis
N export from the leaf to the grain decreases nitrogen fixation because
Then there is less energy available for producing energy to go to the nodule
Describe phases 1 to 5 leading to the formation of the root nodule.
Phase#1: Rhizobia are attracted to the root via positive chemotaxis
Phase#2: Rhizobia release signals to stimulate division forming the root hair that will develop into a nodule
Phase#3: Rhizobia get entrapped in root tip, and embedded in the wall, infection thread develops.
Phase#4: Thread reaches nodal meristem and risobia release into cells to become bacterioids
Phase#5: Nodule size increases, connections made to xylem and phloem
Why are vascular connections needed by the nodule? Explain your arguments in four sentences below:
The bacteria need a source of nutrients and oxygen to function, this is transported by the phloem. The xylem is used to export the nitrogen to other parts of the plant. Without these connections, the nodule would not have the resources to fix nitrogen for the plant. The plant would have no way to carry the nutrients to other areas of the plant
Cite three soil factors that can influence the activity of nitrifying bacteria.
pH, Temperature, Soil Oxygen
There are several biochemical steps that lead to the synthesis of glutamate starting from the uptake of photo-assimilates in the nodule. Group these into 3 main steps and describe them.
Step#1: Transport of photoassimilates: Photoassimilates are transported from the leaves to the nodules to fuel this process.
Step#2: Nitrogen fixation: Nitrate is reduced to ammonia
Step#3: Ammonium assimilation: Ammonia is protonated to ammonium, then synthesized into glutamine by the Glutamate synthase cycle
Explain how water deficit can influence nitrogen fixation using two examples.
Example#1: Stomata closure during drought causes less photosynthesis, less photoassimilates available for N fixation
Example#2: Stomata being closed reduces the O2 in the plant reducing nitrogenase activity, less nitrogen fixing
Using your answers to the above questions, describe two strategies would you apply as a soybean grower in order to mitigate drought effects on your soybean productivity. Discuss their benefits and their potential disadvantages.
Strategy#1: Grow a cultivar that has drought tolerance, it may have stomata characteristics that keep them open longer, could harm plant if drought is persistent
Strategy#2: Improve soil moisture retention, grow cover crops or use compost to improve soil structure, may be expensive and time consuming
Explain why homeostasis is important for plants
Staying functional and being able to maintain the correct conditions for survival in a variety of environments is essential for plants as they cannot move or change their conditions
List five main different factors to be considered when characterizing a stress scenario:
Different organizational levels, Duration, Intensity, Type of stress, Different developmental stages
In the case of drought, stress avoidance involves:
a) Achieving short and rapid seed-to-seed cycle during the favorable period
b) Growing roots that track the water table
c) Reducing transpiration in response to water deficit to save water
d) a) and b)
e) a) and c)
f) b) and c)
d) a) and b)
Photosynthetic efficiency is:
a) The slope of the response of the rate of CO2 assimilation to irradiance under light limited conditions
b) The maximal rate of CO2 assimilation during the light saturated phase
c) The slope of the decrease of the rate of CO2 assimilation under photoinhibitory conditions
a) The slope of the response of the rate of CO2 assimilation to irradiance under light limited conditions
Photosynthetic capacity is:
a) The maximal rate of CO2 assimilation
b) The minimal rate of CO2 assimilation
c) The average of minimal and maximal rates of CO2 assimilation
a) The maximal rate of CO2 assimilation
At maximal photosynthetic capacity, the limiting factor is:
a) The rate at which Rubisco uses RubBP and CO2
b) The rate at which RuBP is re-generated
c) Both
d) Neither
a) The rate at which Rubisco uses RubBP and CO2
Photoinhibition:
a) Decreases only photosynthetic efficiency
b) Decreases only photosynthetic capacity
c) Decreases both photosynthetic efficiency and capacity
d) Does not impact photosynthetic efficiency or capacity
c) Decreases both photosynthetic efficiency and capacity
During photoinhibition:
a) D1 protein is disassembled more frequently resulting in a lower activity of photosystem I
b) D1 protein is disassembled less frequently resulting in a lower activity of photosystem II
c) D1 protein is disassembled more frequently resulting in a lower activity of photosystem II
d) D1 protein is disassembled less frequently resulting in a lower activity of photosystem I
c) D1 protein is disassembled more frequently resulting in a lower activity of photosystem II
Stress avoidance consists of experiencing a stress, and being tolerant to that stress:
False
Achieving a short seed-to-seed growth cycle is a case of drought tolerance:
False
Photoinhibition takes place at very low photon fluence rates:
False
Photoinhibition primarily limits photosystem I function:
False
Photoinhibition-related stresses generally involve an impairment of the D1 protein:
True
The D1 protein normal function could be impaired by multiple stresses:
True
The D1 protein has a very low turnover rate:
False
Stress tolerance consists in experiencing the stress but responding in a way that results in improved fitness or yield:
True
A drought tolerance trait that leads to improving crop performance in a given environment can lead to an opposite result in another environment:
True
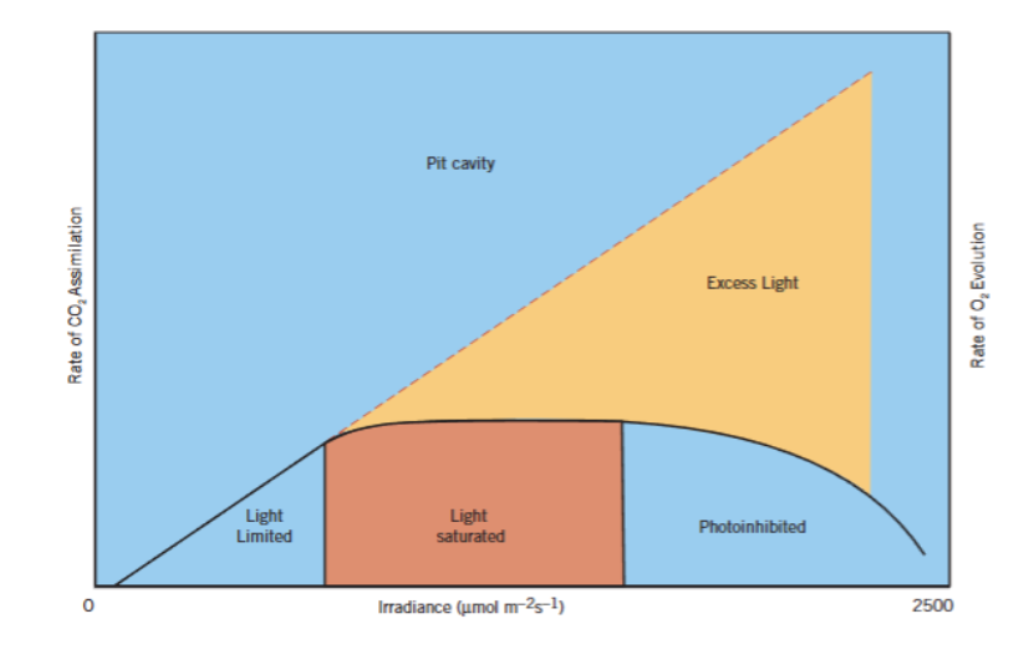
Describe the three phases that you see in this figure.
Phase 1: Light Limeted stage, increase in assimilation so ATP, NADPH, and RuBP generated. CO2 assimilation is the limiting factor
Phase 2: Light saturated, PCR cycle saturated with ATP and NADPH, maximum photosynthetic capacity. Limiting factor is how fast rubisco uses CO2 and RuBP.
Phase 3: Photoinhabition, decrease in photosynthetic assimilation
Cite three environmental stresses under which chronic photoinhibition can occur
Stress#1: Excess light intensity
Stress#2: Water deficit
Stress#3: Low Temperature
Suppose you are a corn grower whose field is exposed to one of those stresses. Identify the stress and exemplify two solutions that you would deploy in the field in order to address the problem:
Stress: Water deficit
Solution#1: Increase irrigation
Solution#2: Improve soil moisture holding capabilities
Compound produced by one part of an organism that is translocated to other parts where it triggers a response in target cells and tissues:
Hormones
List below the 5 main classes of plant hormones:
1) Gibberellin
2) Auxin
3) Cytokinins
4) Ethylene
5) Abcisic Acid
Gibberellins play a role in:
a) Breaking seed dormancy
b) Germination
c) Growth
d) Flowering
e) a) and b)
f) a), b) and c)
g) All of the above
g) All of the above
To be effective, hormones need to be synthesized in large quantities
False
Hormones do not affect gene expression or activities of enzymes:
False
Auxin is the only plant hormone known to be transported polarly
True
Polar transport is acropetal
False
Auxin promotes formation of lateral and adventitious roots
True
Auxin plays a role in the differentiation and regeneration of the xylem and the phloem
True
Cytokinins promote leaf senescence
False
Salicylic acid, jasmonates, polyamines, systemin and nitric oxide are other chemical signals that have similar functions to typical plant hormones
True
Ehylene delays fruit ripening
False
Ethylene is a gas
True
Abscisic acid promotes seed dormancy
True
Auxin
Stimulates stem elongation (at low concentrations), root growth, cell differentiation and branching; enhances apical dominance, promotes xylem differentiation
Cytokinins
Stimulate germination, delays senescence
Gibberellins
Promote seed and bud germination, stem elongation, flowering and development of fruit
Brassinosteroids
Inhibit root growth, retard leaf abscission, promote xylem differentiation
Abscisic acid
Inhibits growth, closes stomata during water stress, promotes seed dormancy
Ethylene
Promotes fruit ripening, opposes auxin effects
Protoplast shrinkage results in:
a) Displacement of membrane proteins
b) Solute leakage
c) Loss of solute selectivity
d) Loss of cellular compartmentation
e) Loss of activity of membrane enzymes
f) a), b) and c)
g) a), b) and e)
h) All of the above
h) All of the above
At the cellular level, the dehydration stress impacts:
a) The plasma membrane
b) The cytosol proteins
c) The organelles
d) a) and b)
e) b) and c)
f) All of the above
f) All of the above
Stomata closure is the result of:
a) A hydropassive closure
b) A hydroactive closure
c) Neither
d) Both
d) Both
Heat and chilling stresses cause damage:
a) Only on reproductive tissues
b) Only on vegetative tissues
c) On both tissues
c) On both tissues
When abscisic acid reaches the guard cell, it:
a) Triggers a movement of Cl-, K+ and water into the cell
b) Triggers a movement of Cl-, K+ into the cell but water will leave the cell
c) Triggers a movement of Cl-, K+ and water out of the cell
c) Triggers a movement of Cl-, K+ and water out of the cell
Protoplast shrinkage is the same thing as plasmolysis
True
A hydropassive mechanism mediated by loss of turgor is responsible for stomata closure
True
ABA is biosynthesized only in response to stress
False