Week 4 ELM 9: Synapses
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering terminology, function, and components of electrical and chemical synapses, neurotransmitter release, and vesicle recycling. Includes information about toxins affecting synaptic transmission.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Aim of Synapse
Transmit signal from one neuron to another
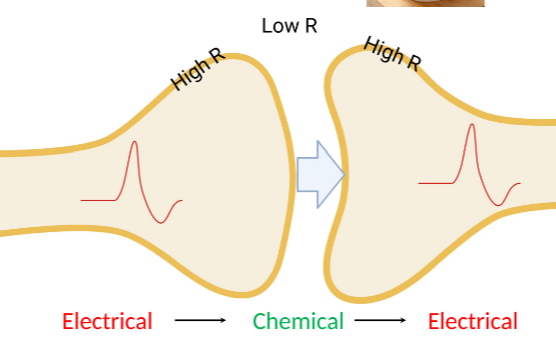
Electrical Synapses
Electrical: Gap junction, direct transfer of ions, non-rectifying, fast transmission, signal often attenuated, made of 2 connexons, each connexon equals 6 connexins
Synaptic Delay
Time taken for signal to cross synapse
Vagusstoff (vagus substance)
Otto Loewi's discovery in 1921
SNARE Proteins
Synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, and syntaxin
Synaptotagmin
Vesicle protein that senses calcium
Steps of Synaptic Transmission
Neurotransmitters are synthesized and stored in vesicles; action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal; voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open, allowing influx of Ca2+; Ca2+ allows vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter release; neurotransmitter binds to receptors, causing channels to open (or close); excitatory (or inhibitory) postsynaptic potential is generated; neurotransmitter is removed by glial uptake (or enzymatic degradation); vesicular membrane is retrieved from the plasma membrane.
1 Quantum
Amount of transmitter per vesicle
Miniature postsynaptic potentials (“mini’s”)
Occur spontaneously, even in zero extracellular Ca2+; have amplitudes that are multiples of a quantal unit; are due to release of one or a few quanta (= vesicles).
‘Quantal Content’
No of quanta released for one AP
Vesicle Cycle Stages
docking, mobilization, storage, priming calcium sensing, loading, sorting, translocation, endocytosis, fusion
Clathrin and Vesicle Recycling
Clathrin and vesicle recycling involves a coated pit, clathrin, clathrin coat, constant vesicle size, constant number of vesicles, and constant size of terminal.
ω-agatoxin IVA
Blocks P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channels
Botulinum Toxin (Botox)
Proteolytic enzyme that cleaves SNARE proteins, stopping neurotransmitter release
ω-conotoxin MVIIC
Blocks N-type voltage-gated calcium channels
α-bungarotoxin
Blocks nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Physostigmine (Eserine)
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor found in the Calabar bean
Post synaptic potential
A change in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron, resulting from neurotransmitter binding to receptors.
Presynaptic neuron
The neuron that releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft to communicate with the postsynaptic neuron.
Postsynaptic neuron
The neuron that receives neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron and undergoes a change in membrane potential.
Synaptic cleft
The small gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons, where neurotransmission occurs.
One way transmission
Rectifying
Two way transmission
Non-rectifying
Chemical synapses
Synaptic delay (time taken for signal cross synapse) = .5-2 ms.
Action potential, vesicle containing neurotransmitter, uptake system for NT or breakdown products, enzyme, postsynaptic receptor (ligand gated channel)
Vesicular release: the SNARE proteins
Snare proteins are synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, syntaxin
They bind to each other, drawing the vesicle close to the membrane
When intracellular calcium concentrations rise, the vesicle fuses with the membrane and the contents (ACh) are released into the synapse
Calcium is sensed by a vesicle protein called synaptomagmin