Brain Basics
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What does the Nervous System break down into?
Central Nervous System(brain and spinal cord) and Peripheral Nervous System(sensory and motor neurons that connect CNS to rest of body)
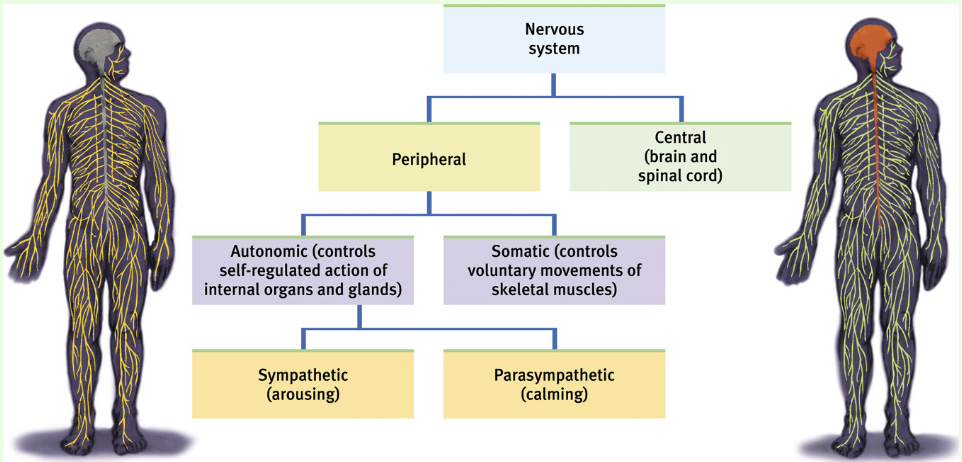
What does the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consist of (material-wise)?
Sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
What are the main divisions of the human brain?
Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain.
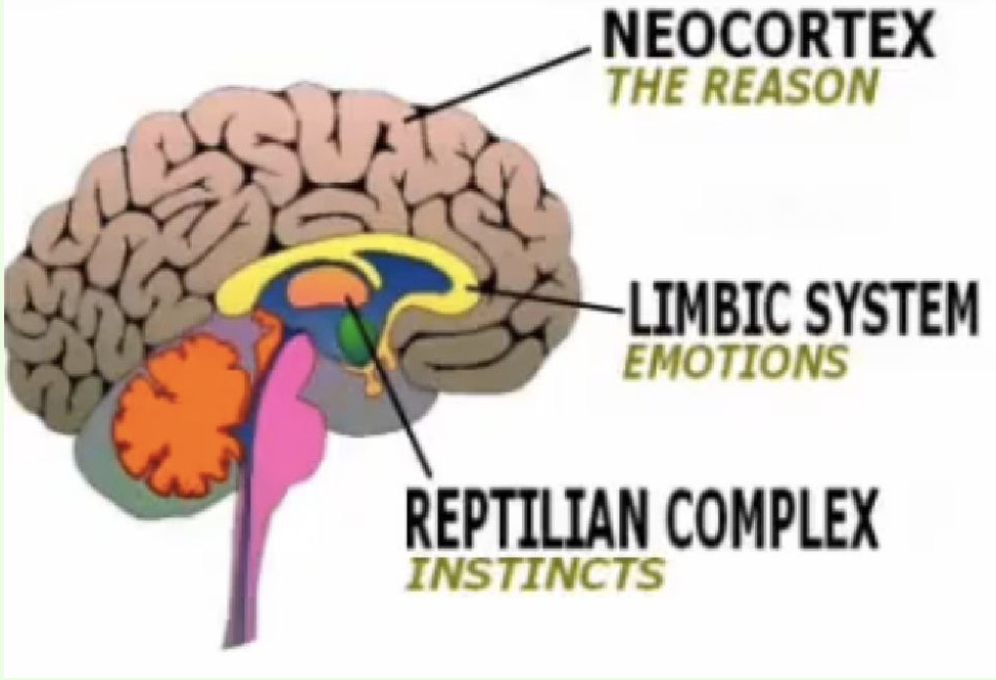
What is the evolutionary oldest part of the brain termed?
Reptilian brain.
What do the convolutions of the cerebral cortex do?
Greatly increase the surface area of the brain, increasing amount of information that can be stored
What structure in the brain is associated with speaking and muscle movements, making plans and judgments, and is in emotional control?
Frontal lobe
What does the primary motor cortex (posterior part of frontal lobe) control?
Voluntary movements
What is mapped on the surface of the primary somatosensory cortex (anterior part of parietal lobe)?
Surface of the body (penfield studies)
What does the occipital lobe primarily deal with?
Visual information, includes primary visual cortex (posterior part of occipital) —> receives visual info from opposite visual field
What does the temporal lobe specialize in?
Auditory information, includes primary auditory cortex (superior part of temporal)
What functions are performed by the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC)?
Working memory, cognitive flexibility, problem solving (coping with life stress), inhibition of rumination and worry
What does the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) contribute to?
Theory of mind (“mind-reading”), self-perception, processing risk and fear, behavioral control, decision making
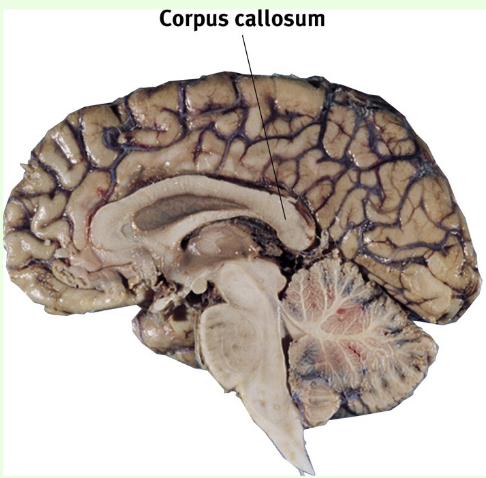
What is the large bundle of axons connecting the two cerebral hemispheres? (interconnects corresponding regions of the association cortex on each side of brain)
Corpus callosum
What cognitive functions are primarily located in the left cerebral hemisphere?
Language, mathematical computation, analysis of information, recognition of serial events (Left = Logical, Linear)
What functions are primarily associated with the right cerebral hemisphere?
Synthesis of information, pattern recognition (ability to perceive things as a whole), identification of emotional expression (Right = non-verbal, holistic), intuition, creativity, art and music
What is the amygdala (2 almond-shaped neural clusters) responsible for?
emotions, particularly fear and aggression.
What is the hippocampus (donut-shaped structure) involved in?
Memory
What is the function of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC, “collar” around front part of corpus callosum)?
Integrates cognitive and affective information, Awareness and processing of conflicting information, Selective attention, Pain perception, Impulse control
What important role does the hypothalamus play (small but important, below thalamus)?
Controls the autonomic nervous system.
What are the 'four f's' controlled by the hypothalamus?
Fighting, Feeding, Fleeing, Mating (organizes behavior relating to survival)
What are the hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and what do they control?
Gonadotropic hormones, oxytocin, vassopressin —> Endocrine glands.
Which area of the brain is crucial for emotional regulation?
amygdala: seat of emotions (mostly neg) //// Prefrontal cortex (PFC), anterior cingulate cortex: Sets goals, makes plans, directs actions, and shapes emotions, in part by guiding and sometimes inhibiting the limbic system
What is the role of the reticular formation (large network of neural tissue in central part of brain stem)?
plays part in sleep, arousal, attention and various vital reflexes
What function does the pons (bulge in brain stem, part of reticular formation) serve?
Important in sleep and arousal AND sensory analysis and movement
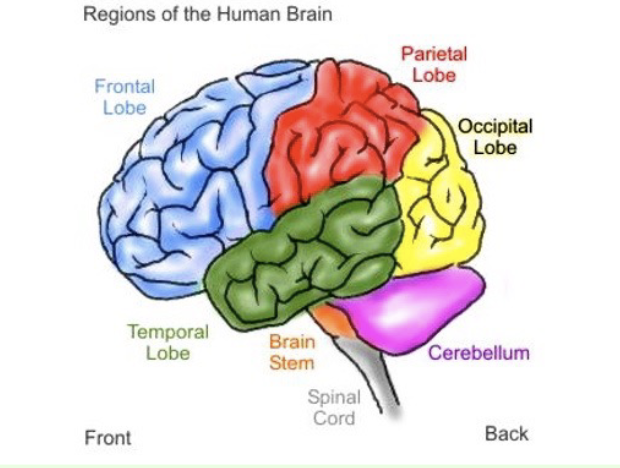
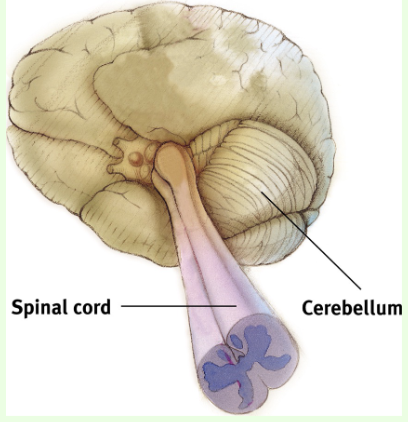
What is the role of the cerebellum (“little brain” attached to rear of brainstem)?
Coordinates voluntary movement and balance.
What does network neuroscience focus on (recent shift in studying)?
How different brain regions work together, functional connectivity, brain as a whole system
What is the 'default mode network' (DMN) (posterior cingulate cortex
and precuneus, medial frontal cortex, and temporoparietal junction)?
brain areas active when a person is resting and not focused on a particular task (also active in certain goal-oriented tasks: self-referencing, recognition of emotions in others, remembering the past, imagining the future)
What does the hypothalamus control besides the autonomic nervous system?
The anterior and posterior pituitary glands (attached to base of hypothalamus) through hypothalamic hormones
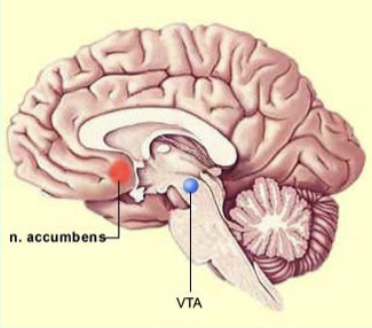
What is the main functionality of the Nucleus Accumbens (lower part of basal ganglia?
Reward center of the brain (A rat will cross an extremely painful electrified grid to press lever hat causes release of dopamine in its nucleus accumbens)
What is the prefrontal cortex (anterior part of the frontal lobe) responsible for?
Making judgments and formulating plans.
What emotional issues are often linked to an overactive amygdala (and underactive PFC/ACC)?
Emotional dyscontrol
What is a primary feature of the limbic system?
associated with emotions and memory, older part of cortex, doughnut-shaped
How is the forebrain subdivided in terms of function?
The neocortex, limbic brain, and reptilian brain.
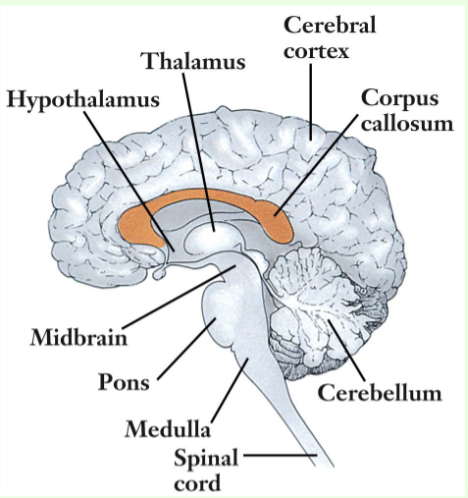
What is the purpose of the thalamus (center of the brain)?
Relay station for neural messages, directs messages to sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
What does the term 'lateralization of function' refer to?
certain cognitive processes and functions are more dominant in one hemisphere of the brain than the other, different functions being localized to one hemisphere of the brain.
What happens to the connections between regions of the brain of a person with schizophrenia and what approach is best for understanding this?
They are not as densely connected, network approach
What types of brain disorders may involve issues with the default mode network?
Alzheimer’s, autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, PTSD.
What is crucial for coordinating voluntary movement?
Cerebellum.
What is significant about the anterior hippocampus (portion closest to amygdala) in relation to memory?
It's involved in regulating behavioral inhibition in response to different contexts
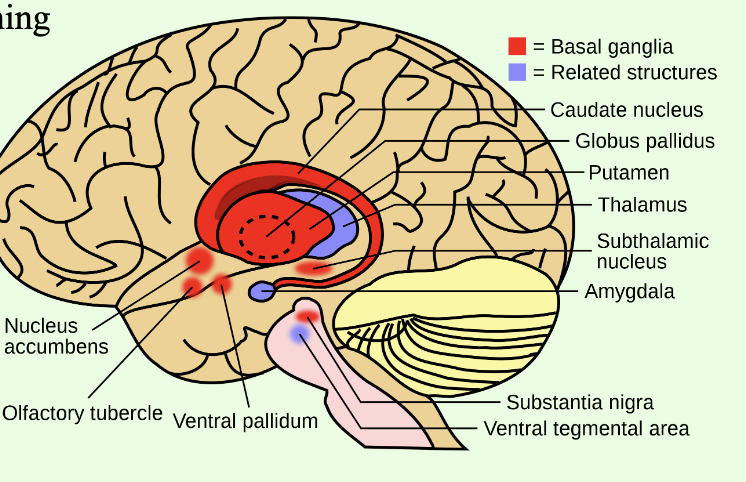
What is a key role of the basal ganglia in the brain?
Action selection, motor inhibition, motor sequencing (upper part—caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus), reward learning (lower part—nucleus accumbens)
What do studies suggest about the size of the prefrontal cortex (frontal lobe) and social network?
The size of the prefrontal cortex is directly related to the size of a person’s social network.
Sympathetic Nervous System functions
controls functions that accompany arousal and expenditure of energy, stimulates increased heart rate, rise in blood sugar level, piloerection (goosebumps)
Sympathetic Nervous System activates
Adrenal medulla: portion of the adrenal gland that secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
Parasympathetic Nervous System
controls functions that occur during a relaxed state, supports activities involved with increases in body’s supply of stored energy (salivation, gastric and intestinal motility, secretes acetylcholine
How many neurons does the cerebral cortex contain?
26 billion
What is the cerebral cortex made of?
glial and cell bodies (gives it a grayish brown appearance)
What does the cerebral cortex contain?
neocortex (newest, has 4 lobes) and the limbic cortex(older part of cortex)
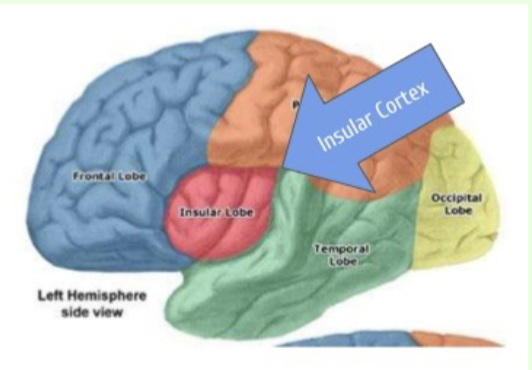
What are the functions of the insular cortex (fissure separating the
temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes, deep within lateral sulcus)
body awareness, sense of self, emotional experience, empathy and compassion, addiction
How is nucleus accumbens related to addiction?
addiction involves the release of dopamine from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra into this area
Loss of what characterizes Parkinson’s?
loss of dopaminergic neurons in nucleus accumbens
Brain Stem
Oldest, central core of brain, responsible for automatic survival functions
Medulla oblongata (base of brain stem)
controls vital functions —> heart rate, breathing, blood pressure
Why is network neuroscience better for conducting studies?
can be done while people are doing nothing at all, closer to person’s natural state (Someone with a psychological disorder will have the disorder
even when they are not engaged in a working memory task) —> localizationalist research involves watching brain activity change while person is engaged in particular task
Besides diagnosis, what are networks useful for?
determining likelihood of patients responding to different types of psychotherapy
What other associations does DMN have?
ruminating about the past, worrying about future, thinking about what other people are thinking about you
How is the Peripheral Nervous System broken down into subdivisions?
Autonomic (controls self-regulated action of internal organs and glands) and Somatic (controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles)