Final exam Science | Sec 3
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Tissue
A group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function
Organ
A distinct structure made up of different types of tissues organized to perform one or more specific functions
Biological System
A group of organs working together to perform functions essential for the organism's survival
What are the main parts of the digestive tract
Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Anus
What is the role of the digestive tract
The digestive system breaks down into complex nutrients into absorbable molecules. Primarily in the small intestine (nutrients) and large intestine (water/electrolytes). The digestive system expels undigested and non-essential materials through the anus
What is the key function of the digestive tract
The mouth chews the food. The stomach breaks down food with its secretes acid and enzymes. The small intestine absorbs ~90% of nutrients, while the large intestine takes water and electrolytes
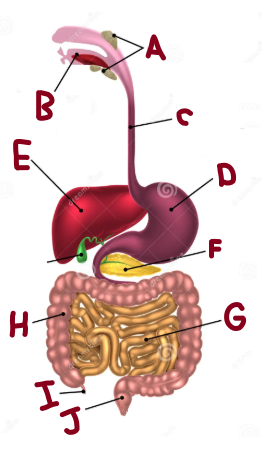
A
Salivary Glands
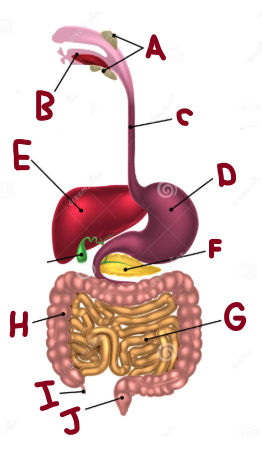
B
Mouth
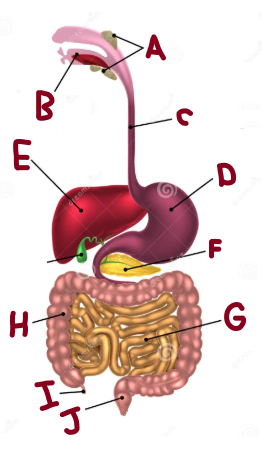
C
Oesophagus
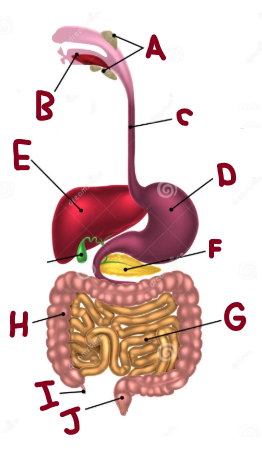
D
Stomach
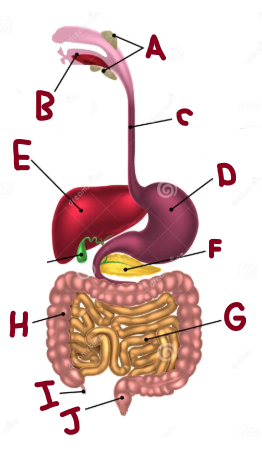
E
Liver
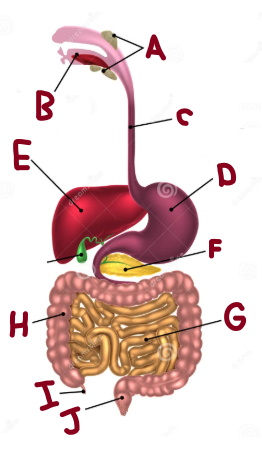
F
Pancreas
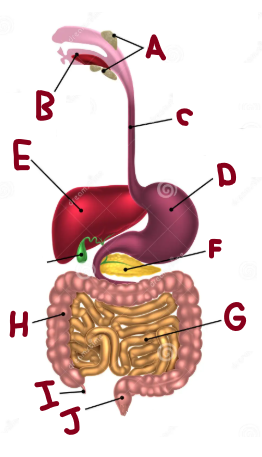
G
Small Intestine
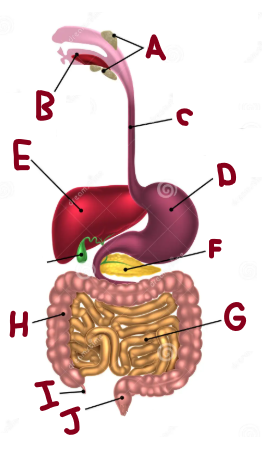
H
Large Intestine
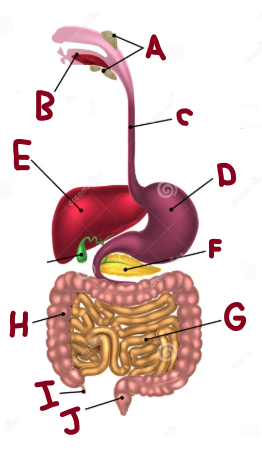
I
Appendix
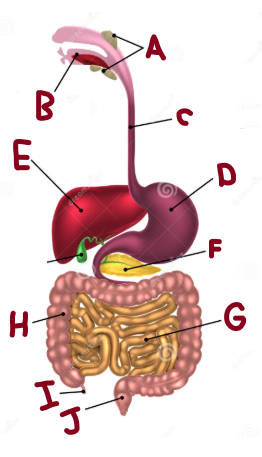
J
Rectum
How does the digestive glands function
The digestive glands support food breakdown and nutrient absorption. Salivary glands start digestion with amylase, gastric glands produce acid and enzymes for proteins, pancreas releases enzymes for fats, carbs, and proteins, liver makes bile to process fats, and intestinal glands complete digestion for absorption. They work together to maintain the body's nutrition
What does water give to the body
Solvent for reactions and for hydration
What does protein give to the body
Tissue repairs and growth
What does carbohydrates give to the body
It’s the primary energy source
What does fat give to the body
Energy storage and cell membranes
What do vitamins give to the body
Metabolism, immunity and bone health
What does minerals give to the body
Bone/teeth structure and Oxygen transport
What is food mechanical transformation
The mouth chewing the food and the stomach turning the food
What is food Chemical Transformation
The mouths saliva goes on the food. Then it goes into the stomachs acid. Finally, it goes into the small intestine
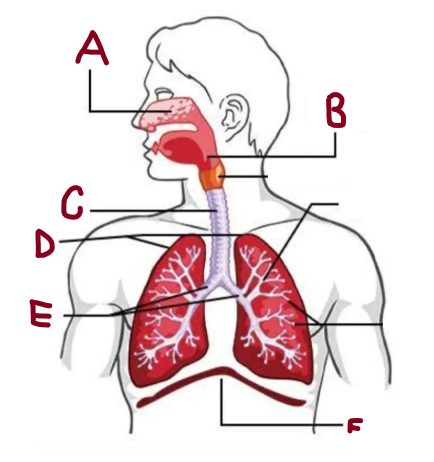
A
Nasal Cavity
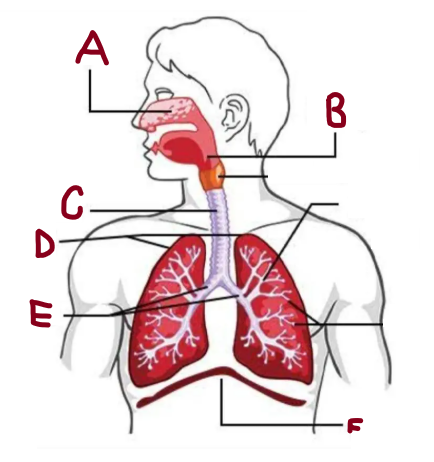
B
Pharynx
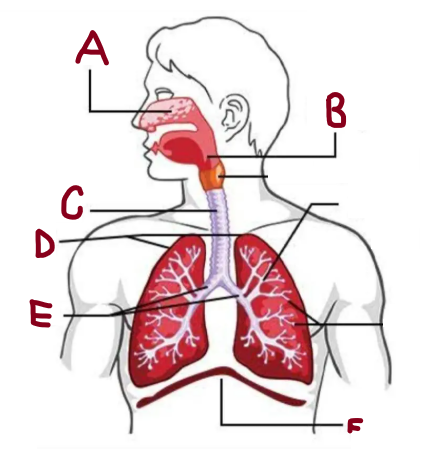
C
Trachea
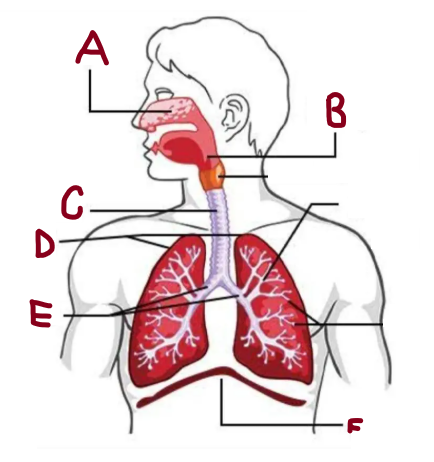
D
Lungs
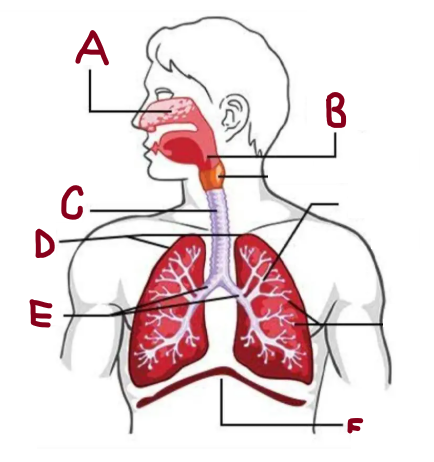
E
Bronchi
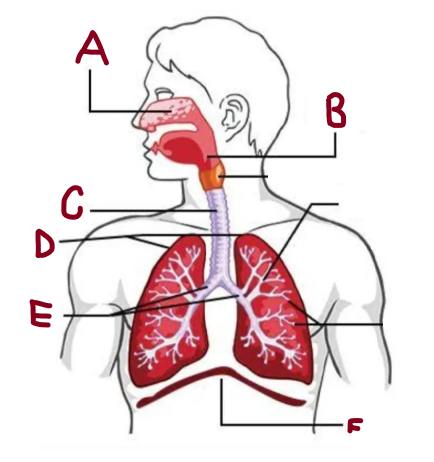
F
Diaphragm
How does the respiratory system work
It brings oxygen for energy and removes carbon dioxide waste. The lungs and airways work together to keep the body supplied with oxygen while expelling harmful gases efficiently.
What does the nasal cavity do
Warms and humidifies air
What does the lungs do
It absorb oxygen and expel carbon dioxide, ensuring efficient respiration
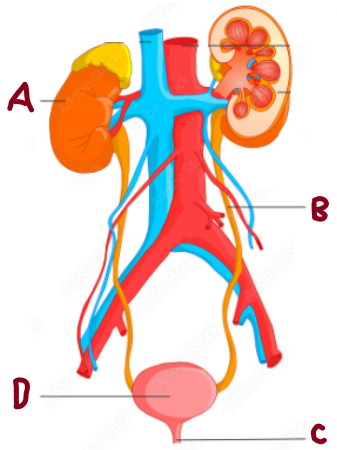
A
Kidney
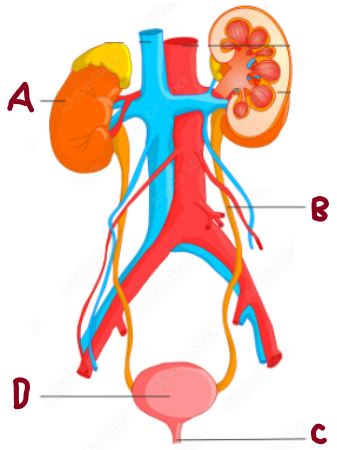
B
Ureter
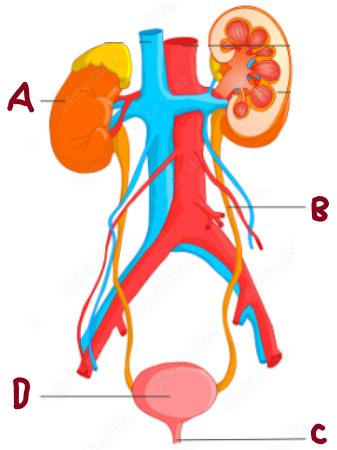
C
Urethra
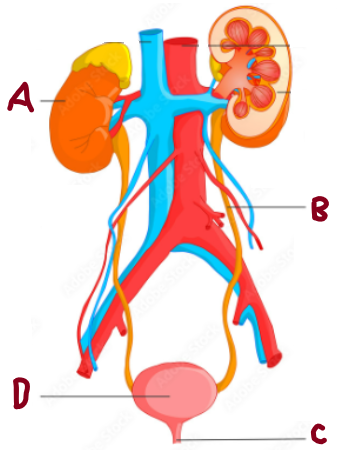
D
Bladder
What is the PNS
It consists of all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, connecting them to the rest of the body
What are Sensory receptors
They are specialized cells that detect and send signals to the nervous system
What is the musculoskeletal system
It is responsible for movement, support, and protection in the human body
Mitosis
It is a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells
Meiosis
is the process of cell division that produces gametes for sexual reproduction
What is the hormones responsible for the formation of spermatozoa
FSH, LH, testosterone
What is a fossils
Traces of organisms preserved in sedimentary rock
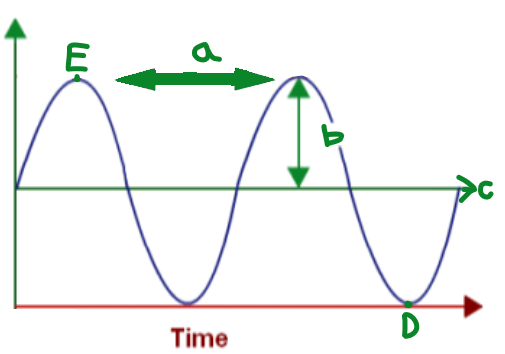
A
Wavelength
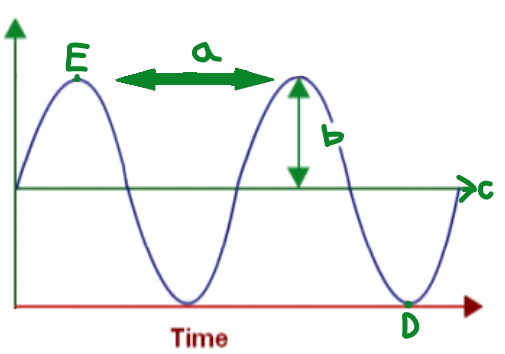
B
Amplitude
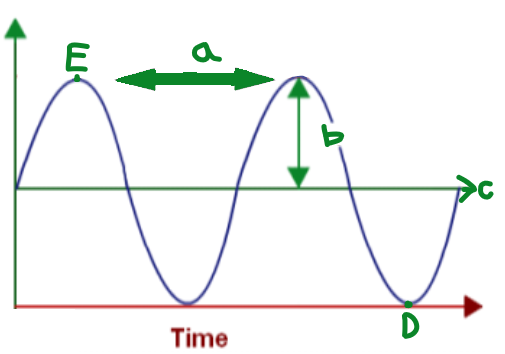
C
Equilibrium
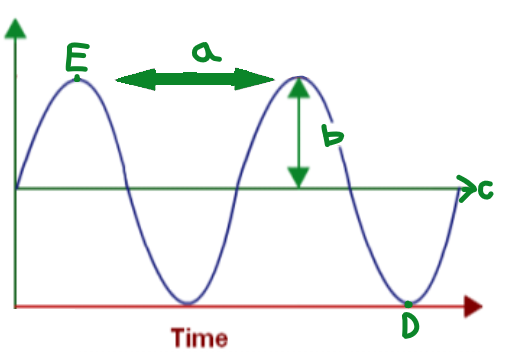
D
Trough
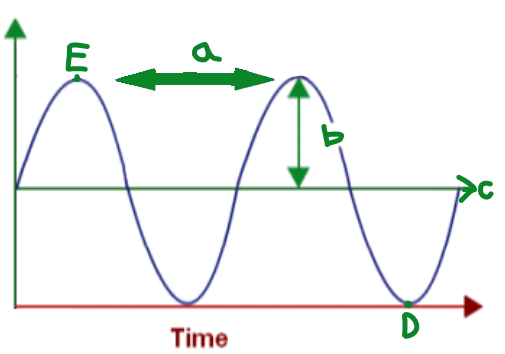
E
Crest
Wavelength
The distance between one point on a wave and the exact same place on the next wave
Phase
Any two points on a wave that are one or more
whole wavelengths apart
Frequency
It is the number of complete wavelengths a point on that wave makes each second.
Amplitude
The greatest distance from equilibrium
Decomposition
A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances
Synthesis
wo or more simple substances combine to form a more complex compound
Homogeneous
Everything is evenly distributed, appearing as a single phase
Heterogeneous
Components remain distinct, forming separate phases
What are the conditions for life
Presence of an Atmosphere, Liquid Water, Has to be in the Goldilocks zone
Linking
Joins two or more components together
Guiding
Directs or controls the motion of a component
Sealing
Prevents fluids or gases from escaping
Lubricating
Reduces friction between moving parts
Direct link
Parts have complementary shapes that provide a direct connection
Indirect link
Parts require a linking component to hold together
Partial link
Allows one component to move without necessarily moving the other
Complete link
Both parts move together
Driver Component
The root of the system power. This is the component that receives force from the user.
Driven Component
The components of a system that receive the motion created by the drive
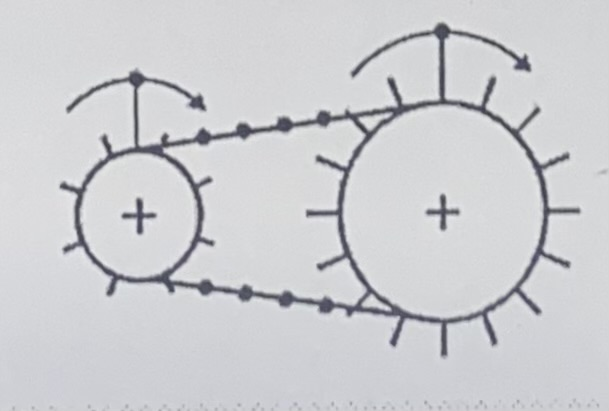
Chain
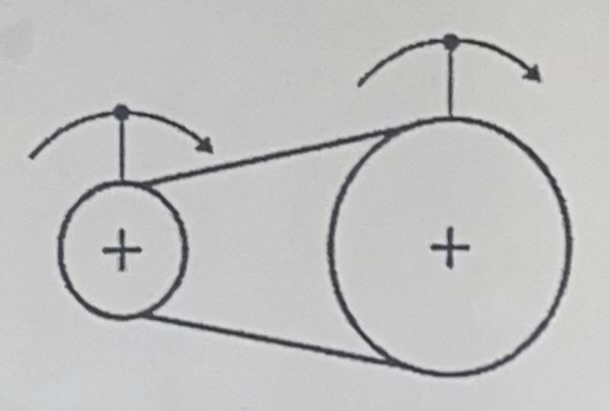
Belt and pulley
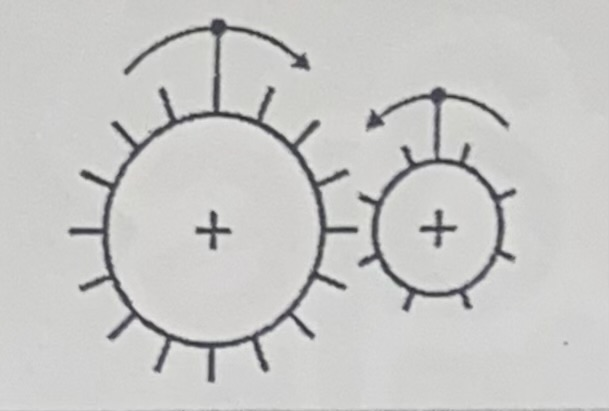
Gears
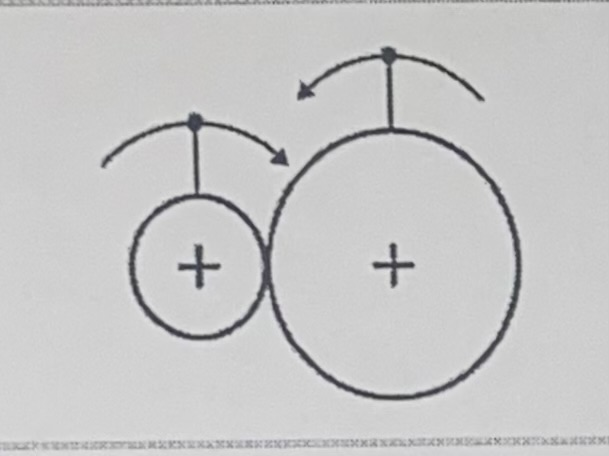
Friction Wheels
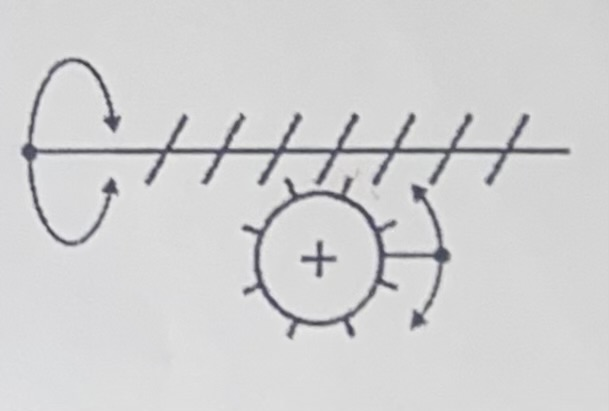
Worm and Worm
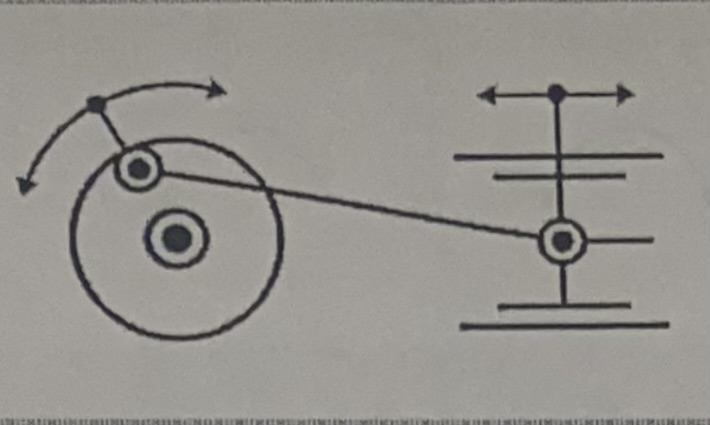
Rod and Crank
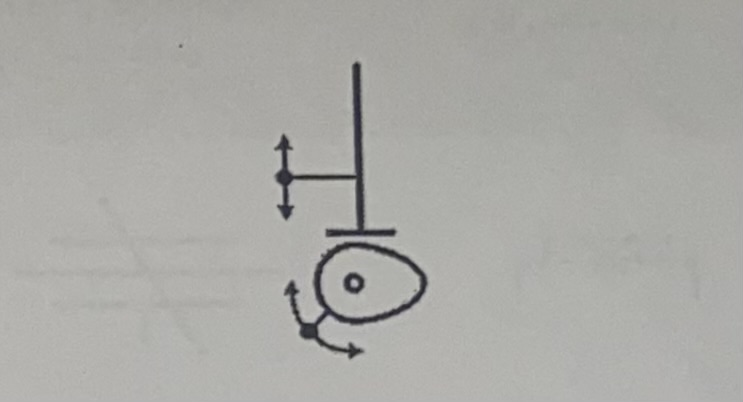
Cam and Follower
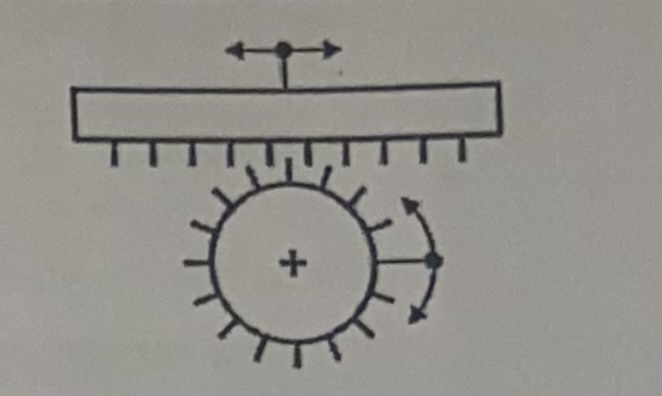
Rank and pinion
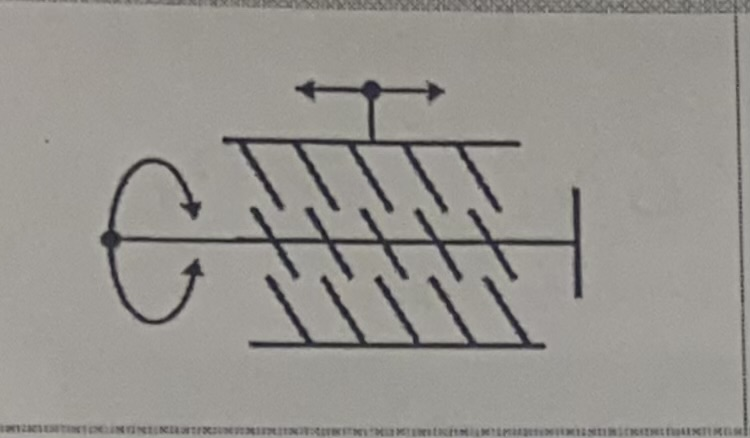
Screw and nut
Helical link
The guided part can undergo helical motion

Translational guide
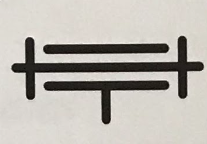
Rotational guide
Translation
Translational motion occurs when an object moves from one position to another without rotating, this is called Linear motion