Prehistoric Architecture
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HOA lesson 1 plng ni huhu
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards

A prehistoric monument consisting of an upright stone, usually standing alone but sometimes aligned with others in parallel rows. (single stones)
MENHIR or MONOLITH
2
New cards

From the words daul, a table, and maen, a stone; A prehistoric monument consisting of two or more large upright stones supporting a horizontal stone slab or capstone, and usually regarded as a tomb. (multiple stones)
DOLMEN
3
New cards
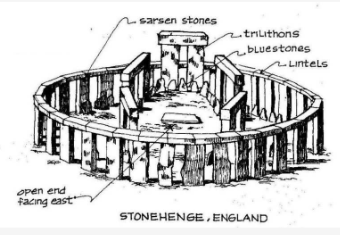
A circular arrangement of megaliths enclosing a dolmen or burial mound; Enclosure formed by huge stones planted on the ground in circular form. (multiple stones)
CROMLECH
4
New cards
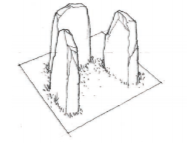
Three standing stones, two on the sides and one at the back.
Cove
5
New cards
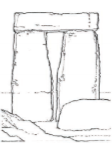
A structure consisting of two upright stones supporting a horizontal lintel.
Trilithon
6
New cards

An artificial mound of earth or stone, especially over an ancient grave.
**TUMULUS**
7
New cards
\- Use of natural stone/rock formations
\- Cliff dwellings
Rock caves
8
New cards

Made of reeds, grass, leaves, tree branches, twigs, wattle and daub, etc. and covered or sheathed by animal skin
Huts
9
New cards
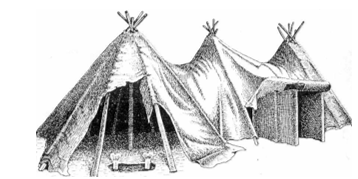
Covered with rush mats and an animal skin door and use of wooden poles as a framework
Tents
10
New cards
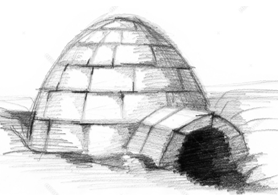
constructed of hard packed snow blocks built up spirally
Igloo
11
New cards
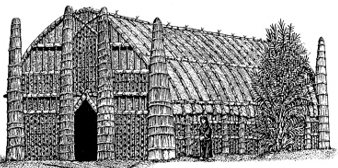
Covered with split reed mats, built on a reed platform to prevent settlement
Iraqi Mudhif
12
New cards

Built with timber and palm leaves with livestock underneath
Sumatran house
13
New cards

One of the world’s oldest continually inhabited city and with plaster floors, surrounded by high walls and towers
Jericho
14
New cards

One of the earliest Neolithic villages and utilized a complex architectural system built according to a preconceived plan, suggesting a structured social organization.
Khirokitia
15
New cards
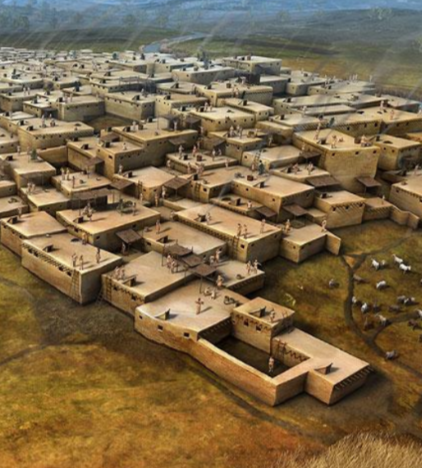

Largest and most well-preserved Neolithic village. It is consisted of rectangular flat roofed houses packed together into a single architectural mass and has no streets or passageways.
Catal Huyuk
16
New cards
referring to the time before people recording history in writing
prehistory
17
New cards
known as modern man who lives a longest period in the past
homo sapiens
18
New cards
refers to the time after invention of writing
History
19
New cards
It traces the origin, growth and decline of architectural styles which have prevailed lands and ages
History of Architecture
20
New cards
Why did man seek shelter?
* · Protection from elements of nature and wild animals
* · Comfort to sleep and rest
* · Food storage
* · Perpetuation of human life
21
New cards
3 stages in the cultural evolution of man
* Stone age
* Bronze age
* Iron age
* Bronze age
* Iron age
22
New cards
What period when they used stone and bone as instruments?
Paleolithic or Old stone age
23
New cards
What period when the livelihood is hunting and food gathering?
Paleolithic or Old stone age
24
New cards
What period when they learned to make fire?
Paleolithic or Old stone age
25
New cards
What period when they lived in caves and rock shelters?
Paleolithic or Old stone age
26
New cards
What period when they fashioned stone tools like a bow?
Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age
27
New cards
What period when they made body coverings from the animal hides?
Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age
28
New cards
What period when they made the canoe for fishing?
Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age
29
New cards
What period when they build huts made from bones, animal hides, reeds, and grass?
Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age
30
New cards
What period when they polished stone tools for grinding, cutting & chopping?
Neolithic or New Stone Age
31
New cards
What period when the pottery developed?
Neolithic or New Stone Age
32
New cards
What period when they do agriculture and domesticated animals?
Neolithic or New Stone Age
33
New cards
What period when they sew clothing from animal hides using fish bones as needles?
Neolithic or New Stone Age
34
New cards
What period when they build huts of stones and mud with thatched roofing?
Neolithic or New Stone Age
35
New cards
What period when they practiced burial rituals and built tombs?
Neolithic or New Stone Age
36
New cards
The packed clay walls of earlier times were replaced by those constructed of prefabricated units
Mud bricks
37
New cards
Structures such as tombs used for rituals and burial for the dead
Funerary buildings
38
New cards
Usually associated with ritual ceremonial activities and activities may be related to religion
Ritual buildings
39
New cards
Evidence of the first practices of religion and buildings used for rituals related to worship and religion
religious buildings
40
New cards
Structure served as places for the dead and places for tracking the course of time and understanding the cosmos
Megalithic structures