Mycology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
2 roles of saprophytic fungi
Decomposer of organic waster
Producers of antibiotics (metabolic waste that is toxic to other organisms)
Fungi are … pathogens
Never obligate => they can always obtain nutrients from dead organisms
Fungi can be divided in
Yeast (unicellular)
Moulds (multicellular)
What’s a dimorphic fungi?
Fungi that exist as mould in the environment and as yeast in human and animals tissues at body temperature.
They take the form of yeast cells in the parasitic stage and appear as mycelia in the saprophytic phase
What’s a mycelia
A mass of molds’ hyphae
Yeast reproduction method
Reproduce asexually by mitosis or by mitosis with budding
Or sexually (in some sp.) under certains conditions, forms sexual spores (ascospores or basidiospores), involving meiosis
What are hyphae
Branching filaments of moulds
Hyphal cell description
One or two nucleus
Many are separated by septa with pores that allow cytoplasm and nucles to travel from cell to cell
Hyphae classification
Septate
Nonseptate (multinucleated)
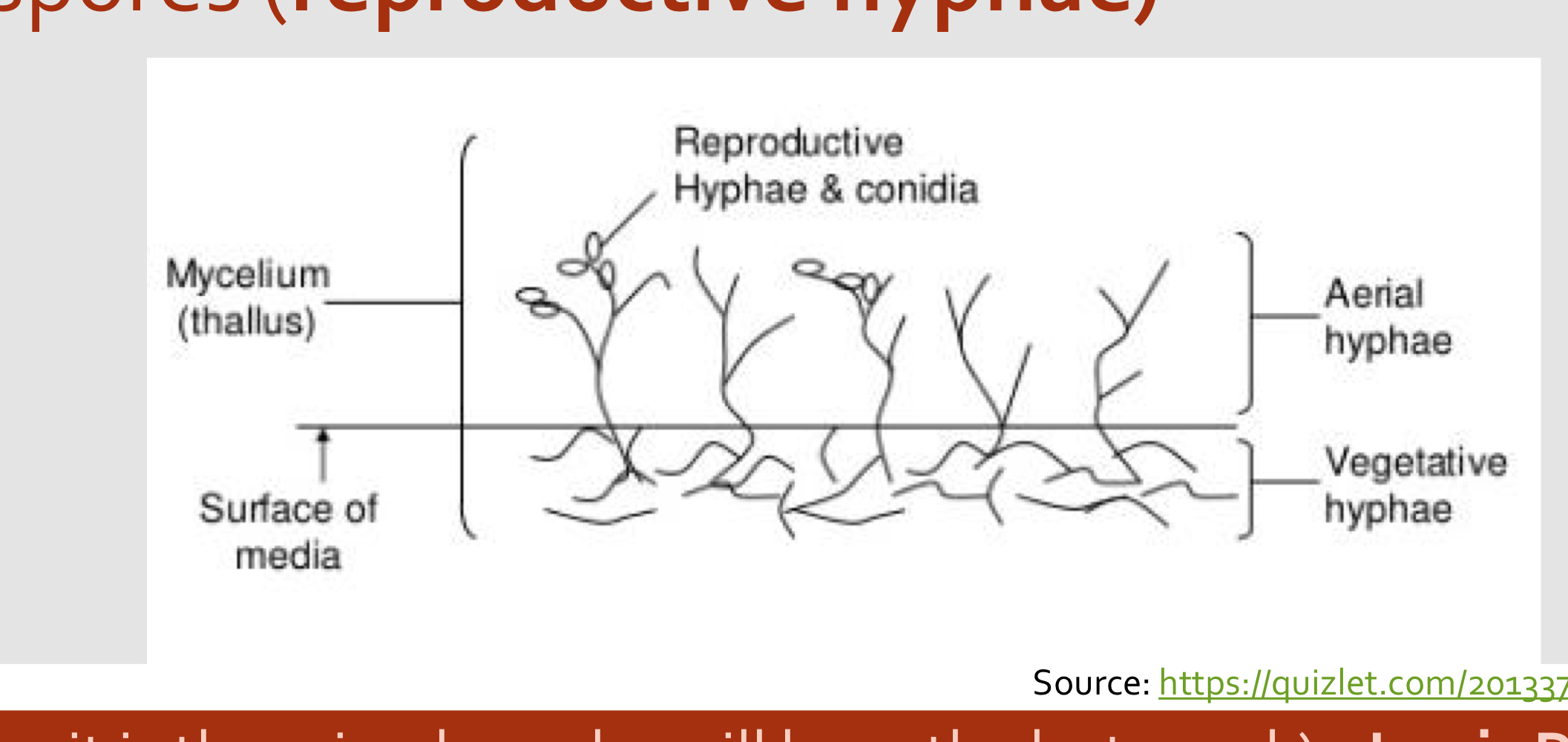
2 types of mycelium
Vegative: part that anchors the mould and absorb nutrient
Aerial: Part that project above the surface of the culture, some produce spore (reproductive hyphae)
How mould reproduce
Asexual
Hyphal growth and tip extension
Fragmentation of part of hyphae
Asexual spores (conidia or sporangiospores)
Sexual
With sexual spore (under certain env conditions)
Sexual spore are produced by specialized sexual structues that produce spors like ascospores or zygospores = bring genetic diversity
Dermatophytes are
Moulds that use keratin for growth
What contains most of fungi’s cell wall
Chitin
Fungal cell membrane contains…
Ergosterol (equivalent of cholesterol in vertebrates)
Fungal ribosomes
80s
How fungi deal with nutrients
They’re heterotroph, they absorb nutrient from envrinoment and stock it in the form of glycogen
Fungal chromosomes
Linear
Fungal organelles
Contain membrane-bound organelles (e.g, mitochondria)
How perfect and imperfect fungi reproduce
Perfect: asexual & sexual
Imperfect: asexual (mitosis) only
Reproductive state of fungi
Anamorph = asexual stage
Teleomorph = sexual
=> Anamorph + teleomorph = holomorph
Spores difference between yeast and mould
Yeast: always unicellar
Mould: can be unicellular or multicellular
Fungal diseases
Mycoses (infection)
Fungal allergies (spores can contain allergens)
Mycotoxicosis (ingestion of fungal toxins)
Mycetoma (invasive infection, usually after implatation of a foreign body in the skin)
Why antibiotics don’t work on fungi
Bacteria = prokaryotic
Fungi = eukaryotic
List few mechanism of actions of antifungal
Mitosis inhibition
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Inhibtion of DNA and protein synthesis
Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis
Binding to membrane sterols